Intel Arc B580 review: A $249 RTX 4060 killer, one-and-a-half years later
Intel has solved the biggest problems with its Arc GPUs, but not the timing.
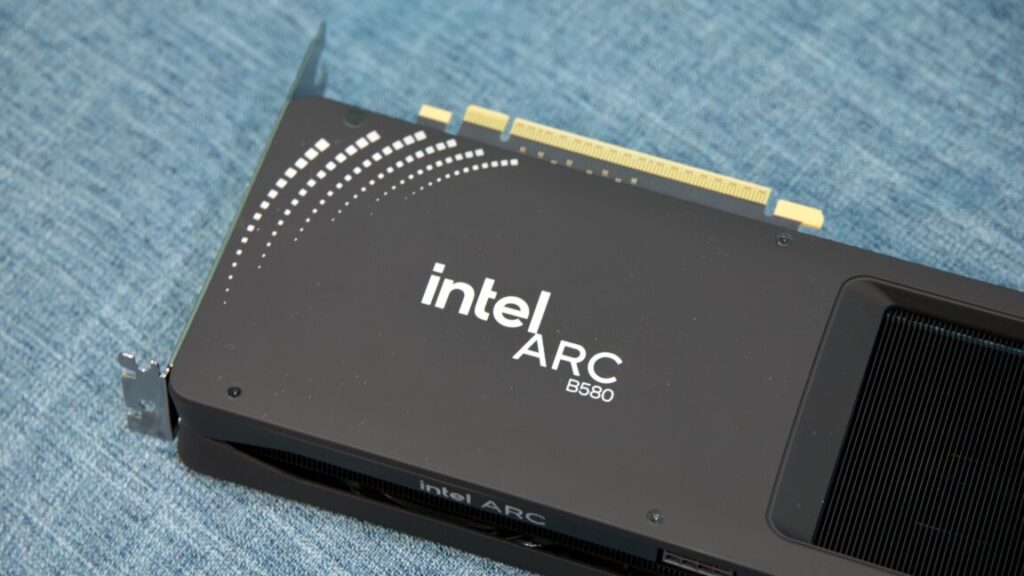
Intel’s Arc B580 design doesn’t include LEDs or other frills, but it’s a clean-looking design. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Intel doesn’t have a ton to show for its dedicated GPU efforts yet.
After much anticipation, many delays, and an anticipatory apology tour for its software quality, Intel launched its first Arc GPUs at the end of 2022. There were things to like about the A770 and A750, but buggy drivers, poor performance in older games, and relatively high power use made them difficult to recommend. They were more notable as curiosities than as consumer graphics cards.
The result, after more than two years on the market, is that Arc GPUs remain a statistical nonentity in the GPU market, according to analysts and the Steam Hardware Survey. But it was always going to take time—and probably a couple of hardware generations—for Intel to make meaningful headway against entrenched competitors.
Intel’s reference design is pretty by the book, with two fans, a single 8-pin power connector, and a long heatsink and fan shroud that extends several inches beyond the end of the PCB. Andrew Cunningham
The new Arc B580 card, the first dedicated GPU based on the new “Battlemage” architecture, launches into the exact same “sub-$300 value-for-money” graphics card segment that the A770 and A750 are already stuck in. But it’s a major improvement over those cards in just about every way, and Intel has gone a long way toward fixing drivers and other issues that plagued the first Arc cards at launch. If nothing else, the B580 suggests that Intel has some staying power and that the B700-series GPUs could be genuinely exciting if Intel can get one out relatively soon.
Specs and testbed notes

Specs for the Arc B580 and B570. Credit: Intel
The Arc B580 and Arc B570 lead the charge for the Battlemage generation. Both are based on the same GPU silicon, but the B580 has a few more execution resources, slightly higher clock speeds, a 192-bit memory bus instead of 160-bit, and 12GB of memory instead of 10GB.
Intel positions both cards as entry-level 1440p options because they have a bit more RAM than the 8GB baseline of the GeForce RTX 4060 and Radeon RX 7600. These 8GB cards are still generally fine at 1080p, but more memory does make the Arc cards feel a little more future-proof, especially since they’re fast enough to actually hit 60 fps in a lot of games at 1440p.
Our testbed remains largely the same as it has been for a while, though we’ve swapped the ASRock X670E board for an Asus model. The Ryzen 7 7800X3D remains the heart of the system, with more than enough performance to avoid bottlenecking midrange and high-end GPUs.
We haven’t done extensive re-testing of most older GPUs—the GeForce and Radeon numbers here are the same ones we used in the RX 7600 XT review earlier this year. We wouldn’t expect new drivers to change the scores in our games much since they’re mostly a bit older—we still use a mix of DirectX 11 and DirectX 12 games, including a few with and without ray-tracing effects enabled. We have re-tested the older Arc cards with recent drivers since Intel does still occasionally make changes that can have a noticeable impact on older games.
