Raspberry Pi-powered AI bike light detects cars, alerts bikers to bad drivers
Group ride —
Data from multiple Copilot devices could be used for road safety improvements.

Velo AI
Whether or not autonomous vehicles ever work out, the effort put into using small cameras and machine-learning algorithms to detect cars could pay off big for an unexpected group: cyclists.
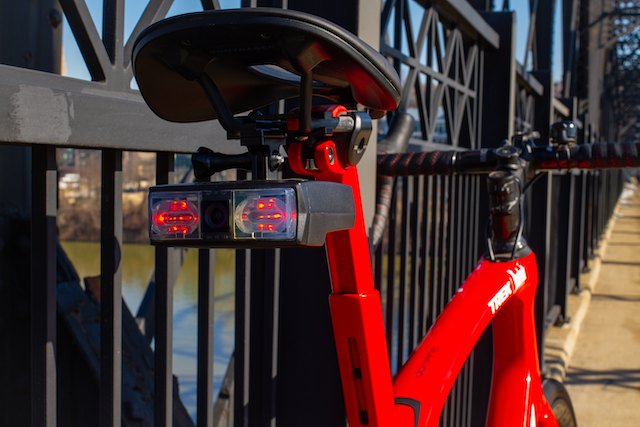
Velo AI is a firm cofounded by Clark Haynes and Micol Marchetti-Bowick, both PhDs with backgrounds in robotics, movement prediction, and Uber’s (since sold-off) autonomous vehicle work. Copilot, which started as a “pandemic passion project” for Haynes, is essentially car-focused artificial intelligence and machine learning stuffed into a Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 and boxed up in a bike-friendly size and shape.
A look into the computer vision of the Copilot.
While car-detecting devices exist for bikes, including the Garmin Varia, they’re largely radar-based. That means they can’t distinguish between vehicles of different sizes and only know that something is approaching you, not, for example, how much space it will allow when passing.
Copilot purports to do a lot more:
- Identify cars, bikes, and pedestrians
- Alert riders audibly about cars “Following,” “Approaching,” and “Overtaking”
- Issue visual warning to drivers who are approaching too close or too fast
- Send visual notifications and a simplified rear road view to an optional paired smartphone
- Record 1080p video and tag “close calls” and “incidents” from your phone
At 330 grams, with five hours of optimal battery life (and USB-C recharging), it’s not for the aero-obsessed rider or super-long-distance rider. And at $400, it might not speak to the most casual and infrequent cyclist. But it’s an intriguing piece of kit, especially for those who already have, or considered, a Garmin or similar action camera for watching their back. What if a camera could do more than just show you the car after you’re already endangered by it?
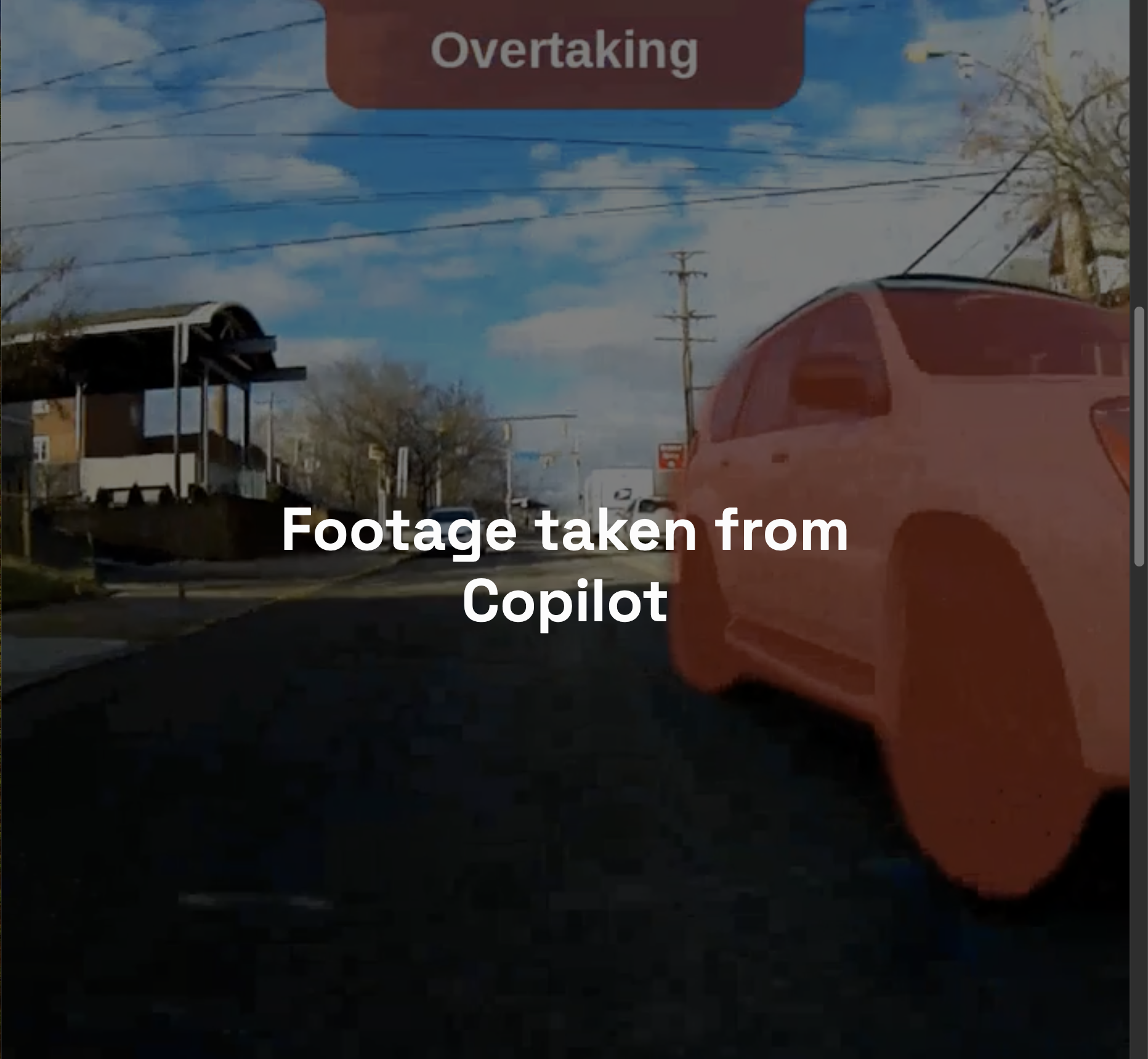
Copilot’s computer vision can alert riders to cars that are “Following,” “Approaching,” and “Overtaking.”
Velo AI
The Velo team detailed some of their building process for the official Raspberry Pi blog. The Compute Module 4 powers the core system and lights, while a custom Hailo AI co-processor helps with the neural networks and computer vision. An Arducam camera provides the vision and recording.
Beyond individual safety, the Velo AI team hopes that data from Copilots can feed into larger-scale road safety improvements. The team told the Pi blog that they’re starting a partnership with Pittsburgh, seeding Copilots to regular bike commuters and analyzing the aggregate data for potential infrastructure upgrades.
The Copilot is available for sale now and shipping, according to Velo AI. A December 2023 pre-order sold out.
Raspberry Pi-powered AI bike light detects cars, alerts bikers to bad drivers Read More »



