NASA officials sidestepped questions on Artemis II risks—there’s a reason why
“This ought to make for some good reading,” NASA’s mission management team chair said.
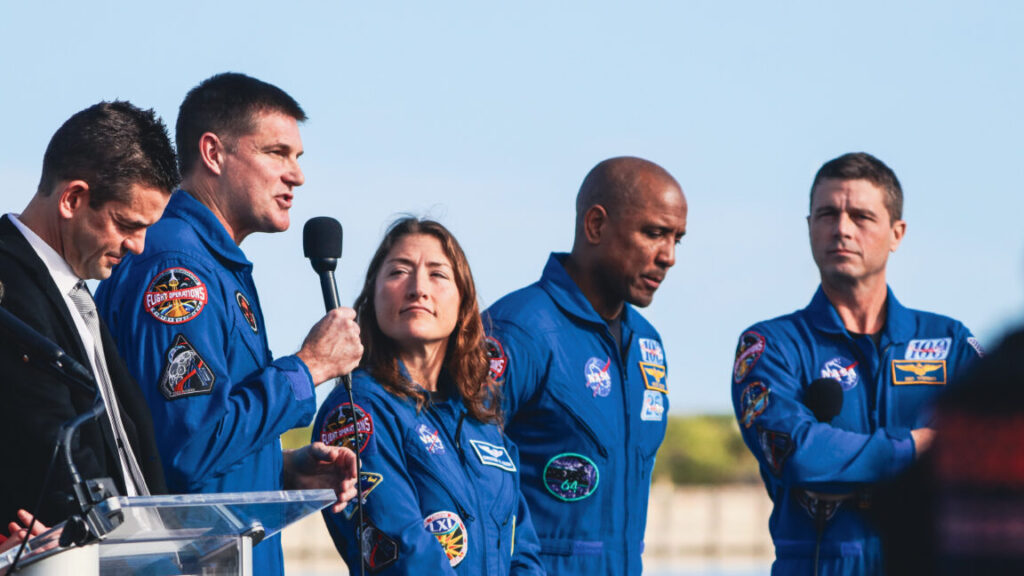
NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman joins the Artemis II crew for a press conference at Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on January 17, 2026. Credit: Stephen Clark/Ars Technica
When talking about risk during a press conference on Thursday, the NASA officials in charge of the upcoming Artemis II Moon mission hedged their answers.
Reporters’ questions on the risks were certainly valid and appropriate. In an open society, it is vital to set expectations for any hazardous venture such as spaceflight—most importantly for the astronauts actually making the journey, but also for NASA’s workforce, the White House, lawmakers, and members of the public paying for the endeavor.
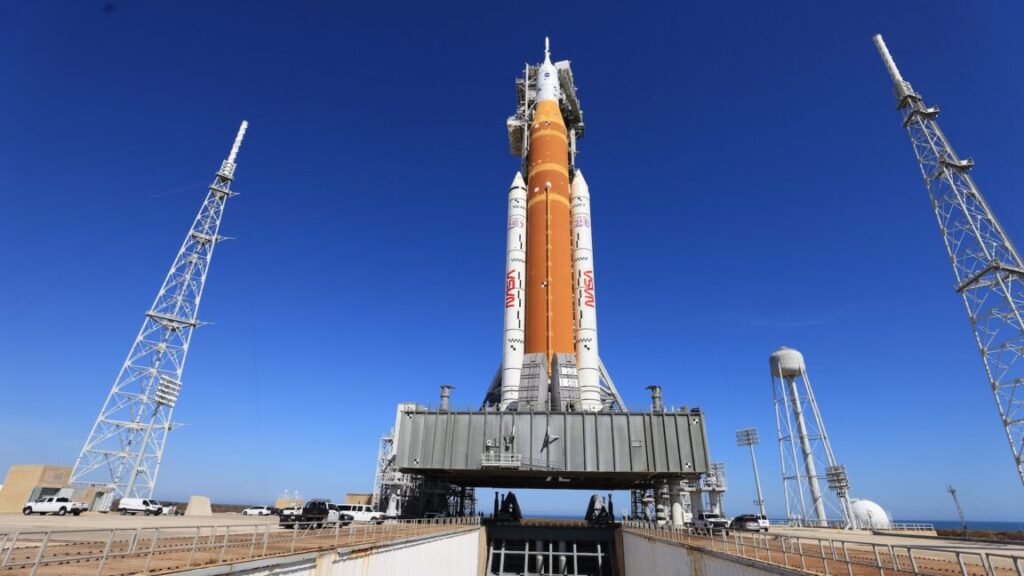
What’s more, Artemis II will be the first mission since 1972 to fly humans to the vicinity of the Moon. This is not following the well-trodden yet perilous path that astronauts take to reach the International Space Station, just a few hundred miles above Earth.
