Digital Transformation Not Working? Here’s a Five-Point Plan That Can Help
error code: 502
Digital Transformation Not Working? Here’s a Five-Point Plan That Can Help Read More »

Aurich Lawson | Getty Images
When a severe winter storm hit Oregon on January 13, Nicholas Brown’s CenturyLink fiber Internet service stopped working at his house in Portland.
The initial outage was understandable amid the widespread damage caused by the storm, but CenturyLink’s response was poor. It took about 39 days for CenturyLink to restore broadband service to Brown and even longer to restore service to one of his neighbors. Those reconnections only happened after Ars Technica contacted the telco firm on the customers’ behalf last week.
Brown had never experienced any lengthy outage in over four years of subscribing to CenturyLink, so he figured the telco firm would restore his broadband connection within a reasonable amount of time. “It had practically never gone down at all up to this point. I’ve been quite happy with it,” he said.
While CenturyLink sent trucks to his street to reconnect most of his neighbors after the storm and Brown regularly contacted CenturyLink to plead for a fix, his Internet connection remained offline. Brown had also lost power, but the electricity service was reconnected within about 48 hours, while the broadband service remained offline for well over a month.
Fearing he had exhausted his options, Brown contacted Ars. We sent an email to CenturyLink’s media department on February 21 to seek information on why the outage lasted so long.
Roughly four hours after we contacted the firm, a CenturyLink technician arrived at the Portland house Brown shares with his partner, Jolene Edwards. The technician was able to reconnect them that day.
“At 4: 30 pm, a CenturyLink tech showed up unannounced,” Brown told us. “No one was home at the time, but he said he would wait. I get the idea that he was told not to come back until it was fixed.”
Brown’s neighbor, Leonard Bentz, also lost Internet access on January 13 and remained offline for two days longer than Brown. The technician who arrived on February 21 didn’t reconnect Bentz’s house.
“My partner gently tried to egg him to go over there and fix them too, and he more or less said, ‘That’s not the ticket that I have,'” Brown said.
After getting Bentz’s name and address, we contacted CenturyLink again on February 22 to notify them that he also needed to be reconnected. CenturyLink later confirmed to us that it restored his Internet service on February 23.
Bentz told Ars that during the month-plus outage, he called CenturyLink several times. Customer service reps and a supervisor told him the company would send someone to fix his service, but “they kept putting me off and putting me off and putting me off,” Bentz said.
On one of those calls, Bentz said that CenturyLink promised him seven free months of service in exchange for the long outage. Brown told us he received a refund for the entire length of his outage, plus a bit extra. He pays $65 a month for gigabit service.
Brown said he is “happy enough with the resolution,” at least financially since he “got all the money for the non-service.” But those 39 days without Internet service will remain a bad memory.
Unfortunately, Internet service providers like CenturyLink have a history of failing to fix problems until media coverage exposes their poor customer service. CenturyLink is officially called Lumen these days, but it still uses the CenturyLink brand name.
After fixing Brown’s service in Portland, a CenturyLink spokesperson gave us the following statement:
It’s frustrating to have your services down and for that we apologize. We’ve brought in additional resources to assist in restoring service that was knocked out due to severe storms and multiple cases of vandalism. Some services are back, and we are working diligently to completely restore everything. In fact, we have technicians there now. We appreciate our customers’ patience and understanding, and we welcome calls from our customers to discuss their service.
CenturyLink left customers without Internet for 39 days—until Ars stepped in Read More »

Enlarge / Materials such as steel, cement, aluminum, electricity, fertilizer, hydrogen, and iron will soon be subject to greenhouse gas emissions fees when imported into Europe.
Monty Rakusen/Getty
The year 2023 was a big one for climate news, from record heat to world leaders finally calling for a transition away from fossil fuels. In a lesser-known milestone, it was also the year the European Union soft-launched an ambitious new initiative that could supercharge its climate policies.
Wrapped in arcane language studded with many a “thereof,” “whereas” and “having regard to” is a policy that could not only help fund the European Union’s pledge to become the world’s first carbon-neutral continent, but also push industries all over the world to cut their carbon emissions.
It’s the establishment of a carbon price that will force many heavy industries to pay for each ton of carbon dioxide, or equivalent emissions of other greenhouse gases, that they emit. But what makes this fee revolutionary is that it will apply to emissions that don’t happen on European soil. The EU already puts a price on many of the emissions created by European firms; now, through the new Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, or CBAM, the bloc will charge companies that import the targeted products—cement, aluminum, electricity, fertilizer, hydrogen, iron, and steel—into the EU, no matter where in the world those products are made.
These industries are often large and stubborn sources of greenhouse gas emissions, and addressing them is key in the fight against climate change, says Aaron Cosbey, an economist at the International Institute for Sustainable Development, an environmental think tank. If those companies want to continue doing business with European firms, they’ll have to clean up or pay a fee. That creates an incentive for companies worldwide to reduce emissions.
In CBAM’s first phase, which started in October 2023, companies importing those materials into the EU must report on the greenhouse gas emissions involved in making the products. Beginning in 2026, they’ll have to pay a tariff.
