“It’s shocking”: Massive raw milk outbreak from 2023 finally reported
The outbreak occurred in 2023–2024, but little information had been shared about it.
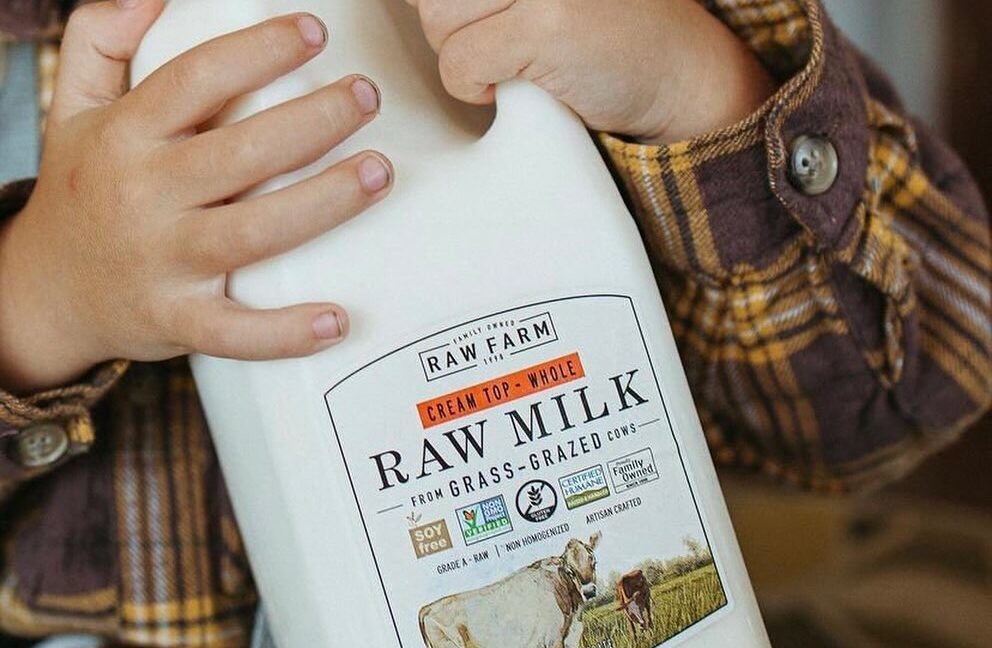
On October 20, 2023, health officials in the County of San Diego, California, put out a press release warning of a Salmonella outbreak linked to raw (unpasteurized) milk. Such an outbreak is not particularly surprising; the reason the vast majority of milk is pasteurized (heated briefly to kill germs) is because milk can easily pick up nasty pathogens in the farmyard that can cause severe illnesses, particularly in children. It’s the reason public health officials have long and strongly warned against consuming raw milk.
At the time of the press release, officials in San Diego County had identified nine residents who had been sickened in the outbreak. Of those nine, three were children, and all three children had been hospitalized.
On October 25, the county put out a second press release, reporting that the local case count had risen to 12, and the suspected culprit—raw milk and raw cream from Raw Farm LLC—had been recalled. The same day, Orange County’s health department put out its own press release, reporting seven cases among its residents, including one in a 1-year-old infant.
Both counties noted that the California Department of Public Health (CDPH), which had posted the recall notice, was working on the outbreak, too. But it doesn’t appear that CDPH ever followed up with its own press release about the outbreak. The CDPH did write social media posts related to the outbreak: One on October 26, 2023, announced the recall; a second on November 30, 2023, noted “a recent outbreak” of Salmonella cases from raw milk but linked to general information about the risks of raw milk; and a third on December 7, 2023, linked to general information again with no mention of the outbreak.
But that seems to be the extent of the information at the time. For anyone paying attention, it might have seemed like the end of the story. But according to the final outbreak investigation report—produced by CDPH and local health officials—the outbreak actually ran from September 2023 to March 2024, spanned five states, and sickened at least 171 people. That report was released last week, on July 24, 2025.
Shocking outbreak
The report was published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a journal run by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The report describes the outbreak as “one of the largest foodborne outbreaks linked to raw milk in recent US history.” It also said that the state and local health department had issued “extensive public messaging regarding this outbreak.”
According to the final data, of the 171 people, 120 (70 percent) were children and teens, including 67 (39 percent) who were under the age of 5. At least 22 people were hospitalized, nearly all of them (82 percent) were children and teens. Fortunately, there were no deaths.
“I was just candidly shocked that there was an outbreak of 170 plus people because it had not been reported—at all,” Bill Marler, a personal injury lawyer specializing in food poisoning outbreaks, told Ars Technica in an interview. With the large number of cases, the high percentage of kids, and cases in multiple states, “it’s shocking that they never publicized it,” he said. “I mean, what’s the point?”
Ars Technica reached out to CDPH seeking answers about why there wasn’t more messaging and information about the outbreak during and soon after the investigation. At the time this story was published, several business days had passed and the department had told Ars in a follow-up email that it was still working on a response. Shortly after publication, CDPH provided a written statement, but it did not answer any specific questions, including why CDPH did not release its own press release about the state-wide outbreak or make case counts public during the investigation.
