Ten cool science stories we almost missed
Bronze Age combat, moral philosophy and Reddit’s AITA, Mondrian’s fractal tree, and seven other fascinating papers.
There is rarely time to write about every cool science paper that comes our way; many worthy candidates sadly fall through the cracks over the course of the year. But as 2024 comes to a close, we’ve gathered ten of our favorite such papers at the intersection of science and culture as a special treat, covering a broad range of topics: from reenacting Bronze Age spear combat and applying network theory to the music of Johann Sebastian Bach, to Spider-Man inspired web-slinging tech and a mathematical connection between a turbulent phase transition and your morning cup of coffee. Enjoy!
Reenacting Bronze Age spear combat

An experiment with experienced fighters who spar freely using different styles. Credit: Valerio Gentile/CC BY
The European Bronze Age saw the rise of institutionalized warfare, evidenced by the many spearheads and similar weaponry archaeologists have unearthed. But how might these artifacts be used in actual combat? Dutch researchers decided to find out by constructing replicas of Bronze Age shields and spears and using them in realistic combat scenarios. They described their findings in an October paper published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
There have been a couple of prior experimental studies on bronze spears, but per Valerio Gentile (now at the University of Gottingen) and coauthors, practical research to date has been quite narrow in scope, focusing on throwing weapons against static shields. Coauthors C.J. van Dijk of the National Military Museum in the Netherlands and independent researcher O. Ter Mors each had more than a decade of experience teaching traditional martial arts, specializing in medieval polearms and one-handed weapons. So they were ideal candidates for testing the replica spears and shields.
Of course, there is no direct information on prehistoric fighting styles, so van Dijk and Mors relied on basic biomechanics of combat movements with similar weapons detailed in historic manuals. They ran three versions of the experiment: one focused on engagement and controlled collisions, another on delivering wounding body blows, and the third on free sparring. They then studied wear marks left on the spearheads and found they matched the marks found on similar genuine weapons excavated from Bronze Age sites. They also gleaned helpful clues to the skills required to use such weapons.
DOI: Journal of Archaeological Science, 2024. 10.1016/j.jas.2024.106044 (About DOIs).
Physics of Ned Kahn’s kinetic sculptures
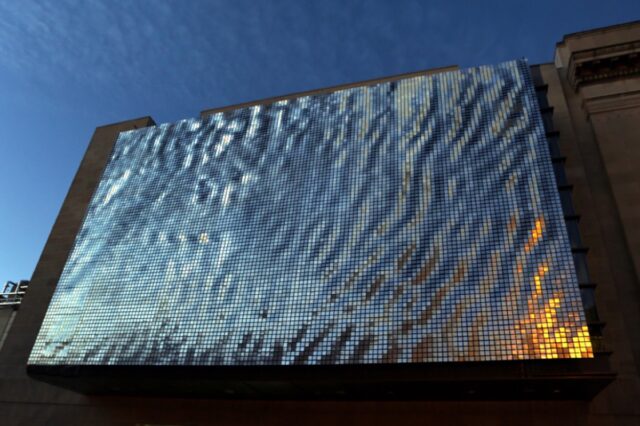

Shimmer Wall, The Franklin Institute, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Credit: Ned Kahn
Environmental artist and sculptor Ned Kahn is famous for his kinematic building facades, inspired by his own background in science. An exterior wall on the Children’s Museum of Pittsburgh, for instance, consists of hundreds of flaps that move in response to wind, creating distinctive visual patterns. Kahn used the same method to create his Shimmer Wall at Philadelphia’s Franklin Institute, as well as several other similar projects.
Physicists at Sorbonne Universite in Paris have studied videos of Kahn’s kinetic facades and conducted experiments to measure the underlying physical mechanisms, outlined in a November paper published in the journal Physical Review Fluids. The authors analyzed 18 YouTube videos taken of six of Kahn’s kinematic facades, working with Kahn and building management to get the dimensions of the moving plates, scaling up from the video footage to get further information on spatial dimensions.
They also conducted their own wind tunnel experiments, using strings of pendulum plates. Their measurements confirmed that the kinetic patterns were propagating waves to create the flickering visual effects. The plates’ movement is driven primarily by their natural resonant frequencies at low speeds, and by pressure fluctuations from the wind at higher speeds.
DOI: Physical Review Fluids, 2024. 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.9.114604 (About DOIs).