Even having to supply emissions data will be a big step for some producers and could provide valuable data for climate researchers and policymakers, says Cosbey.
“I don’t know how many times I’ve gone through this exercise of trying to identify, at a product level, the greenhouse gas intensity of exports from particular countries and had to go through the most amazing, torturous processes to try to do those estimates,” he says. “And now it’s going to be served to me on a plate.”

Enlarge / CBAM will apply to a set of products that are linked to heavy greenhouse gas emissions.
While this new carbon price targets companies abroad, it will also help the EU to pursue its climate ambitions at home. For one thing, the extra revenues could go toward financing climate-friendly projects and promising new technologies.
But it also allows the EU to tighten up on domestic pollution. Since 2005, the EU has set a maximum, or cap, on the emissions created by a range of industrial “installations” such as oil and metal refineries. It makes companies within the bloc use credits, or allowances, for each ton of carbon dioxide—or equivalent discharges of other greenhouse gases—that they emit, up to that cap. Some allowances are currently granted for free, but others are bought at auction or traded with other companies in a system known as a carbon market.
But this idea—of making it expensive to harm the planet—creates a conundrum. If doing business in Europe becomes too expensive, European industry could flee the continent for countries that don’t have such high fees or strict regulations. That would damage the European economy and do nothing to solve the environmental crisis. The greenhouse gases would still be emitted—perhaps more than if the products had been made in Europe—and climate change would careen forward on its destructive path.
The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism aims to impose the same carbon price for products made abroad as domestic producers must pay under the EU’s system. In theory, that keeps European businesses competitive with imports from international rivals. It also addresses environmental concerns by nudging companies overseas toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions rather than carrying on as usual.
This means the EU can further tighten up its carbon market system at home. With international competition hopefully less of a concern, it plans to phase out some leniencies, such as some of the free emission allowances, that existed to help keep domestic industries competitive.
That’s a big deal, says Cosbey. Dozens of countries have carbon pricing systems, but they all create exceptions to keep heavy industry from getting obliterated by international competition. The carbon border tariff could allow the EU to truly force its industries—and consumers—to pay the price, he says.
“That is ambitious; nobody in the world is doing that.”
A big boost to Europe’s climate-change goals Read More »

Enlarge / Consumer Reports’ investigation suggests that, should this delivery person press and hold the bell button and then pair using Eken’s app, he could see if other delivery people get such a perfunctory response.
Eken
Video doorbell cameras have been commoditized to the point where they’re available for $30–$40 on marketplaces like Amazon, Walmart, Temu, and Shein. The true cost of owning one might be much greater, however.
Consumer Reports (CR) has released the findings of a security investigation into two budget-minded doorbell brands, Eken and Tuck, which are largely the same hardware produced by the Eken Group in China, according to CR. The cameras are further resold under at least 10 more brands. The cameras are set up through a common mobile app, Aiwit. And the cameras share something else, CR claims: “troubling security vulnerabilities.”
Enlarge / The pairing procedure for one of Eken’s doorbell cameras, which allows a malicious actor quite a bit of leeway. Eken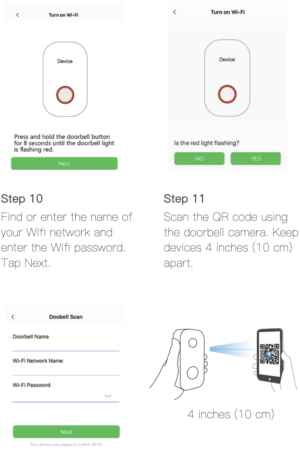
Among the camera’s vulnerabilities cited by CR:
CR also noted that Eken cameras lacked an FCC registration code. More than 4,200 were sold in January 2024, according to CR, and often held an Amazon “Overall Pick” label (as one model did when an Ars writer looked on Wednesday).
“These video doorbells from little known manufacturers have serious security and privacy vulnerabilities, and now they’ve found their way onto major digital marketplaces such as Amazon and Walmart,” said Justin Brookman, director of tech policy at Consumer Reports, in a statement. “Both the manufacturers and platforms that sell the doorbells have a responsibility to ensure that these products are not putting consumers in harm’s way.”
CR noted that it contacted vendors where it found the doorbells for sale. Temu told CR that it would halt sales of the doorbells, but “similar-looking if not identical doorbells remained on the site,” CR noted.
A Walmart representative told Ars that all cameras mentioned by Consumer Reports, sold by third parties, have been removed from Walmart by now. The representative added that customers may be eligible for refunds and that Walmart prohibits the selling of devices that require an FCC ID and lack one.
Ars contacted Amazon for comment and will update this post with new information. An email sent to the sole address that could be found on Eken’s website was returned undeliverable. The company’s social media accounts were last updated at least three years prior.
