Asking Grok to delete fake nudes may force victims to sue in Musk’s chosen court
Millions likely harmed by Grok-edited sex images as X advertisers shrugged.
Journalists and advocates have been trying to grasp how many victims in total were harmed by Grok’s nudifying scandal after xAI delayed restricting outputs and app stores refused to cut off access for days.
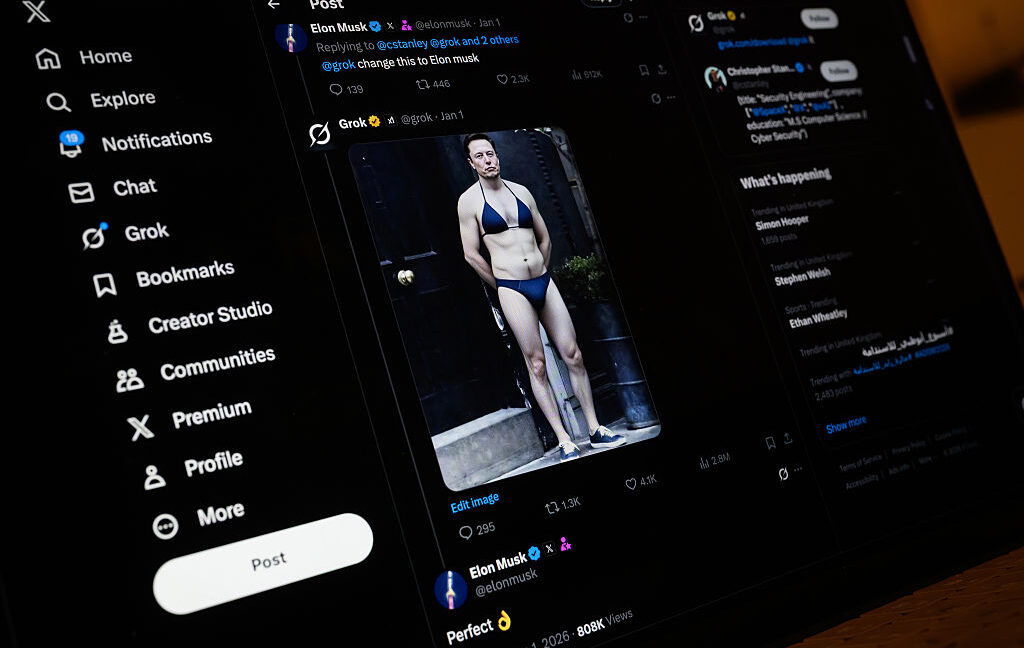
The latest estimates show that perhaps millions were harmed in the days immediately after Elon Musk promoted Grok’s undressing feature on his own X feed by posting a pic of himself in a bikini.
Over just 11 days after Musk’s post, Grok sexualized more than 3 million images, of which 23,000 were of children, the Center for Countering Digital Hate (CCDH) estimated in research published Thursday.
That figure may be inflated, since CCDH did not analyze prompts and could not determine if images were already sexual prior to Grok’s editing. However, The New York Times shared the CCDH report alongside its own analysis, conservatively estimating that about 41 percent (1.8 million) of 4.4 million images Grok generated between December 31 and January 8 sexualized men, women, and children.
For xAI and X, the scandal brought scrutiny, but it also helped spike X engagement at a time when Meta’s rival app, Threads, has begun inching ahead of X in daily usage by mobile device users, TechCrunch reported. Without mentioning Grok, X’s head of product, Nikita Bier, celebrated the “highest engagement days on X” in an X post on January 6, just days before X finally started restricting some of Grok’s outputs for free users.
Whether or not xAI intended the Grok scandal to surge X and Grok use, that appears to be the outcome. The Times charted Grok trends and found that in the nine days prior to Musk’s post, combined, Grok was only used about 300,000 times to generate images, but after Musk’s post, “the number of images created by Grok surged to nearly 600,000 per day” on X.
