MacBook Neo hands-on: Apple build quality at a substantially lower price
NEW YORK CITY—Whether you’re talking about the iBook, MacBook, or MacBook Air, Apple’s most basic laptops have started at or within $100 of the $1,000 price point for over 20 years. Sure, the company had quietly been testing the waters with a Walmart-exclusive M1 MacBook Air configuration for several years, first at $699 and then at $599. But as far as what Apple would actively advertise and offer on its own site and in its own retail stores, we’ve never seen anything for substantially below $1,000.
The new MacBook Neo changes that. Apple has experimented with lower-cost products before, most notably with the $329 and $349 iPads and the old $429 iPhone SE. But this is the first time it has used that strategy for the Mac. The Neo starts at $599 for a version with 256GB of storage and no Touch ID sensor, and $699 for a version with Touch ID and 512GB of storage (each also available to educational customers for $100 less).
We had a chance to poke at a MacBook Neo for a while at Apple’s “special experience” event in New York this morning, and what I can tell you is that this does feel like an Apple laptop despite the lower starting price. It definitely has some spec sheet shortcomings, even compared to older M3 or M4 MacBook Airs that you still might be able to get at a discount from third-party retailers or Apple’s refurbished site—more on that in our full review next week. But it’s priced low enough to (1) appeal to people who might not have considered a Mac before, and (2) to make some of its borderline specs feel reasonable, and that’s enough to keep it interesting.
MacBook Air-ish
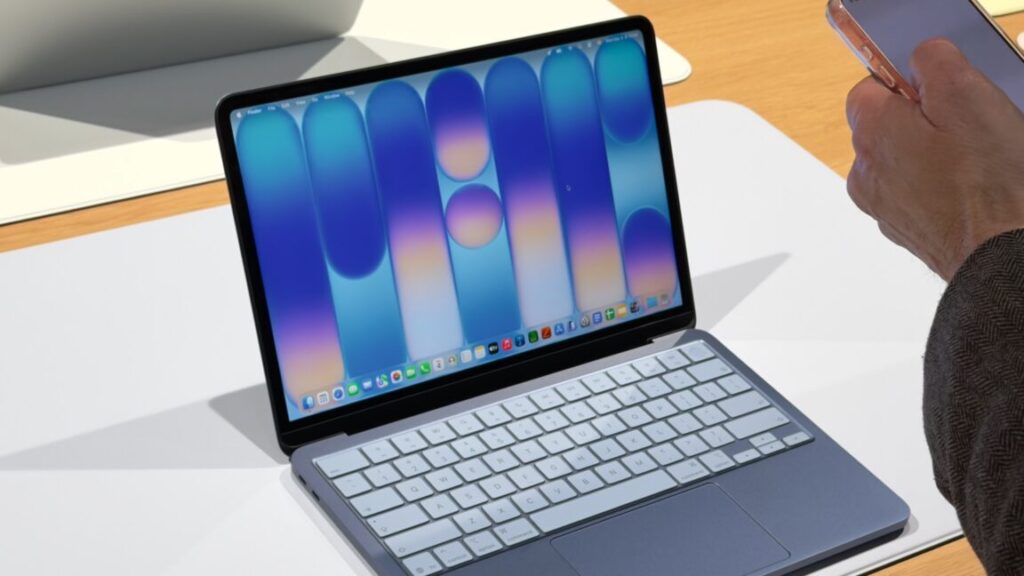
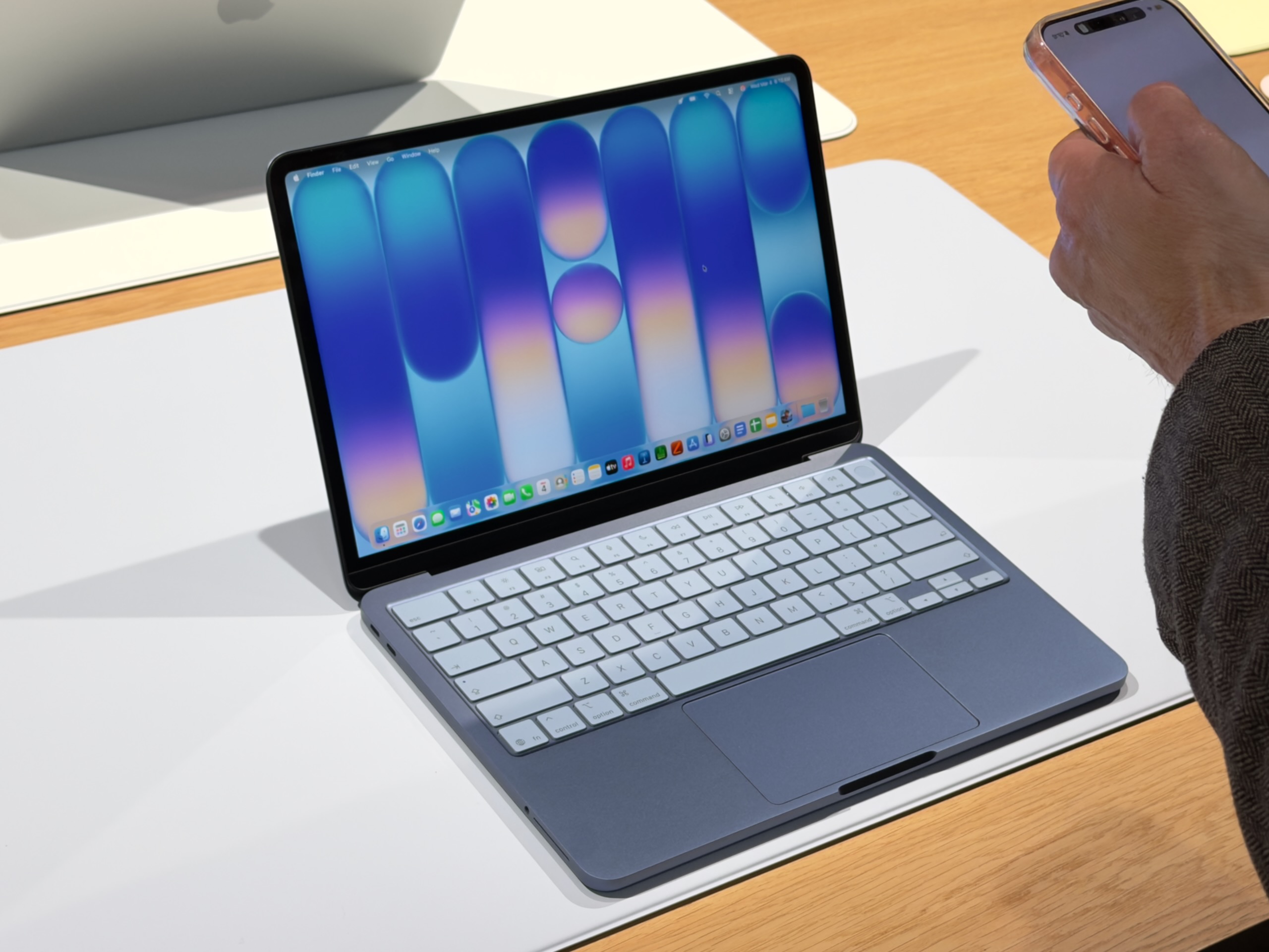
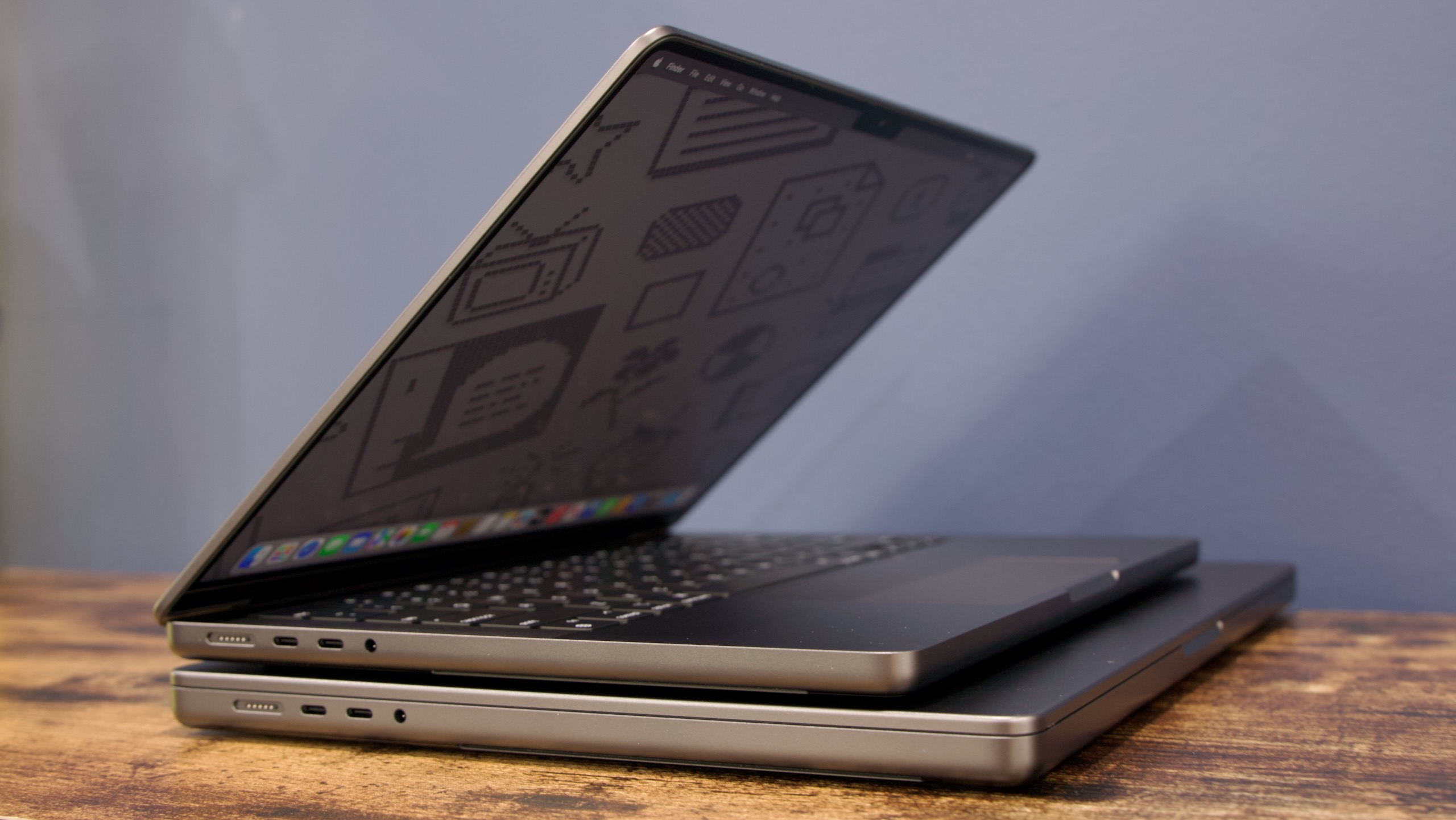
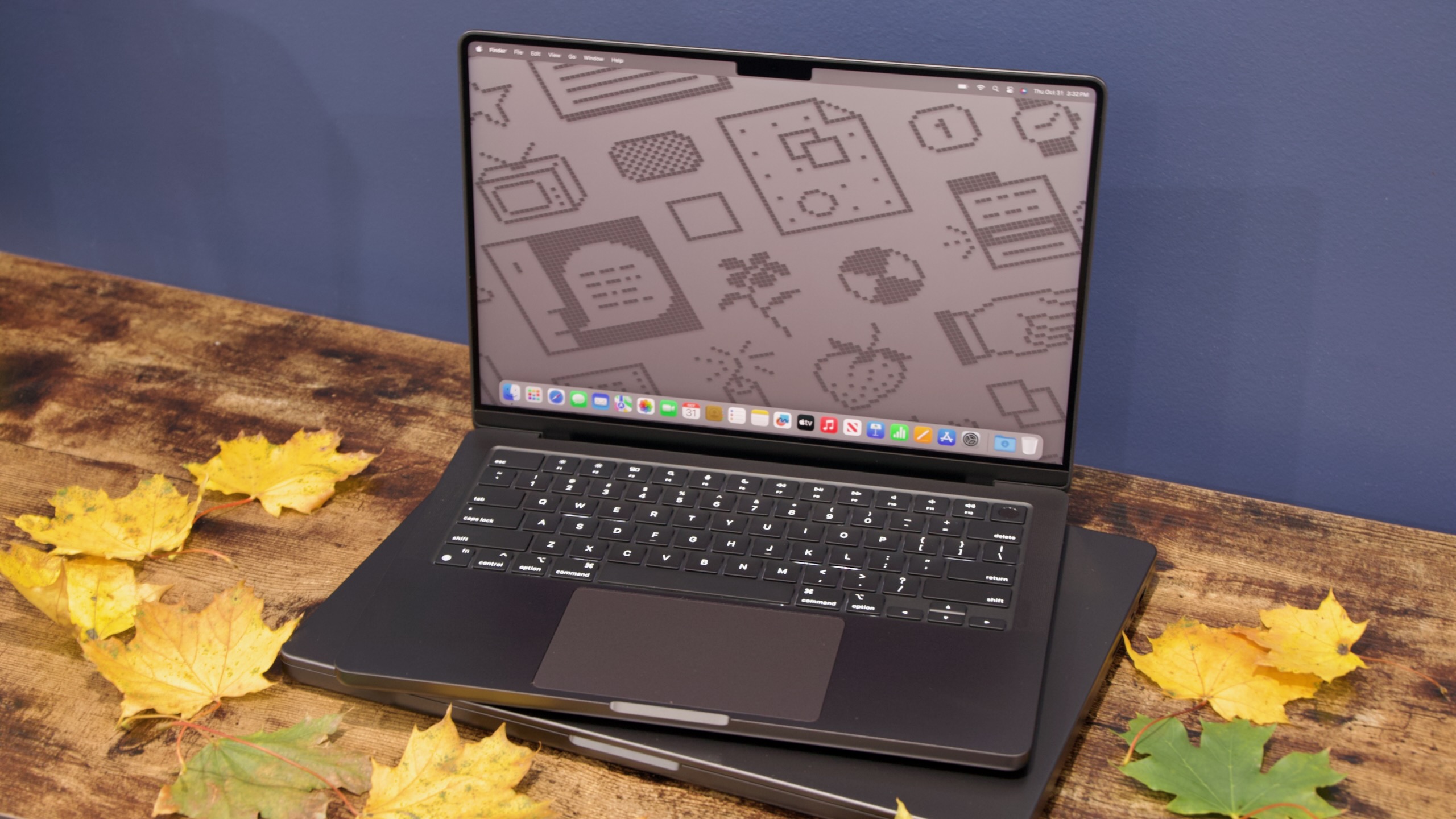
I had assumed, based on Apple’s history with its lower-end iPads and iPhones, that Apple would essentially reuse the design of the old M1 MacBook Air for this new MacBook. The Neo does share quite a few things in common with that older design, including a 13-inch notchless display, a 2.7 lb weight, and a lack of MagSafe connector. But this is actually a new design after all, one that’s more in line with the current Pro and Air iterations.
The Neo is a flat rectangular slab of aluminum with softly rounded edges, more like the current Airs and Pros than the wedge-shaped design of the old M1 Air (also like modern Airs, the words “MacBook Neo” appear nowhere on the exterior of the computer—the name only exists in stores and in software).