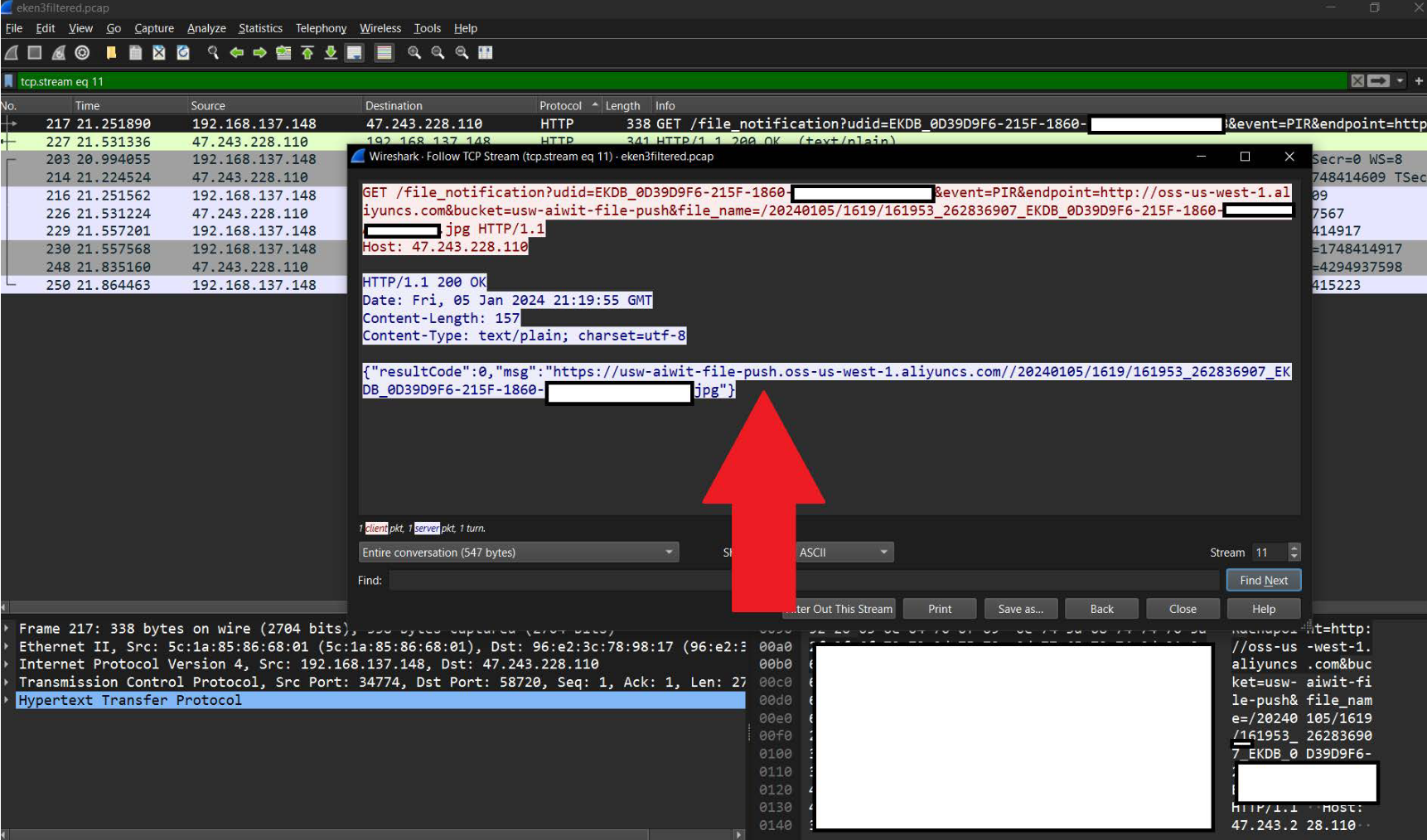
Consumer Reports’ researchers claim to have found JPEG file references passed in plaintext over the network, which could later be viewed without authentication in a browser.
Consumer Reports
CR issued vulnerability disclosures to Eken and Tuck regarding its findings. The disclosures note the amount of data that is sent over the network without authentication, including JPEG files, the local SSID, and external IP address. It notes that after a malicious user has re-paired a doorbell with a QR code generated by the Aiwit app, they have complete control over the device until a user sees an email from Eken and reclaims the doorbell.
With a few exceptions, video doorbells and other IoT cameras tend to rely on cloud connections to stream and store footage, as well as notify their owners about events. This has led to some notable privacy and security concerns. Ring doorbells were found to be pushing Wi-Fi credentials in plaintext in late 2019. Eufy, a company that marketed its “No clouds” offerings, was found to be uploading facial thumbnails to cloud servers to send push alerts and later apologized for that and other vulnerabilities. Camera provider Wyze recently disclosed that, for the second time in five months, images and video feeds were accidentally available to the wrong customers following a lengthy outage.
Listing image by Amazon/Eken
$30 doorbell cameras have multiple serious security flaws, says Consumer Reports Read More »
Enlarge / The Moderna Spikevax COVID-19 vaccine is shown at a CVS in 2023.
People ages 65 and up should get another dose of a COVID-19 vaccine this spring, given the age group’s higher risk of severe disease and death from the pandemic virus, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced Wednesday.
Earlier today, an advisory committee for the CDC voted overwhelmingly in favor of recommending the spring booster dose. And late this afternoon, CDC Director Mandy Cohen signed off on the recommendation, allowing boosting to begin.
