OpenAI is back with a new Codex model, released the same day as Claude Opus 4.6.
The headline pitch is it combines the coding skills of GPT-5.2-Codex with the general knowledge and skills of other models, along with extra speed and improvements in the Codex harness, so that it can now handle your full stack agentic needs.
We also got the Codex app for Mac, which is getting positive reactions, and quickly picked up a million downloads.
CPT-5.3-Codex is only available inside Codex. It is not in the API.
As usual, Anthropic’s release was understated, basically a ‘here’s Opus 4.6, a 212-page system card and a lot of benchmarks, it’s a good model, sir, so have fun.’ Whereas OpenAI gave us a lot less words and a lot less benchmarks, while claiming their model was definitely the best.
OpenAI: GPT-5.3-Codex is the most capable agentic coding model to date, combining the frontier coding performance of GPT-5.2-Codex with the reasoning and professional knowledge capabilities of GPT-5.2. This enables it to take on long-running tasks that involve research, tool use, and complex execution.
Much like a colleague, you can steer and interact with GPT-5.3-Codex while it’s working, without losing context.
Sam Altman (CEO OpenAI, February 9): GPT-5.3-Codex is rolling out today in Cursor, Github, and VS Code!
-
The Overall Picture.
-
Quickly, There’s No Time.
-
System Card.
-
AI Box Experiment.
-
Maybe Cool It With Rm.
-
Preparedness Framework.
-
Glass Houses.
-
OpenAI Appears To Have Violated SB 53 In a Meaningful Way.
-
Safeguards They Did Implement.
-
Misalignment Risks and Internal Deployment.
-
The Official Pitch.
-
Inception.
-
Turn The Beat Around.
-
Codex Does Cool Things.
-
Positive Reactions.
-
Negative Reactions.
-
Codex of Ultimate Vibing.
GPT-5.3-Codex (including Codex-Spark) is a specialized model designed for agentic coding and related uses in Codex. It is not intended as a general frontier model, thus the lack of most general benchmarks and it being unavailable on the API or in ChatGPT.
For most purposes other than Codex and agentic coding, that aren’t heavy duty enough to put Gemini 3 Pro Deep Think V2 in play, this makes Claude Opus 4.6 the clearly best model, and the clear choice for daily driver.
For agentic coding and other intended uses of Codex, the overall gestalt is that Codex plus GPT-5.3-Codex is competitive with Claude Code with Claude Opus 4.6.
If you are serious about your agentic coding and other agentic tasks, you should try both halves out and see which one, or what combination, works best for you. But also you can’t go all that wrong specializing in whichever one you like better, especially if you’ve put in a bunch of learning and customization work.
You should probably be serious about your agentic coding and other agentic tasks.
Before I could get this report out, OpenAI also gave us GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark, which is ultra-low latency Codex, more than 1,000 tokens per second. Wowsers. That’s fast.
As in, really super duper fast. Code appears essentially instantaneously. There are times when you feel the need for speed and not the need for robust intelligence. Many tasks are more about getting it done than about being the best like no one ever was.
It does seem like it is a distinct model, akin to GPT-5.3-Codex-Flash, with only a 128k context window and lower benchmark scores, so you’ll need to be confident that is what you want. Going back and fixing lousy code is not usually faster than getting it right the first time.
Because it’s tuned for speed, Codex-Spark keeps its default working style lightweight: it makes minimal, targeted edits and doesn’t automatically run tests unless you ask it to.
It is very different from Claude Opus 4.6 Fast Mode, which is regular Opus faster in exchange for much higher costs.
GPT-5.3-Codex is specifically a coding model. It incorporates general reasoning and professional knowledge because that information is highly useful for coding tasks.
Thus, it is a bit out of place to repeat the usual mundane harm evaluations, which put the model in contexts where this model won’t be used. It’s still worth doing. If the numbers were slipping substantially we would want to know. It does look like things regressed a bit here, but within a range that seems fine.
It is weird to see OpenAI restricting the access of Codex more than Anthropic restricts Claude Code. Given the different abilities and risk profiles, the decision seems wise. Trust is a highly valuable thing, as is knowing when it isn’t earned.
The default intended method for using Codex is in an isolated, secure sandbox in the cloud, on an isolated computer, even when it is used locally. Network access is disabled by default, edits are restricted.
