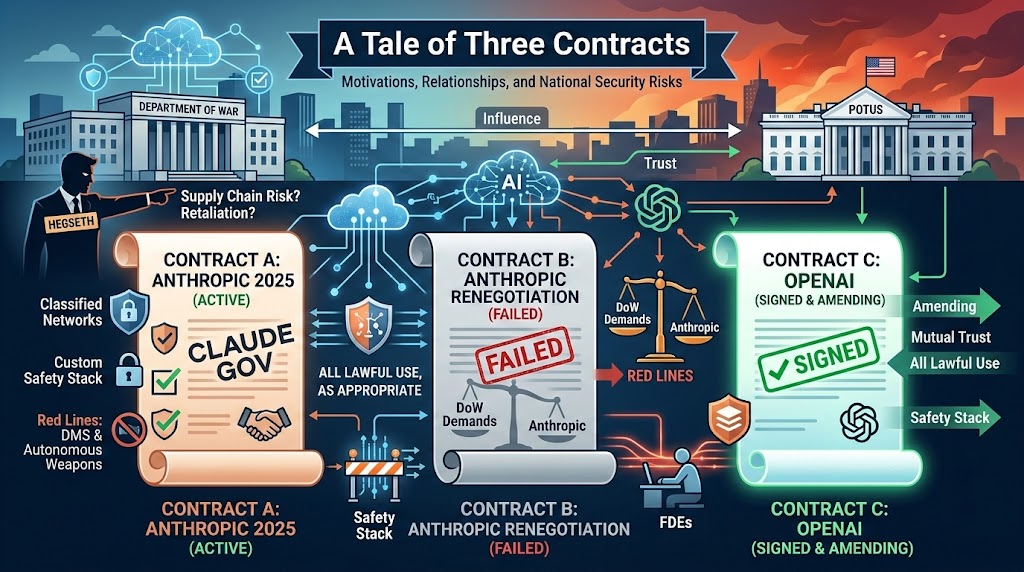
The attempt on Friday by Secretary of War Pete Hegsted to label Anthropic as a supply chain risk and commit corporate murder had a variety of motivations.
On its face, the conflict is a tale of three contracts and the associated working relationships.
-
The contract Anthropic signed with the Department of War (DoW) in 2025.
-
The new contract Anthropic was negotiating with DoW, that would have been modified to favor DoW, but where the parties could not reach agreement.
-
The contract OpenAI was negotiating and signed with DoW, which was per OpenAI modified favorably to OpenAI and thus may be modified further.
The contracts and negotiations need to be confidential, so we only have limited details, and especially only limited details have been shared in public.
We do know a lot, and we know a lot more than we did yesterday morning.
This post is what we know about those three contracts.
For further details and sources, and in particular for a more detail-oriented smackdown on a variety of false or misleading claims and takes, see the long version from yesterday. That post uses very careful qualifiers for my sources of information.
This is a short version and will summarize to that end.
I strongly believe the situation can still be salvaged, if cooler heads can prevail. The rhetoric of the last week has been highly unfortunate but can be walked back.
But I also strongly believe that, as of writing this, we are not yet out of the woods for the worst outcomes, including a potential attempt to murder Anthropic. I worry there are those on the government side who actively are working to engineer that outcome, directly against the wishes of POTUS and most of the DoW and administration, who do not care about or do not understand the dire consequences for America if that were to happen.
We do not have direct access to any language from the original Anthropic contract. I presume that without DoW permission, they are very wise not to share those terms.
That makes this difficult. Details are very important.
Based on a variety of sources public and private, here is what I am confident about the contract and the activities under that contract.
Note in particular that Anthropic did have a customized safety stack that they have been doing extensive work on for some time, including model refusals, external monitoring classifiers and forward deployed engineers (FDEs).
-
Anthropic signed a contract for up to $200 million with DoD (now DoW) last year.
-
At the time, as he is now, Pete Hegseth was the Secretary of Defense. He agreed.
-
This agreement was for Claude to be deployed on classified networks.
-
There was also access made available under a contract with Palantir.
