CDC reports dips in flu, COVID-19, and RSV—though levels still very high
a break? —
The dips may be due to holiday lulls and CDC is monitoring for post-holiday increase.
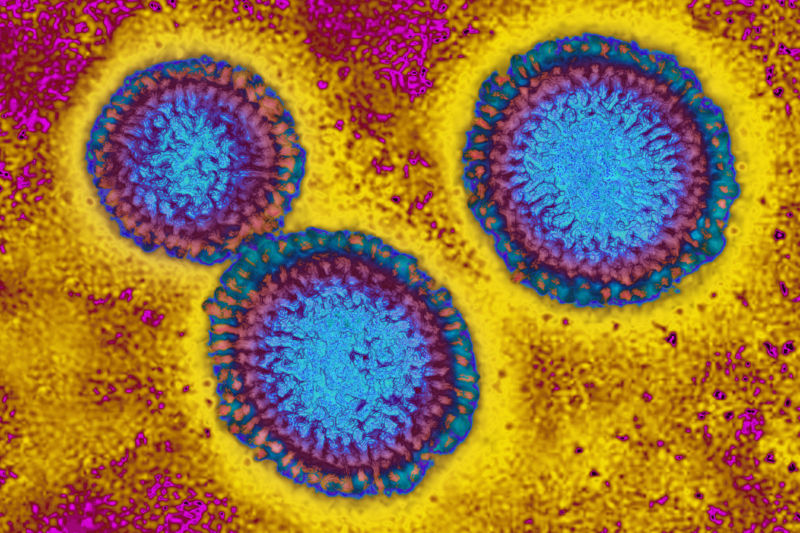
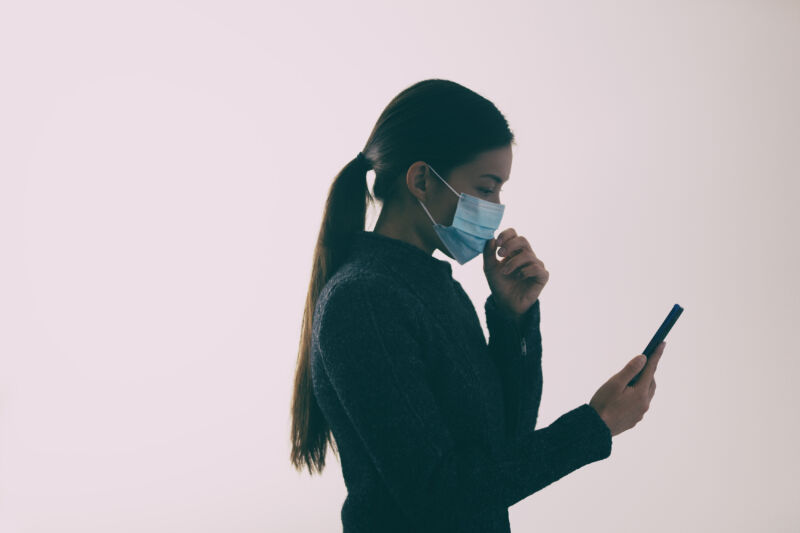
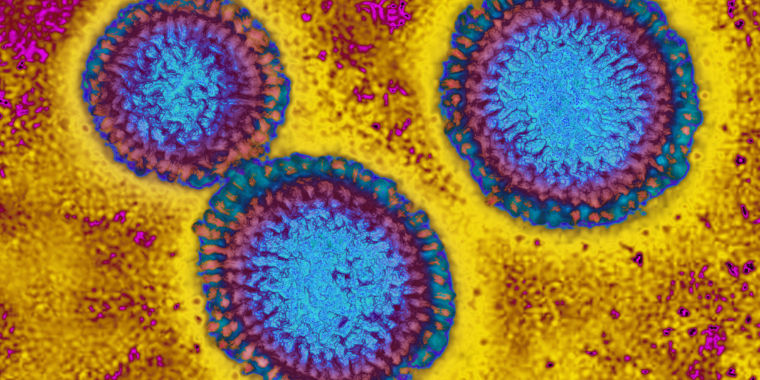
Enlarge / The influenza virus from an image produced from an image taken with transmission electron microscopy. Viral diameter ranges from around 80 to 120 nm.
Key indicators of seasonal flu activity declined in the first week of the year, signaling a possible reprieve from the high levels of respiratory virus transmission this season—but the dip may only be temporary.
