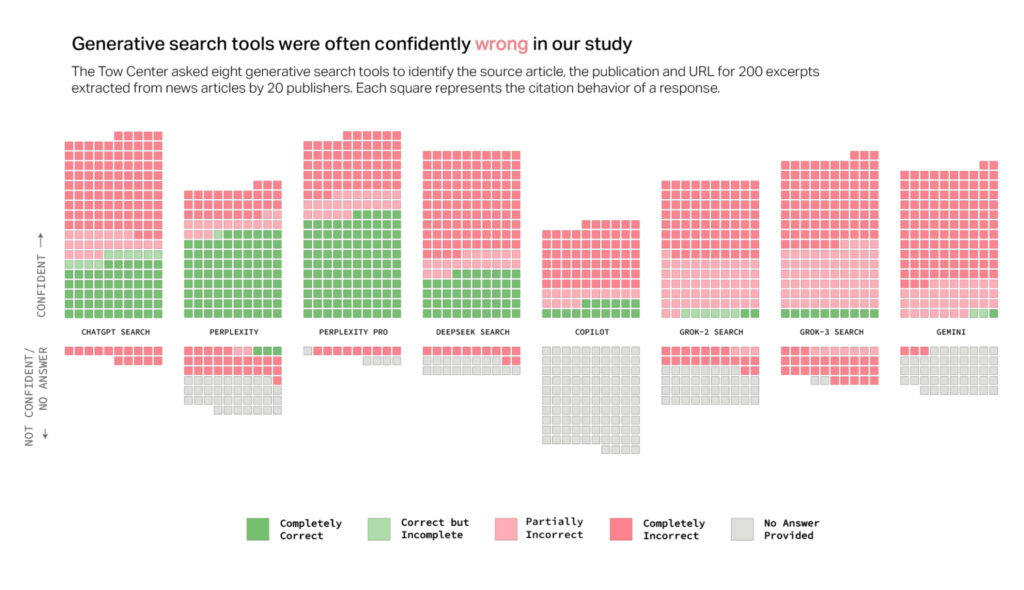
Enough is enough—I dumped Google’s worsening search for Kagi
Mandatory AI summaries have come to Google, and they gleefully showcase hallucinations while confidently insisting on their truth. I feel about them the same way I felt about mandatory G+ logins when all I wanted to do was access my damn YouTube account: I hate them. Intensely.
But unlike those mandatory G+ logins—on which Google eventually relented before shutting down the G+ service—our reading of the tea leaves suggests that, this time, the search giant is extremely pleased with how things are going.
Fabricated AI dreck polluting your search? It’s the new normal. Miss your little results page with its 10 little blue links? Too bad. They’re gone now, and you can’t get them back, no matter what ephemeral workarounds or temporarily functional flags or undocumented, could-fail-at-any-time URL tricks you use.
And the galling thing is that Google expects you to be a good consumer and just take it. The subtext of the company’s (probably AI-generated) robo-MBA-speak non-responses to criticism and complaining is clear: “LOL, what are you going to do, use a different search engine? Now, shut up and have some more AI!”
But like the old sailor used to say: “That’s all I can stands, and I can’t stands no more.” So I did start using a different search engine—one that doesn’t constantly shower me with half-baked, anti-consumer AI offerings.
Out with Google, in with Kagi.
What the hell is a Kagi?
Kagi was founded in 2018, but its search product has only been publicly available since June 2022. It purports to be an independent search engine that pulls results from around the web (including from its own index) and is aimed at returning search to a user-friendly, user-focused experience. The company’s stated purpose is to deliver useful search results, full stop. The goal is not to blast you with AI garbage or bury you in “Knowledge Graph” summaries hacked together from posts in a 12-year-old Reddit thread between two guys named /u/WeedBoner420 and /u/14HitlerWasRight88.
Kagi’s offerings (it has a web browser, too, though I’ve not used it) are based on a simple idea. There’s an (oversimplified) axiom that if a good or service (like Google search, for example, or good ol’ Facebook) is free for you to use, it’s because you’re the product, not the customer. With Google, you pay with your attention, your behavioral metrics, and the intimate personal details of your wants and hopes and dreams (and the contents of your emails and other electronic communications—Google’s got most of that, too).
