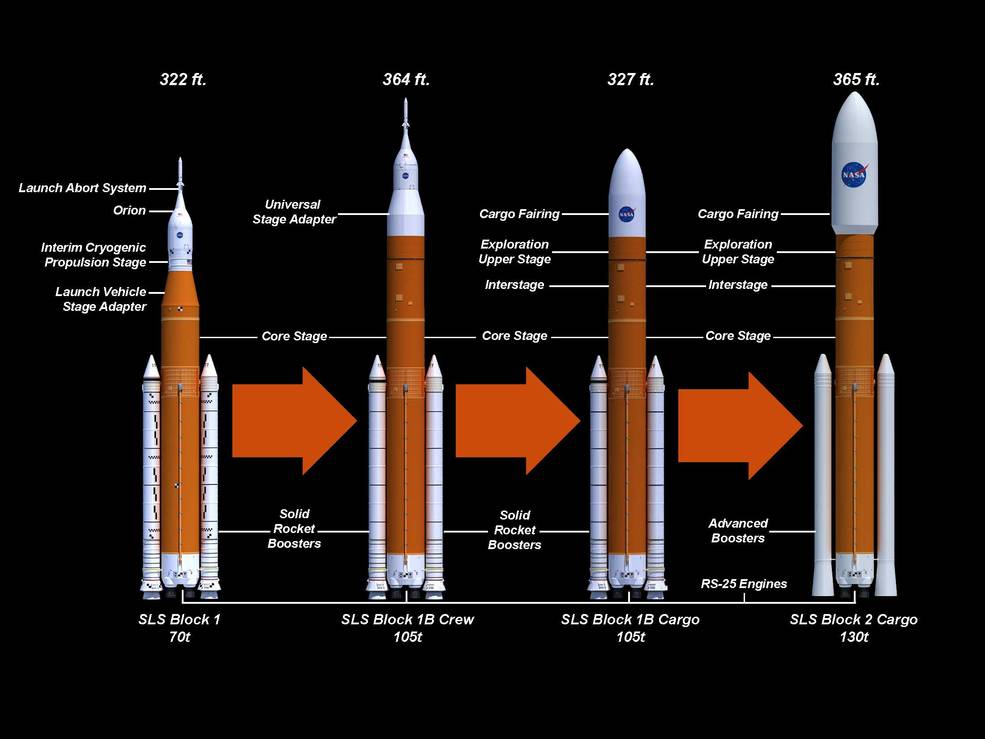
Ding-dong! The Exploration Upper Stage is dead
Now, you might think NASA would ask industry for solutions to this problem. After all, United Launch Alliance was developing a more powerful upper stage for its Vulcan rocket, the Centaur V, that used the same propellant as the core stage of the SLS rocket. And Blue Origin was also developing a powerful upper stage engine, the BE-3U, powered by hydrogen. These options were cheaper, available, and … summarily ignored.
10 years, billions of dollars, and not much to show for it
Congress, smelling jobs, wanted NASA to develop a brand new upper stage. So in 2016, lawmakers allocated $85 million for preliminary work on the upper stage, and have since awarded more than $3.5 billion.
For the development of a rocket’s second stage.
With engines (RL-10s) that have been flying in space for six decades.
And after all of this, a decade later, the upper stage remains years from being ready to fly.
In some ways, the Exploration Upper Stage was the perfect vehicle for pork. It not only spread largesse among Boeing and Aerojet Rocketdyne (for the engines), but it also necessitated a massive new launch tower in Florida. That was good for the Exploration Ground Systems program at Kennedy Space Center.
The original cost estimates of these projects are always instructive to look back on. Boeing’s initial contract to build the Exploration Upper Stage started at $962 million, and NASA planned to launch the rocket on the second flight of the SLS in 2021. Oops. As for the launch tower, the initial estimate for its cost was $383 million, but as of late, it was heading north of $2 billion. So we are talking billions and billions and billions of dollars for a relatively straightforward upper stage, using off-the-shelf engines and a large launch tower.
Ding-dong! The Exploration Upper Stage is dead Read More »