The low-end iPad can feel a bit cheap or hollow, partly because of the small gap between the front glass and the non-laminated LCD display underneath. But holding and interacting with the Neo feels substantially the same as interacting with an Air. It is, however, slightly thicker—an even 0.5 inches, up from 0.44 inches for the M4 Air.
The non-backlit keyboard is a bit of a bummer, although Apple has tried to keep it legible by shifting from white-on-black keycaps to darker legends on a lighter background. But the typing feel is similar to the Air, and we’re told the scissor switches have the same amount of key travel as the switches in the Air keyboards.
The multi-touch trackpad is a little weirder. It looks a lot like Apple’s other trackpads, but it actually has a physical clicking mechanism rather than the haptic feedback Apple has used in its laptop trackpads and Magic Trackpads for years. That means there’s no Force Click functionality and no controls for adjusting the firmness or noisiness of the clicking sensation.
Apple did, at least, figure out a mechanism that makes it feel the same to click anywhere on the trackpad. More traditional physical trackpads, including the ones Apple used to use, had a hinge toward the top of the trackpad that made clicking up there feel stiffer and firmer than clicking at the bottom or in the middle of the trackpad. The Neo’s trackpad doesn’t feel quite as solid, probably because of the space left to make room for a physical clicking mechanism, but, aside from the missing haptics, it seems to work just as well as Apple’s other trackpads.
The laptop’s ports may cause some confusion, for the same reason that any USB-C or Thunderbolt port can cause confusion—the ports look the same but do different things. Either of the laptop’s two USB-C ports can charge the laptop. But only the rear one supports 10 Gbps USB 3 transfer speeds, and it’s also the only one that can drive a display (one 4K screen at up to 60 Hz, down from two higher-resolution external displays for the Air). The port toward the front only supports 480 Mbps USB 2.0 transfer speeds, enough for a keyboard and many other external accessories, but not ideal for external storage.
Neither port is marked in any way, though macOS will apparently alert users if they try to plug something into the USB 2.0 port that won’t work with it.