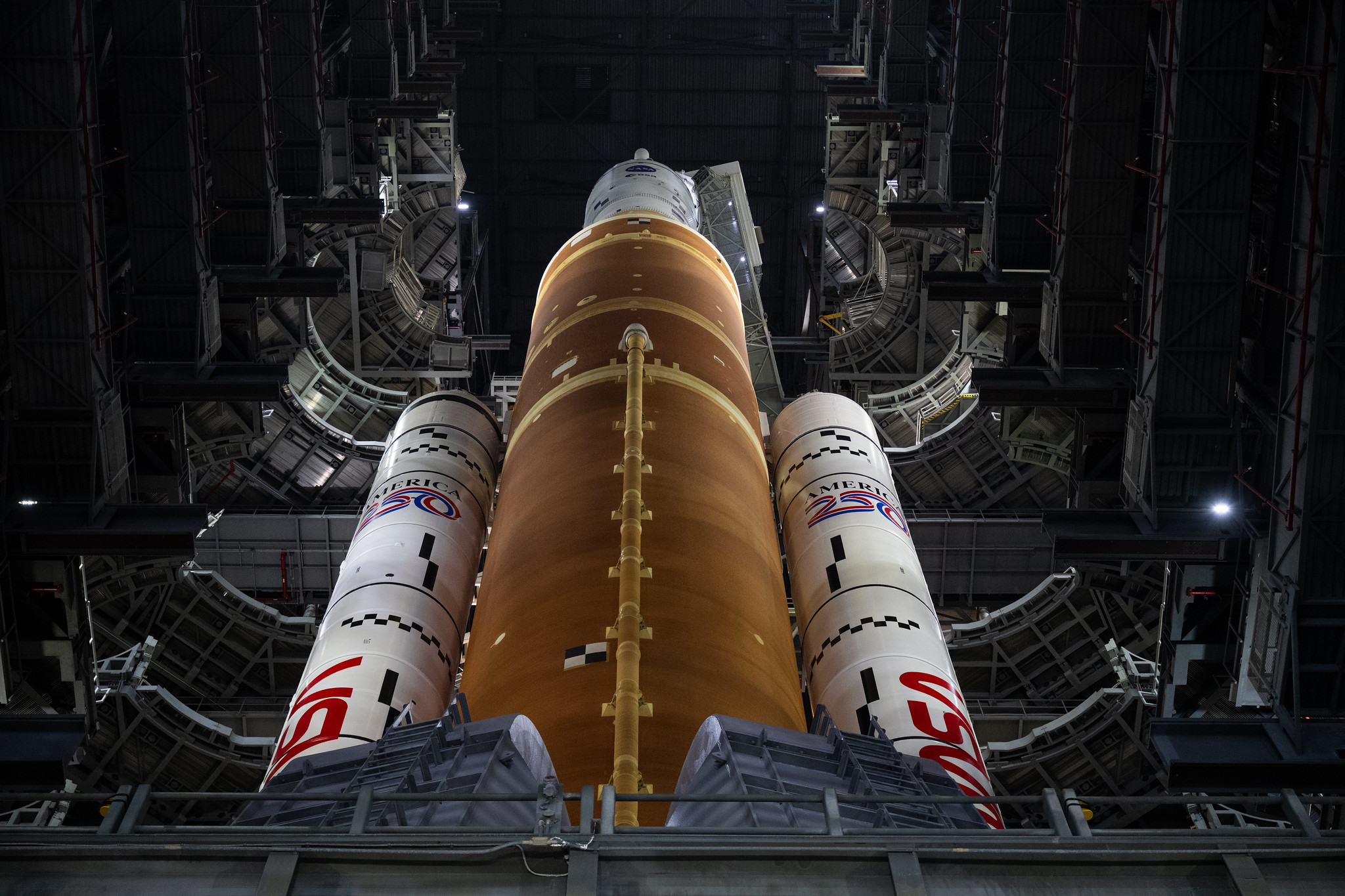
Artemis II will travel more than 1,000 times farther from Earth than the ISS, departing on a trajectory taking the mission several thousand miles beyond the far side of the Moon. The mission will last nine days from liftoff in Florida to splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The four-person crew will ride a rocket and spacecraft—the Space Launch System and Orion—that have flown together just once before. The sheer novelty of the mission makes it difficult to quantify the risk, NASA officials said Thursday.
