Three big OpenAI news items this week were the FT article describing the cutting of corners on safety testing, the OpenAI former employee amicus brief, and Altman’s very good TED Interview.
The FT detailed OpenAI’s recent dramatic cutting back on the time and resources allocated to safety testing of its models.
In the interview, Chris Anderson made an unusually strong effort to ask good questions and push through attempts to dodge answering. Altman did a mix of giving a lot of substantive content in some places while dodging answering in others. Where he chose to do which was, itself, enlightening. I felt I learned a lot about where his head is at and how he thinks about key questions now.
The amicus brief backed up that OpenAI’s current actions are in contradiction to the statements OpenAI made to its early employees.
There are also a few other related developments.
What this post does not cover is GPT-4.1. I’m waiting on that until people have a bit more time to try it and offer their reactions, but expect coverage later this week.
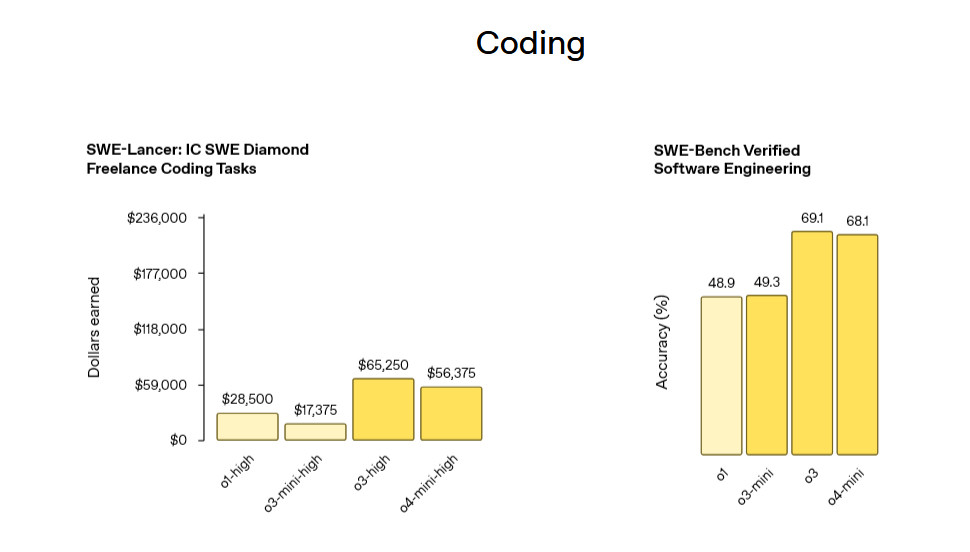
The big headline from TED was presumably the increase in OpenAI’s GPU use.
Steve Jurvetson: Sam Altman at TED today: OpenAI’s user base doubled in just the past few weeks (an accidental disclosure on stage). “10% of the world now uses our systems a lot.”
…
When asked how many users they have: “Last we disclosed, we have 500 million weekly active users, growing fast.”
Chris Anderson: “But backstage, you told me that it doubled in just a few weeks.” @SamA: “I said that privately.”
And that’s how we got the update.
Revealing that private info wasn’t okay but it seems it was an accident, in any case Altman seemed fine with it.
Listening to the details, it seems that Altman was referring not to the growth in users, but instead to the growth in compute use. Image generation takes a ton of compute.
Altman says every day he calls people up and begs them for GPUs, and that DeepSeek did not impact this at all.
Steve Jurvetson: Sam Altman at TED today:
Reflecting on the life ahead for his newborn: “My kids will never be smarter than AI.”
Reaction to DeepSeek:
“We had a meeting last night on our open source policy. We are going to do a powerful open-source model near the frontier. We were late to act, but we are going to do really well now.”
Altman doesn’t explain here why he is doing an open model. The next question from Anderson seems to explain it, that it’s about whether people ‘recognize’ that OpenAI’s model is best? Later Altman does attempt to justify it with, essentially, a shrug that things will go wrong but we now know it’s probably mostly fine.
Regarding the accumulated knowledge OpenAI gains from its usage history: “The upload happens bit by bit. It is an extension of yourself, and a companion, and soon will proactively push things to you.”
Have there been any scary moments?
“No. There have been moments of awe. And questions of how far this will go. But we are not sitting on a conscious model capable of self-improvement.”