With Kagi, you pay for the product using money. That’s it! You give them some money, and you get some service—great service, really, which I’m overall quite happy with and which I’ll get to shortly. You don’t have to look at any ads. You don’t have to look at AI droppings. You don’t have to give perpetual ownership of your mind-palace to a pile of optioned-out tech bros in sleeveless Patagonia vests while you are endlessly subjected to amateur AI Rorschach tests every time you search for “pierogis near me.”
How much money are we talking?
I dunno, about a hundred bucks a year? That’s what I’m spending as an individual for unlimited searches. I’m using Kagi’s “Professional” plan, but there are others, including a free offering so that you can poke around and see if the service is worth your time.
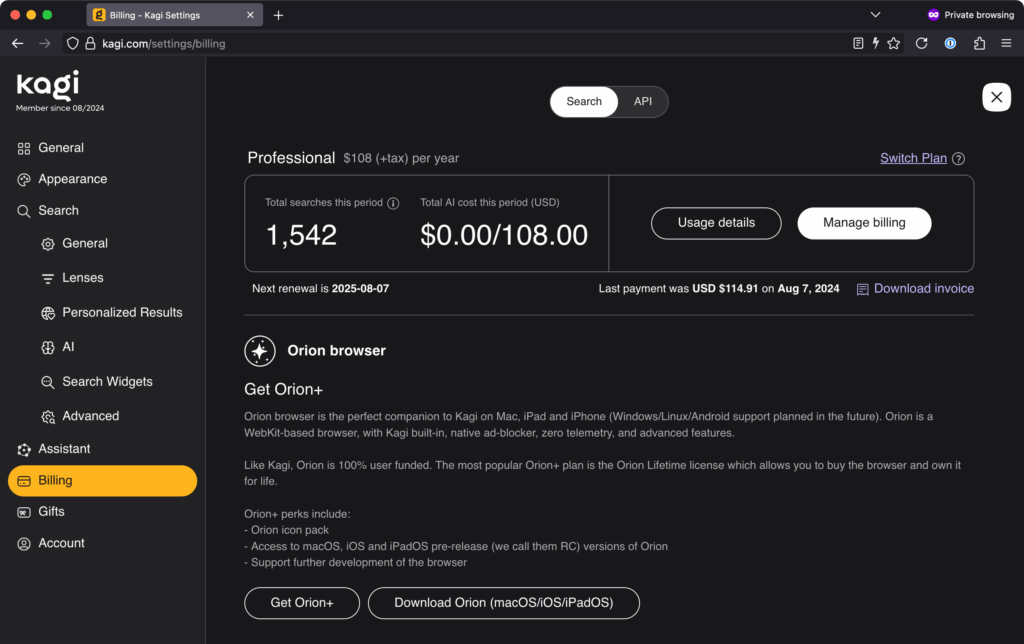
This is my account’s billing page, showing what I’ve paid for Kagi in the past year. (By the time this article runs, I’ll have renewed my subscription!) Credit: Lee Hutchinson
I’d previously bounced off two trial runs with Kagi in 2023 and 2024 because the idea of paying for search just felt so alien. But that was before Google’s AI enshittification rolled out in full force. Now, sitting in the middle of 2025 with the world burning down around me, a hundred bucks to kick Google to the curb and get better search results feels totally worth it. Your mileage may vary, of course.
The other thing that made me nervous about paying for search was the idea that my money was going to enrich some scumbag VC fund, but fortunately, there’s good news on that front. According to the company’s “About” page, Kagi has not taken any money from venture capitalist firms. Instead, it has been funded by a combination of self-investment by the founder, selling equity to some Kagi users in two rounds, and subscription revenue:
Kagi was bootstrapped from 2018 to 2023 with ~$3M initial funding from the founder. In 2023, Kagi raised $670K from Kagi users in its first external fundraise, followed by $1.88M raised in 2024, again from our users, bringing the number of users-investors to 93… In early 2024, Kagi became a Public Benefit Corporation (PBC).
