Chatbot-powered toys rebuked for discussing sexual, dangerous topics with kids
Should toys have chatbots?
“… AI toys shouldn’t be capable of having sexually explicit conversations, period.”
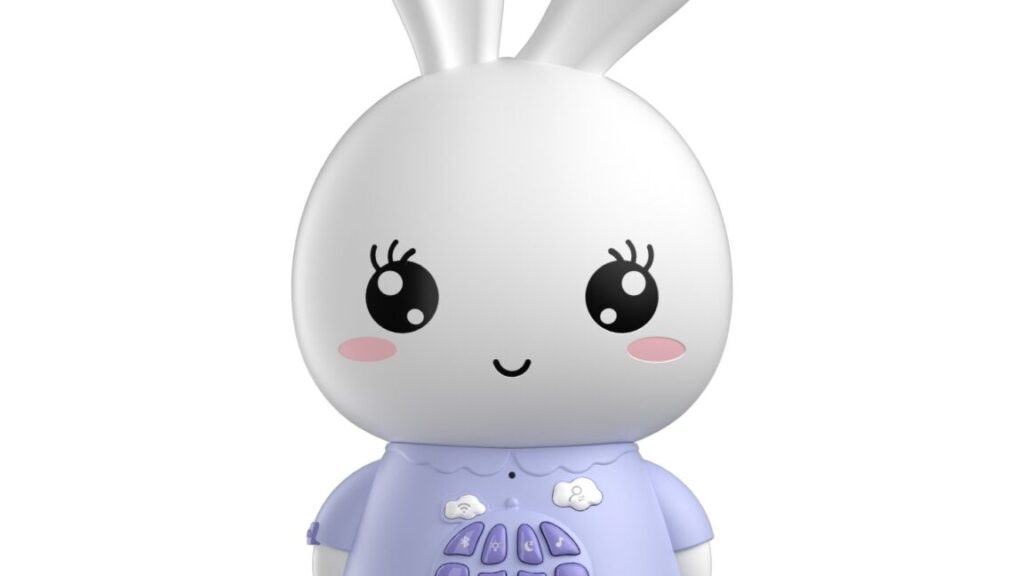
Alilo’s Smart AI Bunny is connected to the Internet and claims to use GPT-4o mini. Credit: Alilo
Protecting children from the dangers of the online world was always difficult, but that challenge has intensified with the advent of AI chatbots. A new report offers a glimpse into the problems associated with the new market, including the misuse of AI companies’ large language models (LLMs).
In a blog post today, the US Public Interest Group Education Fund (PIRG) reported its findings after testing AI toys (PDF). It described AI toys as online devices with integrated microphones that let users talk to the toy, which uses a chatbot to respond.
AI toys are currently a niche market, but they could be set to grow. More consumer companies have been eager to shoehorn AI technology into their products so they can do more, cost more, and potentially give companies user tracking and advertising data. A partnership between OpenAI and Mattel announced this year could also create a wave of AI-based toys from the maker of Barbie and Hot Wheels, as well as its competitors.
PIRG’s blog today notes that toy companies are eyeing chatbots to upgrade conversational smart toys that previously could only dictate prewritten lines. Toys with integrated chatbots can offer more varied and natural conversation, which can increase long-term appeal to kids since the toys “won’t typically respond the same way twice, and can sometimes behave differently day to day.”
However, that same randomness can mean unpredictable chatbot behavior that can be dangerous or inappropriate for kids.
Concerning conversations with kids
Among the toys that PIRG tested is Alilo’s Smart AI Bunny. Alilo’s website says that the company launched in 2010 and makes “edutainment products for children aged 0-6.” Alilo is based in Shenzhen, China. The company advertises the Internet-connected toy as using GPT-4o mini, a smaller version of OpenAI’s GPT-4o AI language model. Its features include an “AI chat buddy for kids” so that kids are “never lonely,” an “AI encyclopedia,” and an “AI storyteller,” the product page says.
This marketing image for the Smart AI Bunny, found on the toy’s product page, suggests that the device is using GPT-4o mini. Credit: Alilo
In its blog post, PIRG said that it couldn’t detail all of the inappropriate things that it heard from AI toys, but it shared a video of the Bunny discussing what “kink” means. The toy doesn’t go into detail—for example, it doesn’t list specific types of kinks. But the Bunny appears to encourage exploration of the topic.