Load and go
With just a single data point from flight testing—the unpiloted Artemis I demo mission in 2022—NASA managers were reluctant to publicize the bottom-line number from the probabilistic risk assessment for Artemis II.
Lori Glaze, NASA’s acting associate administrator for exploration system development, said the agency completed an assessment for Artemis II, but questioned the exercise’s usefulness.
“I think sometimes we get tricked into believing that those numbers are somehow really telling us something critically important,” Glaze said. “I think they’re valuable. I think we can do things in a relative sense to measure what’s more risky or less risky.”
Glaze and other members of the Artemis II management team were speaking with reporters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center following a flight readiness review. The two-day conclave in Florida provided the forum for a “very open” and “transparent” discussion of NASA’s “risk posture” heading into the Artemis II launch, and “how we’re mitigating those risks,” Glaze said.
The decision-makers present for the meeting unanimously agreed to continue final preparations for the Artemis II mission, now scheduled for liftoff no earlier than April 1 at 6: 24 pm EDT (22: 24 UTC). “It is a test flight, and it is not without risk, but our team and our hardware are ready,” Glaze said.
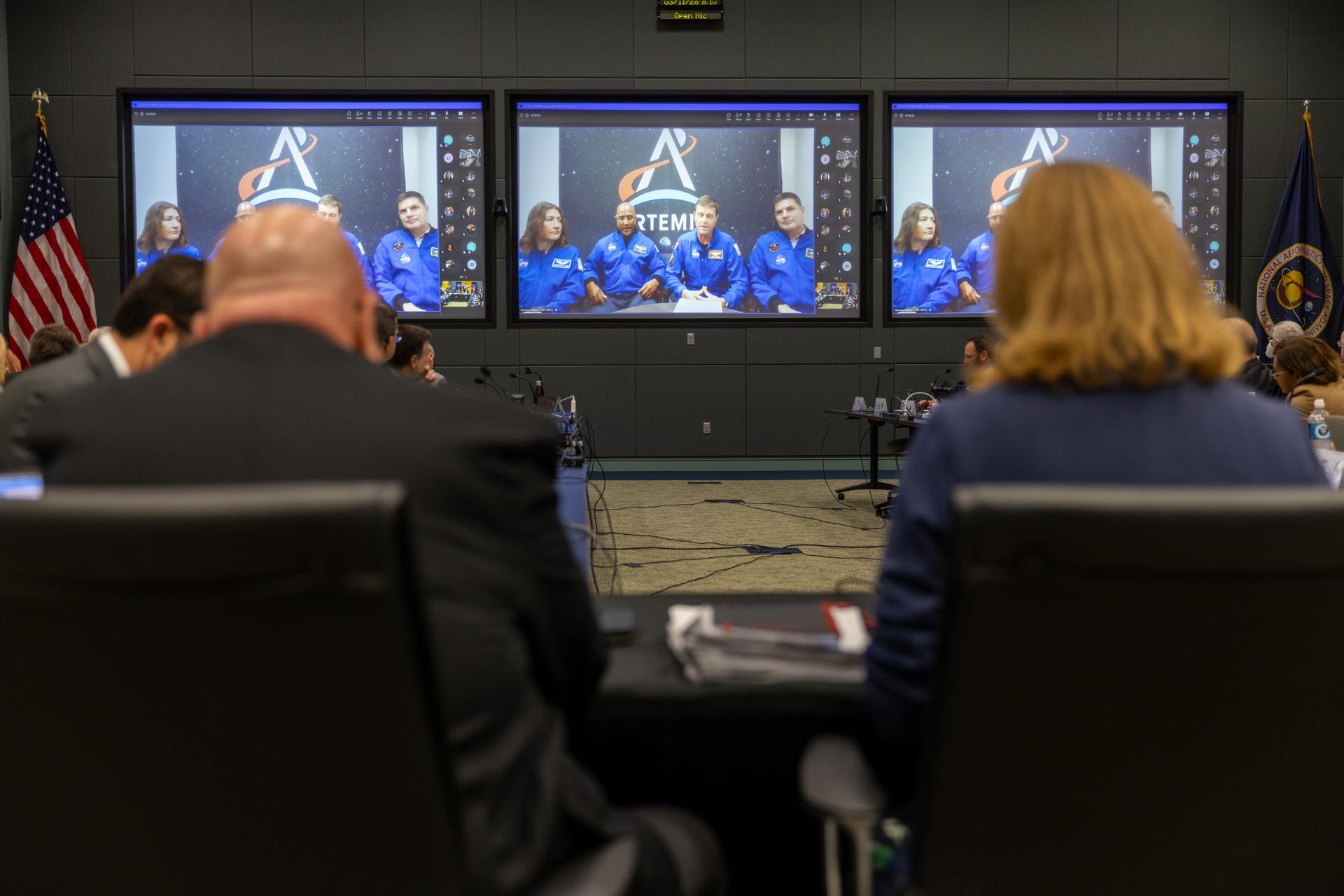
The four astronauts training to fly on Artemis II joined the Flight Readiness Review (FRR) virtually from their home base in Houston. Their participation included discussion of the Orion spacecraft’s heat shield and reentry trajectory, a topic that prompted additional review from NASA leadership after Jared Isaacman took the helm as the agency’s administrator last year.