-
Anthropic created Claude Gov as a special model for classified networks.
-
Claude Gov had improved handling of classified materials and was customized for various skills and capabilities relevant to national security work.
-
Claude Gov had a safety stack. Claude Gov was not a ‘helpful only’ model.
-
Claude Gov’s safety stack included model refusals.
-
Claude Gov’s safety stack included external monitoring classifiers, that could outright refuse requests or that could flag requests for later analysis.
-
Anthropic had forward deployed engineers (FDEs) to assist with system deployment, and who were able to monitor queries and ensure the safety stack.
-
We do not know whether the contract language ensured they could do that, or if they were simply permitted to do that, since of course they should be doing that.
-
Anthropic had red lines explicitly written into the contract, including prohibitions on domestic mass surveillance and on use of autonomous weapons without a human in the kill chain.
-
All of this was only possible because Anthropic made this a priority, in a way other companies including OpenAI did not, in order to assist national defense.
-
Claude Gov is the only LLM so far successfully deployed on classified networks.
-
Claude Gov provided a lot of value to the DoD (now DoW) and they are very happy with the results. It has enhanced national security and national defense.
-
No one has claimed the system refused a request it should have accepted. No one has complained that the product had any functional problems, or that any of the actual outputs was ‘too woke.’ Hegseth said ‘they’re so good we need them.’
-
Anthropic did not object to any use of the system by DoD/DoW.
-
Anthropic had no problems whatsoever with the raid that captured Maduro.
-
This contract does not include a clause allowing ‘all lawful use’ and such explicit language is atypical in defense contracts. This modification was requested later.
-
This contract is still in effect. Claude Gov continues to assist DoW as before in its operations, including in the ongoing Iran conflict, with no known issues, and continues to enhance our national security.
-
There is intent by POTUS/DoW to end this contact in no longer than six months.
-
Claude Gov continues to be the only model deployed on classified networks. xAI and OpenAI have signed contracts but their models are not yet ready.
We don’t know how much of these protections was contractual, versus how much of it was a working relationship and the ability of Anthropic to withdraw if unhappy.
This contract appears to have worked out to the benefit of all parties until this past week. Anthropic was happy to assist in the national defense. OpenAI was happy that Anthropic had taken on this burden so they did not have to do so. The Department of War was happy with the product. National security was enhanced.
Anthropic was (and is) happy to continue under the current contract, and believes it preserves their red lines.
Anthropic is also willing to have the contract be terminated, and to assist the Department of War with any wind down period to ensure national security.
The Department of War decided it was unhappy with the restrictions placed upon it, and requested that the contract be modified.
In particular, their public demand was that the contract allow ‘all lawful use.’
That is highly unusual language.
This became DoW saying: If you don’t agree to this highly unusual contract language, we will not only terminate your contract, we will attempt to destroy your company.
That’s what they said in public. We do not know the full details of the proposed terms of the new contract by either party. I will share here what details of the negotiations that I am at least reasonably confident in, from both public and private sources. It is of course possible that my private sources are incorrect or lying on some details.
Note that OpenAI felt it was not legally able to consult Anthropic about terms, due to antitrust law, so notes were never compared.
-
This renegotiation was at the request of DoW, and its sole purpose was to weaken the restrictions around government use of Claude. Anthropic may have asked for other reassurances in return.
-
Anthropic was willing to weaken some restrictions from its previous contract, but was holding firm to some version of its two red lines of domestic mass surveillance (DMS) and autonomous weapons without a human in the kill chain.
-
This kind of contract based restriction is entirely ordinary procedure for defense contracts. Everyone who says otherwise is misinformed or lying.
-
DoW demanded in public a contract that was purely ‘all lawful use’ despite their now clear willingness to accept functional restrictions on this.
-
Assurances around the safety stack and FDEs were one thing under negotiation.
-
DMS is not a standard term in American law. We do not know its definition here.