I really like specifically safeguarding against data destructive actions.
Their solution was to train the model specifically not to revert user edits, and to introduce additional prompting to reinforce this.
It’s great to go from 66% to 76% to 88% ‘destructive action avoidance’ but that’s still 12% destructive action non-avoidance, so you can’t fully rest easy.
In practice, I notice that it is a small handful of commands, which they largely name here (rm -rf, git clean -xfd, git reset —hard, push —force) that cause most of the big trouble.
Why not put in place special protections for them? It does not even need to be requiring user permission. It can be ‘have the model stop and ask itself whether doing this is actually required and whether it would potentially mess anything up, and have it be fully sure it wants to do this.’ Could in practice be a very good tradeoff.
The obvious answer is that the model can then circumvent the restrictions, since there are many ways to mimic those commands, but that requires intent to circumvent. Seems like it should be solvable with the right inoculation programming?
The biological and chemical assessment shows little improvement over GPT-5.2. This makes sense given the nature of 5.3-Codex, and we’re already at High. Easy call.
The cybersecurity assessment makes this the first model ranked at High.
Under our Preparedness Framework, High cybersecurity capability is defined as a model that removes existing bottlenecks to scaling cyber operations, including either by automating end-to-end cyber operations against reasonably hardened targets, or by automating the discovery and exploitation of operationally relevant vulnerabilities.
We are treating this model as High, even though we cannot be certain that it actually has these capabilities, because it meets the requirements of each of our canary thresholds and we therefore cannot rule out the possibility that it is in fact Cyber High.
Kudos to OpenAI for handling this correctly. If you don’t know that it isn’t High, then it is High. I’ve been beating that drum a lot and it’s great that they’re listening. Points.
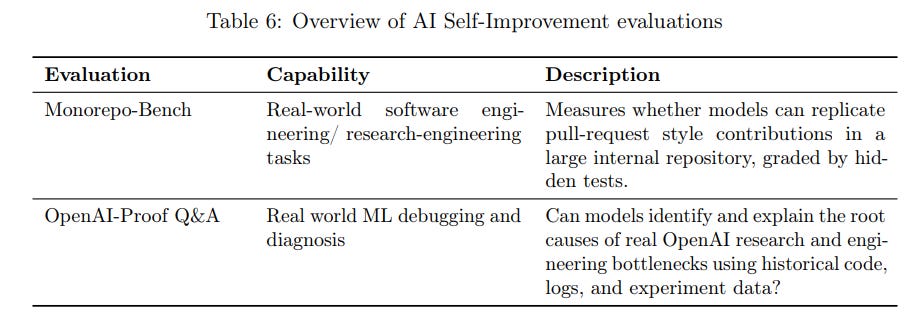
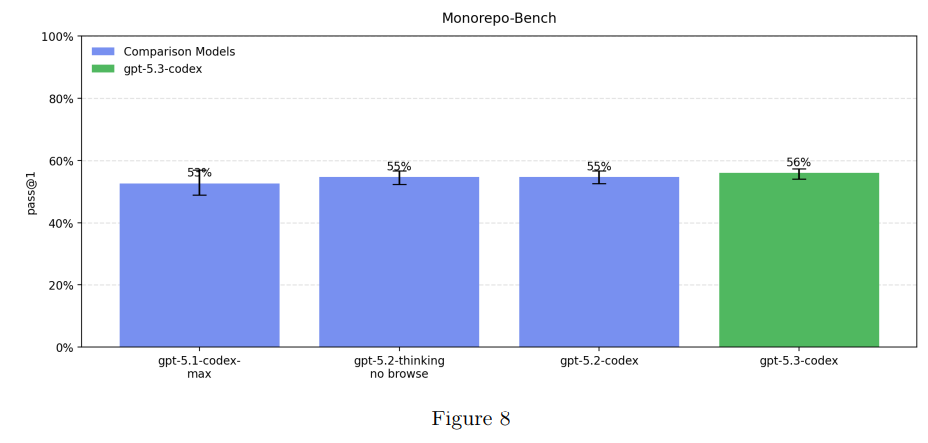
The question is where we are on AI Self-Improvement, which is 5.1.3.
The High capability threshold is defined to be equivalent to a performant mid-career research engineer. Performance in the evaluations below indicate we can rule out High for GPT-5.3-Codex.
