More bad news for psychedelic drug company: FDA expands probe after rejection
trippy trip up —
Psychedelic drug company Lykos already slashed staff and overhauled leadership.
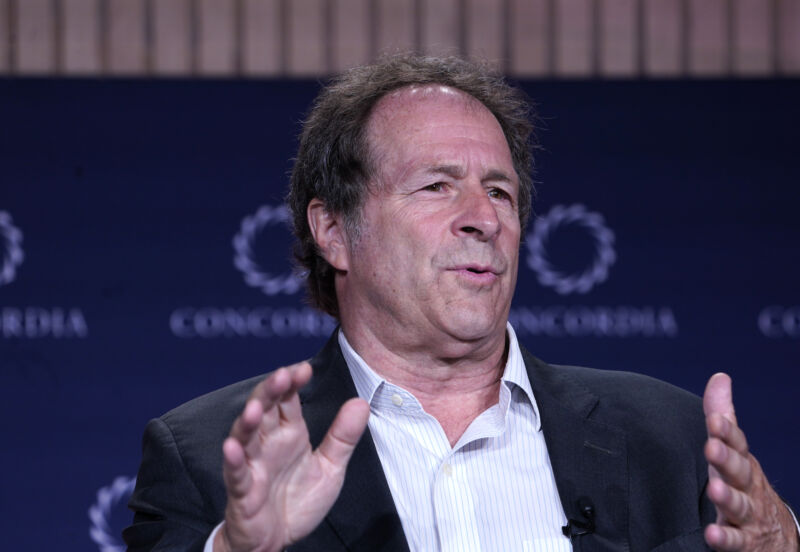

Enlarge / President of Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) Rick Doblin speaks onstage during the 2023 Concordia Annual Summit at Sheraton New York on September 18, 2023, in New York City.
There’s more bad news for the company behind an experimental MDMA therapy for post-traumatic stress disorder, which the Food and Drug Administration roundly rejected earlier this month.
According to a report from The Wall Street Journal, the FDA is now expanding an investigation into clinical trials behind the experimental psychedelic therapy—even though the agency has already rejected it. Agency investigators reportedly interviewed four additional people last week, asking questions regarding whether the trials underreported side effects.
People involved in the trial have previously alleged, among other things, that ill effects, such as suicidal thoughts, went undocumented, and trial participants were discouraged from reporting them to bolster the chances of FDA approval. Overall, the MDMA trials faced crushing criticism amid the FDA’s review, with outside experts and agency advisors calling out allegations of sexual misconduct at one trial site, as well as flaws in overall trial designs, multiple sources of biases, and claims of that the company behind the therapy, Lykos, fostered a cult-like belief in psychedelics.
According to the Journal, the recent interviews were being conducted by the FDA’s Office of Regulatory Affairs, which oversees inspections, and a subdivision of that office called Biomedical Research Monitoring Program, which works to ensure the quality and integrity of data submitted to FDA. Notably, when the agency rejected MDMA, it advised Lykos to conduct a new trial.
While the FDA’s rejection and expanded investigation are bad enough for Lykos, the company announced this month that it’s laying off 75 percent of its staff and overhauling its leadership. The moves were in response to the FDA’s rejections, the company said. Additionally, a scientific journal retracted three of the company’s MDMA studies, citing “protocol violations amounting to unethical conduct” in its trials, echoing claims raised amid the FDA review.
Troubling roots
Underpinning the allegations and criticisms against Lykos is its roots in drug advocacy. Lykos is a commercial spinoff of the psychedelic advocacy nonprofit Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS). For decades, MAPS has worked to legalize psychedelics and research their use as potential treatments, particularly mental health conditions, including PTSD, anxiety, and substance use disorders. MAPS was founded by Rick Doblin, a longtime psychedelic activist and advocate who openly believes the use of psychedelics will lead to world peace. Amid the leadership overhaul this month, Doblin left his position on Lykos’ board.
“After 38 plus years of work, I’m profoundly saddened by the FDA decision around this critically needed therapy, but am heartened that Lykos will still move forward continuing clinical research that addresses the FDA’s questions,” Doblin said in a statement. “I can speak more freely as a public advocate by resigning from the Lykos Board. The FDA delays make it more important than ever that I work at MAPS toward developing global legal access to MDMA and other psychedelics for public benefit through MAPS’ multidisciplinary research, education, and drug policy reform.”
Lykos did not immediately respond to Ars’ request for comment on the FDA’s investigation. In a response to the Journal, a company spokesperson said that “Lykos is committed to engaging with the FDA and addressing any questions it raises.” The spokesperson also noted that the company is planning to meet with the FDA about the rejection, which it is appealing.
But, trial participants and outsiders have levied heavy criticism against the company that will likely be hard to move beyond.
“The prospect of a therapy cult guiding a suggestibility-enhancing drug through clinical trials highlights unique risks that have never been publicly discussed,” Neşe Devenot, a Johns Hopkins University senior lecturer in the university’s writing program who focuses on the issue of drugs in society, said in public comments prior to the FDA rejection. “The trials should be scrutinized as if Scientology or NXIVM had submitted a new drug application to the FDA.”
Those public comments appeared in a damning report from Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which concluded that there was insufficient evidence to back MDMA-based therapy. According to the Journal report, Devenot was among the people interviewed by FDA investigators recently.
Lykos’ saga has been a blow to the psychedelic community in general and to many patients, particularly veterans, who have reported benefits from using MDMA to treat PTSD, a condition in desperate need of effective treatments.
Amid Lykos’ troubles, the company has brought in David Hough as senior medical advisor to oversee clinical and regulatory work. Hough is a former vice president at Johnson & Johnson, where he notably helped develop Spravato—esketamine—a compound related to ketamine that was approved for use against treatment-resistant depression in 2019.
More bad news for psychedelic drug company: FDA expands probe after rejection Read More »