I listened to the clip and this scary moment question specifically refers to capabilities of new models, so it isn’t trivially false. It still damn well should be false, given what their models can do and the leaps and awe involved. The failure to be scared here is a skill issue that exists between keyboard and chair.
How do you define AGI? “If you ask 10 OpenAI engineers, you will get 14 different definitions. Whichever you choose, it is clear that we will go way past that. They are points along an unbelievable exponential curve.”
So AGI will come and your life won’t change, but we will then soon get ASI. Got it.
“Agentic AI is the most interesting and consequential safety problem we have faced. It has much higher stakes. People want to use agents they can trust.”
Sounds like an admission that they’re not ‘facing’ the most interesting or consequential safety problems at all, at least not yet? Which is somewhat confirmed by discussion later in the interview.
I do agree that agents will require a much higher level of robustness and safety, and I’d rather have a ‘relatively dumb’ agent that was robust and safe, for most purposes.
When asked about his Congressional testimony calling for a new agency to issue licenses for large model builders: “I have since learned more about how government works, and I no longer think this is the right framework.”
I do appreciate the walkback being explicit here. I don’t think that’s the reason why.
“Having a kid changed a lot of things in me. It has been the most amazing thing ever. Paraphrasing my co-founder Ilya, I don’t know what the meaning of life is, but I am sure it has something to do with babies.”
Statements like this are always good to see.
“We made a change recently. With our new image model, we are much less restrictive on speech harms. We had hard guardrails before, and we have taken a much more permissive stance. We heard the feedback that people don’t want censorship, and that is a fair safety discussion to have.”
I agree with the change and the discussion, and as I’ve discussed before if anything I’d like to see this taken further with respect to these styles of concern in particular.
Altman is asked about copyright violation, says we need a new model around the economics of creative output and that ‘people build off each others creativity all the time’ and giving creators tools has always been good. Chris Anderson tries repeatedly to nail down the question of consent and compensation. Altman repeatedly refuses to give a straight answer to the central questions.
Altman says (10: 30) that the models are so smart that, for most things people want to do with them, they’re good enough. He notes that this is true based on user expectations, but that’s mostly circular. As in, we ask the models to do what they are capable of doing, the same way we design jobs and hire humans for them based on what things particular humans and people in general can and cannot do. It doesn’t mean any of us are ‘smart enough.’
Nor does it imply what he says next, that everyone will ‘have great models’ but what will differentiate will be not the best model but the best product. I get that productization will matter a lot for which AI gets the job in many cases, but continue to think this ‘AGI is fungible’ claim is rather bonkers crazy.
A key series of moments start at 35: 00 in. It’s telling that other coverage of the interview sidestepped all of this, essentially entirely.
Anderson has put up an image of The Ring of Power, to talk about Elon Musk’s claim that Altman has been corrupted by The Ring, a claim Anderson correctly notes also plausibly applies to Elon Musk.
Altman goes for the ultimate power move. He is defiant and says, all right, you think that, tell me examples. What have I done?
So, since Altman asked so nicely, what are the most prominent examples of Altman potentially being corrupted by The Ring of Power? Here is an eightfold path.
-
We obviously start with Elon Musk’s true objection, which stems from the shift of OpenAI from a non-profit structure to a hybrid structure, and the attempt to now go full for-profit, in ways he claims broke covenants with Elon Musk. Altman claimed to have no equity and not be in this for money, and now is slated to get a lot of equity. I do agree with Anderson that Altman isn’t ‘in it for the money’ because I think Altman correctly noticed the money mostly isn’t relevant.
-
Altman is attempting to do so via outright theft of a huge portion of the non-profit’s assets, then turn what remains into essentially an OpenAI marketing and sales department. This would arguably be the second biggest theft in history.
-
Altman said for years that it was important the board could fire him. Then, when the board did fire him in response (among other things) to Altman lying to the board in an attempt to fire a board member, he led a rebellion against the board, threatened to blow up the entire company and reformulate it at Microsoft, and proved that no, the board cannot fire Altman. Altman can and did fire the board.
-
Altman, after proving he cannot be fired, de facto purged OpenAI of his enemies. Most of the most senior people at OpenAI who are worried about AI existential risk, one by one, reached the conclusion they couldn’t do much on the inside, and resigned to continue their efforts elsewhere.
-
Altman used to talk openly and explicitly about AI existential risks, including attempting to do so before Congress. Now, he talks as if such risks don’t exist, and instead pivots to jingoism and the need to Beat China, and hiring lobbyists who do the same. He promised 20% of compute to the superalignment team, never delivered and then dissolved the team.