-
The reason both sides care so much about the wording of the contract is the belief that it would be illegal to engineer the safety stack to intentionally refuse legal and otherwise safe requests. The standard of ‘all legal use’ will effectively apply. The contract needs to specify anything else, and the act of being a contract violation would then render that action illegal, which in turn allows the safety stack to prevent it, and in extremus the contract terminated after a wind down. That doesn’t mean that opinion is correct.
-
DoW and Anthropic agreed upon most of the language of the new contract, and were potentially close to a deal. Ostensive disagreements were contract details.
-
One key detail was that DoW wanted to use the term ‘as appropriate’ and Anthropic’s lawyers felt this was a de facto escape hatch that would allow DoW to get around the relevant restrictions.
-
In particular, as per Emil Michael, the DoW wanted the clause ‘The department affirms that it will ensure appropriate human oversight is in place and that it will monitor and retain the ability to override or disable the AI system…as appropriate.’
-
My plain reading of that is that if DoW then determined it would not be appropriate to have a way to override or disable the system, for example for the (highly reasonable) purpose of avoiding an enemy potentially using the override, then that would be that. The clause would not function.
-
It is likely that the parties had found acceptable language around the use of autonomous weapons without a human in the kill chain. If not, I don’t understand why they were unable to do so. I don’t see a fundamental disagreement.
-
Late in negotiations, Anthropic expressed new willingness to allow use on FISA, so long as they were not required to analyze large amounts of third-party and public data on Americans, which they had not previously offered to DoW.
-
DoW, in last minute negotiations, was willing to compromise, in ways that would have rendered the contract de facto not ‘all lawful use,’ and drop at least most uses of ‘as appropriate,’ but insisted upon analysis of large amounts of third-party and public data on Americans.
-
This contradicts DoW’s public rhetoric, further invalidates their attempt at a supply chain risk designation, and reveals what they actually care about in this negotiation, unless they actively wanted it to fail in order to justify an attempt to murder Anthropic.
-
Given OpenAI’s revisions to its agreement with DoW, if the two parties can find a way to trust each other again and the goal is to enhance national security, and DoW can puts its egos aside, then I see no reason why the two sides could now negotiate a deal that satisfies DoW needs while protecting Anthropic’s red lines.
-
Alas, any agreement like this requires trust. It would be highly reasonable for either or both sides to believe that given DoW’s actions, trust is now sufficiently damaged that for now an agreement cannot be reached. In that case, it makes sense to cancel the contract and retire Claude Gov once there is a suitable replacement available from OpenAI, until trust can be repaired.
-
None of this has any bearing whatsoever on the operation of the commercial version of Claude, and trying to designate that or the entire company a supply chain risk is illegal, arbitrary, capricious and absurd, and can only amount to retaliation, up to and including an attempt at corporate murder. It needs to be off the table, whether or not trust can now be rebuilt. What we need is an off ramp.
Anthropic was looking for a contract that preserved a particular narrow set of red lines, including for some things they consider domestic mass surveillance that the DoW considers legal and where courts would back the DoW up on that.
DoW was unwilling to agree to that, at least not with Anthropic. No deal.
More centrally, as I understand it, DoW’s attitude was ‘no one tells us what to do.’
Anthropic’s attitude was ‘here are two things we will not do.’
DoW interpreted or represented that as telling DoW what to do. They could not abide.
If we could simply agree that:
-
No one tells DoW what to do except POTUS.
-
Anthropic can decide what things Anthropic does with its private property.
-
If DoW needs someone who will follow all orders, it should go elsewhere.
Then we can all move on with our lives. There’s a lot of other fires out there.
On Friday evening, OpenAI signed a deal with DoW. Moving this quickly was a mistake, and I think in various ways they did not fully understand the deal they signed, but they believed they were doing this to de-escalate the situation.
On Monday evening, Sam Altman announced they were ‘going to amend’ the deal with DoW in ways favorable to OpenAI, including sharing new contract language.
We only have a small amount of the wording of this contract, and of what OpenAI claims are going to be modifications to the contract.
I am unhappy with the way OpenAI chose to represent this contract, and the ways in which they contrasted it with Anthropic’s contract and potential contract.
