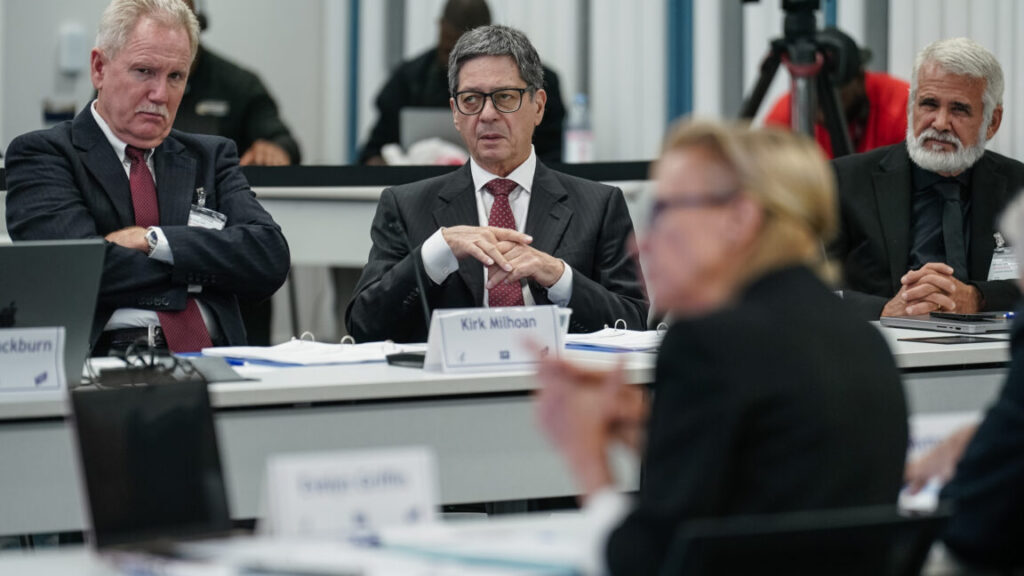
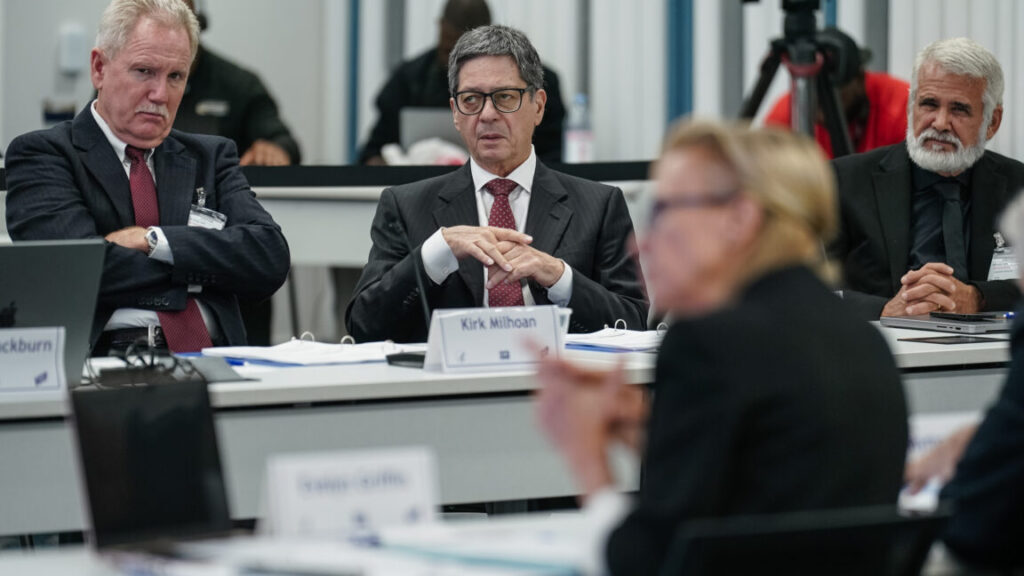
Doctors face-palm as RFK Jr.’s top vaccine advisor questions need for polio shot
He then pondered out loud what would happen if people stopped getting vaccinated. “If we take away all of the herd immunity, then does that switch, does that teeter-totter switch in a different direction?” he asked.