-
Altman pledged that OpenAI would support regulation of AI. Now he says he has changed his mind, and OpenAI lobbies against bills like SB 1047 and its AI Action Plan is vice signaling that not only opposes any regulations but seeks government handouts, the right to use intellectual property without compensation and protection against potential regulations.
-
Altman has been cutting corners on safety, as noted elsewhere in this post. OpenAI used to be remarkably good in terms of precautions. Now it’s not.
-
Altman has been going around saying ‘AGI will arrive and your life will not much change’ when it is common knowledge that this is absurd.
One could go on. This is what we like to call a target rich environment.
Anderson offers only #1, the transition to a for-profit model and the most prominent example, which is the most obvious response, but he proactively pulls the punch. Altman admits he’s not the same person he was and that it all happens gradually, if it happened all at once it would be jarring, but says he doesn’t feel any different.
Anderson essentially says okay and pivots to Altman’s son and how that has shaped Altman, which is indeed great. And then he does something that impressed me, which is tie this to existential risk via metaphor, asking if there was a button that was 90% to give his son a wonderful life and 10% to kill him (I’d love those odds!), would he press the button? Altman says literally no, but points out the metaphor, and says he doesn’t think OpenAI is doing that. He says he really cared about not destroying the world before, and he really cares about it now, he didn’t need a kid for that part.
Anderson then moves to the question of racing, and whether the fact that everyone thinks AGI is inevitable is what is creating the risk, asking if Altman and his colleagues believe it is inevitable and asks if maybe they could coordinate to ‘slow down a bit’ and get societal feedback.
As much as I would like that, given the current political climate I worry this sets up a false dichotomy, whereas right now there is tons of room to take more responsibility and get societal feedback, not only without slowing us down but enabling more and better diffusion and adaptation. Anderson seems to want a slowdown for its own sake, to give people time to adapt, which I don’t think is compelling.
Altman points out we slow down all the time for lack of reliability, also points out OpenAI has a track record of their rollouts working, and claims everyone involved ‘cares deeply’ about AI safety. Does he simply mean mundane (short term) safety here?
His discussion of the ‘safety negotiation’ around image generation, where I support OpenAI’s loosening of restrictions, suggests that this is correct. So does the next answer: Anderson asks if Altman would attend a conference of experts to discuss safety, Altman says of course but he’s more interested in what users think as a whole, and ‘asking everyone what they want’ is better than asking people ‘who are blessed by society to sit in a room and make these decisions.’
But that’s an absurd characterization of trying to solve an extremely difficult technical problem. So it implies that Altman thinks the technical problems are easy? Or that he’s trying to rhetorically get you to ignore them, in favor of the question of preferences and an appeal to some form of democratic values and opposition to ‘elites.’ It works as an applause line. Anderson points out that the hundreds of millions ‘don’t always know where the next step leads’ which may be the understatement of the lightcone in this context. Altman says the AI can ‘help us be wiser’ about those decisions, which of course would mean that a sufficiently capable AI or whoever directs it would de facto be making the decisions for us.
OpenAI’s Altman ‘Won’t Rule Out’ Helping Pentagon on AI Weapons, but doesn’t expect to develop a new weapons platform ‘in the foreseeable future,’ which is a period of time that gets shorter each time I type it.
Altman: I will never say never, because the world could get really weird.
…
I don’t think most of the world wants AI making weapons decisions.
…
I don’t think AI adoption in the government has been as robust as possible.
…
There will be “exceptionally smart” AI systems by the end of next year.
I think I can indeed forsee the future where OpenAI is helping the Pentagon with its AI weapons. I expect this to happen.
I want to be clear that I don’t think this is a bad thing. The risk is in developing highly capable AIs in the first place. As I have said before, Autonomous Killer Robots and AI-assisted weapons in general are not how we lose control over the future to AI, and failing to do so is a key way America can fall behind. It’s not like our rivals are going to hold back.
To the extent that the AI weapons scare the hell out of everyone? That’s a feature.
On the issue of the attempt to sideline and steal from the nonprofit, 11 former OpenAI employees filed an amicus brief in the Musk vs. Altman lawsuit, on the side of Musk.
Todor Markov: Today, myself and 11 other former OpenAI employees filed an amicus brief in the Musk v Altman case.