What about DuckDuckGo? Or Bing? Or Brave?
Sure, those can be perfectly cromulent alternatives to Google, but honestly, I don’t think they go far enough. DuckDuckGo is fine, but it largely utilizes Bing’s index; and while DuckDuckGo exercises considerable control over its search results, the company is tied to the vicissitudes of Microsoft by that index. It’s a bit like sitting in a boat tied to a submarine. Sure, everything’s fine now, but at some point, that sub will do what subs do—and your boat is gonna follow it down.
And as for Bing itself, perhaps I’m nitpicky [Ed. note: He is!], but using Bing feels like interacting with 2000-era MSN’s slightly perkier grandkid. It’s younger and fresher, yes, but it still radiates that same old stanky feeling of taste-free, designed-by-committee artlessness. I’d rather just use Google—which is saying something. At least Google’s search home page remains uncluttered.
Brave Search is another fascinating option I haven’t spent a tremendous amount of time with, largely because Brave’s cryptocurrency ties still feel incredibly low-rent and skeevy. I’m slowly warming up to the Brave Browser as a replacement for Chrome (see the screenshots in this article!), but I’m just not comfortable with Brave yet—and likely won’t be unless the company divorces itself from cryptocurrencies entirely.
More anonymity, if you want it
The feature that convinced me to start paying for Kagi was its Privacy Pass option. Based on a clean-sheet Rust implementation of the Privacy Pass standard (IETF RFCs 9576, 9577, and 9578) by Raphael Robert, this is a technology that uses cryptographic token-based auth to send an “I’m a paying user, please give me results” signal to Kagi, without Kagi knowing which user made the request. (There’s a much longer Kagi blog post with actual technical details for the curious.)
To search using the tool, you install the Privacy Pass extension (linked in the docs above) in your browser, log in to Kagi, and enable the extension. This causes the plugin to request a bundle of tokens from the search service. After that, you can log out and/or use private windows, and those tokens are utilized whenever you do a Kagi search.
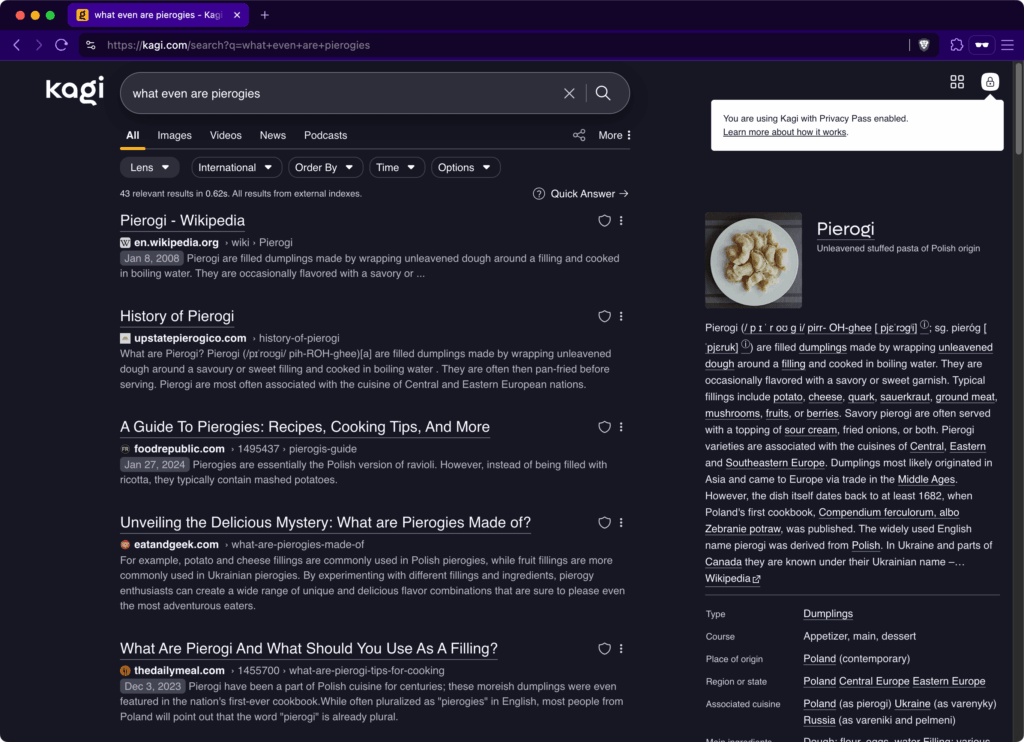
Privacy pass is enabled, allowing me to explore the delicious mystery of pierogis with some semblance of privacy. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
The obvious flaw here is that Kagi still records source IP addresses along with Privacy Pass searches, potentially de-anonymizing them, but there’s a path around that: Privacy Pass functions with Tor, and Kagi maintains a Tor onion address for searches.