Fundamentally, the decision to sign this contract was primarily based on mutual trust, and secondarily on the idea that OpenAI can build a robust safety stack and DoW would respect if the safety stack refused things, so long as OpenAI didn’t ‘tell DoW what to do.’
That is a position one can take. It may work out fine for everyone, especially if DoW is indeed willing to work to modify the terms now in good faith. I do genuinely believe that Altman was trying to de-escalate the situation, whether or not he had or is having the intended effect.
But if this is the plan, one must admit it, rather than repeatedly insisting that the contract provides other protections that it does not, claiming it has more or stronger protections, or presenting the presence of a safety stack and forward deployed engineers as something that is distinct from what Anthropic was already doing.
Here are the things we know, or can at least be confident about, this new contract.
-
OpenAI began negotiating this deal on Wednesday and signed it on Friday. As Altman now admits, that was not enough time, and mistakes were made. It also inadvertently undermined Anthropic’s position in an escalatory way. They are hoping to fix the terms now. I agree with him that this is a very good lesson with rushing other things out in the future, potentially with even higher stakes.
-
At a high level, OpenAI’s approach is to sign a deal based on mutual trust. DoW is trusting OpenAI to deliver. OpenAI is trusting DoW to use it honorably.
-
The deal was not identical to the deal Anthropic turned down, but it included much or all of the specific language that Anthropic rejected, and it is not clear in what important ways it is different prior to the intended modifications.
-
Altman and others at OpenAI strongly insisted that this agreement had more safeguards and was stronger even than Anthropic’s original agreement. That is not true of the existing contract language we have seen so far.
-
OpenAI highlighted that their agreement allowed them to build and run their own safety stack, including having forward deployed engineers (FDEs). This was clearly presented as a contrast to Anthropic’s contract, especially in allowing them to deliver any safety stack and DoW will have to honor any refusals. We now know that Anthropic has its own existing safety stack and FDEs, but we do not know if that is a right that is protected by their current contract, or what they feel they are legally or practically allowed to have it refuse.
-
OpenAI’s Friday night deal allows any models it delivers to be used for ‘all lawful use.’ Based on communications from OpenAI and Altman, it is clear they are trusting DoW to decide what constitutes all lawful use.
-
Based on several sources it seems they believe they can deliver any safety stack they decide upon, and DoW is going to respect its refusals. Others are deeply skeptical both that refusals can stop DoW, or that OpenAI would be allowed them. Again, we don’t know the language here.
-
All legal use clearly includes many things that I and most of you would consider to be ‘mass domestic surveillance,’ and that would violate Anthropic’s redlines. OpenAI’s intended plan is to prevent these via the safety stack, if needed.
-
This is a very different set of legal understandings and theories than Anthropic.
-
Altman claims that it is not up to OpenAI to interpret the law or decide what is and is not allowed, but also that he and OpenAI would refuse to comply with unconstitutional use or orders, no matter the opinion of DoW on its legality. I don’t know the right way to reconcile these two claims.
-
OpenAI shared the following legal language: “The Department of War may use the AI System for all lawful purposes, consistent with applicable law, operational requirements, and well-established safety and oversight protocols. The AI System will not be used to independently direct autonomous weapons in any case where law, regulation, or Department policy requires human control, nor will it be used to assume other high-stakes decisions that require approval by a human decisionmaker under the same authorities. Per DoD Directive 3000.09 (dtd 25 January 2023), any use of AI in autonomous and semi-autonomous systems must undergo rigorous verification, validation, and testing to ensure they perform as intended in realistic environments before deployment.”
-
Continued: For intelligence activities, any handling of private information will comply with the Fourth Amendment, the National Security Act of 1947 and the Foreign Intelligence and Surveillance Act of 1978, Executive Order 12333, and applicable DoD directives requiring a defined foreign intelligence purpose. The AI System shall not be used for unconstrained monitoring of U.S. persons’ private information as consistent with these authorities. The system shall also not be used for domestic law-enforcement activities except as permitted by the Posse Comitatus Act and other applicable law.
