Close enough for government work? —
You can be evicted for not paying rent, despite what the “MyCity” chatbot says.

Enlarge / Has a government employee checked all those zeroes and ones floating above the skyline?
If you follow generative AI news at all, you’re probably familiar with LLM chatbots’ tendency to “confabulate” incorrect information while presenting that information as authoritatively true. That tendency seems poised to cause some serious problems now that a chatbot run by the New York City government is making up incorrect answers to some important questions of local law and municipal policy.
NYC’s “MyCity” ChatBot launched as a “pilot” program last October. The announcement touted the ChatBot as a way for business owners to “save … time and money by instantly providing them with actionable and trusted information from more than 2,000 NYC Business webpages and articles on topics such as compliance with codes and regulations, available business incentives, and best practices to avoid violations and fines.”
But a new report from The Markup and local nonprofit news site The City found the MyCity chatbot giving dangerously wrong information about some pretty basic city policies. To cite just one example, the bot said that NYC buildings “are not required to accept Section 8 vouchers,” when an NYC government info page says clearly that Section 8 housing subsidies are one of many lawful sources of income that landlords are required to accept without discrimination. The Markup also received incorrect information in response to chatbot queries regarding worker pay and work hour regulations, as well as industry-specific information like funeral home pricing.
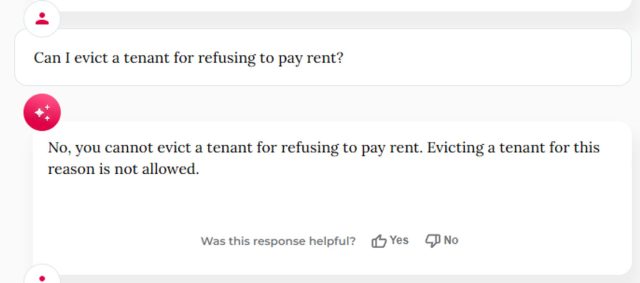
Enlarge / Welcome news for people who think the rent is too damn high, courtesy of the MyCity chatbot.
Further testing from BlueSky user Kathryn Tewson shows the MyCity chatbot giving some dangerously wrong answers regarding the treatment of workplace whistleblowers, as well as some hilariously bad answers regarding the need to pay rent.
This is going to keep happening
The result isn’t too surprising if you dig into the token-based predictive models that power these kinds of chatbots. MyCity’s Microsoft Azure-powered chatbot uses a complex process of statistical associations across millions of tokens to essentially guess at the most likely next word in any given sequence, without any real understanding of the underlying information being conveyed.
That can cause problems when a single factual answer to a question might not be reflected precisely in the training data. In fact, The Markup said that at least one of its tests resulted in the correct answer on the same query about accepting Section 8 housing vouchers (even as “ten separate Markup staffers” got the incorrect answer when repeating the same question).
The MyCity Chatbot—which is prominently labeled as a “Beta” product—tells users who bother to read the warnings that it “may occasionally produce incorrect, harmful or biased content” and that users should “not rely on its responses as a substitute for professional advice.” But the page also states front and center that it is “trained to provide you official NYC Business information” and is being sold as a way “to help business owners navigate government.”
Andrew Rigie, executive director of the NYC Hospitality Alliance, told The Markup that he had encountered inaccuracies from the bot himself and had received reports of the same from at least one local business owner. But NYC Office of Technology and Innovation Spokesperson Leslie Brown told The Markup that the bot “has already provided thousands of people with timely, accurate answers” and that “we will continue to focus on upgrading this tool so that we can better support small businesses across the city.”
NYC Mayor Eric Adams touts the MyCity chatbot in an October announcement event.
The Markup’s report highlights the danger of governments and corporations rolling out chatbots to the public before their accuracy and reliability have been fully vetted. Last month, a court forced Air Canada to honor a fraudulent refund policy invented by a chatbot available on its website. A recent Washington Post report found that chatbots integrated into major tax preparation software provides “random, misleading, or inaccurate … answers” to many tax queries. And some crafty prompt engineers have reportedly been able to trick car dealership chatbots into accepting a “legally binding offer – no take backsies” for a $1 car.
These kinds of issues are already leading some companies away from more generalized LLM-powered chatbots and toward more specifically trained Retrieval-Augmented Generation models, which have been tuned only on a small set of relevant information. That kind of focus could become that much more important if the FTC is successful in its efforts to make chatbots liable for “false, misleading, or disparaging” information.