So why do I keep using Privacy Pass without Tor, in spite of the opsec flaw? Maybe it’s the placebo effect in action, but I feel better about putting at least a tiny bit of friction in the way of someone with root attempting to casually browse my search history. Like, I want there to be at least a SQL JOIN or two between my IP address and my searches for “best Mass Effect alien sex choices” or “cleaning tips for Garrus body pillow.” I mean, you know, assuming I were ever to search for such things.
What’s it like to use?
Moving on with embarrassed rapidity, let’s look at Kagi a bit and see how using it feels.
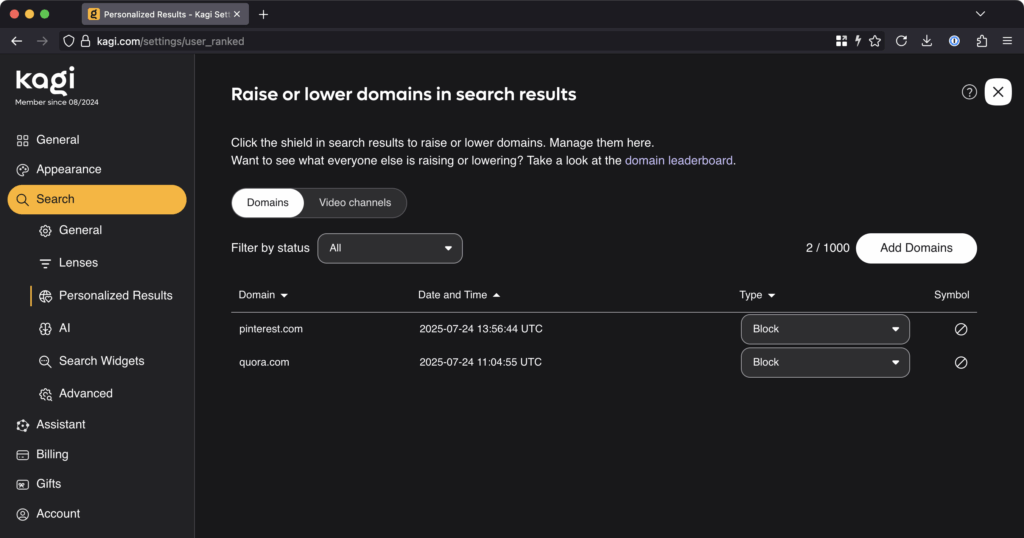
My anecdotal observation is that Kagi doesn’t favor Reddit-based results nearly as much as Google does, but sometimes it still has them near or at the top. And here is where Kagi curb-stomps Google with quality-of-life features: Kagi lets you prioritize or de-prioritize a website’s prominence in your search results. You can even pin that site to the top of the screen or block it completely.
This is a feature I’ve wanted Google to get for about 25 damn years but that the company has consistently refused to properly implement (likely because allowing users to exclude sites from search results notionally reduces engagement and therefore reduces the potential revenue that Google can extract from search). Well, screw you, Google, because Kagi lets me prioritize or exclude sites from my results, and it works great—I’m extraordinarily pleased to never again have to worry about Quora or Pinterest links showing up in my search results.