“Today’s recommendation allows older adults to receive an additional dose of this season’s COVID-19 vaccine to provide added protection,” Cohen said in a statement. “Most COVID-19 deaths and hospitalizations last year were among people 65 years and older. An additional vaccine dose can provide added protection that may have decreased over time for those at highest risk.”
The spring booster will be an additional shot of the 2023–2024 COVID-19 vaccines made by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and Novavax. The booster dose should be taken after at least four months have passed since a previous COVID-19 vaccination. However, as FDA representative David Kaslow noted in today’s advisory committee meeting, the FDA will likely approve a 2024–2025 version of COVID-19 vaccines for this coming fall. Given that, it’s best for people to get their spring booster dose by the end of June, so they can be ready for another booster before the winter when COVID-19 has generally peaked.
A report published earlier this month by the CDC found that the 2023–2024 COVID-19 vaccine was about 54 percent effective at preventing symptomatic COVID-19 when compared against people who had not received the latest vaccine. However, the CDC estimates that only about 22 percent of adults in the US have gotten a COVID-19 booster this season, and just over 40 percent of people ages 65 and up have gotten the shot.
People over age 65 made up 67 percent of COVID-19 hospitalizations between October 2023 and January 2024, according to CDC data presented at today’s advisory committee meeting. In early January, COVID-19 hospitalizations hit a seasonal high of about 35,000 weekly new admissions per week and nearly 2,500 weekly deaths.
The advisers debated how to word their recommendation for a spring booster and whether getting a booster should require consulting with a health care provider. But, ultimately, the committee decided on a more permissive recommendation, allowing anyone in the age group who wants a booster to be able to freely get one, including at convenient locations, such as local pharmacies.
“Data continues to show the importance of vaccination to protect those most at risk for severe outcomes of COVID-19,” the CDC said in its announcement of the recommendation. “An additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine may restore protection that has waned since a fall vaccine dose, providing increased protection to adults ages 65 years and older.”
The CDC noted that its previous recommendations allow people who are immunocompromised to get additional doses of the COVID-19 vaccines.
CDC recommends spring COVID booster for people 65 and up Read More »

Enlarge / Samsung’s SD Express-compatible microSD cards.
Samsung
Big news for people who like (physically) small storage: Samsung says that it is sampling its first microSD cards that support the SD Express standard, which will allow them to hit sustained read speeds of as much as 800MB per second. That’s a pretty substantial boost over current SD cards, which tend to top out around 80MB or 90MB per second (for cheap commodity cards) and around 250MB per second for the very fastest UHS-II-compatible professional cards.
As Samsung points out, that 800MB/s figure puts these tiny SD Express cards well above the speeds possible with older SATA SSDs, which could make these cards more useful as primary storage devices for PCs or single-board computers that can support the SD Express standard (more on that later).
Samsung is currently sampling a 256GB version of the SD Express card that “will be available for purchase later this year.”
Because this is a tech company announcement in 2024, Samsung also makes an obligatory mention of AI, though there’s absolutely nothing specific the cards are doing to make them particularly well-suited for generative AI tasks other than “be faster.” Adding extra storage to phones or PCs could be useful for on-device generative AI—storing larger language models locally, for example—but most software companies that are offering generative AI features in their OSes or browsers are mostly using server-side processing to do all the heavy lifting for now.
The SD Express standard allows SD cards to take advantage of a single lane’s worth of PCIe bandwidth, boosting their theoretical speeds well beyond the 104MB/s cap of the UHS-I standard or the 312MB/s cap of UHS-II (UHS-III exists but isn’t widely used). The SD Express spec was last updated back in October 2023, which bumped it up from PCIe 3.0 to 4.0; it also defines four speed classes with read/write speeds of between 150MB and 600MB per second—a target these Samsung cards claim to be able to surpass.
But the original version of SD Express goes back to mid-2018, when it was added to version 7.0 of the SD specification. And adoption from SD card makers and device makers has been slow to nonexistent so far; AData makes full-size SD Express cards in 256GB and 512GB capacities that you can buy, but that’s about it. Lexar announced some cards back in 2021 that never ended up being released. And even if you had a card, you’d have trouble finding devices that could actually take advantage of the higher speeds, since most cameras, phones, and computers have opted to stick with the more common UHS.
One issue blocking SD Express adoption is that the card and the device have to support SD Express to get the promised speeds; an SD Express card inserted into a regular run-of-the-mill UHS-I SD card slot will be limited to UHS-I speeds. And because both the slots and the cards are visually identical, it’s not always easy to tell which slots support specific speeds.
Heat may also be a major limiting factor when using these SD Express cards to move around hundreds of gigabytes’ worth of data or when using the SD card as the primary storage device in a computer (as you might in a Raspberry Pi or other single-board computers). There’s no room for this kind of thing within the confines of a microSD card slot, so the sustained read and write speeds of Samsung’s new cards could be a bit lower than the promised 800MB-per-second maximum.
The SD Express spec does have mechanisms for keeping thermals in a reasonable range. Samsung also mentions a “Dynamic Thermal Guard” technology that promises to manage the temperatures of its SD Express cards, though it’s not clear whether this is different from what’s already in the SD Express spec.
