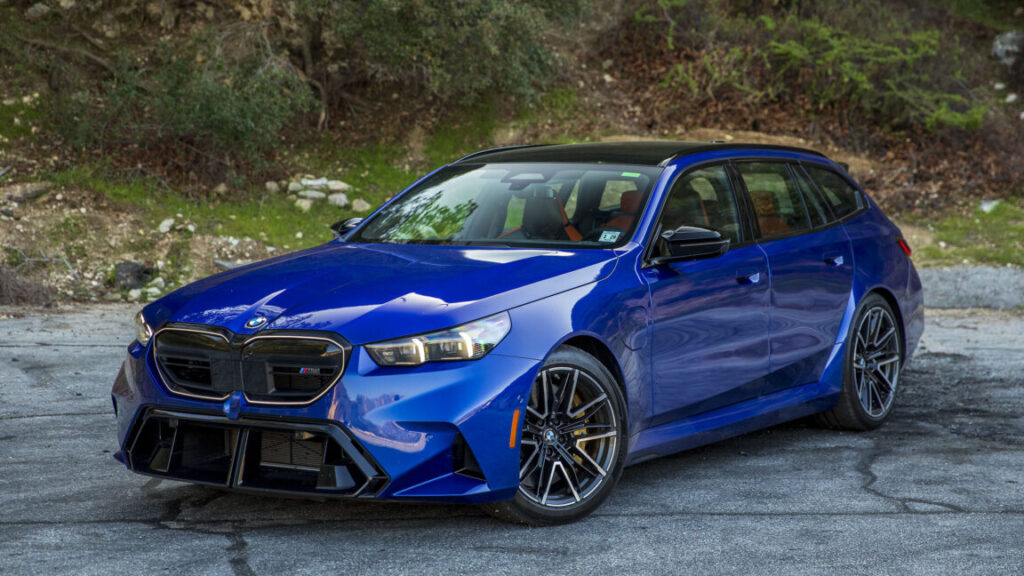
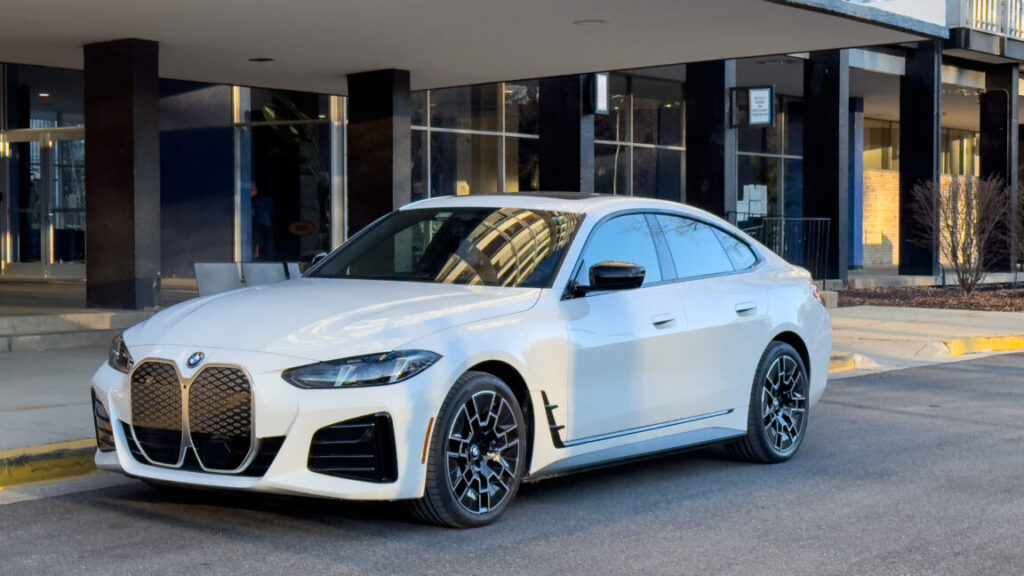
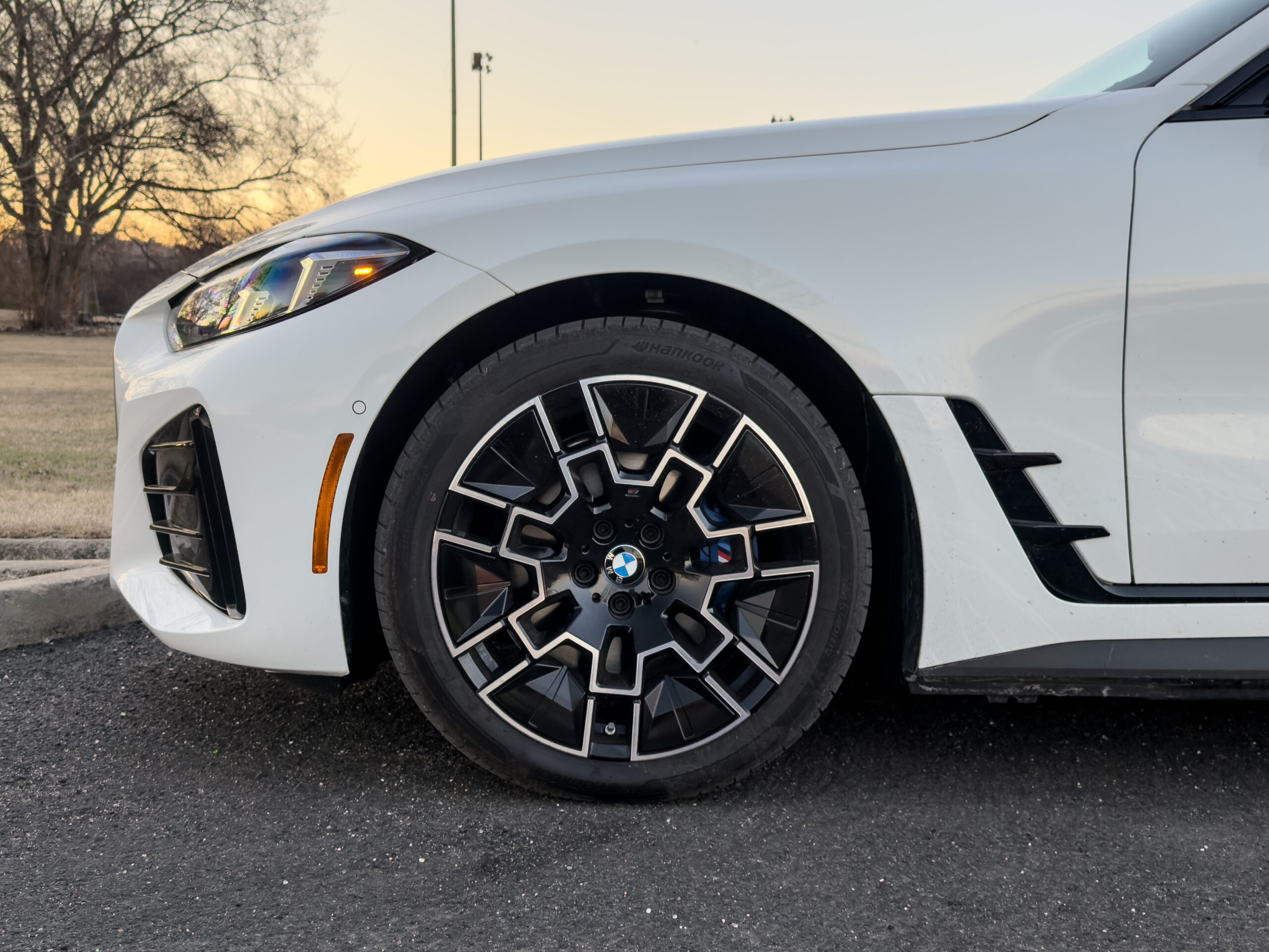
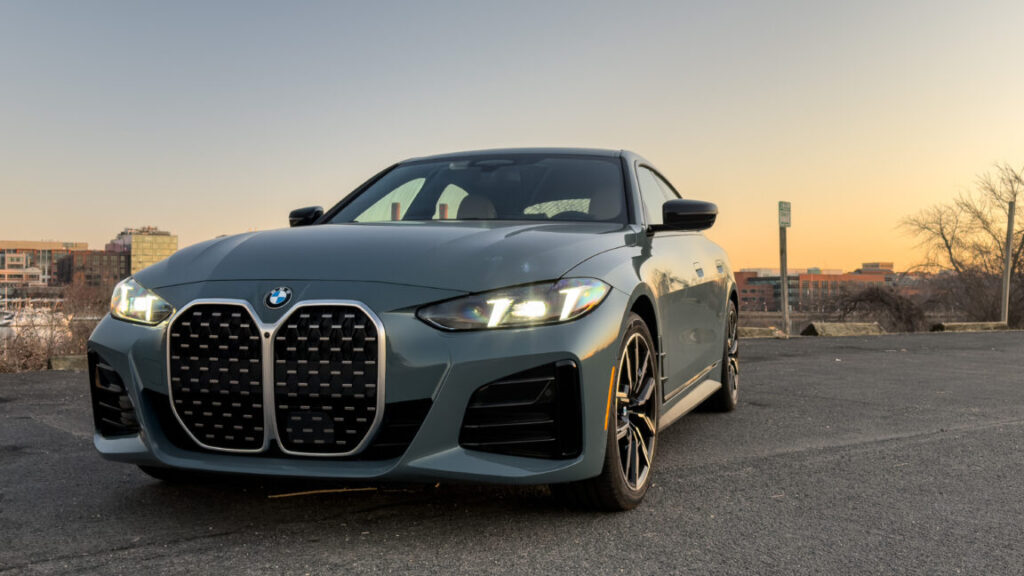
The 2025 BMW M5 Touring review: Way more power, way too much weight
Basic functions like adjusting the fan speed of the air conditioning system require taking your attention off of the road to call up the comfort settings on the display, and if you dare to venture further down the rabbit hole to adjust something else, you’ll find an app drawer-style menu filled with ambiguously named icons that rarely get you where you want to go the first time out.
Do I change the damper stiffness by pressing the M Mode button on the center console, or is it in the Drivetrain and chassis submenu under Driving Settings? The answer is neither. (In fact, you should use iDrive’s excellent voice commands so you can keep your hands on the wheel and your eyes on the road—Ed.)