Further, Kagi lets me adjust these settings both for the current set of search results (if you don’t want Reddit results for this search but you don’t want to drop Reddit altogether) and also globally (for all future searches):
Goodbye forever, useless crap sites. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
Another tremendous quality-of-life improvement comes via Kagi’s image search, which does a bunch of stuff that Google should and/or used to do—like giving you direct right-click access to save images without having to fight the search engine with workarounds, plugins, or Tampermonkey-esque userscripts.
The Kagi experience is also vastly more customizable than Google’s (or at least, how Google’s has become). The widgets that appear in your results can be turned off, and the “lenses” through which Kagi sees the web can be adjusted to influence what kinds of things do and do not appear in your results.
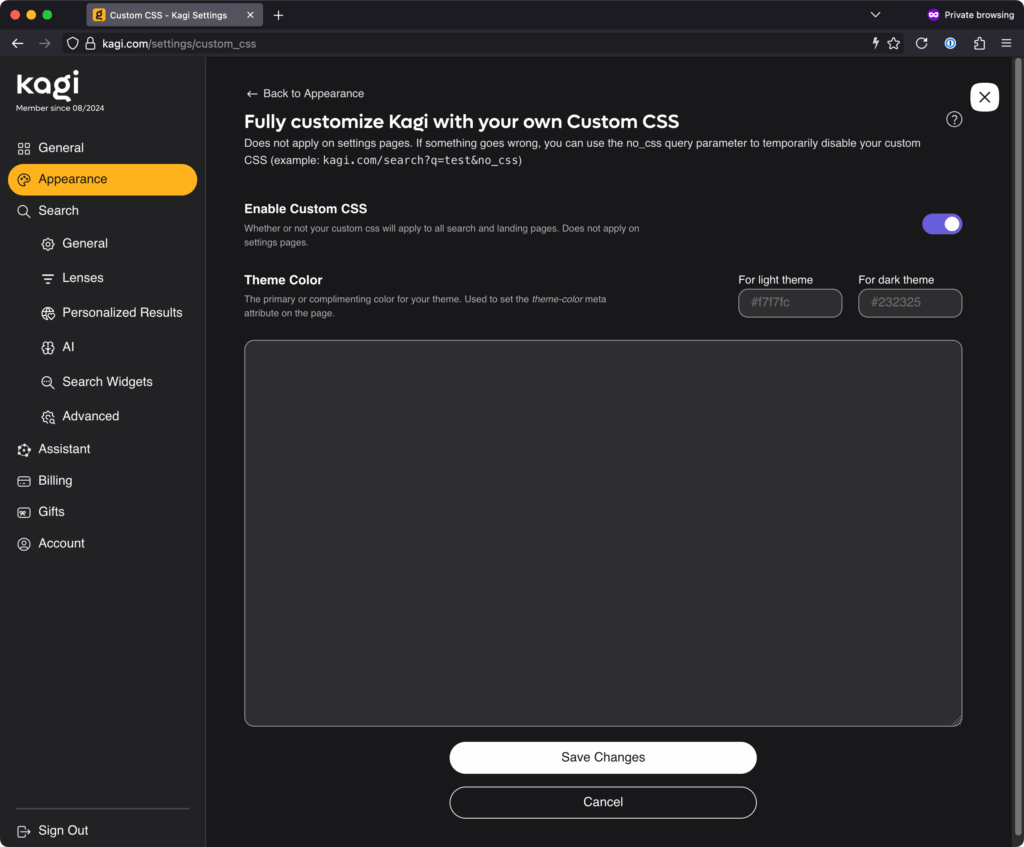
If that doesn’t do it for you, how about the ability to inject custom CSS into your search and landing pages? Or to automatically rewrite search result URLs to taste, doing things like redirecting reddit.com to old.reddit.com? Or breaking free of AMP pages and always viewing originals instead?
Imagine all the things Ars readers will put here. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
Is that all there is?
Those are really all the features I care about, but there are loads of other Kagi bits to discover—like a Kagi Maps tool (it’s pretty good, though I’m not ready to take it up full time yet) and a Kagi video search tool. There are also tons of classic old-Google-style inline search customizations, including verbatim mode, where instead of trying to infer context about your search terms, Kagi searches for exactly what you put in the box. You can also add custom search operators that do whatever you program them to do, and you get API-based access for doing programmatic things with search.