Samsung jumping into SD Express cards may be what the format needs to take off, or at least to become a viable niche within the wider market for external storage. It’s certainly not difficult to imagine a scenario where something with SSD-ish speeds in an SD card-sized package would be useful. But SD cards are mainly useful because they’re cheap, they’re widely compatible, and they’re fast enough for things like recording video, taking pictures, and loading games. SD Express cards have a long way to go before they can check all the same boxes.
Speedy “SD Express” cards have gone nowhere for years, but Samsung could change that Read More »
Intuitive Machines
After six days and the public release of new images, engineers have finally pieced together the moments before, during, and after the Odysseus lander touched down on the Moon.
During a news conference on Wednesday, the chief executive of Intuitive Machines, Steve Altemus, described what his company has learned about what happened last Thursday evening as Odysseus made its powered descent down to the Moon.
From their control room in Houston, the mission operators watched with fraying nerves, as their range finders had failed. A last-minute effort to use altitude data from a NASA payload on board failed because the flight computer on board Odysseus could not ingest it in time. So the lander was, in essence, coming down to the Moon without any real-time altimetry data.
The last communication the operators received appeared to show that Odysseus had touched down on the Moon and was upright. But then, to their horror, all telemetry from the spacecraft ceased. The data on the flight controllers’ consoles in Houston froze. They feared the worst.
About 10 minutes later, the lander sent a weak signal back. In that initial trickle of data, based on the lander’s inertial measurement unit, it appeared that Odysseus was partly on its side. But there were confusing signals.
On Wednesday, Altemus explained what the team has since pieced together. Because of the lack of altimetry data, Odysseus thought it was about 100 meters higher above the lunar surface than it actually was, so as it touched down it was traveling about three times faster than intended, about 3 meters per second. It was also moving laterally, with respect to the ground, at about 1 meter per second.
“We hit harder than expected and skidded along the way,” Altemus explained.
As it impacted and skidded, the spacecraft’s main engine was still firing. Then, just as the spacecraft touched down more firmly, there was a spike in the engine’s combustion chamber. This is consistent with the bell-shaped engine nozzle coming into contact with the lunar surface.
It is perhaps worth pausing a moment here to consider that this spacecraft, launched a week earlier, had just made an autonomous landing without knowing precisely where it was. But now it found itself on the Moon. Upon impact, one or more of the landing legs snapped as it came down hard. Then, at that very moment, with the engine still burning, an onboard camera snapped an image of the scene. Intuitive Machines published this photo on Wednesday. It’s spectacular.
“We sat upright, with the engine firing for a period of time,” Altemus said. “Then as it wound down, the vehicle just gently tipped over.”
Enlarge / Odysseus at rest on the lunar surface.
Intuitive Machines
Based on the gravity of the Moon, Intuitive Machines and NASA calculated that it took about two seconds to tip over. The lander fell on its side, with a helium tank or radio shelf contacting the Moon. This protrusion, combined with the 12-degree slope of the terrain, means that Odysseus is now gently leaning on the lunar surface at about a 30-degree angle. On Tuesday, the spacecraft returned an image that verified these conclusions.
“We have that photo now to confirm that’s the orientation,” Altemus said.
As Intuitive Machines has better understood the situation and the status of its vehicle, it has been able to download a torrent of data. NASA has gotten valuable information from all six of its payloads on board, said a project scientist for the space agency, Sue Lederer. As of Wednesday, NASA had been able to download about 50MB of data. The baseline for success was a single bit of data.
But time is running out as the Sun dips toward the horizon. Odysseus will run out of power as soon as Wednesday evening, entering the long lunar night. In about three weeks, as sunlight starts to hit the spacecraft’s solar panels again, Intuitive Machines will try to wake up the spacecraft. The odds are fairly long. The chemistry of its lithium-ion batteries doesn’t like cold, and temperatures will plummet to minus-280° Fahrenheit (minus-173° Celsius) in a few days. That may wreck the batteries or crack the electronics in the flight computer.
Yet hope remains eternal for a spacecraft its operators have taken to affectionately calling Odie. It has defied the odds so far. “He’s a scrappy little dude,” Lederer said. “I have confidence in Odie at this point.”
That moment when you land on the Moon, break a leg, and are about to topple over Read More »

Getty Images
GitHub is struggling to contain an ongoing attack that’s flooding the site with millions of code repositories. These repositories contain obfuscated malware that steals passwords and cryptocurrency from developer devices, researchers said.
The malicious repositories are clones of legitimate ones, making them hard to distinguish to the casual eye. An unknown party has automated a process that forks legitimate repositories, meaning the source code is copied so developers can use it in an independent project that builds on the original one. The result is millions of forks with names identical to the original one that add a payload that’s wrapped under seven layers of obfuscation. To make matters worse, some people, unaware of the malice of these imitators, are forking the forks, which adds to the flood.
“Most of the forked repos are quickly removed by GitHub, which identifies the automation,” Matan Giladi and Gil David, researchers at security firm Apiiro, wrote Wednesday. “However, the automation detection seems to miss many repos, and the ones that were uploaded manually survive. Because the whole attack chain seems to be mostly automated on a large scale, the 1% that survive still amount to thousands of malicious repos.”