“CDPH takes its charge to protect public health seriously and works closely with all partners when a foodborne illness outbreak is identified,” the statement reads. It then referenced only the social media posts and the press releases from San Diego County and Orange County mentioned previously in this story as examples of its public messaging.
“This is pissing me off”
Marler, who represents around two dozen of the 171 people sickened in the outbreak, was one of the first people to get the full picture of the outbreak from California officials. In July of 2024, he obtained an interim report of the investigation from state health officials. At that point, they had documented at least 165 of the cases. And in December 2024, he got access to a preliminary report of the full investigation dated October 15, 2024, which identified the final 171 cases and appears to contain much of the data published in the MMWR, which has had its publication rate slowed amid the second Trump administration.
Getting that information from California officials was not easy, Marler told Ars. “There was one point in time where they wouldn’t give it to me. And I sent them a copy of a subpoena and I said, ‘you know, I’ve been working with public health for 32 years. I’m a big supporter of public health. I believe in your mission, but,’ I said, ‘this is pissing me off.'”
At that point, Marler knew that it was a multi-county outbreak and the CDPH and the state’s Department of Food and Agriculture were involved. He knew there was data. But it took threatening a subpoena to get it. “I’m like ‘OK, you don’t give it to me. I’m going to freaking drop a subpoena on you, and the court’s going to force you to give it.’ And they’re like, ‘OK, we’ll give it to you.'”
The October 15 state report he finally got a hold of provides a breakdown of the California cases. It reports that San Diego had a total of 25 cases (not just the 12 initially reported in the press releases), and Orange County had 19 (not just the seven). Most of the other 171 cases were spread widely across California, spanning 35 local health departments. Only four of the 171 cases were outside of California—one each in New Mexico, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Washington. It’s unclear how people in these states were exposed, given that it’s against federal law to sell raw milk for human consumption across state lines. But two of the four people sickened outside of California specifically reported that they consumed dairy from Raw Farm without going to California.
Of the 171 cases, 159 were confirmed cases, which were defined as being confirmed using whole genome sequencing that linked the Salmonella strain causing a person’s infection to the outbreak strain also found in raw milk samples and a raw milk cheese sample from Raw Farm. The remaining 12 probable cases were people who had laboratory-confirmed Salmonella infections and also reported consuming Raw Farm products within seven days prior to falling ill.
“We own it”
In an interview with Ars Technica, the owner and founder of Raw Farm, Mark McAfee, disputed much of the information in the MMWR study and the October 2024 state report. He claimed that there were not 171 cases—only 19 people got sick, he said, presumably referring to the 19 cases collectively reported in the San Diego and Orange County press releases in October 2023.
“We own it. It’s ours. We’ve got these 19 people,” he told Ars.
But he said he did not believe that the genomic data was accurate and that the other 140 cases confirmed with genetic sequencing were not truly connected to his farm’s products. He also doubted that the outbreak spanned many months and into early 2024. McAfee says that a single cow that had been purchased close to the start of the outbreak had been the source of the Salmonella. Once that animal had been removed from the herd by the end of October 23, subsequent testing was negative. He also outright did not accept that testing identified the Salmonella outbreak strain in the farm’s raw cheese, which was reported in the MMWR and the state report.
Overall, McAfee downplayed the outbreak and claimed that raw milk has significant health benefits, such as being a cure for asthma—a common myth among raw milk advocates that has been debunked. He rejects the substantial number of scientific studies that have refuted the variety of unproven health claims made by raw-milk advocates. (You can read a thorough run-down of raw milk myths and the data refuting them in this post by the Food and Drug Administration.) McAfee claims that he and his company are “pioneers” and that public health experts who warn of the demonstrable health risks are simply stuck in the past.
Outbreak record
McAfee is a relatively high-profile raw milk advocate in California. For example, health secretary and anti-vaccine advocate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. is reportedly a customer. Amid an outbreak of H5N1 on his farm last year, McAfee sent Ars press material claiming that McAfee “has been asked by the RFK transition team to apply for the position of ‘FDA advisor on Raw Milk Policy and Standards Development.'” But McAfee’s opinion of Kennedy has soured since then. In an interview with Ars last week, he said Kennedy “doesn’t have the guts” to loosen federal regulations on raw milk.
On his blog, Marler has a running tally of at least 11 outbreaks linked to the farm’s products.
In this outbreak, illnesses were caused by Salmonella Typhimurium, which generally causes diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and abdominal pain. In some severe cases, the infection can spread outside the gastrointestinal tract and into the blood, brain, bones, and joints, according to the CDC.
Marler noted that, for kids, infections can be severe. “Some of these kids who got sick were hospitalized for extended periods of time,” he said of the some of the cases he is representing in litigation. And those hospitalizations can lead to hundreds of thousands of dollars in medical expenses, he said. “It’s not just tummy aches.”
This post has been updated to include the response from CDPH.
Beth is Ars Technica’s Senior Health Reporter. Beth has a Ph.D. in microbiology from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and attended the Science Communication program at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She specializes in covering infectious diseases, public health, and microbes.
“It’s shocking”: Massive raw milk outbreak from 2023 finally reported Read More »