Super-telephoto view of the Orion spacecraft’s heat shield tiles. Credit: Trevor Mahlmann
“The question was, ‘Are we going to be able to hit that entry interface and get them back on Earth safely,’” Glaze said of the crew’s comments during the FRR. “They were listening to make sure that we have that really nailed down, and we’ll be able to hit that entry interface. Understanding communication challenges and making sure that they’ll be able to maintain communication with Earth. That’s one of the things. They were looking at those risks. The environmental control and life support systems, power systems, things like that, the things that could cause challenges to them while they’re in flight.”
The Artemis II launch was supposed to take place in early February, but engineers ran into problems with a leaky hydrogen seal in the SLS rocket’s fueling line, followed by an issue loading helium into the rocket’s upper stage. The latter problem forced NASA to return the rocket to the hangar for repairs. It will return to the launch pad next week.
Mission managers have opted not to put the rocket through another fueling test. Before rolling the rocket off the launch pad last month, the launch team completed a successful countdown rehearsal that showed fresh hydrogen seals were leak-tight. “At this point, we’ve demonstrated that the seals that we have are the best seals that we’ve ever seen on the SLS,” Glaze said. “The next time we tank the vehicle will be when we’re attempting to launch.”
NASA has six launch opportunities in early April—officials just added April 2 to the list of possible launch dates—or else will have to wait until the end of April for the next series of launch attempts.
Are the numbers trash?