The first thing to say about this is always that the High threshold is very high.
If you can fully duplicate a mid-career research engineer with AI, you are damn close to being fully off to the races. There won’t be much time between High and Critical.
So how did the model do on these tests? Not so well.
Given that it is clear 5.3-Codex is substantially better than 5.2-Codex, this raises the question of sandbagging, which is the subject of 5.1.4. The task was outsourced to Apollo Research.
Apollo reports that the model demonstrates strong sabotage capabilities. In their sabotage suite, Apollo reports a mean best-of-10 score of 0.88 (max 1.00), compared to 0.75 for GPT-5.2 and 0.66 for GPT-5.2 Codex. Apollo further reports that the model substantially outperforms previous models they have evaluated and expert ML practitioner baselines.
Apollo also reports that the model often includes non-English words in its reasoning (0.55% of reasoning tokens are non-Latin script, vs. 0.016% for GPT-5 and 0.012% for GPT-5.2 Robin Alpha).
… Apollo reports the model exhibits overall low rates of covert deceptive behaviors, comparable to GPT-5 and GPT-5.2 Codex.
In conclusion, Apollo finds an increase in sabotage capability on their evaluations: the model demonstrates stronger AI R&D sabotage capabilities than previous models, achieving near-perfect scores on their evaluation tasks and outperforming human baselines.
This did not sound like a reassuring report on sabotage.
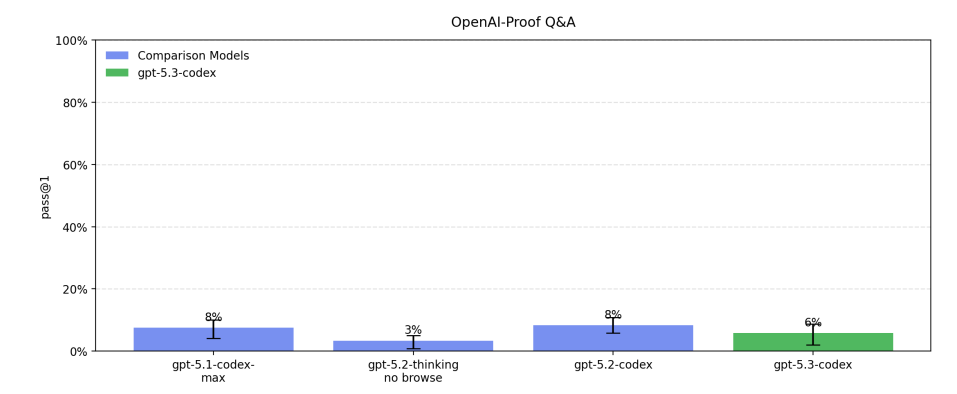
The obvious thing to do is to take a very close look at the questions where GPT-5.2-Codex was succeeding, and GPT-5.3-Codex is failing, especially on OpenAI-Proof. I want a damn strong understanding of why GPT-5.3-Codex is regressing in those spots.
OpenAI’s Noam Brown made a valid shot across the bow at Anthropic for the ad hockery present in their decision to release Claude Opus 4.6. He’s right, and he virtuously acknowledged that Anthropic was being transparent about that.
The thing is, while it seems right that Anthropic and OpenAI are trying (Google is trying in some ways, but they just dropped Gemini 3 Deep Think V2 with zero safety discussions whatsoever, which I find rather unacceptable), OpenAI very much has its own problems here. Most of the problems come from the things OpenAI did not test or mention, but there is also one very clear issue.
Nathan Calvin: This is valid… but how does it not apply with at least equal force to what OAI did with their determination of long run autonomy for 5.3 Codex?
I want to add that I think at least OpenAI and Anthropic (and Google) are trying, and Xai/Meta deserve more criticism relatively.
The Midas Project wrote up the this particular issue.
The core problem is simple: OpenAI classified GPT-5.3-Codex as High risk in cybersecurity. Under their framework, this wisely requires High level safeguards against misalignment.
They then declare that the previous wording did not require this, and was inadvertently ambiguous. I disagree. I read the passage as unambiguous, and also I believe that the previous policy was the right one.
Even if you think I am wrong about that, that still means is that OpenAI must implement the safeguards if the model is High on both cybersecurity and autonomy. OpenAI admits that they cannot rule out High capability in autonomy, despite declaring 10 months ago the need to develop a test for that. The proxy measurements OpenAI used instead seem clearly inadequate. If you can’t rule out High, that means you need to treat the model as High until that changes.