How brewing coffee connects to turbulence
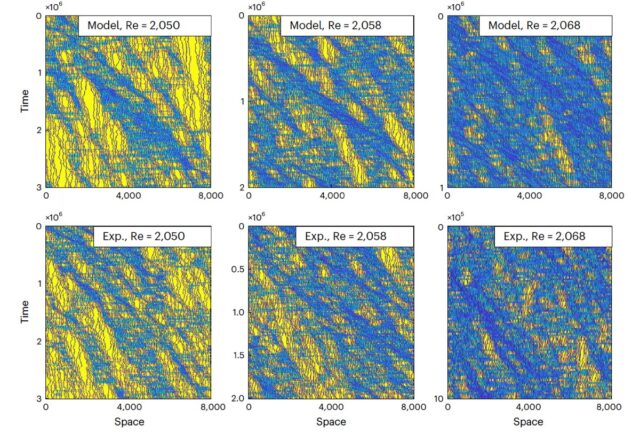
Trajectories in time traced out by turbulent puffs as they move along a simulated pipe and in experiments, with blue regions indicate puff “traffic jams.” Credit: Grégoire Lemoult et al., 2024
Physicists have been studying turbulence for centuries, particularly the transitional period where flows shift from predictably smooth (laminar flow) to highly turbulent. That transition is marked by localized turbulent patches known as “puffs,” which often form in fluids flowing through a pipe or channel. In an October paper published in the journal Nature Physics, physicists used statistical mechanics to reveal an unexpected connection between the process of brewing coffee and the behavior of those puffs.
Traditional mathematical models of percolation date back to the 1940s. Directed percolation is when the flow occurs in a specific direction, akin to how water moves through freshly ground coffee beans, flowing down in the direction of gravity. There’s a sweet spot for the perfect cuppa, where the rate of flow is sufficiently slow to absorb most of the flavor from the beans, but also fast enough not to back up in the filter. That sweet spot in your coffee brewing process corresponds to the aforementioned laminar-turbulent transition in pipes.
Physicist Nigel Goldenfeld of the University of California, San Diego, and his coauthors used pressure sensors to monitor the formation of puffs in a pipe, focusing on how puff-to-puff interactions influenced each other’s motion. Next, they tried to mathematically model the relevant phase transitions to predict puff behavior. They found that the puffs behave much like cars moving on a freeway during rush hour: they are prone to traffic jams—i.e., when a turbulent patch matches the width of the pipe, causing other puffs to build up behind it—that form and dissipate on their own. And they tend to “melt” at the laminar-turbulent transition point.
DOI: Nature Physics, 2024. 10.1038/s41567-024-02513-0 (About DOIs).
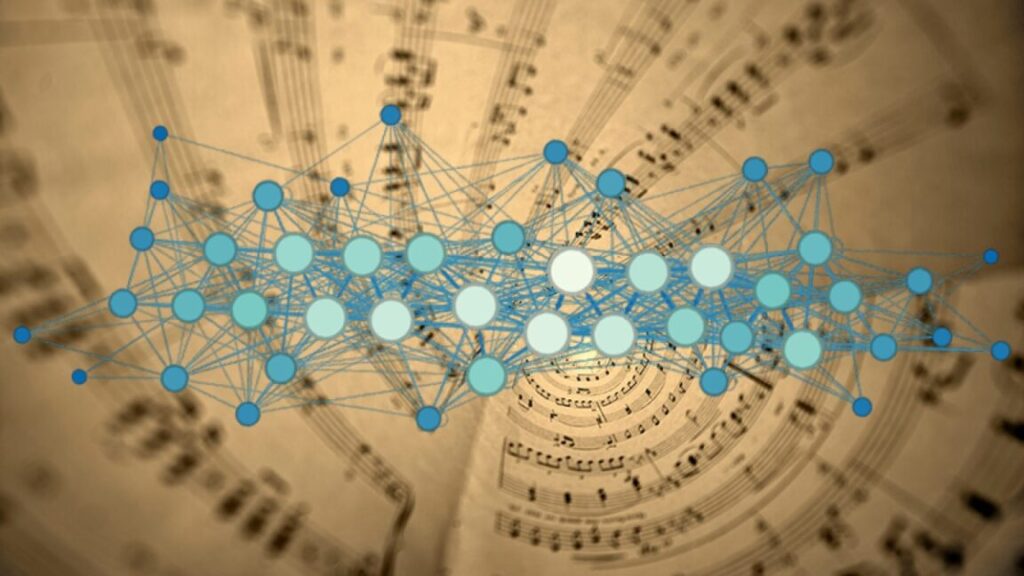
Network theory and Bach’s music
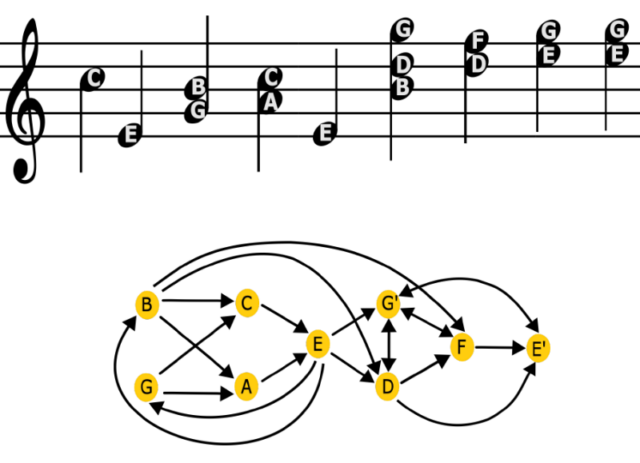
In a network representation of music, notes are represented by nodes, and transition between notes are represented by directed edges connecting the nodes. Credit: S. Kulkarni et al., 2024
When you listen to music, does your ability to remember or anticipate the piece tell you anything about its structure? Physicists at the University of Pennsylvania developed a model based on network theory to do just that, describing their work in a February paper published in the journal Physical Review Research. Johann Sebastian Bach’s works were an ideal choice given the highly mathematical structure, plus the composer was so prolific, across so many very different kinds of musical compositions—preludes, fugues, chorales, toccatas, concertos, suites, and cantatas—as to allow for useful comparisons.
First, the authors built a simple “true” network for each composition, in which individual notes served as “nodes” and the transitions from note to note served as “edges” connecting them. Then they calculated the amount of information in each network. They found it was possible to tell the difference between compositional forms based on their information content (entropy). The more complex toccatas and fugues had the highest entropy, while simpler chorales had the lowest.