With adjustments for throttle response, brake regeneration, steering weight, brake pedal responsiveness, transmission behavior, all-wheel drive system modes, simulated engine noise volume, and other performance-related features, you can create literally hundreds of different combinations of vehicle settings, but thankfully, the aforementioned M1 and M2 buttons on the steering wheel provide an easy way to call up one of your two favorite presets on the fly. The bigger concern, though, is how all of these augmentations and enhancements seem to conspire to hide the shortcomings of BMW’s design decisions but aren’t successful in doing so.
Chassis upgrades are a prerequisite for an M car, and with an M-tuned adaptative suspension, additional structural bracing, massive brake discs with six-piston calipers up front, four-wheel steering, and torque vectoring all on board as standard, the M5 certainly isn’t short on them. Given that, it’s reasonable to expect that an M model will have a firmer ride quality than its garden-variety counterpart.
But the vehicle has an additional measure of harshness as compared to previous M5 models, even under normal driving situations with the dampers set to their most relaxed mode, which I theorize is related to the suspension tuning needed to keep body motions controlled and maintain a sport-oriented feel despite the weight involved.
Don’t get me wrong, this is still a grand tourer of the highest order. Triple-digit speeds can be accessed with a brief stab of the throttle, and thanks to the improved ergonomics of the latest 5-Series and the model-specific sport seats that are both comfortable and supportive, the M5 will still devour highway miles with the best of them. At times when both the electric motor and the V8 are working together, the hybridized powertrain also delivers the kind of instant-on throttle response that’s typically reserved for EVs.
The 2025 BMW M5 Touring review: Way more power, way too much weight Read More »