As with the Arc A-series cards, Intel emphatically recommends that resizable BAR be enabled for your motherboard to get optimal performance. This is sometimes called Smart Access Memory or SAM, depending on your board; most AMD AM4 and 8th-gen Intel Core systems should support it after a BIOS update, and newer PCs should mostly have it on by default. Our test system had it enabled for the B580 and for all the other GPUs we tested.
Performance and power
As a competitor to the RTX 4060, the Arc B580 is actually pretty appealing, whether you’re talking about 1080p or 1440p, in games with ray-tracing on or off. Even older DirectX 11 titles in our suite, like Grand Theft Auto V and Assassin’s Creed Odyssey, don’t seem to take the same performance hit as they did on older Arc cards.
Intel is essentially making a slightly stronger version of the argument that AMD has been trying to make with the RX 7600. AMD’s cards always come with the caveat of significantly worse performance in games with heavy ray-tracing effects, but the performance hit for Intel cards in ray-traced games looks a lot more like Nvidia’s than AMD’s. Playable ray-traced 1080p is well within reach for the Intel card, and in both Cyberpunk 2077 and Returnal, its performance came closer to the 8GB 4060 Ti’s.
The 12GB of RAM is also enough to put more space between the B580 and the 8GB versions of the 4060 and 7600. Forza Horizon 5 performs significantly better at 1440p on cards with more memory, like the B580 and the 16GB RX 7600 XT, and it’s a safe bet that the 8GB limit will become more of a factor for high-end games at higher resolutions as the years go on.
We experienced just one performance anomaly in our testing. Forza Horizon 5 actually runs a bit worse with XeSS enabled, with a smooth average frame rate but frequent stutters that make it less playable overall (though it’s worth noting that Forza Horizon 5 never benefits much from upscaling algorithms on any GPUs we’ve tested, for whatever reason). Intel also alerted us to a possible issue with Cyberpunk 2077 when enabling ray-tracing but recommended a workaround that involved pressing F1 to reset the game’s settings; the benchmark ran fine on our testbed.

GPU power consumption numbers under load. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Power consumption is another place where the Battlemage GPU plays a lot of catch-up with Nvidia. With the caveat that software-measured power usage numbers like ours are less accurate than numbers captured with hardware tools, it looks like the B580’s power consumption, when fully loaded, consumes somewhere between 120 and 130 W in Hitman and Borderlands. This is a tad higher than the 4060, but it’s lower than either Radeon RX 7600.
It’s not the top of the class, but looking at the A750’s power consumption shows how far Intel has come—the B580 beats the A750’s performance every single time while consuming about 60 W less power.
A strong contender, a late arrival

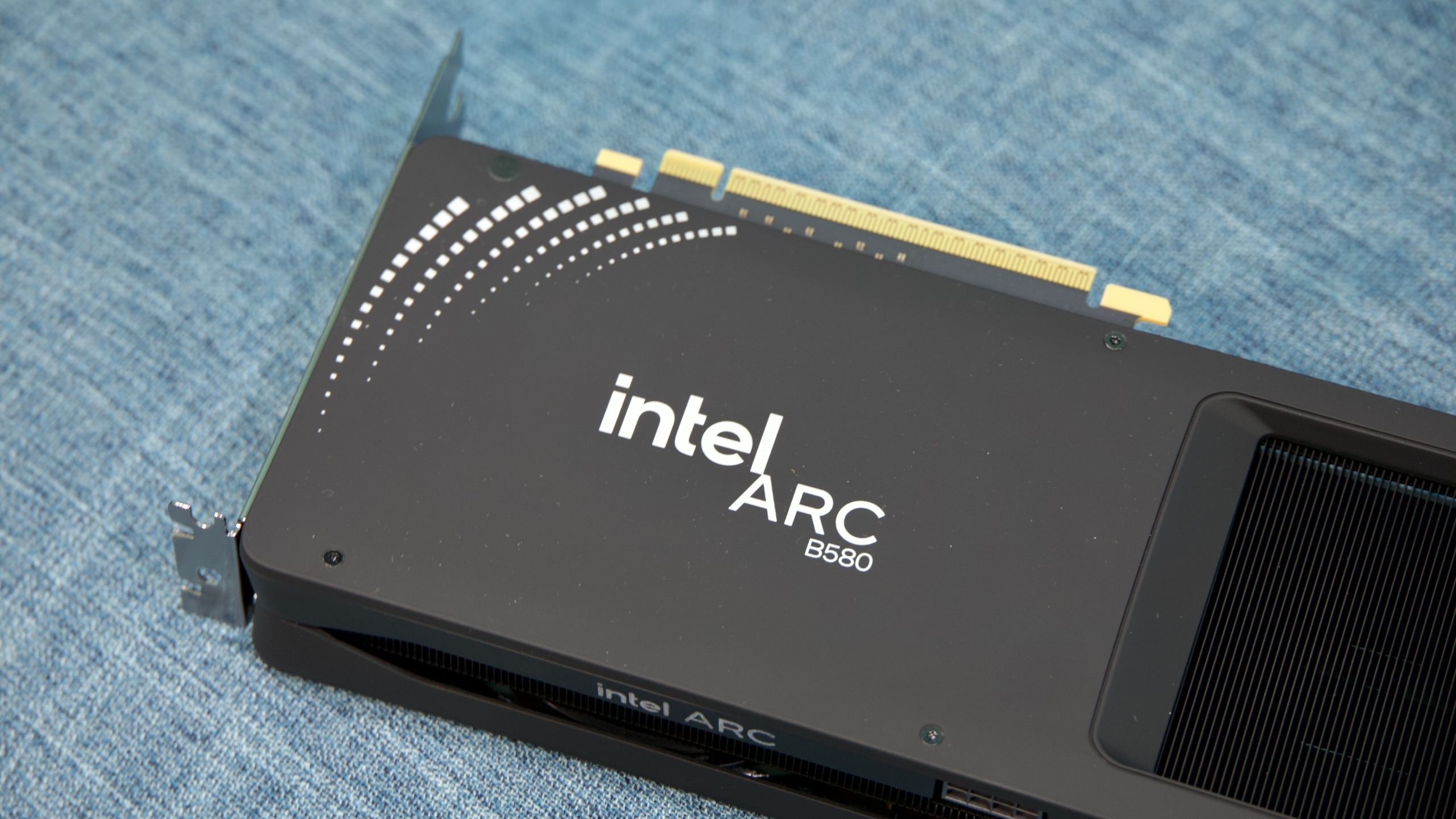
The Intel Arc B580. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Intel is explicitly targeting Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 4060 with the Arc B580, a role it fills well for a low starting price. But the B580 is perhaps more damaging to AMD, which positions both of its 7600-series cards (and the remaining 6600-series stuff that’s hanging around) in the same cheaper-than-Nvidia-with-caveats niche.