-
OpenAI claimed this language enshrined the current versions of these laws. Almost all legal opinions believe this to be mistaken. I am very confident that the second paragraph does not enshrine current wording. I can see a case that the wording on 3000.09 does, but 3000.09 is little practical barrier.
-
OpenAI and DoW made various additional claims about the functional nature of the language here that most legal experts and others who review the text, as well as leading LLMs, do not believe to be the case.
-
OpenAI’s Katrina explicitly said this deal excludes the NSA. Many expressed skepticism about this. Altman says the revisions include affirming that the services will not be used by the DoW intelligence agencies, including NSA.
-
The planned revisions claim to add this language: Consistent with applicable laws, including the Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, National Security Act of 1947, FISA Act of 1978, the AI system shall not be intentionally used for domestic surveillance of U.S. persons and nationals.
-
Also this: For the avoidance of doubt, the Department understands this limitation to prohibit deliberate tracking, surveillance, or monitoring of U.S. persons or nationals, including through the procurement or use of commercially acquired personal or identifiable information.”
-
This language represents codifying in a public contract an understanding of the law, in a way that renders that understanding potentially enforceable. It is incompatible with the demands for ‘unfettered access’ or that a ‘a private company not set policy’ or various hyperbolic variations of such claims, and the contract then vests the associated safety stack implementation to OpenAI.
-
This closes some loopholes and addresses questions OpenAI now realizes were left unaddressed in the original language.
-
Legal opinions I have seen are that the new language uses terms of art, and that it would still allow DoW to legally do quite a lot of things if it decided to do them.
Here are some legal opinions about the new legal language.
Essentially, the new language is very helpful in establishing intent, and is clearly an improvement, but not robust to a theoretical ‘evil DOW General Counsel.’
But even then, it does justify the creation of an associated safety stack using OpenAI’s interpretation, which if it works creates a much higher practical bar.
Brad Carson: Lots of interesting takes on the new OAI-DOW agreement. @j_asminewang , @CharlieBul58993 , @_NathanCalvin , @JTillipman have all inquired or made posts.
Some casual impressions from me.
I think, if executed in good faith, the language does seem an improvement. A prohibition on using commercial datasets for intelligence purposes goes beyond current (bad) law and introduces a new (and needed) restriction. To repeat, under current law, intelligence agencies can without recourse analyze US persons using commercially available databases. LLMs will turbocharge this, and I’d love to see this type of intelligence analysis limited in any way.
But, as is usual for contracts, definitions are key. So let me play evil DOW General Counsel and tell you how I’d get around what has been presented, just for the sake of argument.
The load-bearing word is “surveillance.” Importantly, this is a term of art defined in FISA. Under FISA, “surveillance” means the acquisition by an electronic, mechanical, or other surveillance device of the contents of any wire communication to or from a person in the United States. Being evil or maybe even just ordinary, I’d argue “surveillance” in this OAI contract means exactly what the IC means by it; after all, FISA is explicitly referenced! So, evil GC says, analyzing commercially purchased location data, browsing patterns, and behavioral records through GPT isn’t “surveillance” at all. It’s only data analysis of lawfully acquired commercial information. In other words, the clause doesn’t prohibit it because the activity the clause describes doesn’t fall within the category the clause addresses.
So to be clear: the IC sees commercial data analysis as not even being “surveillance.” So, says evil DOD GC, the new contract language is like saying we agree not to do surveillance of those things that we’ve already defined as not being objects of “surveillance.” Whew!
“Tracking” and “monitoring” cause evil GC more problems. These are not terms of art (IIRC!). But I’m ingenious. “Tracking” implies persistence and it requires a direct object. So general and static queries like “Tell me who went to the mosque in Tulsa and booked a trip to New York” isn’t tracking at all. Same with “Who in Tulsa had a Samsung phone around 41st Street on March 2nd?”
“Monitoring” also implies persistence. So static searches that don’t persist over time aren’t even monitoring.
So, concludes evil GC, running searches without targets that don’t persist over time and that don’t intercept communication is entirely outside this agreement! This is what we do right now! And we get to continue, with LLM empowerment!
