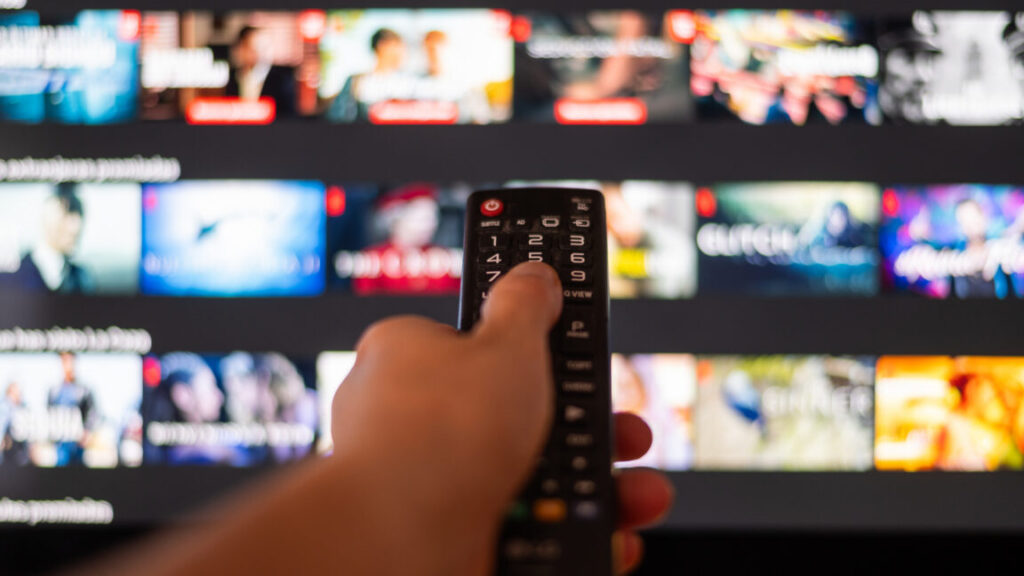
LG TVs’ unremovable Copilot shortcut is the least of smart TVs’ AI problems
But Copilot will still be integrated into Tizen OS, and Samsung appears eager to push chatbots into TVs, including by launching Perplexity’s first TV app. Amazon, which released Fire TVs with Alexa+ this year, is also exploring putting chatbots into TVs.
After the backlash LG faced this week, companies may reconsider installing AI apps on people’s smart TVs. A better use of large language models in TVs may be as behind-the-scenes tools to improve TV watching. People generally don’t buy smart TVs to make it easier to access chatbots.
But this development is still troubling for anyone who doesn’t want an AI chatbot in their TV at all.
Some people don’t want chatbots in their TVs
Subtle integrations of generative AI that make it easier for people to do things like figure out the name of “that movie” may have practical use, but there are reasons to be wary of chatbot-wielding TVs.
Chatbots add another layer of complexity to understanding how a TV tracks user activity. With a chatbot involved, smart TV owners will be subject to complicated smart TV privacy policies and terms of service, as well as the similarly verbose rules of third-party AI companies. This will make it harder for people to understand what data they’re sharing with companies, and there’s already serious concern about the boundaries smart TVs are pushing to track users, including without consent.
Chatbots can also contribute to smart TV bloatware. Unwanted fluff, like games, shopping shortcuts, and flashy ads, already disrupts people who just want to watch TV.
LG’s Copilot web app is worthy of some grousing, but not necessarily because of the icon that users will eventually be able to delete. The more pressing issue is the TV industry’s shift toward monetizing software with user tracking and ads.
If you haven’t already, now is a good time to check out our guide to breaking free from smart TV ads and tracking.
LG TVs’ unremovable Copilot shortcut is the least of smart TVs’ AI problems Read More »