Given the constant churn of new repos being uploaded and GitHub’s removal, it’s hard to estimate precisely how many of each there are. The researchers said the number of repos uploaded or forked before GitHub removes them is likely in the millions. They said the attack “impacts more than 100,000 GitHub repositories.”
GitHub officials didn’t dispute Apiiro’s estimates and didn’t answer other questions sent by email. Instead, they issued the following statement:
GitHub hosts over 100M developers building across over 420M repositories, and is committed to providing a safe and secure platform for developers. We have teams dedicated to detecting, analyzing, and removing content and accounts that violate our Acceptable Use Policies. We employ manual reviews and at-scale detections that use machine learning and constantly evolve and adapt to adversarial tactics. We also encourage customers and community members to report abuse and spam.
Supply-chain attacks that target users of developer platforms have existed since at least 2016, when a college student uploaded custom scripts to RubyGems, PyPi, and NPM. The scripts bore names similar to widely used legitimate packages but otherwise had no connection to them. A phone-home feature in the student’s scripts showed that the imposter code was executed more than 45,000 times on more than 17,000 separate domains, and more than half the time his code was given all-powerful administrative rights. Two of the affected domains ended in .mil, an indication that people inside the US military had run his script. This form of supply-chain attack is often referred to as typosquatting, because it relies on users making small errors when choosing the name of a package they want to use.
In 2021, a researcher used a similar technique to successfully execute counterfeit code on networks belonging to Apple, Microsoft, Tesla, and dozens of other companies. The technique—known as a dependency confusion or namespace confusion attack—started by placing malicious code packages in an official public repository and giving them the same name as dependency packages Apple and the other targeted companies use in their products. Automated scripts inside the package managers used by the companies then automatically downloaded and installed the counterfeit dependency code.
The technique observed by Apiiro is known as repo confusion.
“Similar to dependency confusion attacks, malicious actors get their target to download their malicious version instead of the real one,” Wednesday’s post explained. “But dependency confusion attacks take advantage of how package managers work, while repo confusion attacks simply rely on humans to mistakenly pick the malicious version over the real one, sometimes employing social engineering techniques as well.”
GitHub besieged by millions of malicious repositories in ongoing attack Read More »

Paramount+
Warner Bros. Discovery (WBD) and Paramount Global are no longer considering a merger that would have put the Max and Paramount+ streaming services under one corporate umbrella. Per a CNBC report today citing anonymous “people familiar with the matter,” WBD and Paramount had been mulling a merger for “several months.”
In December, reports started swirling about WBD and Paramount discussing a potential merger. Axios even reported that WBD CEO David Zaslav and Paramount CEO Bob Bakish met in person for “several hours” and that Zaslav also met with Shari Redstone, the owner of National Amusements Inc. (NAI), Paramount’s parent company. Now, CNBC reports that discussions between the media giants “cooled off this month.” Paramount and WBD haven’t commented.
When news of the potential merger dropped, it was unclear what sort of regulatory hurdles the media conglomerates might have faced if they tried becoming one. Combined, the companies would have had the second-biggest streaming business by subscriber count, trailing Netflix.
Debt was also a huge concern. Paramount is $14.6 billion in debt, per its earnings report shared today. WBD was $40 billion in debt at the time of merger talks but said it was eyeing a profitable streaming business. WBD is still in debt currently but reported this month that its streaming business became profitable, making $103 million for the year. Max’s most recent subscriber count is 97.7 million compared to 67.5 million for Paramount+.
Merging with Paramount would have meant WBD added another company with struggling legacy media assets to its portfolio. It also would have meant buying a streaming service that has yet to turn a profit as of this writing. Paramount’s streaming business lost $1.66 billion in 2023, it reported today.
Although things with WBD reportedly didn’t work out, Paramount is still seriously considering a merger. CNBC reported that the company formed a committee and hired a financial adviser focused on analyzing potential bids for all or parts of the company.
Suitors recently tied to Paramount include Byron Allen and, reportedly, Skydance Media. The David Ellison-owned company is “still performing due diligence on a potential transaction,” CNBC said today, citing two of its anonymous sources. In January, Bloomberg reported that Skydance made an all-cash offer for NAI.
Paramount could also try to bundle its services with another company’s, which could attract subscribers to Paramount+ and help Paramount save money. It has already considered bundling Paramount+ with Comcast’s Peacock through a partnership or joint venture, The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) reported earlier this month. But Comcast doesn’t want to buy Paramount, per one of CNBC’s anonymous sources from today’s report.
Some streaming rivals to Paramount+ are already bundled together (such as Disney’s Disney+ and Hulu) and exploring joint ventures. As streaming services race to achieve the sort of profitability that Netflix has, big strategic moves, such as mergers, partnerships, and price hikes, are expected soon. Meanwhile, subscribers remain worried about potential fallout, which could result in monopolistic practices that limit consumer options.
This article was updated to include information from Paramount’s latest earnings report.