We worked at OpenAI; we know the promises it was founded on and we’re worried that in the conversion those promises will be broken. The nonprofit needs to retain control of the for-profit. This has nothing to do with Elon Musk and everything to do with the public interest.
OpenAI claims ‘the nonprofit isn’t going anywhere’ but has yet to address the critical question: Will the nonprofit actually retain control over the for-profit? This distinction matters.
You can find the full amicus here.
On this question, Timothy Lee points out that you don’t need to care about existential risk to notice that what OpenAI is trying to do to its non-profit is highly not cool.
Timothy Lee: I don’t think people’s views on the OpenAI case should have anything to do with your substantive views on existential risk. The case is about two questions: what promises did OpenAI make to early donors, and are those promises legally enforceable?
A lot of people on OpenAI’s side seem to be taking the view that non-profit status is meaningless and therefore donors shouldn’t complain if they get scammed by non-profit leaders. Which I personally find kind of gross.
I mean I would be pretty pissed if I gave money to a non-profit promising to do one thing and then found out they actually did something different that happened to make their leaders fabulously wealthy.
This particular case comes down to that. A different case, filed by the Attorney General, would also be able to ask the more fundamental question of whether fair compensation is being offered for assets, and whether the charitable purpose of the nonprofit is going to be wiped out, or even pivoted into essentially a profit center for OpenAI’s business (as in buying a bunch of OpenAI services for nonprofits and calling that its de facto charitable purpose).
The mad dash to be first, and give the perception that the company is ‘winning’ is causing reckless rushes to release new models at OpenAI.
This is in dramatic contrast to when there was less risk in the room, and despite this OpenAI used to take many months to prepare a new release. At first, by any practical standard, OpenAI’s track record on actual model release decisions was amazingly great. Nowadays? Not so much.
Would their new procedures pot the problems it is vital that we spot in advance?
Joe Weisenthal: I don’t have any views on whether “AI Safety” is actually an important endeavor.
But if it is important, it’s clear that the intensity of global competition in the AI space (DeepSeek etc.) will guarantee it increasingly gets thrown out the window.
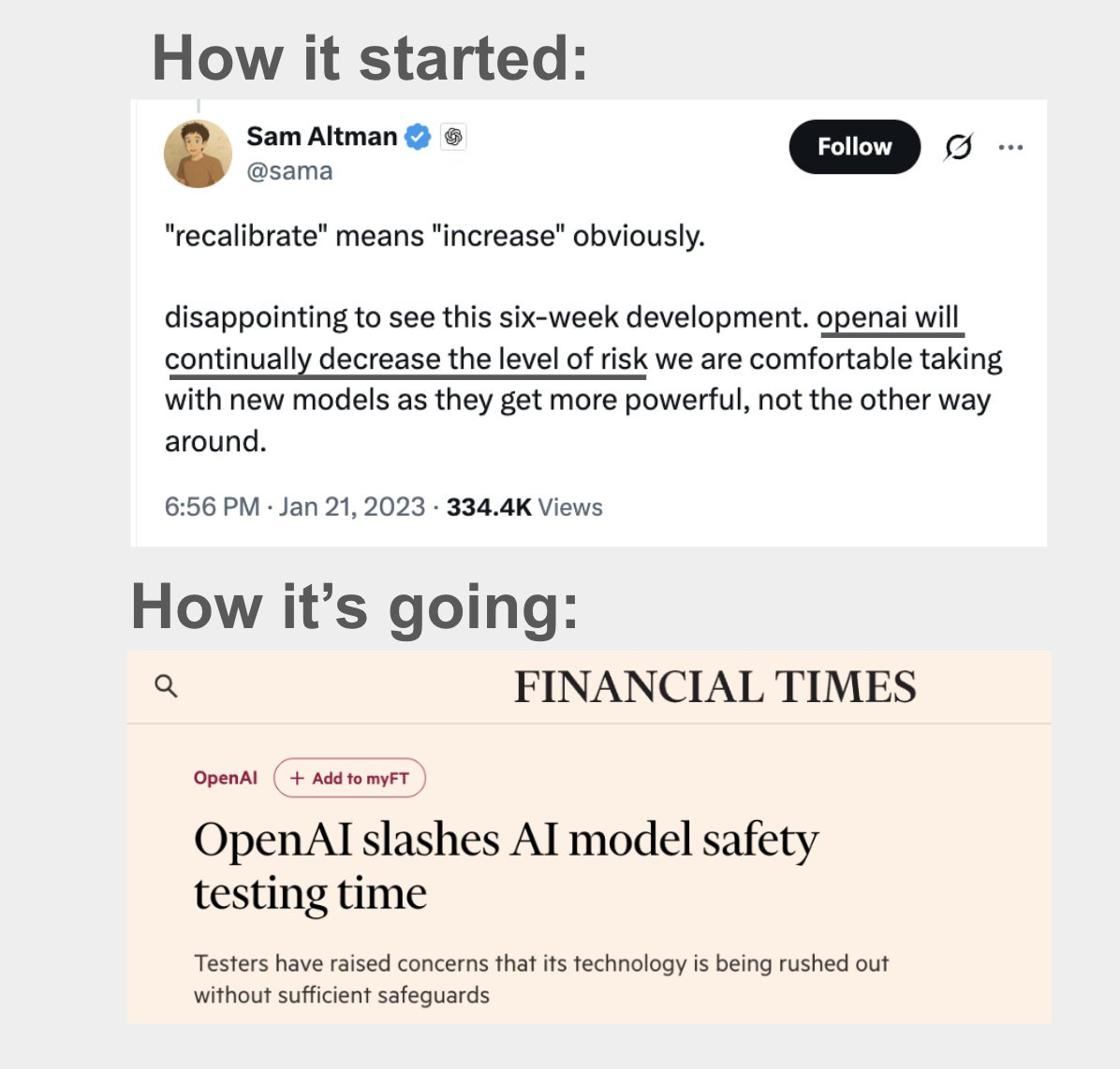
Christina Criddle: EXC: OpenAI has reduced the time for safety testing amid “competitive pressures” per sources:
Timeframes have gone from months to days
Specialist work such as finetuning for misuse (eg biorisk) has been limited
Evaluations are conducted on earlier versions than launched