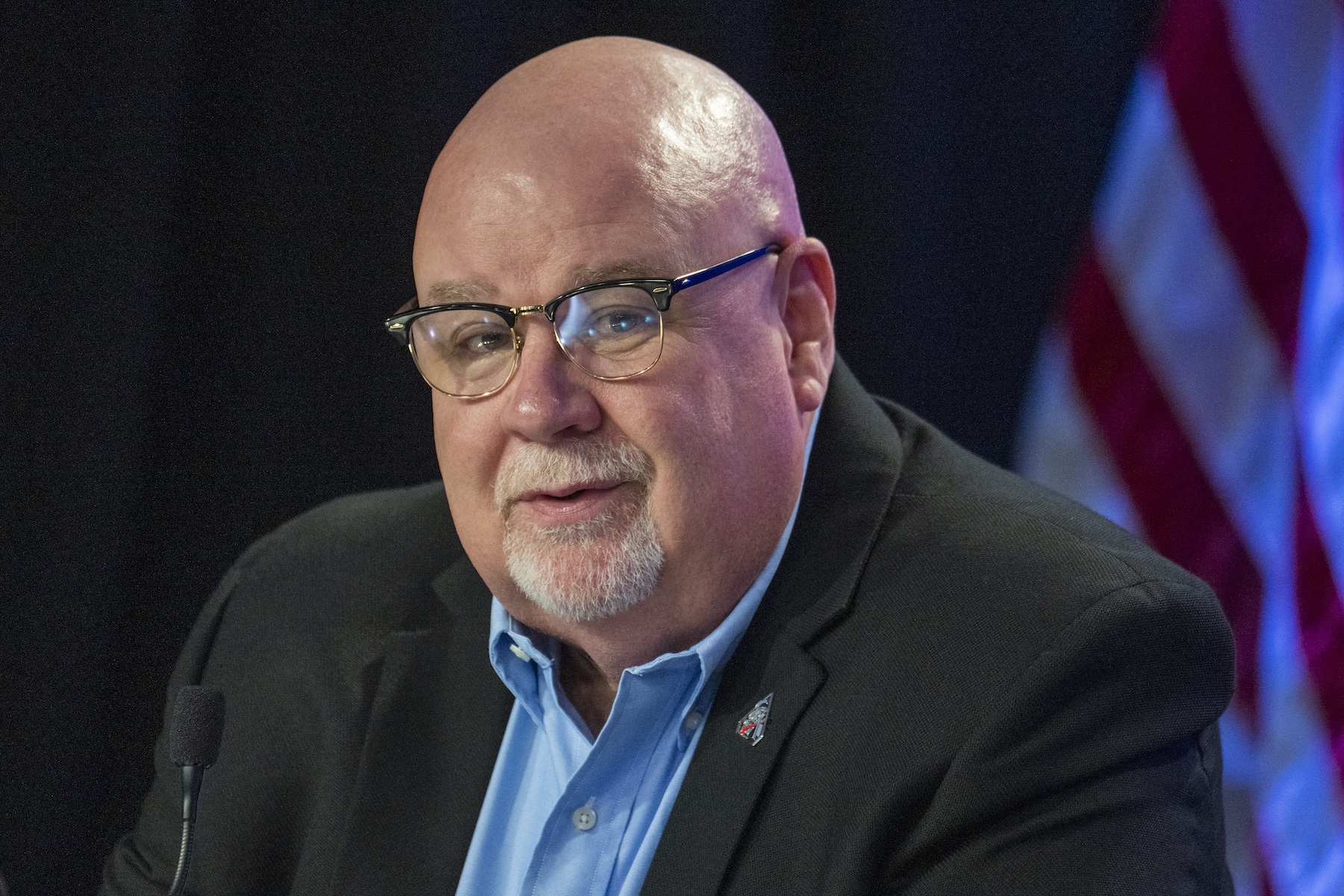
John Honeycutt, chair of the Artemis II mission management team, discussed the mission’s risk uncertainties in an uncharacteristically blunt fashion for a NASA official.
NASA wants to avoid succumbing to a failure of imagination, a term invoked by astronaut Frank Borman after the fatal fire inside the Apollo 1 spacecraft on its launch pad in 1967. “We use that term a lot in human spaceflight,” Honeycutt said. “We want to be sure that we’re thinking about everything that can possibly go wrong, and have we assessed and adjudicated all the risk to put us in the best posture to be successful.”
So, what is the risk of a catastrophic accident on Artemis II? Honeycutt said NASA has “grappled” with the risk probability for some time. “What I would say is we understand the risk associated with the individual components, the subsystems, and then the overall systems.”
Statistically, Honeycutt said, about half of all rockets fail on their first flights. This is essentially true, with the global success rate for new types of orbital-class rockets somewhere between 50 and 60 percent over the last decade, depending on what exactly qualifies as a new launch vehicle. The SLS rocket performed marvelously after clearing the launch pad on Artemis I.
