OpenAI board first learned about ChatGPT from Twitter, according to former member
It’s a secret to everybody —
Helen Toner, center of struggle with Altman, suggests CEO fostered “toxic atmosphere” at company.
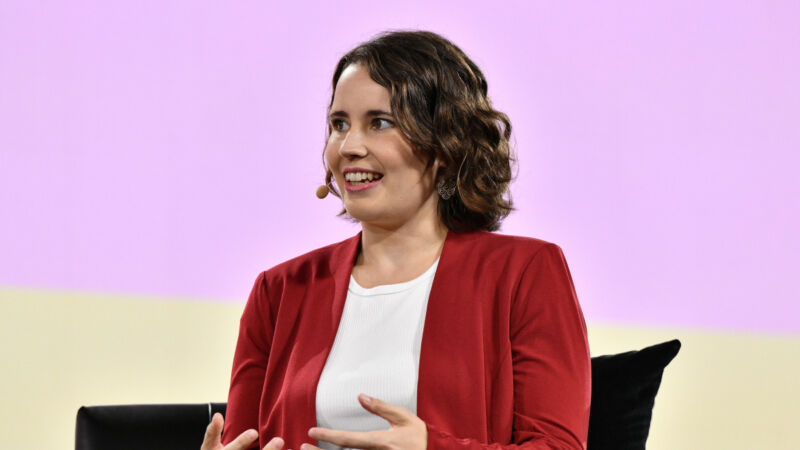

Enlarge / Helen Toner, former OpenAI board member, speaks during Vox Media’s 2023 Code Conference at The Ritz-Carlton, Laguna Niguel on September 27, 2023.
In a recent interview on “The Ted AI Show” podcast, former OpenAI board member Helen Toner said the OpenAI board was unaware of the existence of ChatGPT until they saw it on Twitter. She also revealed details about the company’s internal dynamics and the events surrounding CEO Sam Altman’s surprise firing and subsequent rehiring last November.
OpenAI released ChatGPT publicly on November 30, 2022, and its massive surprise popularity set OpenAI on a new trajectory, shifting focus from being an AI research lab to a more consumer-facing tech company.
“When ChatGPT came out in November 2022, the board was not informed in advance about that. We learned about ChatGPT on Twitter,” Toner said on the podcast.
Toner’s revelation about ChatGPT seems to highlight a significant disconnect between the board and the company’s day-to-day operations, bringing new light to accusations that Altman was “not consistently candid in his communications with the board” upon his firing on November 17, 2023. Altman and OpenAI’s new board later said that the CEO’s mismanagement of attempts to remove Toner from the OpenAI board following her criticism of the company’s release of ChatGPT played a key role in Altman’s firing.
“Sam didn’t inform the board that he owned the OpenAI startup fund, even though he constantly was claiming to be an independent board member with no financial interest in the company on multiple occasions,” she said. “He gave us inaccurate information about the small number of formal safety processes that the company did have in place, meaning that it was basically impossible for the board to know how well those safety processes were working or what might need to change.”
Toner also shed light on the circumstances that led to Altman’s temporary ousting. She mentioned that two OpenAI executives had reported instances of “psychological abuse” to the board, providing screenshots and documentation to support their claims. The allegations made by the former OpenAI executives, as relayed by Toner, suggest that Altman’s leadership style fostered a “toxic atmosphere” at the company:
In October of last year, we had this series of conversations with these executives, where the two of them suddenly started telling us about their own experiences with Sam, which they hadn’t felt comfortable sharing before, but telling us how they couldn’t trust him, about the toxic atmosphere it was creating. They use the phrase “psychological abuse,” telling us they didn’t think he was the right person to lead the company, telling us they had no belief that he could or would change, there’s no point in giving him feedback, no point in trying to work through these issues.
Despite the board’s decision to fire Altman, Altman began the process of returning to his position just five days later after a letter to the board signed by over 700 OpenAI employees. Toner attributed this swift comeback to employees who believed the company would collapse without him, saying they also feared retaliation from Altman if they did not support his return.
“The second thing I think is really important to know, that has really gone under reported is how scared people are to go against Sam,” Toner said. “They experienced him retaliate against people retaliating… for past instances of being critical.”
“They were really afraid of what might happen to them,” she continued. “So some employees started to say, you know, wait, I don’t want the company to fall apart. Like, let’s bring back Sam. It was very hard for those people who had had terrible experiences to actually say that… if Sam did stay in power, as he ultimately did, that would make their lives miserable.”
In response to Toner’s statements, current OpenAI board chair Bret Taylor provided a statement to the podcast: “We are disappointed that Miss Toner continues to revisit these issues… The review concluded that the prior board’s decision was not based on concerns regarding product safety or security, the pace of development, OpenAI’s finances, or its statements to investors, customers, or business partners.”
Even given that review, Toner’s main argument is that OpenAI hasn’t been able to police itself despite claims to the contrary. “The OpenAI saga shows that trying to do good and regulating yourself isn’t enough,” she said.
OpenAI board first learned about ChatGPT from Twitter, according to former member Read More »