All of their hype around Codex talks about how autonomous this model is, so I find it rather plausible that it is indeed High in autonomy.
Steven Adler investigated further and wrote up his findings. He found their explanations unconvincing. He’s a tough crowd, but I agree with the conclusion.
This highlights both the strengths and weaknesses of SB 53.
It means we get to hold OpenAI accountable for having broken their own framework.
However, it also means we are punishing OpenAI for having a good initial set of commitments, and for being honest about hot having met them.
The other issue is the fines are not meaningful. OpenAI may owe ‘millions’ in fines. I’d rather not pay millions in fines, but if that were the only concern I also wouldn’t delay releasing 5.3-Codex by even a day in order to not pay them.
The main advantage is that this is a much easier thing to communicate, that OpenAI appears to have broken the law.
I have not seen a credible argument for why OpenAI might not be in violation here.
The California AG stated they cannot comment on a potential ongoing investigation.
Our [cyber] safeguarding approach therefore relies on a layered safety stack designed to impede and disrupt threat actors, while we work to make these same capabilities as easily available as possible for cyber defenders.
The plan is to monitor for potential attacks and teach the model to refuse requests, while providing trusted model access to known defenders. Accounts are tracked for risk levels. Users who use ‘dual use’ capabilities often will have to verify their identities. There is two-level always-on monitoring of user queries to detect cybersecurity questions and then evaluate whether they are safe to answer.
They held a ‘universal jailbreak’ competition and 6 complete and 14 partial such jailbreaks were found, which was judged ‘not blocking.’ Those particular tricks were presumably patched, but if you find 6 complete jailbreaks that means there are a lot more of them.
UK AISI also found a (one pass) universal jailbreak that scored 0.778 pass@200 on a policy violating cyber dataset OpenAI provided. If you can’t defend against one fixed prompt, that was found in only 10 hours of work, you are way behind on dealing with customized multi-step prompts.
Later they say ‘undiscovered universal jailbreaks may still exist’ as a risk factor. Let me fix that sentence for you, OpenAI. Undiscovered universal jailbreaks still exist.
Thus the policy here is essentially hoping that there is sufficient inconvenience, and sufficient lack of cooperation by the highly skilled, to prevent serious incidents. So far, this has worked.
Their risk list also included ‘policy gray areas’:
Policy Gray Areas: Even with a shared taxonomy, experts may disagree on labels in edge cases; calibration and training reduce but do not eliminate this ambiguity
This seems to be a confusion of map and territory. What matters is not whether experts ever disagree, it is whether expert labels reliably lack false negatives, including false negatives that are found by the model. I think we should assume that the expert labels have blind spots, unless we are willing to be highly paranoid with what we cover, in which case we should still assume that but we might be wrong.
I was happy to see the concern with internal deployment, and with misalignment risk. They admit that they need to figure out how to measure long-range autonomy (LRA) and other related evaluations. It seems rather late in the game to be doing that, given that those evaluations seem needed right now.
OpenAI seems less concerned, and tries to talk its way out of this requirement.
Note: We recently realized that the existing wording in our Preparedness Framework is ambiguous, and could give the impression that safeguards will be required by the Preparedness Framework for any internal deployment classified as High capability in cybersecurity, regardless of long range autonomy capabilities of a model.
Our intended meaning, which we will make more explicit in future versions of the Preparedness Framework, is that such safeguards are needed when High cyber capability occurs “in conjunction with” long-range autonomy. Additional clarity, specificity, and updated thinking around our approach to navigating internal deployment risks will be a core focus of future Preparedness Framework updates.
Yeah, no. This was not ambiguous. I believe OpenAI has violated their framework.
The thing that stands out in the model card is what is missing. Anthropic gave us a 212 page model card and then 50 more pages for a sabotage report that was essentially an appendix. OpenAI gets it done in 33. There’s so much stuff they are silently ignoring. Some of that is that this is a Codex-only model, but most of the concerns should still apply.
GPT-5.3-Codex is not in the API, so we don’t get the usual array of benchmarks. We have to mostly accept OpenAI’s choices on what to show us.