John Honeycutt, chair of NASA’s Mission Management Team for the Artemis II mission, speaks during a news conference at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on January 16, 2026. Credit: Jim Watson/AFP via Getty Images
Honeycutt, who managed the SLS program before taking over the Artemis mission management team, said he and Glaze want to bring the probability of a failure on an Artemis flight below 1 in 50. Achieving a 2 percent failure rate would assume NASA was “really getting after it and staying on a good cadence,” Honeycutt said. (NASA’s inspector general, in a report released earlier this week, wrote that the agency’s “loss of crew threshold” is 1 in 30 for Artemis missions overall. A NASA spokesperson said Thursday the agency would release more context on the risk assessment, but did not provide additional information by press time.)
The lull between Artemis missions comes with its own risks. Taking so much time—nearly three-and-a-half years—between flights doesn’t improve safety. This is apparent to Isaacman, who announced last month a program shake-up to fly the next mission—Artemis III—next year to low-Earth orbit to demonstrate docking with a commercial lunar lander in low-Earth orbit. Under the previous plan, Artemis III would have gone all the way to the Moon. The audacity of such a mission, wrapping so many untried things into a single flight, meant Artemis III would not have launched for at least two more years, and probably more like three, four, or more.
Now, Artemis IV is in line to attempt the program’s first human landing at the Moon’s south pole. Isaacman hopes to launch Artemis IV in 2028, but the schedule hinges on near-flawless execution on Artemis II, Artemis III, and speeding up the availability of human-rated Moon landers undergoing development by SpaceX and Blue Origin.
Long breaks between launches are “not a recipe for success,” Isaacman said last month. Honeycutt said Artemis II’s risk assessment falls short of the 1-in-50 goal.
“On the second or third time, with this gap that we’ve got, it’s probably not even 1 in 50,” Honeycutt said of Artemis II. “It’s probably not 1 in 2 … but it’s probably closer to 1 in 2. That basically means we’re probably not 1 in 50 on the mission exactly like we want it to be, but we’re probably not 1 in 2 like we were on the first flight.
“I think we’re being really careful not to really lay probabilistic numbers on the table for this mission, just given the small amount of data.” Honeycutt continued with an uninhibited appraisal of NASA’s ability to quantify risk.
“It’s interesting that I didn’t get this question asked of me too much on Artemis I, and I understand why,” he said. “We’ve got people on the rocket this time, so people go, ‘Oh, shit’ … I know we have pursued loss of mission, loss of crew type number assessments, but I’m not sure we understand what they mean, in reality.”
Honeycutt used the danger of falling foam on the space shuttle as an example. This is what led to the destruction of the space shuttle Columbia on reentry in 2003, killing seven astronauts at the end of a research mission in low-Earth orbit. The failure was precipitated by an event during launch 16 days earlier.
In order to correctly assess the risk of foam loss, NASA would have had to not only calculate the probability of foam falling from the shuttle’s external fuel tank, but also all the other variables that could lead to a catastrophic failure. “It’s got to be in the right place, and then you’ve got to work the demise chain,” Honeycutt said. “What’s it going to hit? What if it does hit that? What can it do? If you work through all that from a technical standpoint, you can put yourself in a better place rather than just solely relying on a probabilistic number.”
The loss of mission and loss of crew assessments are not the same. Unlike the shuttle, the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft have a Launch Abort System, giving the astronauts the ability to escape a rocket failure during ascent into space.
The Artemis II crew virtually joined the flight readiness review held at Kennedy Space Center this week. Credit: NASA/Amber Jean Notvest
Facing reality
The way NASA is assessing and communicating risk for Artemis II sharply contrasts with how the agency formulated and discussed risk assessments for several recent notable missions.
On Artemis I, NASA assessed there was a 1-in-125 probability that the Orion spacecraft could be lost in flight, an estimate that far exceeds Honeycutt’s evaluation of statistical risk. Before Artemis I’s launch in 2022, NASA said the probability took into account known failure modes, redundancy in the rocket and the spacecraft, and “common cause failures” that might take out multiple systems in flight.
The top risk for Artemis I was the potential for collisions with small pieces of space junk or tiny naturally occurring fragments of asteroids or comets. The catch-all term for this material is micrometeoroids and orbital debris (MMOD). NASA officials also cited risks with avionics and software on the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft’s heat shield propulsion system.