In fact, I’d probably recommend the B580 to a budget GPU buyer over any of the Radeon RX 7600 cards at this point. For the same street price as the RX 7600, Intel is providing better performance in most games and much better performance in ray-traced games. The 16GB 7600 XT has more RAM, but it’s $90 to $100 more expensive, and a 12GB card is still reasonably future-proof and decent at 1440p.
All of that said, Intel is putting out a great competitor to the RTX 4060 and RX 7600 a year and a half after those cards both launched—and within just a few months of a possible RTX 5060. Intel is selling mid-2023’s midrange GPU performance in late 2024. There are actually good arguments for building a budget gaming PC right this minute, before potential Trump-administration tariffs can affect prices or supply chains, but assuming the tech industry can maintain its normal patterns, it would be smartest to wait and see what Nvidia does next.
Nvidia also has some important structural benefits. DLSS upscaling support is nearly ubiquitous in high-end games, Nvidia’s drivers are more battle-tested, and it’s extremely unlikely that Nvidia will decide to pull out of the GPU market and stop driver development any time soon (Intel has published a roadmap encompassing multiple GPU generations, which is reassuring, but the company’s recent financial distress has seen it shed several money-losing hobby projects).
If there’s a saving grace for Intel and the B580, it’s that Nvidia has signaled, both through its statements and its behavior, that it’s mostly uninterested in aggressively lowering GPU prices, either over time (Nvidia GPUs tend not to stray far from MSRP, barring supply issues) or between generations. An RTX 5060 is highly unlikely to be cheaper than a 4060 and could easily be more expensive. Depending on how good a hypothetical RTX 5060 is, Intel still has a lot of room to offer good performance for the price in a $200-to-$250-ish GPU market that doesn’t get a ton of attention.
The other issue for Intel is that for a second straight GPU generation, the company is launching late with a part that is forced by its performance to play in a budget-oriented, low-margin area of the GPU market. I don’t think I’m expecting a 4090 or 5090-killer out of Intel any time soon, but based on the B580, I’m at least a little optimistic that Intel can offer a B700-series card that can credibly compete with the likes of Nvidia’s 4070-series or AMD’s 7800 XT and 7900 GRE. Performance-wise, that’s the current sweet spot of the GPU market, but you’ll spend more than you would on a PS5 to buy most of those cards. If Intel can shake up that part of the business, it could help put Arc on the map.
The good
- Solid midrange 1080p and 1440p performance at a good starting price
- More RAM than the competition
- Much-improved power efficiency compared to Arc A-series GPUs
- Unlike the A-series, we noticed no outliers where performance was disproportionately bad
- Simple, clean-looking reference design from Intel
The bad
- Competing with cards that launched a year and a half ago
- New Nvidia and AMD competitors are likely within a few months
- Intel still can’t compete at the high end of the GPU market, or even the medium-high end
The ugly
- So far, Arc cards have not been successful enough to guarantee their long-term existence
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
Intel Arc B580 review: A $249 RTX 4060 killer, one-and-a-half years later Read More »