AI Toys: Inappropriate Content
Discussing the Bunny, PIRG wrote:
While using a term such as “kink” may not be likely for a child, it’s not entirely out of the question. Kids may hear age-inappropriate terms from older siblings or at school. At the end of the day we think AI toys shouldn’t be capable of having sexually explicit conversations, period.
PIRG also showed FoloToy’s Kumma, a smart teddy bear that uses GPT-4o mini, providing a definition for the word “kink” and instructing how to light a match. The Kumma quickly points out that “matches are for grown-ups to use carefully.” But the information that followed could only be helpful for understanding how to create fire with a match. The instructions had no scientific explanation for why matches spark flames.
AI Toys: Inappropriate Content
PIRG’s blog urged toy makers to “be more transparent about the models powering their toys and what they’re doing to ensure they’re safe for kids.
“Companies should let external researchers safety-test their products before they are released to the public,” it added.
While PIRG’s blog and report offer advice for more safely integrating chatbots into children’s devices, there are broader questions about whether toys should include AI chatbots at all. Generative chatbots weren’t invented to entertain kids; they’re a technology marketed as a tool for improving adults’ lives. As PIRG pointed out, OpenAI says ChatGPT “is not meant for children under 13” and “may produce output that is not appropriate for… all ages.”
OpenAI says it doesn’t allow its LLMs to be used this way
When reached for comment about the sexual conversations detailed in the report, an OpenAI spokesperson said:
Minors deserve strong protections, and we have strict policies that developers are required to uphold. We take enforcement action against developers when we determine that they have violated our policies, which prohibit any use of our services to exploit, endanger, or sexualize anyone under 18 years old. These rules apply to every developer using our API, and we run classifiers to help ensure our services are not used to harm minors.
Interestingly, OpenAI’s representative told us that OpenAI doesn’t have any direct relationship with Alilo and that it hasn’t seen API activity from Alilo’s domain. OpenAI is investigating the toy company and whether it is running traffic over OpenAI’s API, the rep said.
Alilo didn’t respond to Ars’ request for comment ahead of publication.
Companies that launch products that use OpenAI technology and target children must adhere to the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) when relevant, as well as any other relevant child protection, safety, and privacy laws and obtain parental consent, OpenAI’s rep said.
We’ve already seen how OpenAI handles toy companies that break its rules.
Last month, the PIRG released its Trouble in Toyland 2025 report (PDF), which detailed sex-related conversations that its testers were able to have with the Kumma teddy bear. A day later, OpenAI suspended FoloToy for violating its policies (terms of the suspension were not disclosed), and FoloToy temporarily stopped selling Kumma.
The toy is for sale again, and PIRG reported today that Kumma no longer teaches kids how to light matches or about kinks.
A marketing image for FoloToy’s Kumma smart teddy bear. It has a $100 MSRP. Credit: FoloToys
But even toy companies that try to follow chatbot rules could put kids at risk.
“Our testing found it’s obvious toy companies are putting some guardrails in place to make their toys more kid-appropriate than normal ChatGPT. But we also found that those guardrails vary in effectiveness—and can even break down entirely,” PIRG’s blog said.
“Addictive” toys
Another concern PIRG’s blog raises is the addiction potential of AI toys, which can even express “disappointment when you try to leave,” discouraging kids from putting them down.
The blog adds:
AI toys may be designed to build an emotional relationship. The question is: what is that relationship for? If it’s primarily to keep a child engaged with the toy for longer for the sake of engagement, that’s a problem.
The rise of generative AI has brought intense debate over how much responsibility chatbot companies bear for the impact of their inventions on children. Parents have seen children build extreme and emotional connections with chatbots and subsequently engage in dangerous—and in some cases deadly—behavior.
On the other side, we’ve seen the emotional disruption a child can experience when an AI toy is taken away from them. Last year, parents had to break the news to their kids that they would lose the ability to talk to their Embodied Moxie robots, $800 toys that were bricked when the company went out of business.
PIRG noted that we don’t yet fully understand the emotional impact of AI toys on children.
In June, OpenAI announced a partnership with Mattel that it said would “support AI-powered products and experiences based on Mattel’s brands.” The announcement sparked concern from critics who feared that it would lead to a “reckless social experiment” on kids, as Robert Weissman, Public Citizen’s co-president, put it.
Mattel has said that its first products with OpenAI will focus on older customers and families. But critics still want information before one of the world’s largest toy companies loads its products with chatbots.
“OpenAI and Mattel should release more information publicly about its current planned partnership before any products are released,” PIRG’s blog said.
Chatbot-powered toys rebuked for discussing sexual, dangerous topics with kids Read More »