Americans trust Fauci over RFK Jr. and career scientists over Trump officials
Anti-vaccine activist and current Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has worked hard to villainize infectious disease expert Anthony Fauci, even writing a conspiracy-laden book lambasting the former director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
But a year into the job as the country’s top health official, Kennedy—who has no background in medicine, science, or public health—still holds less sway with Americans than the esteemed physician-scientist.
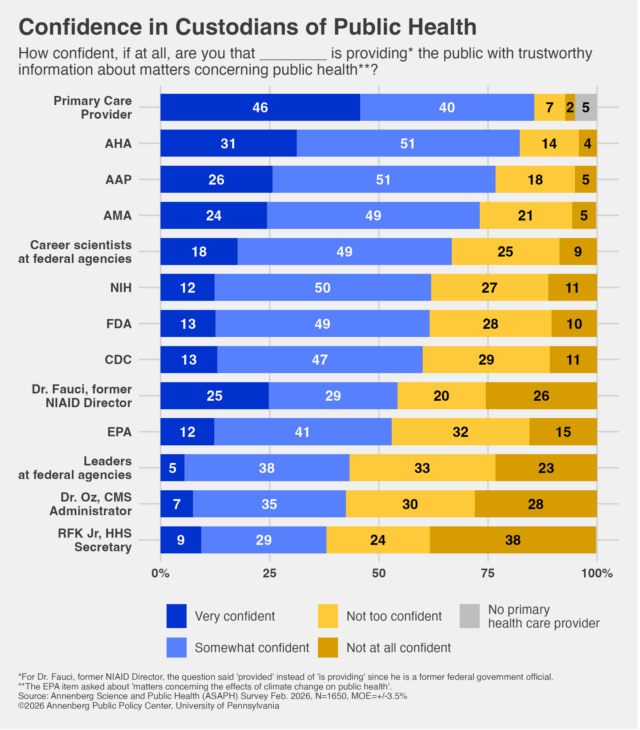
In a nationally representative survey conducted in February by the Annenberg Public Policy Center at the University of Pennsylvania, 54 percent of respondents said they had confidence in Fauci, while only 38 percent had confidence in Kennedy. Breaking those supporters down further, 25 percent of respondents said they were “very confident” in Fauci, while only 9 percent said the same for Kennedy.
Overall, the survey found a clear divide between the confidence in Kennedy and other Trump administration officials and that of career scientists and medical associations.
Among federal agencies, 67 percent said they had confidence in career scientists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Food and Drug Administration, and the National Institutes of Health. But only 43 percent said they had confidence in the leaders of those agencies.
“The public is differentiating the trustworthiness of career scientists in the CDC, NIH, and FDA from that of the leaders of those agencies and recalling substantially higher confidence in the guidance that former director Fauci provided than that offered by Secretary Kennedy or Dr. Oz,” Ken Winneg, APPC’s managing director of survey research, said in a statement.
Americans trust Fauci over RFK Jr. and career scientists over Trump officials Read More »