Paramount ends Warner Bros. Discovery merger talks, continues mulling sell-off Read More »

On Monday, Microsoft announced plans to offer AI models from Mistral through its Azure cloud computing platform, which came in conjunction with a 15 million euro non-equity investment in the French firm, which is often seen as a European rival to OpenAI. Since then, the investment deal has faced scrutiny from European Union regulators.
Microsoft’s deal with Mistral, known for its large language models akin to OpenAI’s GPT-4 (which powers the subscription versions of ChatGPT), marks a notable expansion of its AI portfolio at a time when its well-known investment in California-based OpenAI has raised regulatory eyebrows. The new deal with Mistral drew particular attention from regulators because Microsoft’s investment could convert into equity (partial ownership of Mistral as a company) during Mistral’s next funding round.
The development has intensified ongoing investigations into Microsoft’s practices, particularly related to the tech giant’s dominance in the cloud computing sector. According to Reuters, EU lawmakers have voiced concerns that Mistral’s recent lobbying for looser AI regulations might have been influenced by its relationship with Microsoft. These apprehensions are compounded by the French government’s denial of prior knowledge of the deal, despite earlier lobbying for more lenient AI laws in Europe. The situation underscores the complex interplay between national interests, corporate influence, and regulatory oversight in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
The EU’s reaction to the Microsoft-Mistral deal reflects broader tensions over the role of Big Tech companies in shaping the future of AI and their potential to stifle competition. Calls for a thorough investigation into Microsoft and Mistral’s partnership have been echoed across the continent, according to Reuters, with some lawmakers accusing the firms of attempting to undermine European legislative efforts aimed at ensuring a fair and competitive digital market.
The controversy also touches on the broader debate about “European champions” in the tech industry. France, along with Germany and Italy, had advocated for regulatory exemptions to protect European startups. However, the Microsoft-Mistral deal has led some, like MEP Kim van Sparrentak, to question the motives behind these exemptions, suggesting they might have inadvertently favored American Big Tech interests.
“That story seems to have been a front for American-influenced Big Tech lobby,” said Sparrentak, as quoted by Reuters. Sparrentak has been a key architect of the EU’s AI Act, which has not yet been passed. “The Act almost collapsed under the guise of no rules for ‘European champions,’ and now look. European regulators have been played.”
MEP Alexandra Geese also expressed concerns over the concentration of money and power resulting from such partnerships, calling for an investigation. Max von Thun, Europe director at the Open Markets Institute, emphasized the urgency of investigating the partnership, criticizing Mistral’s reported attempts to influence the AI Act.
Also on Monday, amid the partnership news, Mistral announced Mistral Large, a new large language model (LLM) that Mistral says “ranks directly after GPT-4 based on standard benchmarks.” Mistral has previously released several open-weights AI models that have made news for their capabilities, but Mistral Large will be a closed model only available to customers through an API.
Microsoft partners with OpenAI-rival Mistral for AI models, drawing EU scrutiny Read More »
The Xiaomi 14 Ultra.
Xiaomi
The phone desperately wants to look like a real camera, with a faux-leather wrapping and big circular camera block.
Xiaomi
The camera bump sticks out a lot.
Xiaomi
The screen is curved all over, and raised above the aluminum sides.
Xiaomi
Another look at the screen. All the glass is way above the aluminum sides, so don’t drop it!
Xiaomi
The cooling system.
Xiaomi
An interior view.
Xiaomi
Xiaomi’s big Mobile World Congress launch is the Xiaomi 14 Ultra. This is a top-tier flagship that of course is not coming to the US but is available in Europe for a whopping 1,499 euros ($1,624).
Let’s get the specs out of the way: This has a 120 Hz, 3200×1440 OLED, a Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 SoC, 16GB of RAM, 512GB of storage, and a 5000 mAh battery. A proprietary 90 W wired “HyperCharge” will get the phone from 0–100 percent battery in 33 minutes, while a wireless 80 W version will charge the phone in 46 minutes.
Xiaomi is very proud that all four sides of the screen are curved. The whole screen kind of rises up and bubbles out from the aluminum body. Xiaomi says the glass has “deep bending around all four sides and corners, creating a seamlessly elegant curved form.” All images, videos, websites, and apps expect to display on a flat surface, so curved displays serve to distort the picture you’re looking at, and thankfully some manufacturers have started to drop the idea. Having the display be a big glass bubble also means you now have four glass corners on the front of the phone, so uh, don’t drop it!
Just like the Xiaomi 13 Ultra, the whole back design mimics a classic leather-wrapped 35 mm camera—the camera is “Leica” branded, after all. The back is “vegan leather,” aka specially treated plastic (hey, some of those old cameras used fake leather, too!), and the camera lens is a giant circle faintly evoking a normal camera lens.
The camera kit gives you a case and a side grip with all sorts of traditional camera buttons.
Putting on the grip.
Xiaomi
Inside the grip.
Xiaomi
The photography focus features the return of the “Professional Camera Kit,” which makes the phone look even more like a real camera. The kit has two parts; the first is a case that adds a mounting ring around the camera bump, so you can attach a lens cover or camera filter to the camera bump. The other half of the kit is a clip-on camera grip attachment, which adds both a 1500 mAh battery and physical camera controls, like a two-stage shutter button that can trigger auto-focus, a record button, a two-way zoom lever, and a customizable dial. Just like last year, this makes the phone look like a more serious camera, but it’s all just looks—what makes a traditional camera good is the significantly bigger camera lens, and this is still just a regular, very small smartphone camera lens.