Next, the team wanted to quantify how effectively this information was communicated to the listener, a task made more difficult by the innate subjectivity of human perception. They developed a fuzzier “inferred” network model for this purpose, capturing an essential aspect of our perception: we find a balance between accuracy and cost, simplifying some details so as to make it easier for our brains to process incoming information like music.
The results: There were fewer differences between the true and inferred networks for Bach’s compositions than for randomly generated networks, suggesting that clustering and the frequent repetition of transitions (represented by thicker edges) in Bach networks were key to effectively communicating information to the listener. The next step is to build a multi-layered network model that incorporates elements like rhythm, timbre, chords, or counterpoint (a Bach specialty).
DOI: Physical Review Research, 2024. 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.013136 (About DOIs).
The philosophy of Reddit’s AITA

Count me among the many people practically addicted to Reddit’s “Am I the Asshole” (AITA) forum. It’s such a fascinating window into the intricacies of how flawed human beings navigate different relationships, whether personal or professional. That’s also what makes it a fantastic source of illustrative common-place dilemmas of moral decision-making for philosophers like Daniel Yudkin of the University of Pennsylvania. Relational context matters, as Yudkin and several co-authors ably demonstrated in a PsyArXiv preprint earlier this year.
For their study, Yudkin et al. compiled a dataset of nearly 370,000 AITA posts, along with over 11 million comments, posted between 2018 and 2021. They used machine learning to analyze the language used to sort all those posts into different categories. They relied on an existing taxonomy identifying six basic areas of moral concern: fairness/proportionality, feelings, harm/offense, honesty, relational obligation, and social norms.
Yudkin et al. identified 29 of the most common dilemmas in the AITA dataset and grouped them according to moral theme. Two of the most common were relational transgression and relational omission (failure to do what was expected), followed by behavioral over-reaction and unintended harm. Cheating and deliberate misrepresentation/dishonesty were the moral dilemmas rated most negatively in the dataset—even more so than intentional harm. Being judgmental was also evaluated very negatively, as it was often perceived as being self-righteous or hypocritical. The least negatively evaluated dilemmas were relational omissions.
As for relational context, cheating and broken promise dilemmas typically involved romantic partners like boyfriends rather than one’s mother, for example, while mother-related dilemmas more frequently fell under relational omission. Essentially, “people tend to disappoint their mothers but be disappointed by their boyfriends,” the authors wrote. Less close relationships, by contrast, tend to be governed by “norms of politeness and procedural fairness.” Hence, Yudkin et al. prefer to think of morality “less as a set of abstract principles and more as a ‘relational toolkit,’ guiding and constraining behavior according to the demands of the social situation.”
