A telltale toilet reveals “lost” site shown in Bayeux Tapestry
Seats of power
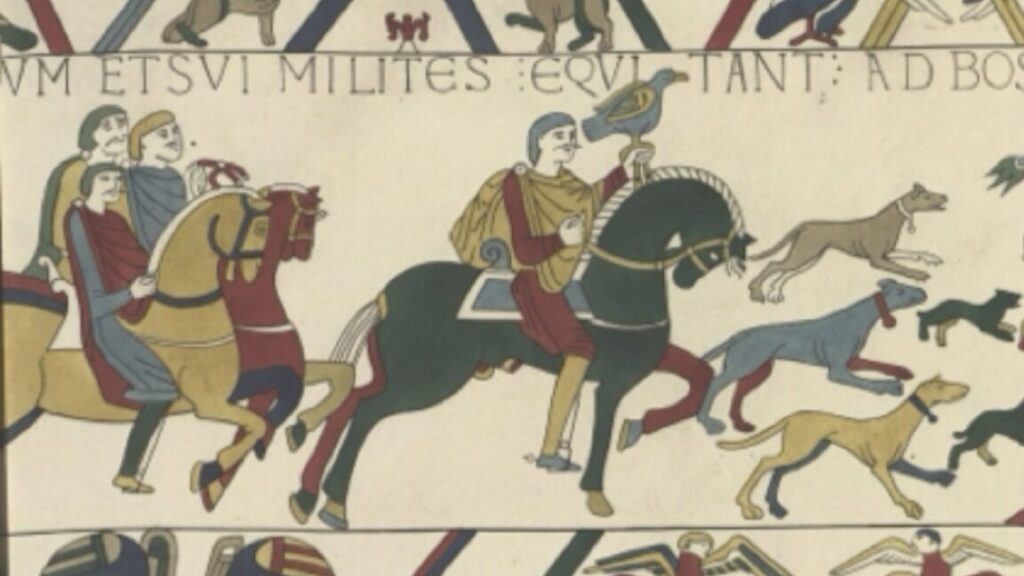
The Bayeux Tapestry, showing King Harold riding to Bosham, where he attends church and feasts in a hall, before departing for France. The Society of Antiquaries of London
According to Creighton and his co-authors, there has been quite a lot of research on castles, which dominated aristocratic sites in England after the Norman Conquest. That event “persists as a deep schism that continues to be seen as the watershed moment after which elites finally tapped into the European mainstream of castle construction,” they wrote. The study of residences (or “lordly enclaves”) has been more peripheral, yet the authors argue that up until 1066, aristocrats and rulers like King Harold invested heavily in residences, often co-located with churches and chapels.
The “Where Power Lies” project employed a wide range of research methodology—including perusing old maps and records, a re-analysis of past excavations, geophysics, ground-penetrating radar (GPR), and photogrammatic modeling—to define the signatures of such enclaves and map them into a single geographic information database (GIS). The project has identified seven such “lordly centers,” two of which are discussed in the current paper: an early medieval enclosure at Hornby in North Yorkshire and Bosham in West Sussex.
It has long been suspected that one particular manor house in Bosham (now a private residence) stands on the site of what was once King Harold’s residence. Per the authors, the original residence was clearly connected with Holy Trinity Church just to the south, parts of which date back to the 11th century, as evidenced by the posthole remains of what was once a bridge or causeway. More evidence can be found in a structure known as the “garden ruin,” little of which survives above ground—and even that was heavily overgrown. GPR data showed buried features that would have been the eastern wall of King Harold’s lordly enclave.
The biggest clue was the discovery in 2006 of a latrine within the remains of a large timber building. Its significance was not recognized at the time, but archaeologists have since determined that high-status homes began integrating latrines in the 10th century, so the structure was most likely part of King Harold’s residence. Co-author Duncan Wright of Newcastle University believes this “Anglo-Saxon en suite,” along with all the other evidence, proves “beyond all reasonable doubt that we have here the location of Harold Godwinson’s private power center, the one famously depicted on the Bayeux Tapestry.”
DOI: The Antiquaries Journal, 2025. 10.1017/S0003581524000350 (About DOIs).
A telltale toilet reveals “lost” site shown in Bayeux Tapestry Read More »