Backlash
In a statement, AMA Trustee Sandra Adamson Fryhofer blasted the question. “This is not a theoretical debate—it is a dangerous step backward,” she said. “Vaccines have saved millions of lives and virtually eliminated devastating diseases like polio in the United States. There is no cure for polio. When vaccination rates fall, paralysis, lifelong disability, and death return. The science on this is settled.”
Fryhofer also took aim at Milhoan’s repeated argument that the focus of vaccination policy should move from population-level health to individual autonomy. Moving away from routine immunizations, which include discussions between clinicians and patients, “does not increase freedom—it increases suffering,” she said, adding that the weakening of recommendations “will cost lives.”
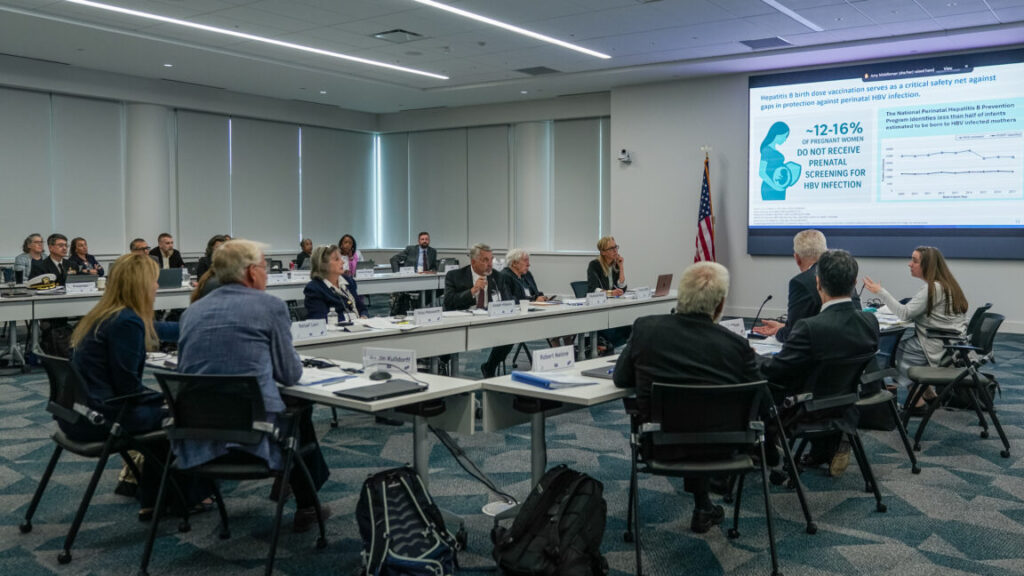
Overall, Milhoan’s comments only further erode the relevance of ACIP and federal vaccine policy among the medical community and states. According to a KFF policy brief, 27 states and Washington, DC, have already announced they will not follow current CDC vaccine recommendations, which Kennedy dramatically overhauled earlier this month without even consulting the ACIP. Instead, the majority of states are relying on previous recommendations or recommendations made within states or by medical organizations.
On Monday, the American Academy of Pediatrics announced the 2026 update to its childhood and adolescent vaccine schedule, which it has held up as an alternative to the CDC’s schedule and has been widely embraced by pediatricians. In the announcement, AAP noted that 12 other medical organizations have endorsed the schedule, including the AMA, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
The AAP’s updated recommendations are largely the same as the schedule from last year, but it is significantly different from the CDC’s recommendations, which “depart from longstanding medical evidence and no longer offer the optimal way to prevent illnesses in children,” the AAP said.
“The AAP will continue to provide recommendations for immunizations that are rooted in science and are in the best interest of the health of infants, children and adolescents of this country,” AAP President Andrew Racine said in the announcement.
Doctors face-palm as RFK Jr.’s top vaccine advisor questions need for polio shot Read More »