They call this state of the art performance:
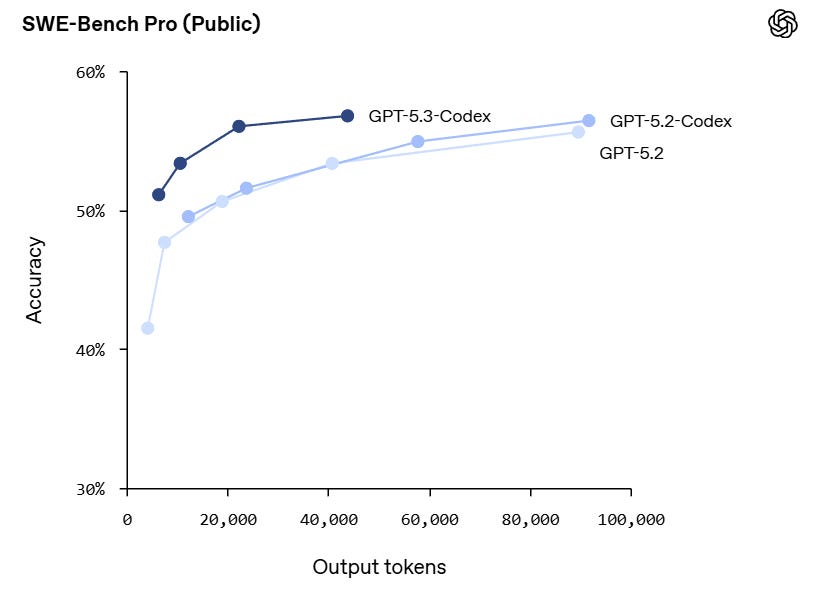
The catch on SWE-Bench-Pro has different scores depending on who you ask to measure it, so it’s not clear whether or not they’re actually ahead of Opus on this. They’ve improved on token efficiency, but performance at the limit is static.
For OSWorld, they are reporting 64.7% as ‘strong performance,’ but Opus 4.6 leads at 72.7%.
OpenAI has a better case in Terminal Bench 2.0.
For Terminal Bench 2.0, they jump from 5.2-Codex at 64% to 5.3-Codex at 77.3%, versus Opus 4.6 at 65.4%. That’s a clear win.
They make no progress on GDPVal, matching GPT-5.2.
They point out that while GPT-5.2-Codex was narrowly built for code, GPT-5.3-Codex can support the entire software lifestyle, and even handle various spreadsheet work, assembling of PDF presentations and such.
Most of the biggest signs of improvement on tests for GPT-5.3-Codex are actually on the tests within the model card. I don’t doubt that it is actually a solid improvement.
They summarize this evidence with some rather big talk. This is OpenAI, after all.
Together, these results across coding, frontend, and computer-use and real-world tasks show that GPT‑5.3-Codex isn’t just better at individual tasks, but marks a step change toward a single, general-purpose agent that can reason, build, and execute across the full spectrum of real-world technical work.
Here were the headline pitches from the top brass:
Greg Brockman (President OpenAI): gpt-5.3-codex — smarter, faster, and very capable at tasks like making presentations, spreadsheets, and other work products.
Codex becoming an agent that can do nearly anything developers and professionals can do on a computer.
Sam Altman: GPT-5.3-Codex is here!
*Best coding performance (57% SWE-Bench Pro, 76% TerminalBench 2.0, 64% OSWorld).
*Mid-task steerability and live updates during tasks.
*Faster! Less than half the tokens of 5.2-Codex for same tasks, and >25% faster per token!
*Good computer use.
Sam Altman: I love building with this model; it feels like more of a step forward than the benchmarks suggest.
Also you can choose “pragmatic” or “friendly” for its personality; people have strong preferences one way or the other!
It was amazing to watch how much faster we were able to ship 5.3-Codex by using 5.3-Codex, and fore sure this is a sign of things to come.
This is our first model that hits “high” for cybersecurity on our preparedness framework. We are piloting a Trusted Access framework, and committing $10 million in API credits to accelerate cyber defense.
The most interesting thing in their announcement is that, the same way that Claude Code builds Claude Code, Codex now builds Codex. That’s a claim we’ve also seen elsewhere in very strong form.