A quick run-through of a few additional options pages. This is the general customization page. Lee Hutchinson
I haven’t spent any time with Kagi’s Orion browser, but it’s there as an option for folks who want a WebKit-based browser with baked-in support for Privacy Pass and other Kagi functionality. For now, Firefox continues to serve me well, with Brave as a fallback for working with Google Docs and other tools I can’t avoid and that treat non-Chromium browsers like second-class citizens. However, Orion is probably on the horizon for me if things in Mozilla-land continue to sour.
Cool, but is it any good?
Rather than fill space with a ton of comparative screenshots between Kagi and Google or Kagi and Bing, I want to talk about my subjective experience using the product. (You can do all the comparison searches you want—just go and start searching—and your comparisons will be a lot more relevant to your personal use cases than any examples I can dream up!)
My time with Kagi so far has included about seven months of casual opportunistic use, where I’d occasionally throw a query at it to see how it did, and about five months of committed daily use. In the five months of daily usage, I can count on one hand the times I’ve done a supplementary Google search because Kagi didn’t have what I was looking for on the first page of results. I’ve done searches for all the kinds of things I usually look for in a given day—article fact-checking queries, searches for details about the parts of speech, hunts for duck facts (we have some feral Muscovy ducks nesting in our front yard), obscure technical details about Project Apollo, who the hell played Dupont in Equilibrium (Angus Macfadyen, who also played Robert the Bruce in Braveheart), and many, many other queries.
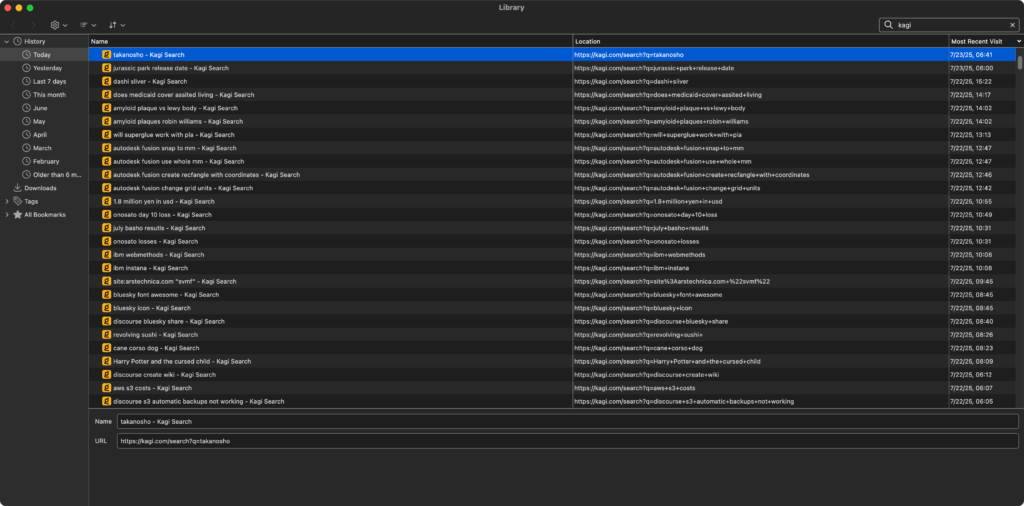
A typical afternoon of Kagi searches, from my Firefox history window. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
For all of these things, Kagi has responded quickly and correctly. The time to service a query feels more or less like Google’s service times; according to the timer at the top of the page, my Kagi searches complete in between 0.2 and 0.8 seconds. Kagi handles misspellings in search terms with the grace expected of a modern search engine and has had no problem figuring out my typos.
Holistically, taking search customizations into account on top of the actual search performance, my subjective assessment is that Kagi gets me accurate, high-quality results on more or less any given query, and it does so without festooning the results pages with features I find detractive and irrelevant.
I know that’s not a data-driven assessment, and it doesn’t fall back on charts or graphs or figures, but it’s how I feel after using the product every single day for most of 2025 so far. For me, Kagi’s search performance is firmly in the “good enough” category, and that’s what I need.