DOI: PsyArXiv, 2024. 10.31234/osf.io/5pcew (About DOIs).
Fractal scaling of trees in art
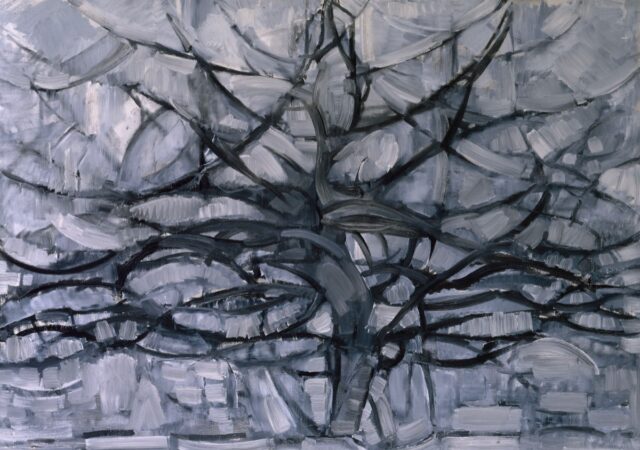

De grijze boom (Gray tree) by Piet Mondrian, 1911. Credit: Public domain
Leonardo da Vinci famously invented a so-called “rule of trees” as a guide to realistically depicting trees in artistic representations according to their geometric proportions. In essence, if you took all the branches of a given tree, folded them up and compressed them into something resembling a trunk, that trunk would have the same thickness from top to bottom. That rule in turn implies a fractal branching pattern, with a scaling exponent of about 2 describing the proportions between the diameters of nearby boughs and the number of boughs with a given diameter.
According to the authors of a preprint posted to the physics arXiv in February, however, recent biological research suggests a higher scaling exponent of 3 known as Murray’s Law, for the rule of trees. Their analysis of 16th century Islamic architecture, Japanese paintings from the Edo period, and 20th century European art showed fractal scaling between 1.5 and 2.5. However, when they analyzed an abstract tree painting by Piet Mondrian, they found it exhibited fractal scaling of 3, before mathematicians had formulated Murray’s Law, even though Mondrian’s tree did not feature explicit branching.
The findings intrigued physicist Richard Taylor of the University of Oregon, whose work over the last 20 years includes analyzing fractal patterns in the paintings of Jackson Pollock. “In particular, I thought the extension to Mondrian’s ‘trees’ was impressive,” he told Ars earlier this year. “I like that it establishes a connection between abstract and representational forms. It makes me wonder what would happen if the same idea were to be applied to Pollock’s poured branchings.”
Taylor himself published a 2022 paper about climate change and how nature’s stress-reducing fractals might disappear in the future. “If we are pessimistic for a moment, and assume that climate change will inevitably impact nature’s fractals, then our only future source of fractal aesthetics will be through art, design and architecture,” he said. “This brings a very practical element to studies like [this].”
DOI: arXiv, 2024. 10.48550/arXiv.2402.13520 (About DOIs).
IDing George Washington’s descendants

A DNA study identified descendants of George Washington from unmarked remains. Credit: Public domain
DNA profiling is an incredibly useful tool in forensics, but the most common method—short tandem repeat (STR) analysis—typically doesn’t work when remains are especially degraded, especially if said remains have been preserved with embalming methods using formaldehyde. This includes the remains of US service members who died in such past conflicts as World War II, Korea, Vietnam, and the Cold War. That’s why scientists at the Armed Forces Medical Examiner System’s identification lab at the Dover Air Force Base have developed new DNA sequencing technologies.
They used those methods to identify the previously unmarked remains of descendants of George Washington, according to a March paper published in the journal iScience. The team tested three sets of remains and compared the results with those of a known living descendant, using methods for assessing paternal and maternal relationships, as well as a new method for next-generation sequencing data involving some 95,000 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in order to better predict more distant ancestry. The combined data confirmed that the remains belonged to Washington’s descendants and the new method should help do the same for the remains of as-yet-unidentified service members.
In related news, in July, forensic scientists successfully used descendant DNA to identify a victim of the 1921 Tulsa massacre in Oklahoma City, buried in a mass grave containing more than a hundred victims. C.L. Daniel was a World War I veteran, still in his 20s when he was killed. More than 120 such graves have been found since 2020, with DNA collected from around 30 sets of remains, but this is the first time those remains have been directly linked to the massacre. There are at least 17 other victims in the grave where Daniel’s remains were found.
