This may be the grossest eye pic ever—but the cause is what’s truly horrifying
Savage microbe
Whatever was laying waste to his eye seemed to have come from inside his own body, carried in his bloodstream—possibly the same thing that could explain the liver mass, lung nodules, and brain lesions. There was one explanation that fit the condition perfectly: hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae or hvKP.
Classical K. pneumoniae is a germ that dwells in people’s intestinal tracts and is one that’s familiar to doctors. It’s known for lurking in health care settings and infecting vulnerable patients, often causing pneumonia or urinary tract infections. But hvKP is very different. In comparison, it’s a beefed-up bacteria with a rage complex. It was first identified in the 1980s in Taiwan—not for stalking weak patients in the hospital but for devastating healthy people in normal community settings.
An infection with hvKP—even in otherwise healthy people—is marked by metastatic infection. That is, the bacteria spreads throughout the body, usually starting with the liver, where it creates a pus-filled abscess. It then goes on a trip through the bloodstream, invading the lungs, brain, soft tissue, skin, and the eye (endogenous endophthalmitis). Putting it all together, the man had a completely typical clinical case of an hvKP infection.
Still, definitively identifying hvKP is tricky. Mucus from the man’s respiratory tract grew a species of Klebsiella, but there’s not yet a solid diagnostic test to differentiate hvKP from the classical variety. Since 2024, researchers have worked out a strategy of using the presence of five different virulence genes found on plasmids (relatively small, circular pieces of DNA, separate from chromosomal DNA, that can replicate on their own and be shared among bacteria.) But the method isn’t perfect—some classical K. pneumoniae can also carry the five genes.
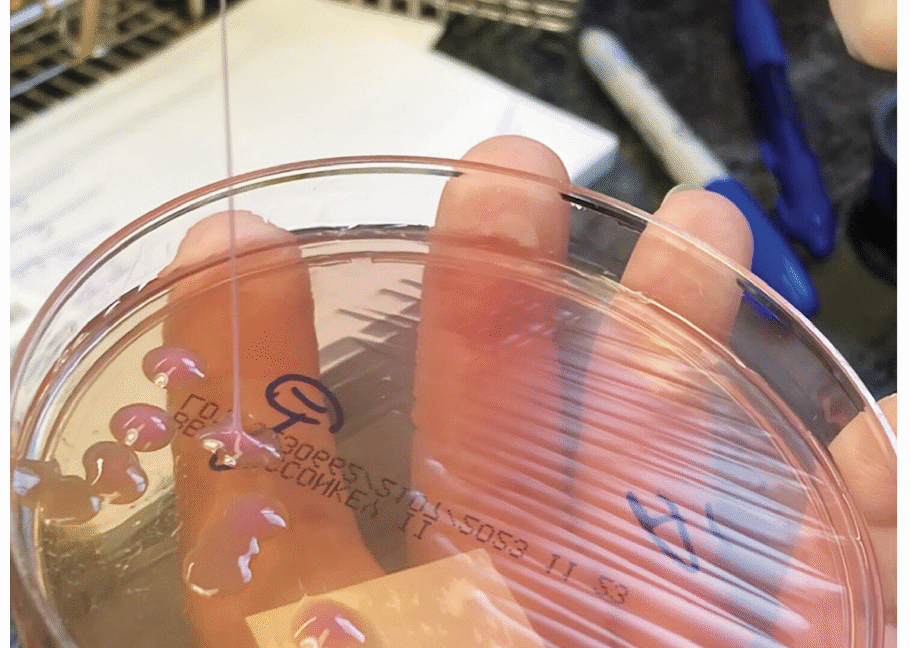
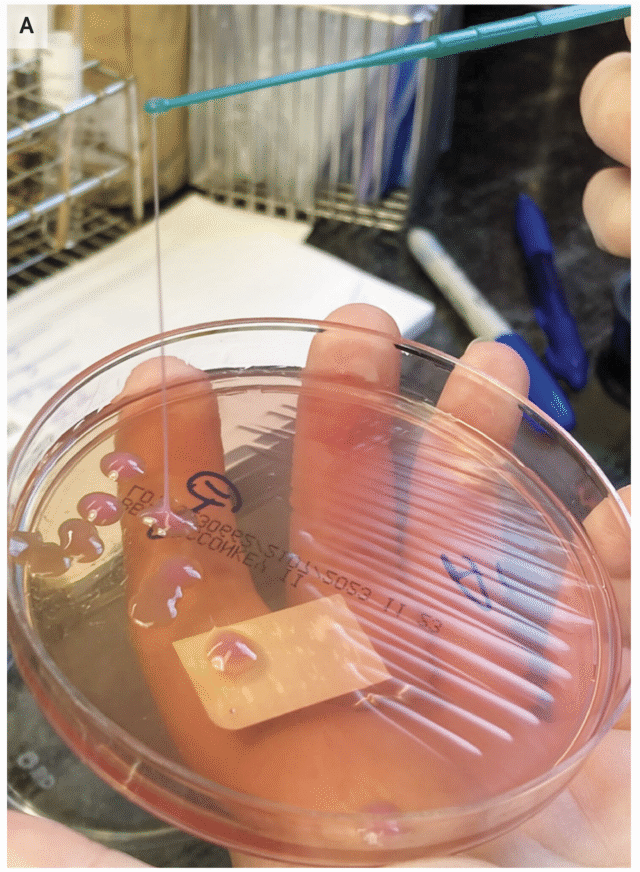
A string test performed on the rare growth of Klebsiella pneumoniae from the sputum culture shows a positive result, with the formation of a viscous string with a height of greater than 5 mm. Credit: NEJM 2026
Another much simpler method is the string test, in which clinicians basically test the goopy-ness of the bacteria—hvKP is known for being sticky. For this test, a clinician grows the bacteria into a colony on a petri dish, then touches an inoculation loop to the colony and pulls up. If the string of attached goo stretches more than 5 mm off the petri dish, it’s considered positive for hvKP. This is (obviously) not a precise test.
This may be the grossest eye pic ever—but the cause is what’s truly horrifying Read More »