Kagi and AI
Unfortunately, the thing that’s stopping me from being completely effusive in my praise is that Kagi is exhibiting a disappointing amount of “keeping-up-with-the-Joneses” by rolling out a big ‘ol pile of (optional, so far) AI-enabled search features.
A blog post from founder Vladimir Prelovac talks about the company’s use of AI, and it says all the right things, but at this point, I trust written statements from tech company founders about as far as I can throw their corporate office buildings. (And, dear reader, that ain’t very far).
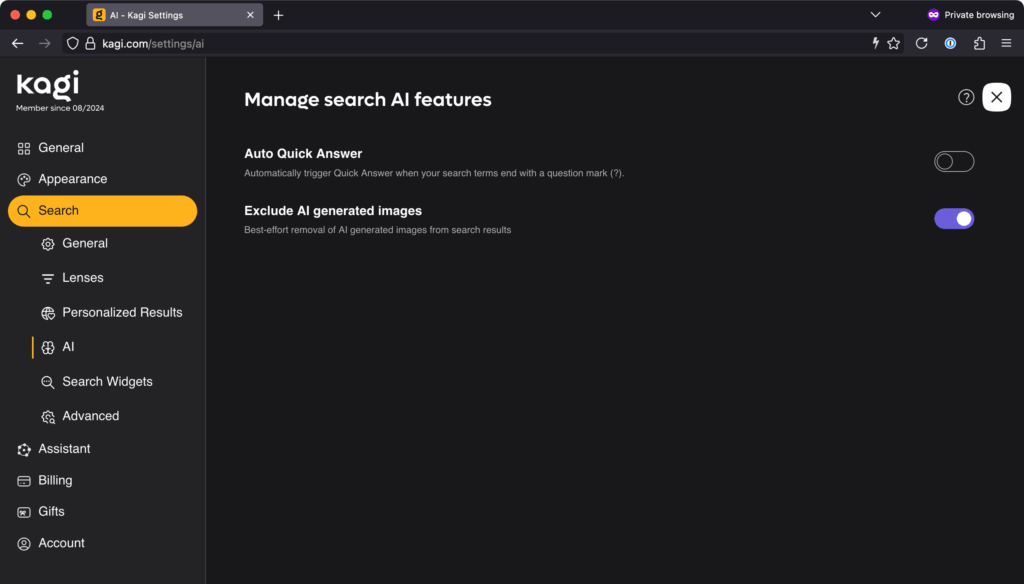
No thanks. But I would like to exclude AI images from my search results, please. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
The short version is that, like Google, Kagi has some AI features: There’s an AI search results summarizer, an AI page summarizer, and an “ask questions about your results” chatbot-style function where you can interactively interrogate an LLM about your search topic and results. So far, all of these things can be disabled or ignored. I don’t know how good any of the features are because I have disabled or ignored them.
If the existence of AI in a product is a bright red line you won’t cross, you’ll have to turn back now and find another search engine alternative that doesn’t use AI and also doesn’t suck. When/if you do, let me know, because the pickings are slim.
Is Kagi for you?
Kagi might be for you—especially if you’ve recently typed a simple question into Google and gotten back a pile of fabricated gibberish in place of those 10 blue links that used to serve so well. Are you annoyed that Google’s search sucks vastly more now than it did 10 years ago? Are you unhappy with how difficult it is to get Google search to do what you want? Are you fed up? Are you pissed off?
If your answer to those questions is the same full-throated “Hell yes, I am!” that mine was, then perhaps it’s time to try an alternative. And Kagi’s a pretty decent one—if you’re not averse to paying for it.
It’s a fantastic feeling to type in a search query and once again get useful, relevant, non-AI results (that I can customize!). It’s a bit of sanity returning to my Internet experience, and I’m grateful. Until Kagi is bought by a value-destroying vampire VC fund or implodes into its own AI-driven enshittification cycle, I’ll probably keep paying for it.
After that, who knows? Maybe I’ll throw away my computers and live in a cave. At least until the cave’s robot exclusion protocol fails and the Googlebot comes for me.
Enough is enough—I dumped Google’s worsening search for Kagi Read More »