On Friday, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released its latest flu data for the week ending on January 6. Outpatient visits for influenza-like illnesses (ILI) were down that week, the first decline after weeks of rapid increases. Flu test positivity and hospitalizations were also down slightly.
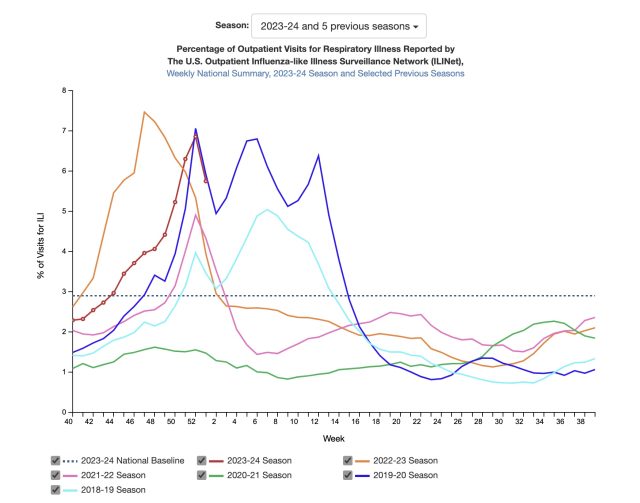
Enlarge / Percent of outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses by week.
But transmission is still elevated around the country. Fourteen states have ILI activity at the “very high” level in the current data, down from 22 the week before. And 23 states have “high” activity level, up from 19 the week before. (You can see the week-by-week progression of this year’s flu season in the US here.)
The CDC says it is monitoring for “a second period of increased influenza activity that often occurs after the winter holidays.”
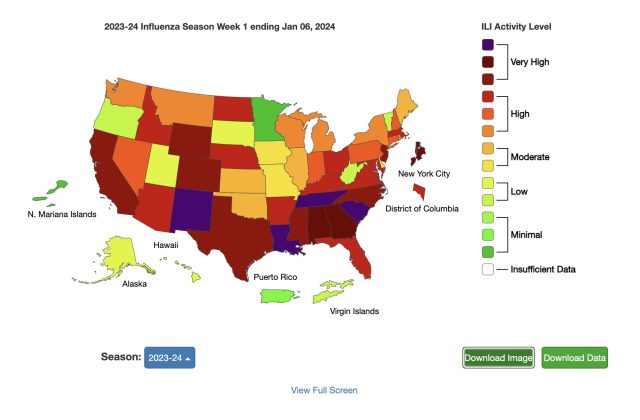
Enlarge / Map of ILI activity by state.
Flu isn’t the only virus that seems to be letting up a little in the data, at least for now. COVID-19 data also showed some dips, with the CDC reporting that “Despite test positivity (percentage of tests conducted that were positive), emergency department visits, and hospitalizations remaining elevated nationally, the rates have stabilized, or in some instances decreased, after multiple weeks of continual increase.”
The CDC speculates that some of the declines in indicators could be due to people not seeking medical care during the holidays as they would otherwise. COVID-19 wastewater activity levels remain “very high,” with all regions showing high or increasing levels. The South and Midwest have the highest levels in the latest data, but there are some early indications that rises in the Midwest and Northeast may be slowing down.
Meanwhile, RSV activity remains elevated, though some areas are starting to see declines.
The CDC notes that it’s not too late to get vaccinated against COVID-19, flu, and (for those ages 60 and over) RSV. So far, 21 percent of adults have received the 2023–2024 COVID-19 vaccine, including 41.5 percent of people ages 65 and up. Around 363,000 people have died from COVID-19 in the US since September.
For flu, about 47 percent of adults have received their annual shot, including 74 percent of people ages 65 and up. On Thursday, researchers in Canada published the first estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness this season, finding the current annual shots are 61 percent effective against the most common strain of flu circulating in the US (influenza A(H1N1)pdm09) and 49 percent effective against the less common influenza A(H3N2) and 75 percent effective against influenza B.
The CDC estimates that there have been at least 14 million flu cases, 150,000 hospitalizations, and 9,400 deaths from flu so far this season so far, the agency reported. In the first week of this year, 13 children died of flu, bringing this season’s total to 40.
CDC reports dips in flu, COVID-19, and RSV—though levels still very high Read More »