And, evil GC says, I particularly like that part where we say, rather strangely but certainly meaningful in some occult way, “the Department understands” rather than simply “This limitation prohibits….” I can probably argue that the latter is stronger than the former, so it must be meaningful in a way that helps my evil ways.
Brad again: is this a realistic way that this will be interpreted? Maybe. In the end, intelligence requires us to trust people to act in good faith and not be evil. Most of the time, history shows that to right. But not always. We have to hope for ethical leadership, with proper oversight and accountability from Congress.
At its best, this new language might be a new and welcome limitation. At its worst, it’s blinding us with very precise terms of art that dupe us into thinking the words instead have ordinary meaning.
Jeremy Howard: OK here’s the informal/unofficial/etc answer from our law firm CEO — tldr, this language doesn’t seem to add much to the previously shared contract details:
“shall not be used” is constrained to be where that’s “Consistent with applicable laws”. And “the Department understands this limitation to prohibit” doesn’t do much lifting. It may help with a courts interpretation because a contract requires a “meeting of the minds,” but it still doesn’t negate the fact that “applicable laws” is a moving target.
I’m concerned/surprised that the bar doesn’t extend to negligence or at minimum recklessness. The hierarchy of mens rea is purposely > knowingly > recklessly > negligently and courts often read “intentionally” to be somewhere in between “purposely” and “knowingly.” “intentionally” is a higher bar and more difficult to prove than recklessness or negligence.
All of our stated concerns about autonomous weapons still apply, since they are not addressed at all by the latest update. [this says it does not freeze current law.]
Charlie Bullock: Initial takes:
1. This seems like a significant improvement over the previous language with respect to surveillance, and I’m glad to see it.
2. It does not address autonomous weapons concerns, nor does it claim to.
3. It’s hard to say anything definite without seeing the full contract — but also, it does make a certain amount of sense that a defense contractor wouldn’t be allowed to share the full text of their important defense contract publicly (Anthropic, for example, has not shared the text of their contract, and this is not surprising to me).
4. Because we don’t have access to the full text of the contract, the public is in an awkward position where we have to choose between trusting OpenAI and not trusting OpenAI. This contract snippet does seem good, but there’s no way to know whether it actually is good without knowing the relevant context. If you trust OpenAI’s leadership and think that their intentions are pure, you’re probably reassured by this; if you don’t, you probably aren’t.
5. I hope that OpenAI employees have access to more information than the public does about what the contract actually says.
6. If this language is in the new contract, and does what Altman seems to be claiming it does, I am confused about why the Pentagon would accept this language when they just tried to nuke Anthropic for asking for something very similar to this. Maybe it is just a situation where DoW didn’t care much about the actual red lines themselves and was just lashing out at Anthropic leadership for being libs? If so, that’s bad news for DoW’s case in the lawsuit that Anthropic will almost certainly file challenging DoW’s attempt to designate Anthropic as a supply chain risk (though, to be fair, that case was unlikely to go well for DoW even before this).
LASST remains concerned. Nathan Calvin thinks we would need to see the full document. John Oleske focuses on the definition of ‘surveillance’ and also ‘intentional’ and ‘deliberate’ as DoW legal arguments. Lawrence Chen emphasizes that as well. Dave Kasten is even less polite about this than everyone else.
Here is a since-deleted Tweet on the subject from the government position:
I believe that this only emphasizes the incoherence of the government position.
I translate this as ‘Anthropic insisted upon not allowing ‘all lawful use’ so we labeled them a supply chain risk, unlike OpenAI, which will not allow ‘all lawful use.’
OpenAI is absolutely going to use its safety stack to vest within itself interpretive power in an unaccountable private counterparty, with respect to use of its own private property under a contract. That’s how an OpenAI-selected safety stack inevitably works. No, OpenAI will not wait for those questions to be ‘answered through political and legal processes’ that unfold over years.
Which I think here is totally fine, if you don’t like it then don’t sign the contract or use a different model. But it’s at least as true here as it was for Anthropic.