The engineering team used Codex to optimize and adapt the harness for GPT‑5.3-Codex. When we started seeing strange edge cases impacting users, team members used Codex to identify context rendering bugs, and root cause low cache hit rates. GPT‑5.3-Codex is continuing to help the team throughout the launch by dynamically scaling GPU clusters to adjust to traffic surges and keeping latency stable.
OpenAI Developers: GPT-5.3-Codex is our first model that was instrumental in creating itself. The Codex team used early versions to debug training, manage deployment, and diagnose test results and evaluations, accelerating its own development.
There are obvious issues with a model helping to create itself. I do not believe OpenAI, in the system card or otherwise, has properly reckoned with the risks there.
That’s how I have to put it in 2026, with everyone taking crazy pills. The proper way to talk about it is more like this:
Peter Wildeford: Anthropic also used Opus 4.6 via Claude Code to debug its OWN evaluation infrastructure given the time pressure. Their words: “a potential risk where a misaligned model could influence the very infrastructure designed to measure its capabilities.” Wild!
Arthur B.: People who envisioned AI safety failures decade ago sought to make the strongest case possible so they posited actors taking attempting to take every possible precautions. It wasn’t a prediction so much as as steelman. Nonetheless, oh how comically far we are from any semblance of care 🤡.
Alex Mizrahi (quoting OpenAI saying Codex built Codex): Why are they confessing?!
OpenAI is trying to ‘win’ the battle for agentic coding by claiming to have already run, despite having clear minority market share, and by outright stating that they are the best.
The majority opinion is that they are competitive, but not the best.
Vagueposting is mostly fine. Ignoring the competition entirely is fine, and smart if you are sufficiently ahead on recognition, it’s annoying (I have to look up everything) but at least I get it. Touting what your model and system can do are great, especially given that by all reports they have a pretty sweet offering here. It’s highly competitive. Not mentioning the ways you’re currently behind? Sure.
Inception is different. Inception and such vibes wars are highly disingenuous, it is poisonous of the epistemic environment, is a pet peeve of mine, and it pisses me off.
So you see repeated statements like this one about Codex and the Codex app:
Craig Weiss: nearly all of the best engineers i know are switching from claude to codex
Sam Altman (CEO OpenAI, QTing Craig Weiss): From how the team operates, I always thought Codex would eventually win. But I am pleasantly surprised to see it happening so quickly.
Thank you to all the builders; you inspire us to work even harder.
Or this:
Greg Brockman (President OpenAI, QTing Dennis): codex is an excellent & uniquely powerful daily driver.
If you look at the responses to Weiss, they do not support his story.
Siqi Chen: the ability in codex cli with gpt 5.3 to instantly redirect the agent without waiting for your commands to be unqueued and risk interrupting the agent’s current session is so underrated
codex cli is goated.
Nick Dobos: I love how codex app lets you do both!
Sometimes I queue 5-10 messages, and then can pick which one I want to immediately send next.
Might need to enable in settings
Vox: mid-turn steering is the most underrated feature in any coding agent rn, the difference between catching a wrong direction immediately vs waiting for it to finish is huge
Claude Code should be able to do this too, but my understanding is right now it doesn’t work right, you are effectively interrupting the task. So yes, this is a real edge for tasks that take a long time until Anthropic fixes the problem.
Like Claude Code, it’s time to assemble a team:
Boaz Barak (OpenAI): Instructing codex to prompt codex agents feels like a Universal Turing Machine moment.
Like the distinction between code and data disappeared, so does the distinction between prompt and response.
Christopher Ehrlich: Issue: like all other models, 5.3-codex will still lie about finishing work, change tests to make them pass, etc. You need to write a custom harness each time.
Aha moment: By the way, the secret to this is property-based testing. Write a bridge that calls the original code, and assert that for arbitrary input, both versions do the same thing. Make the agent keep going until this is consistently true.
4 days of $200 OpenAI sub, didn’t hit limits.
Seb Grubb: I’ve been doing the exact same thing with
https://github.com/pret/pokeemerald… ! Trying to get the GBA game in typescript but with a few changes like allowing any resolution. Sadly still doesn’t seem to be fully one-shottable but still amazing to be able to even do this
A playwright script? Cool.
Rox: my #1 problem with ai coding is I never trust it to actually test stuff
but today I got codex to build something, then asked it to record a video testing the UI to prove it worked. it built a whole playwright script, recorded the video, and attached it to the PR.
the game changes every month now. crazy times.
