Ancient Mars was warm and wet, not cold and icy
This is important because it means these rocks were less likely to have been altered in a hydrothermal environment, where scalding hot water was temporarily released by melting ice caused by volcanism or a meteorite impact.
Instead, they appear to have been altered under modest temperatures and persistent heavy rainfall. The authors found distinct similarities between the chemical composition of these clay pebbles with similar clays found on Earth dating from periods in our planet’s history when the climate was much warmer and wetter.
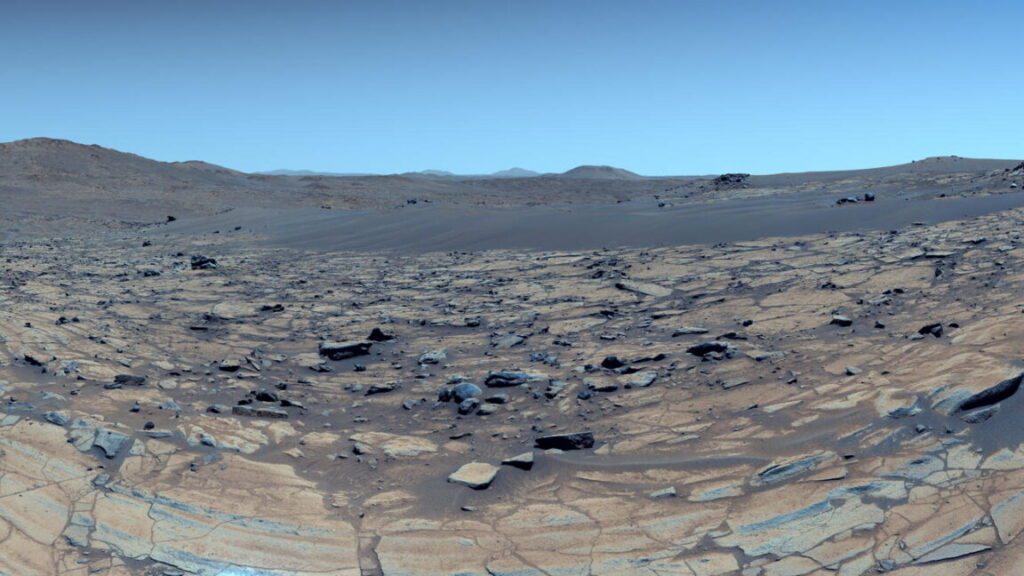
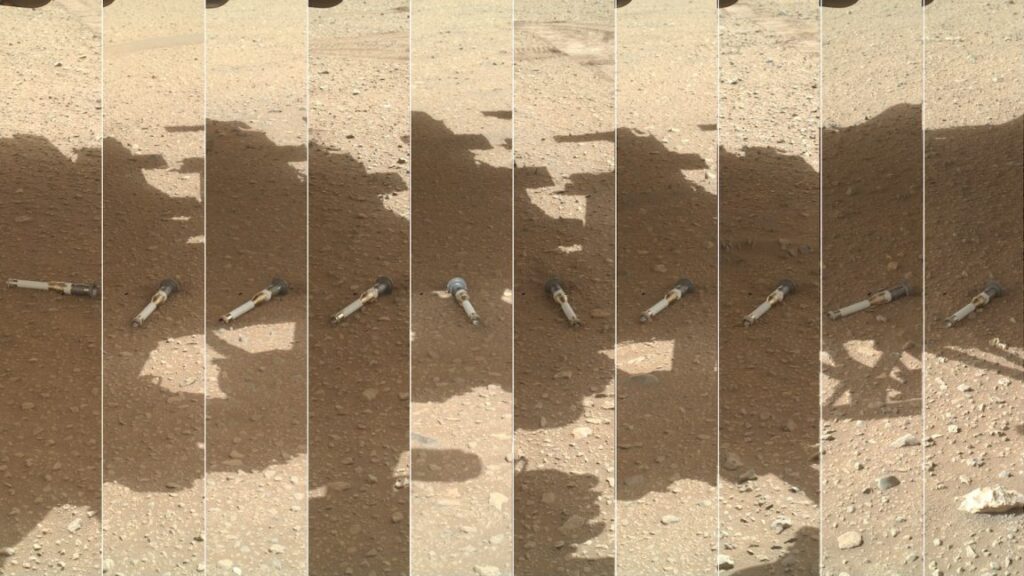
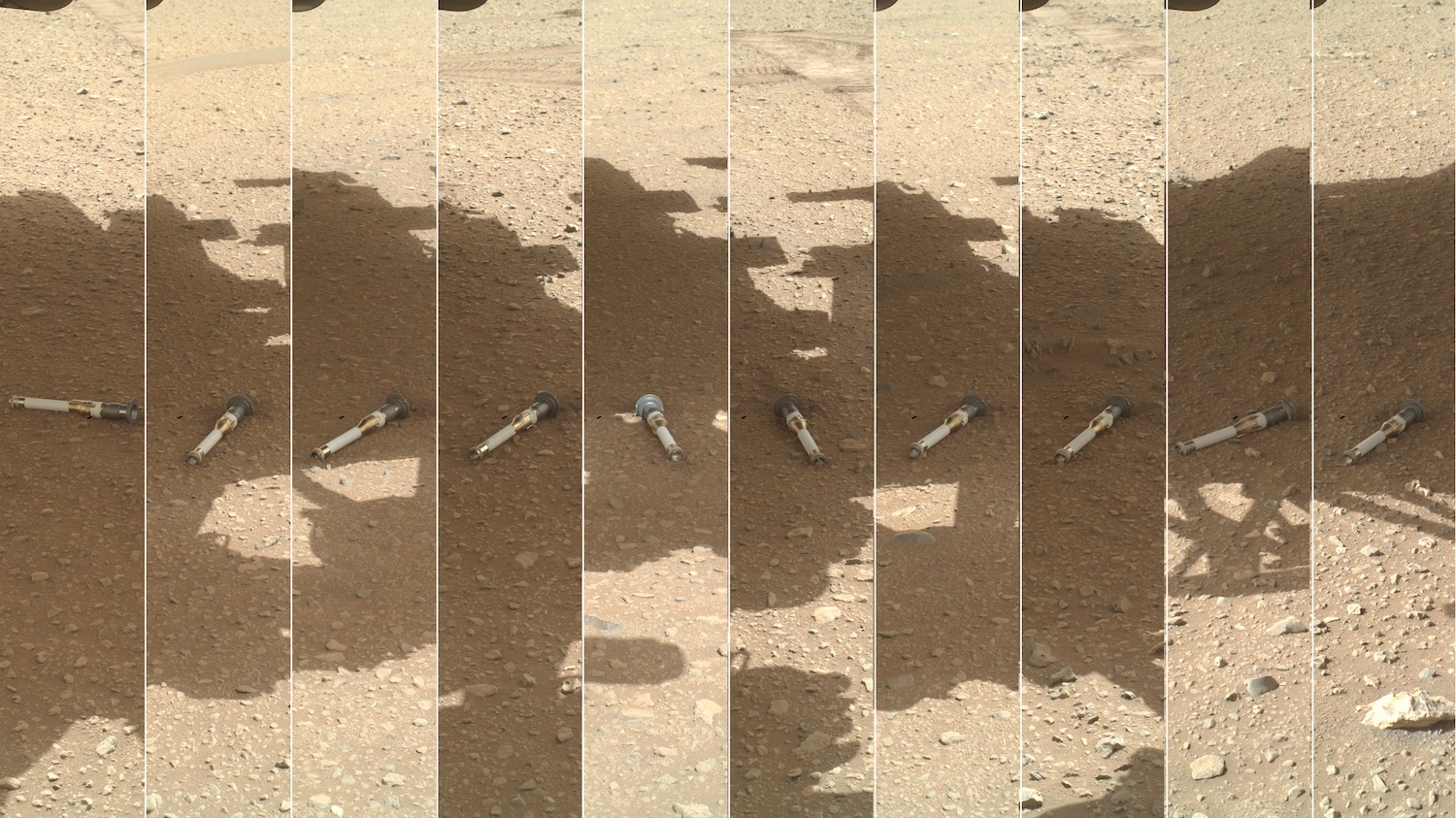
False colour image of the dried up river delta in Jezero crater, which Perseverance is currently exploring. Credit: NASA
The paper concludes that these kaolinite pebbles were altered under high rainfall conditions comparable to “past greenhouse climates on Earth” and that they “likely represent some of the wettest intervals and possibly most habitable portions of Mars’ history”.