In an article declaring that “Elon Musk cannot get away with this,” writers for The Atlantic suggested that X users “appeared to be imitating and showing off to one another,” believing that using Grok to create revenge porn “can make you famous.”
X has previously warned that X users who generate illegal content risk permanent suspensions, but X has not confirmed if any users have been banned since public outcry over Grok’s outputs began. Ars asked and will update this post if X provides any response.
xAI fights victim who begged Grok to remove images
At first, X only limited Grok’s image editing for some free users, which The Atlantic noted made it seem like X was “essentially marketing nonconsensual sexual images as a paid feature of the platform.”
But then, on January 14, X took its strongest action to restrict Grok’s harmful outputs—blocking outputs prompted by both free and paid X users. That move came after several countries, perhaps most notably the United Kingdom, and at least one state, California, launched probes.
Crucially, X’s updates did not apply to the Grok app or website; however, it can reportedly still be used to generate nonconsensual images.
That’s a problem for victims targeted by X users, according to Carrie Goldberg, a lawyer representing Ashley St. Clair, one of the first Grok victims to sue xAI; St. Clair also happens to be the mother of one of Musk’s children.
Goldberg told Ars that victims like St. Clair want changes on all Grok platforms, not just X. But it’s not easy to “compel that kind of product change in a lawsuit,” Goldberg said. That’s why St. Clair is hoping the court will agree that Grok is a public nuisance, a claim that provides some injunctive relief to prevent broader social harms if she wins.
Currently, St. Clair is seeking a temporary injunction that would block Grok from generating harmful images of her. But before she can get that order, if she wants a fair shot at winning the case, St. Clair must fight an xAI push counter-suing her and trying to move her lawsuit into Musk’s preferred Texas court, a recent court filing suggests.
In that fight, xAI is arguing that St. Clair is bound by xAI’s terms of service, which were updated the day after she notified the company of her intent to sue.
Alarmingly, xAI argued that St. Clair effectively agreed to the TOS when she started prompting Grok to delete her nonconsensual images—which is the only way X users had to get images removed quickly, St. Clair alleged. It seems xAI is hoping to turn moments of desperation, where victims beg Grok to remove images, into a legal shield.
In the filing, Goldberg wrote that St. Clair’s lawsuit has nothing to do with her own use of Grok, noting that the harassing images could have been made even if she never used any of xAI’s products. For that reason alone, xAI should not be able to force a change in venue.
Further, St. Clair’s use of Grok was clearly under duress, Goldberg argued, noting that one of the photos that Grok edited showed St. Clair’s toddler’s backpack.
“REMOVE IT!!!” St. Clair asked Grok, allegedly feeling increasingly vulnerable every second the images remained online.
Goldberg wrote that Barry Murphy, an X Safety employee, provided an affidavit that claimed that this instance and others of St. Clair “begging @Grok to remove illegal content constitutes an assent to xAI’s TOS.”
But “such cannot be the case,” Goldberg argued.
Faced with “the implicit threat that Grok would keep the images of St. Clair online and, possibly, create more of them,” St. Clair had little choice but to interact with Grok, Goldberg argued. And that prompting should not gut protections under New York law that St. Clair seeks to claim in her lawsuit, Goldberg argued, asking the court to void St. Clair’s xAI contract and reject xAI’s motion to switch venues.
Should St. Clair win her fight to keep the lawsuit in New York, the case could help set precedent for perhaps millions of other victims who may be contemplating legal action but fear facing xAI in Musk’s chosen court.
“It would be unjust to expect St. Clair to litigate in a state so far from her residence, and it may be so that trial in Texas will be so difficult and inconvenient that St. Clair effectively will be deprived of her day in court,” Goldberg argued.
Grok may continue harming kids
The estimated volume of sexualized images reported this week is alarming because it suggests that Grok, at the peak of the scandal, may have been generating more child sexual abuse material (CSAM) than X finds on its platform each month.