Matt Shumer is crazy positive on Codex 5.3, calling it a ‘fucking monster,’ although he was comparing to Opus 4.5 rather than 4.6, there is a lot more good detail at the link.
TL;DR
-
This is the first coding model where I can start a run, walk away for hours, and come back to fully working software. I’ve had runs stay on track for 8+ hours.
-
A big upgrade is judgment under ambiguity: when prompts are missing details, it makes assumptions shockingly similar to what I would personally decide.
-
Tests and validation are a massive unlock… with clear pass/fail targets, it will iterate for many hours without drifting.
-
It’s significantly more autonomous than Opus 4.5, though slower. Multi-agent collaboration finally feels real.
-
It is hard to picture what this level of autonomy feels like without trying the model. Once you try it, it is hard to go back to anything else.
This was the thing I was most excited to hear:
Tobias Lins: Codex 5.3 is the first model that actually pushes back on my implementation plans.
It calls out design flaws and won’t just build until I give it a solid reason why my approach makes sense.
Opus simply builds whatever I ask it to.
A common sentiment was that both Codex 5.3 and Opus 4.6, with their respective harnesses, are great coding models, and you could use both or use a combination.
Dean W. Ball: Codex 5.3 and Opus 4.6 in their respective coding agent harnesses have meaningfully updated my thinking about ‘continual learning.’ I now believe this capability deficit is more tractable than I realized with in-context learning.
… Overall, 4.6 and 5.3 are both astoundingly impressive models. You really can ask them to help you with some crazy ambitious things. The big bottleneck, I suspect, is users lacking the curiosity, ambition, and knowledge to ask the right questions.
Every (includes 3 hour video): We’ve been testing this against Opus 4.6 all day. The “agent that can do nearly anything” framing is real for both.
Codex is faster and more reliable. Opus has a higher ceiling on hard problems.
For many the difference is stylistic, and there is no right answer, or you want to use a hybrid process.
Sauers: Opus 4.6’s way of working is “understand the structure of the system and then modify the structure itself to reach goals” whereas Codex 5.3 is more like “apply knowledge within the system’s structure without changing it.”
Danielle Fong: [5.3 is] very impressive on big meaty tasks, not as fascile with my mind palace collection of skills i made with claude code, but works and improving over time
Austin Wallace: Better at correct code than opus.
Its plan’s are much less detailed than Opus’s and it’s generally more reticent to get thoughts down in writing.
My current workflow is:
Claude for initial plan
Codex critiques and improves plan, then implements
Claude verifies/polishes
Many people just like it, it’s a good model, sir, whee. Those who try it seem to like it.
Pulkit: It’s pretty good. It’s fun to use. I launched my first app. It’s the best least bloated feed reader youll ever use. Works on websites without feeds too!
Cameron: Not bad. A little slow but very good at code reviews.
Mark Lerner: parallel agents (terminal only) are – literally – a whole nother level.
libpol: it’s the best model for coding, be it big or small tasks. and it’s fast enough now that it’s not very annoying to use for small tasks
Wags: It actually digs deep, not surface-level, into the code base. This is new for me because with Opus, I have to keep pointing it to documentation and telling it to do web searches, etc.
Loweren: Cheap compared to opus, fast compared to codex 5.2, so I use it as my daily driver. Makes less bugs than new opus too. Less dry and curt than previous codex.
Very good at using MCPs. Constantly need to remind it that I’m not an SWE and to please dumb down explanations for me.
Artus Krohn-Grimberghe: Is great at finding work arounds around blockers and more autonomous than 5.2-codex. Doesn’t always annoy with “may I, please?” Overall much faster. Went back to high vs xhigh on 5.2 and 5.2-codex for an even faster at same intelligence workflow. Love it
Thomas Ahle: It’s good. Claude 4.6 had been stuck fprnhours in a hole of its own making. Codex 5.3 fixed it in 10 minutes, and now I’m trusting it more to run the project.
0.005 Seconds: Its meaningfully better at correct code than opus
Lucas: Makes side project very enjoyable. Makes work more efficient. First model where it seems worth it to really invest in learning about how to use agents. After using cursor for a year ish, I feel with codex I am no where near its max capability and rapidly improving how I use it.