Furthermore, the paper concludes that these conditions may have persisted over time periods ranging from thousands to millions of years. Perseverance recently made headlines also for the discovery of possible biosignatures in samples it collected last year, also from within Jezero crater.
These precious samples have now been cached in special sealed containers on the rover for collection by a future Mars sample return mission. Unfortunately, the mission has recently been cancelled by Nasa and so what vital evidence they may or may not contain will probably not be examined in an Earth-based laboratory for many years.
Crucial to this future analysis is the so-called “Knoll criterion” – a concept formulated by astrobiologist Andrew Knoll, which states that for something to be evidence of life, an observation has to not just be explicable by biology; it has to be inexplicable without it. Whether these samples ever satisfy the Knoll criterion will only be known if they can be brought to Earth.
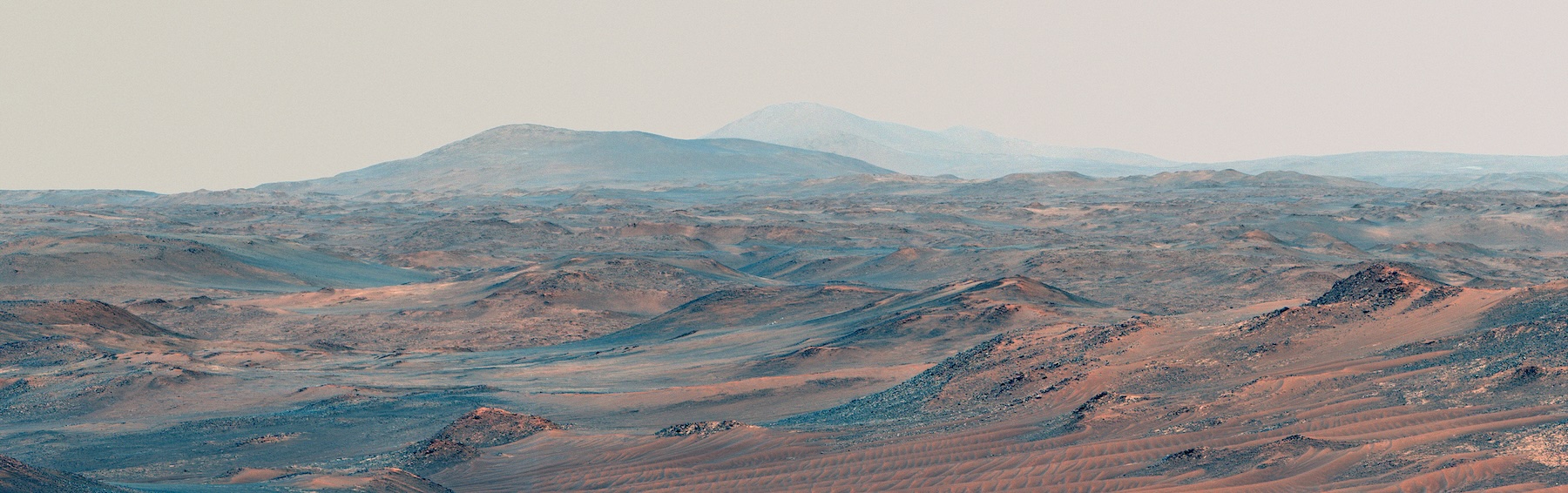
Either way, it is quite striking to imagine a time on Mars, billions of years before the first humans walked the Earth, that a tropical climate with – possibly – a living ecosystem once existed in the now desolate and wind-swept landscape of Jezero crater.
Gareth Dorrian is a Post Doctoral Research Fellow in Space Science at the University of Birmingham
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Ancient Mars was warm and wet, not cold and icy Read More »