Financial Times (Gated): OpenAI has slashed the time and resources it spends on testing the safety of its powerful AI models, raising concerns that its technology is being rushed out the door without sufficient safeguards.
Staff and third-party groups have recently been given just days to conduct “evaluations,” the term given to tests for assessing models’ risks and performance, on OpenAI’s latest LLMs, compared to several months previously.
According to eight people familiar with OpenAI’s testing processes, the start-up’s tests have become less thorough, with insufficient time and resources dedicated to identifying and mitigating risks, as the $300 billion startup comes under pressure to release new models quickly and retain its competitive edge.
Steven Adler (includes screenshots from FT): Skimping on safety-testing is a real bummer. I want for OpenAI to become the “leading model of how to address frontier risk” they’ve aimed to be.
Peter Wildeford: I can see why people say @sama is not consistently candid.
Dylan Hadfield Menell: I remember talking about competitive pressures and race conditions with the @OpenAI’s safety team in 2018 when I was an intern. It was part of a larger conversation about the company charter.
It is sad to see @OpenAI’s founding principles cave to pressures we predicted long ago.
It is sad, but not surprising.
This is why we need a robust community working on regulating the next generation of AI systems. Competitive pressure is real.
We need people in positions of genuine power that are shielded from them.
Peter Wildeford:
Dylan Hadfield Menell: Where did you find an exact transcription of our conversation?!?! 😅😕😢
You can’t do this kind of testing properly in a matter of days. It’s impossible.
If people don’t have time to think let alone adapt, probe and build tools, how they can see what your new model is capable of doing? There are some great people working on these issues at OpenAI but this is an impossible ask.
Testing on a version that doesn’t even match what you release? That’s even more impossible.
Part of this is that it is so tragic how everyone massively misinterpreted and overreacted to DeepSeek.
To reiterate since the perception problem persists, yes, DeepSeek cooked, they have cracked engineers and they did a very impressive thing with r1 given what they spent and where they were starting from, but that was not DS being ‘in the lead’ or even at the frontier, they were always many months behind and their relative costs were being understated by multiple orders of magnitude. Even today I saw someone say ‘DeepSeek still in the lead’ when this is so obviously not the case. Meanwhile, no one was aware Google Flash Thinking even existed, or had the first visible CoT, and so on.
The result of all that? Talk similar to Kennedy’s ‘Missile Gap,’ abject panic, and sudden pressure to move up releases to show OpenAI and America have ‘still got it.’