Claude’s AI research mode now runs for up to 45 minutes before delivering reports
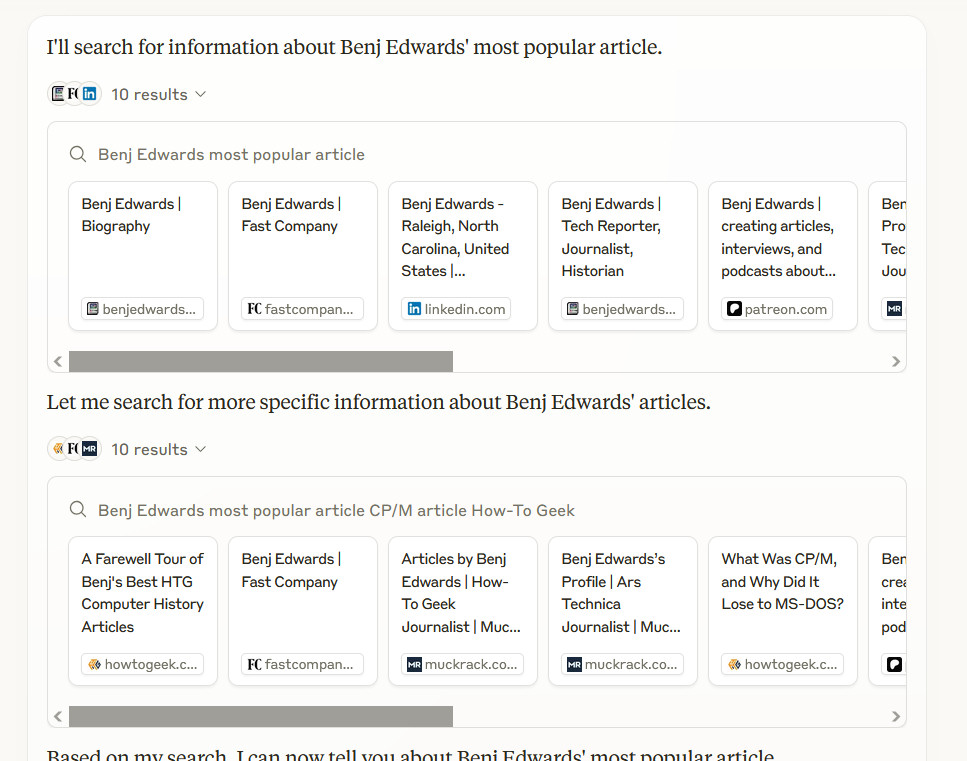
Still, the report contained a direct quote statement from William Higinbotham that appears to combine quotes from two sources not cited in the source list. (One must always be careful with confabulated quotes in AI because even outside of this Research mode, Claude 3.7 Sonnet tends to invent plausible ones to fit a narrative.) We recently covered a study that showed AI search services confabulate sources frequently, and in this case, it appears that the sources Claude Research surfaced, while real, did not always match what is stated in the report.
There’s always room for interpretation and variation in detail, of course, but overall, Claude Research did a relatively good job crafting a report on this particular topic. Still, you’d want to dig more deeply into each source and confirm everything if you used it as the basis for serious research. You can read the full Claude-generated result as this text file, saved in markdown format. Sadly, the markdown version does not include the source URLS found in the Claude web interface.
Integrations feature
Anthropic also announced Thursday that it has broadened Claude’s data access capabilities. In addition to web search and Google Workspace integration, Claude can now search any connected application through the company’s new “Integrations” feature. The feature reminds us somewhat of OpenAI’s ChatGPT Plugins feature from March 2023 that aimed for similar connections, although the two features work differently under the hood.
These Integrations allow Claude to work with remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers across web and desktop applications. The MCP standard, which Anthropic introduced last November and we covered in April, connects AI applications to external tools and data sources.
At launch, Claude supports Integrations with 10 services, including Atlassian’s Jira and Confluence, Zapier, Cloudflare, Intercom, Asana, Square, Sentry, PayPal, Linear, and Plaid. The company plans to add more partners like Stripe and GitLab in the future.
Each integration aims to expand Claude’s functionality in specific ways. The Zapier integration, for instance, reportedly connects thousands of apps through pre-built automation sequences, allowing Claude to automatically pull sales data from HubSpot or prepare meeting briefs based on calendar entries. With Atlassian’s tools, Anthropic says that Claude can collaborate on product development, manage tasks, and create multiple Confluence pages and Jira work items simultaneously.
Anthropic has made its advanced Research and Integrations features available in beta for users on Max, Team, and Enterprise plans, with Pro plan access coming soon. The company has also expanded its web search feature (introduced in March) to all Claude users on paid plans globally.
Claude’s AI research mode now runs for up to 45 minutes before delivering reports Read More »