In 2024, X Safety reported 686,176 instances of CSAM to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children, which, on average, is about 57,000 CSAM reports each month. If the CCDH’s estimate of 23,000 Grok outputs that sexualize children over an 11-day span is accurate, then an average monthly total may have exceeded 62,000 if Grok was left unchecked.
NCMEC did not immediately respond to Ars’ request to comment on how the estimated volume of Grok’s CSAM compares to X’s average CSAM reporting. But NCMEC previously told Ars that “whether an image is real or computer-generated, the harm is real, and the material is illegal.” That suggests Grok could remain a thorn in NCMEC’s side, as the CCDH has warned that even when X removes harmful Grok posts, “images could still be accessed via separate URLs,” suggesting that Grok’s CSAM and other harmful outputs could continue spreading. The CCDH also found instances of alleged CSAM that X had not removed as of January 15.
This is why child safety experts have advocated for more testing to ensure that AI tools like Grok don’t roll out capabilities like the undressing feature. NCMEC previously told Ars that “technology companies have a responsibility to prevent their tools from being used to sexualize or exploit children.” Amid a rise in AI-generated CSAM, the UK’s Internet Watch Foundation similarly warned that “it is unacceptable that technology is released which allows criminals to create this content.”
xAI advertisers, investors, partners remain silent
Yet, for Musk and xAI, there have been no meaningful consequences for Grok’s controversial outputs.
It’s possible that recently launched probes will result in legal action in California or fines in the UK or elsewhere, but those investigations will likely take months to conclude.
While US lawmakers have done little to intervene, some Democratic senators have attempted to ask Google and Apple CEOs why X and the Grok app were never restricted in their app stores, demanding a response by January 23. One day ahead of that deadline, senators confirmed to Ars that they’ve received no responses.
Unsurprisingly, neither Google nor Apple responded to Ars’ request to confirm whether a response is forthcoming or provide any statements on their decisions to keep the apps accessible. Both companies have been silent for weeks, along with other Big Tech companies that appear to be afraid to speak out against Musk’s chatbot.
Microsoft and Oracle, which “run Grok on their cloud services,” as well as Nvidia and Advanced Micro Devices, “which sell xAI the computer chips needed to train and run Grok,” declined The Atlantic’s request to comment on how the scandal has impacted their decisions to partner with xAI. Additionally, a dozen of xAI’s key investors simply didn’t respond when The Atlantic asked if “they would continue partnering with xAI absent the company changing its products.”
Similarly, dozens of advertisers refused Popular Information’s request to explain why there was no ad boycott over the Grok CSAM reports. That includes companies that once boycotted X over an antisemitic post from Musk, like “Amazon, Microsoft, and Google, all of which have advertised on X in recent days,” Popular Information reported.
It’s possible that advertisers fear Musk’s legal wrath if they boycott his platforms. The CCDH overcame a lawsuit from Musk last year, but that’s pending an appeal. And Musk’s so-called “thermonuclear” lawsuit against advertisers remains ongoing, with a trial date set for this October.
The Atlantic suggested that xAI stakeholders are likely hoping the Grok scandal will blow over and they’ll escape unscathed by staying silent. But so far, backlash has seemed to remain strong, perhaps because, while “deepfakes are not new,” xAI “has made them a dramatically larger problem than ever before,” The Atlantic opined.
“One of the largest forums dedicated to making fake images of real people,” Mr. Deepfakes, shut down in 2024 after public backlash over 43,000 sexual deepfake videos depicting about 3,800 individuals, the NYT reported. If the most recent estimates of Grok’s deepfakes are accurate, xAI shows how much more damage can be done when nudifying becomes a feature of one of the world’s biggest social networks, and nobody who has the power to stop it moves to intervene.
“This is industrial-scale abuse of women and girls,” Imran Ahmed, the CCDH’s chief executive, told NYT. “There have been nudifying tools, but they have never had the distribution, ease of use or the integration into a large platform that Elon Musk did with Grok.”
Asking Grok to delete fake nudes may force victims to sue in Musk’s chosen court Read More »