DOI: iScience, 2024. 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109353 (About DOIs).
Spidey-inspired web-slinging tech
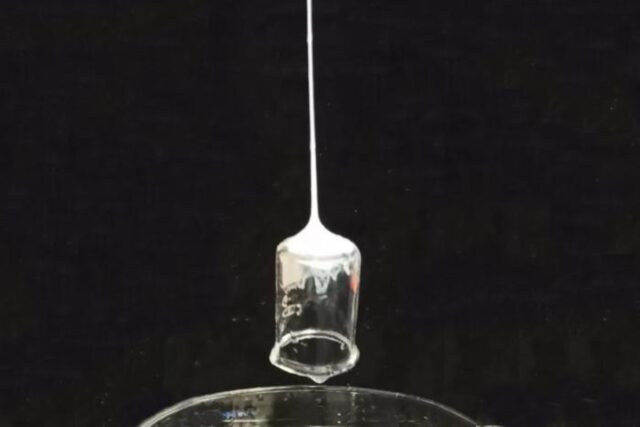

stream of liquid silk quickly turns to a strong fiber that sticks to and lifts objects. Credit: Marco Lo Presti et al., 2024
Over the years, researchers in Tufts University’s Silklab have come up with all kinds of ingenious bio-inspired uses for the sticky fibers found in silk moth cocoons: adhesive glues, printable sensors, edible coatings, and light-collecting materials for solar cells, to name a few. Their latest innovation is a web-slinging technology inspired by Spider-Man’s ability to shoot webbing from his wrists, described in an October paper published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Coauthor Marco Lo Presti was cleaning glassware with acetone in the lab one day when he noticed something that looked a lot like webbing forming on the bottom of a glass. He realized this could be the key to better replicating spider threads for the purpose of shooting the fibers from a device like Spider-Man—something actual spiders don’t do. (They spin the silk, find a surface, and draw out lines of silk to build webs.)
The team boiled silk moth cocoons in a solution to break them down into proteins called fibroin. The fibroin was then extruded through bore needles into a stream. Spiking the fibroin solution with just the right additives will cause it to solidify into fiber once it comes into contact with air. For the web-slinging technology, they added dopamine to the fibroin solution and then shot it through a needle in which the solution was surrounded by a layer of acetone, which triggered solidification.
The acetone quickly evaporated, leaving just the webbing attached to whatever object it happened it hit. The team tested the resulting fibers and found they could lift a steel bolt, a tube floating on water, a partially buried scalpel and a wooden block—all from as far away as 12 centimeters. Sure, natural spider silk is still about 1000 times stronger than these fibers, but it’s still a significant step forward that paves the way for future novel technological applications.
DOI: Advanced Functional Materials, 2024. 10.1002/adfm.202414219
Solving a mystery of a 12th century supernova
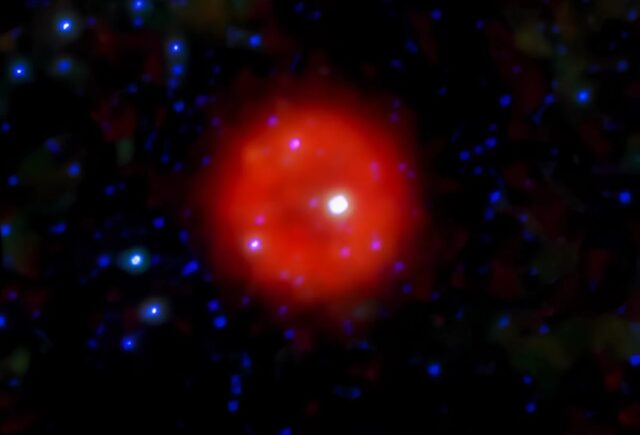

Pa 30 is the supernova remnant of SN 1181. Credit: unWISE (D. Lang)/CC BY-SA 4.0
In 1181, astronomers in China and Japan recorded the appearance of a “guest star” that shone as bright as Saturn and was visible in the sky for six months. We now know it was a supernova (SN1181), one of only five such known events occurring in our Milky Way. Astronomers got a closer look at the remnant of that supernova and have determined the nature of strange filaments resembling dandelion petals that emanate from a “zombie star” at its center, according to an October paper published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The Chinese and Japanese astronomers only recorded an approximate location for the unusual sighting, and for centuries no one managed to make a confirmed identification of a likely remnant from that supernova. Then, in 2021, astronomers measured the speed of expansion of a nebula known as Pa 30, which enabled them to determine its age: around 1,000 years, roughly coinciding with the recorded appearance of SN1181. PA 30 is an unusual remnant because of its zombie star—most likely itself a remnant of the original white dwarf that produced the supernova.