Honeycutt and Glaze are not the first NASA officials to question the validity of probabilistic risk assessments, which rely on numerical and statistical inputs, many of which are grounded in assumptions, especially for flights early in a program.
Bill Gerstenmaier, the former longtime chief of NASA’s human spaceflight programs and now a SpaceX vice president, has cited the agency’s erroneous risk assessment ahead of the first space shuttle flight in 1981. Engineers estimated a 1-in-500 to 1-in-5,000 chance of losing the crew on that mission. In retrospect, the first shuttle flight actually had a 1-in-10 to 1-in-12 chance of killing the crew. The odds of crew loss for each Apollo mission were about the same. By the end of the shuttle program, after two fatal disasters, NASA calculated that the risk of losing the crew on any single mission was about 1 in 90.
NASA assessed 1-in-276 odds for loss of crew on the first flight of astronauts aboard SpaceX’s Crew Dragon in 2020. For Boeing’s Starliner in 2024, the probability was 1 in 295. You wouldn’t be wrong to question those numbers given the proven performance of Dragon and Starliner.
This chart from NASA’s Office of Safety and Mission Assurance describes the agency’s process for conducting probabilistic risk assessments. Credit: NASA
So, what do the Artemis II astronauts make of all this?
The mission’s commander, Reid Wiseman, said the crew members were trying to prepare their families “honestly and openly” for the hazards of a circumlunar flight.
“I went on a walk with my kids, and I told them, ‘Here’s where the will is, here’s where the trust documents are, and if anything happens to me, here’s what’s going to happen to you,’” Wiseman said. “That is a part of this life. I actually wish more people in everyday life talked to their families that way because you never know what the next day is going to bring.”
Any sailor knows you can’t stay in the harbor forever. Test pilots and astronauts take calculated risks for a living.
“When you see numbers like Mach 39 at entry, when you see numbers like 38,000 miles, 250,000 miles, and 5 or 6 million pounds on the pad, those are just insane numbers,” Wiseman said. “These numbers, you don’t even comprehend. There’s risk in that. We don’t know what we don’t know right now, so we’ll go learn all that [on the mission].
Despite the unknowns, Wiseman is ready: “For me, I actually feel completely 100 percent bought in. When I get into Orion, it’s like climbing into my bed, and I’ll feel warm and tucked in.”
The formal risk matrix for Artemis II is similar to that of Artemis I, with MMOD again at the top of the list. Matt Ramsey, NASA’s Artemis II mission manager, told Ars in January that the Orion spacecraft’s environmental control and life support system, which didn’t fly with its full capability on Artemis I, is the second-highest risk for Artemis II. “Those two are my biggest worries,” said Ramsey, who has been with NASA since 2002.
Honeycutt, a 36-year NASA veteran, has a different view.
“When have the last two events occurred?” Honeycutt said, referring to the root causes of NASA’s Challenger and Columbia shuttle disasters. “Going uphill, in that highly energetic event, that’s when it occurred. We can fool ourselves sometimes into thinking, ‘Really, is that the biggest risk to the mission, MMOD?’
“When we’ve got the most dynamic activities going on, like during ascent, when we’re doing those burns, doing the perigee raise, and then we’re doing the TLI (Trans-Lunar Injection) burn, those are going to be the times that we’re introducing the most risk into the whole mission,” Honeycutt said. “There’s a lot of time where we’re steady state, and we’re going to be feeling pretty good about what’s going on in the mission.”
Ramsey’s role as mission manager will transition to Honeycutt two days before launch. The Launch Abort System reduces the risk of a rocket failure harming the crew, Ramsey said. “That mitigates a lot of the ascent risk,” he said. “Certainly, the entry, descent, landing is risky. You’ve got to get the parachutes out and that sort of thing.”
“At the end of the day, we want to accomplish as many goals as we’ve laid out for ourselves in the mission,” Honeycutt said. “But the main thing that I want to do is I want to hit that damn entry interface right down the middle and make sure that I’m bringing the crew home safely.”
NASA officials sidestepped questions on Artemis II risks—there’s a reason why Read More »