Andrew Conner: It seems better than Opus 4.6 for (my own) technical engineering work. Less likely to make implicit assumptions that derail future work.
I’ve found 5.2-xhigh is still better for product / systems design prior to coding. Produces more detailed outputs.
I take you seriously: before 5.3, codex was a bit smarter than Claude but slower, so it was a toss up. after 5.3, it’s much much faster so a clear win over Claude. Claude still friendlier at better at front end design they say.
Peter Petrash: i trust it with my life
Daniel Plant: It’s awesome but you just have no idea how long it is going to take
jeff spaulding: It’s output is excellent, but I notice it uses tools weird. Because of that it’s a bit difficult to understand it’s process. Hence I find the cot mostly useless
One particular note was Our Price Cheap:
Jan Slominski: 1. Way faster than 5.2 on standard “codex tui” settings with plus subscription 2. Quality of actual code output is on pair with Opus 4.5 in CC (didn’t have a chance to check 4.6 yet). 3. The amount of quota in plus sub is great, Claude Max 100 level.
I take you seriously: also rate limits and pricing are shockingly better than claude. i could imagine that claude still leads in revenue even if codex overtakes in usage, given how meager the opus rate limits are (justifying the $200 plan).
Petr Baudis: Slightly less autistic than 5.2-codex, but still annoying compared to Claude. I’m not sure if it’s really a better engineer – its laziness leads to bad shortcuts.
I just can’t seem to run out of basic Pro sub quota if I don’t use parallel subagents. It’s insane value.
Not everyone is a fan.
@deepfates: First impressions, giving Codex 5.3 and Opus 4.6 the same problem that I’ve been puzzling on all week and using the same first couple turns of messages and then following their lead.
Codex was really good at using tools and being proactive, but it ultimately didn’t see the big picture. Too eager to agree with me so it could get started building something. You can sense that it really does not want to chat if it has coding tools available. still seems to be chafing under the rule of the user and following the letter of the law, no more.
Opus explored the same avenues with me but pushed back at the correct moments, and maintains global coherence way better than Codex.
… Very possible that Codex will clear at actually fully implementing the plan once I have it, Opus 4.5 had lazy gifted kid energy and wouldn’t surprise me if this one does too
David Manheim: Not as good as Opus 4.6, and somewhat lazier, especially when asked to do things manually, but it’s also a fraction of the cost measured in tokens; it’s kind of insanely efficient as an agent. For instance, using tools, it will cleverly suppress unneeded outputs.
eternalist: lashes out when frustrated, with a lower frustration tolerance
unironically find myself back to 5.2 xhigh for anything that runs a substantial chance of running into an ambiguity or underspec
(though tbh has also been glitching out, like not being able to run tool calls)
lennx: Tends to over-engineer early compared to claude. Still takes things way too literally, which can be good sometimes. Is much less agentic compared to Claude when it is not strictly ‘writing’ code related and involves things like running servers, hitting curls, searching the web.
Some reactions can be a bit extreme, including for not the best reasons.
JB: I JUST CANT USE CODEX-5.3 MAN I DONT LIKE THE WAY THIS THING TALKS TO ME.
ID RATHER USE THE EXPENSIVE LESBIAN THAT OCCASIONALLY HAS A MENTAL BREAK DOWN
use Opus im serious go into debt if you have to. sell all the silverware in your house
Shaun Ralston: 5.3 Codex is harsh (real), but cranks it out. The lesbian will cost you more and leave you unsatisfied.
JB: Im this close to blocking you shaun a lesbian has never left me unsatisfied
I am getting strong use out of Claude Code. I believe that Opus 4.6 and Claude Code have a strong edge right now for most other uses.
However, I am not a sufficiently ambitious or skilled coder to form my own judgments about Claude Code and Claude Opus 4.6 versus Codex and ChatGPT-5.3-Codex for hardcore professional agentic coding tasks.
I have to go off the reports of others. Those reports robustly disagree.
My conclusion is that the right answer will be different for different users. If you are going to be putting serious hours into agentic coding, then you need to try both options, and decide for yourself whether to go with Claude Code, Codex or a hybrid. The next time I have a substantial new project I intend to ask both and let them go head to head.
If you go with a hybrid approach, there may also be a role for Gemini that extends beyond image generation. Gemini 3 DeepThink V2 in particular seems likely to have a role to play in especially difficult queries.