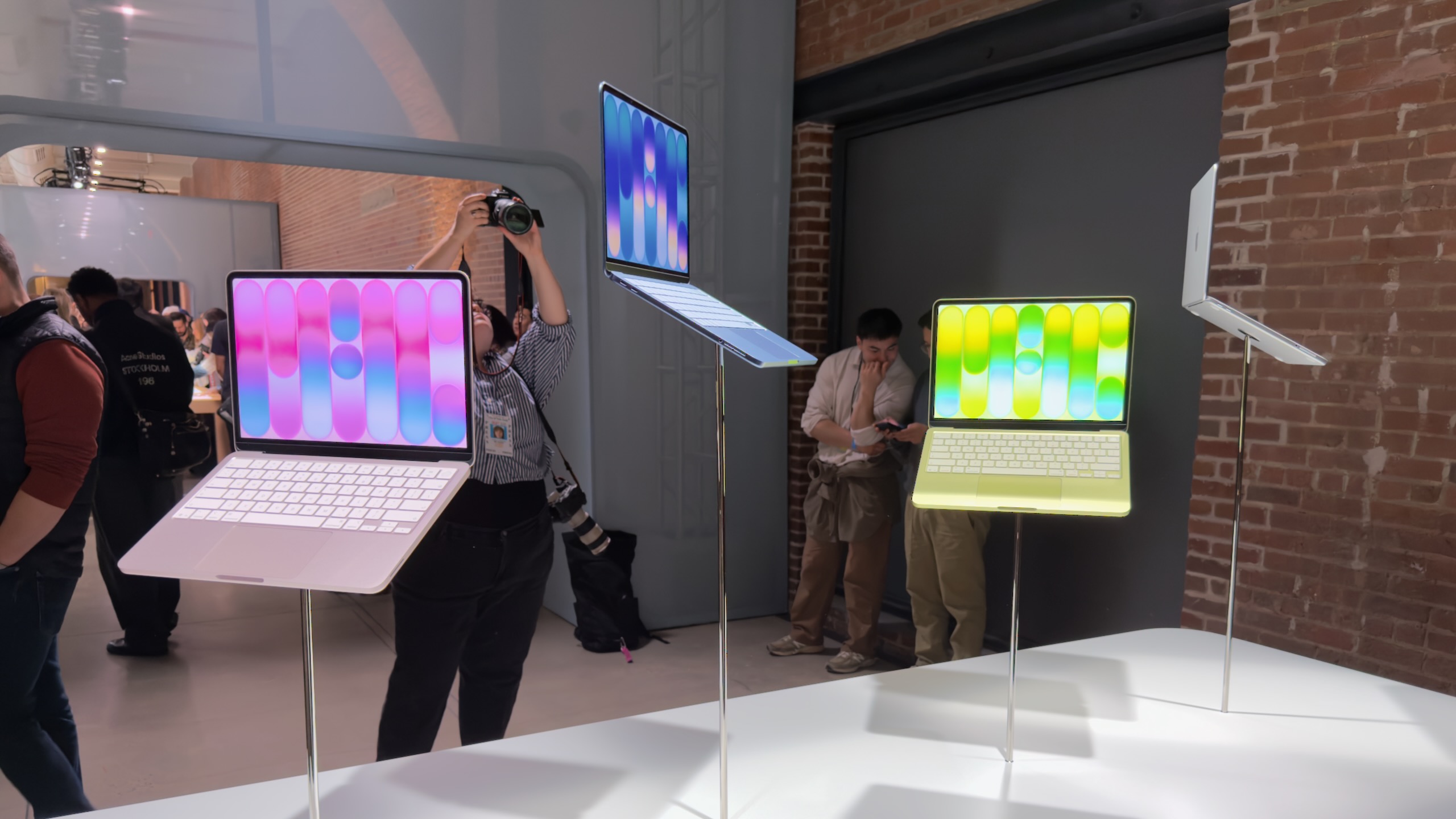
The four colors of Neo: the pink-ish Blush, blue-tinted Indigo, yellowy Citrus, and traditional MacBook silver. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
The internal display is great for the price, though it falls a bit short of both the current Airs and the M1 Air. The 13-inch 2408×1506 IPS LCD screen is just shy of the old M1 Air’s resolution, and it supports both 500 nits of maximum brightness and full coverage of the sRGB color gamut, both relatively rare in similarly priced PCs. But it’s missing DCI-P3 wide color support and the True Tone feature that subtly adjusts the color temperature of the display based on ambient lighting, two things that were still supported by the old M1 Air.
The biggest sticking point for many buyers will be the processor, an Apple A18 Pro that first appeared in the iPhone 16 Pro.
This chip includes six CPU cores (two performance, four efficiency) and a five-core GPU, which worked just fine under casual use in the hands-on area and in our briefing. We saw it running Safari with multiple tabs open, playing a game, and running Pixelmator Pro, and it handled all three tasks well. But the higher-end apps that aren’t bottlenecked by the CPU or GPU may be bottlenecked by its 8GB of RAM instead.
We’ll do more testing in our review to figure out where people will notice the specs in the real world and where they won’t, but suffice it to say, this isn’t the best laptop to pick if you want to make the most of a Creator Studio subscription.
All in all, the MacBook Neo seems well-positioned to satisfy those whom Apple is marketing it toward. Predominantly, that seems to be iPhone users who don’t have any kind of computer yet, or people who are unhappy with their budget Windows PC or Chromebook. Apple’s product page makes a big deal about the features that work across iOS and macOS and has a dedicated “new to Mac” section that pitches the platform to people who have never used it. The biggest downside for Apple is the risk that the Neo’s 8GB RAM limit and less-powerful chip will end up frustrating people who buy a Mac hoping to use Final Cut or Logic and bump into the limits of the hardware.
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
MacBook Neo hands-on: Apple build quality at a substantially lower price Read More »