This latest study relied on data collected by Caltech’s Keck Cosmic Web Imager, a spectrograph at the Keck Observatory in Hawaii. One of the unique features of this instrument is that it can measure the motion of matter in a supernova and use that data to create something akin to a 3D movie of the explosion. The authors were able to create such a 3D map of P 30 and calculated that the zombie star’s filaments have ballistic motion, moving at approximately 1,000 kilometers per second.
Nor has that velocity changed since the explosion, enabling them to date that event almost exactly to 1181. And the findings raised fresh questions—namely, the ejected filament material is asymmetrical—which is unusual for a supernova remnant. The authors suggest that asymmetry may originate with the initial explosion.
There’s also a weird inner gap around the zombie star. Both will be the focus of further research.
DOI: Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024. 10.3847/2041-8213/ad713b (About DOIs).
Reviving a “lost” 16th century score
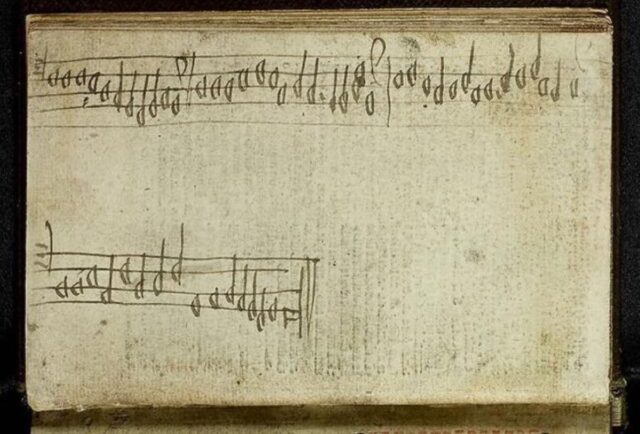

Fragment of music from The Aberdeen Breviary: Volume 1 Credit: National Library of Scotland /CC BY 4.0
Never underestimate the importance of marginalia in old manuscripts. Scholars from the University of Edinburgh and KU Leuven in Belgium can attest to that, having discovered a fragment of “lost” music from 16th-century pre-Reformation Scotland in a collection of worship texts. The team was even able to reconstruct the fragment and record it to get a sense of what music sounded like from that period in northeast Scotland, as detailed in a December paper published in the journal Music and Letters.
King James IV of Scotland commissioned the printing of several copies of The Aberdeen Breviary—a collection of prayers, hymns, readings, and psalms for daily worship—so that his subjects wouldn’t have to import such texts from England or Europe. One 1510 copy, known as the “Glamis copy,” is currently housed in the National Library of Scotland in Edinburgh. It was while examining handwritten annotations in this copy that the authors discovered the musical fragment on a page bound into the book—so it hadn’t been slipped between the pages at a later date.
The team figured out the piece was polyphonic, and then realized it was the tenor part from a harmonization for three or four voices of the hymn “Cultor Dei,” typically sung at night during Lent. (You can listen to a recording of the reconstructed composition here.) The authors also traced some of the history of this copy of The Aberdeen Breviary, including its use at one point by a rural chaplain at Aberdeen Cathedral, before a Scottish Catholic acquired it as a family heirloom.
“Identifying a piece of music is a real ‘Eureka’ moment for musicologists,” said coauthor David Coney of Edinburgh College of Art. “Better still, the fact that our tenor part is a harmony to a well-known melody means we can reconstruct the other missing parts. As a result, from just one line of music scrawled on a blank page, we can hear a hymn that had lain silent for nearly five centuries, a small but precious artifact of Scotland’s musical and religious traditions.”
DOI: Music and Letters, 2024. 10.1093/ml/gcae076 (About DOIs).
Jennifer is a senior reporter at Ars Technica with a particular focus on where science meets culture, covering everything from physics and related interdisciplinary topics to her favorite films and TV series. Jennifer lives in Baltimore with her spouse, physicist Sean M. Carroll, and their two cats, Ariel and Caliban.
Ten cool science stories we almost missed Read More »