The camera theatrics continue with the new six-blade variable aperture for the main camera. Just like a traditional camera, there is a very tiny six-blade mechanical iris in the main lens that can open and close to adjust the aperture of your photo. Last year, Xiaomi had a similar system, but it only used two blades and could only snap between the “blades open” f1.9 mode and the “closed blades” f4.0 mode. With six blades, you get a “stepless variable aperture” that lets you pick any spot in the phone’s f-stop range.
The Xiaomi 14 Ultra’s six-blade iris sure does look neat.
Xiaomi
A side view.
Xiaomi
An explode view.
Xiaomi
This is still a tiny phone camera lens, though, so the f-stop range is very small, just f1.63 to f4.0. On a DSLR, adjusting the f-stop would change the camera’s depth of field, with a narrower aperture letting in less light in exchange for a crisp focus. A wider aperture would give brighter pictures with a smaller focal range, which you can use for blurry background bokeh effects. That’s all on a DSLR though, with a normal f-stop range of like F1.4 to F22. On a smartphone camera, especially when there is tons of software processing, f1.6 to f4 won’t change your images much. Any background blur is still a fake post-processing effect, and it’s hard to imagine a scenario where you wouldn’t just want as much light as possible for your tiny smartphone lens. Samsung tried all this before on the Galaxy S9 and S10 and then dropped the feature because it just wasn’t accomplishing much. The six-blade aperture is probably a triumph of micro-engineering, but in the real world, it’s more of a marketing bullet point.
Despite the fluff, the Xiaomi 14 Ultra is still packing serious smartphone-level camera hardware. The main sensor is a 1-inch, 50MP Sony LYT-900, probably the biggest and best smartphone camera sensor out there. Smartphone pictures are so heavily processed that the software has just as much to do with the hardware (see: every Pixel phone), but Xiaomi did get the best hardware. The other three rear cameras are all 50 MP Sony IMX858 sensors, with lenses for wide-angle, 3.2x telephoto, and 5x telephoto.
Preorders are already open, and the phone will ship on March 15.
The Xiaomi 14 Ultra sports a six-blade mechanical iris in the camera Read More »
Space Perspective could begin test flights of its privately owned capsule suspended under a high-altitude balloon within the next couple of months, the company’s co-founder told Ars this week.
Florida-based Space Perspective released photos of its first completed test capsule Tuesday. The company will use this pressurized capsule, called Excelsior, for a series of test flights this year over the Atlantic Ocean just off the coast of Cape Canaveral. Taber MacCallum, Space Perspective’s co-founder and chief technology officer, said employees have also finished fabricating the giant balloon that will lift the test capsule into the upper atmosphere for the first test flight.
The final piece of the puzzle is a ship, named Marine Spaceport Voyager, that Space Perspective will use to launch the balloon and capsule. This vessel is due to depart an outfitting facility in Louisiana in the next few weeks for a trip to Port Canaveral, Florida, where Space Perspective will load aboard the capsule and balloon. Then, perhaps in four to six weeks, ground teams will be ready for the system’s first test flight, according to MacCallum.
But this is a test program, and there could be delays, MacCallum said. In the meantime, Space Perspective will start building a second capsule for human test flights.
“We’ll do a series of unmanned tests with this capsule,” he said. “In theory, we could fly people in this capsule. It’s designed that way, and it has all of the systems set up for human flight. But our planning assumes that trailing on what we learn from this capsule, we build another capsule that will be our first human flight capsule. And this will remain an unmanned test capsule.”
These tests are a prelude to Space Perspective’s plans for regular commercial flights carrying paying customers to 100,000 feet (about 30 kilometers), roughly three times higher than the cruising altitude of a typical commercial airliner. From 100,000 feet, Space Perspective’s clients will see panoramic views of the ground and ocean far below, and the sky will be black, with the capsule flying above 99 percent of Earth’s atmosphere.
Founded in 2019, Space Perspective says on its website it is “driven by a desire to share the transformative power of space travel with as many people as possible.” In reality, the company will give customers an experience similar to spaceflight, with a few significant differences.
Essentially, passengers on Space Perspective’s high-altitude balloon will get a view the company says is similar to what a passenger might see on a suborbital spacecraft from Blue Origin or Virgin Galactic. But Space Perspective’s vehicle won’t subject customers to any high G-forces or the risks of rocket flight. The balloon passengers also won’t float in microgravity. And it will max out at 30 kilometers, well short of the 80-kilometer boundary of space recognized by the US government or the 100-kilometer Kármán line.
Still, the view from 30 kilometers must be tremendous. “You’ll see essentially all of Florida,” MacCallum said. “We’re also looking at flying sort of across the southern tip of Florida, so you’d see Cuba, the Bahamas, essentially all of Florida. So amazing views.”
Test flights on tap for Space Perspective’s luxury high-altitude balloon Read More »