Stranger Things S5 trailer teases Vol. 2
We’re 10 days away from the next installment of the fifth and final season of Stranger Things, and Netflix has released a new trailer for what it’s calling Volume 2. This will cover episodes five through seven, with the final episode comprising Vol. 3.
(Spoilers for Season 5, Vol. 1 below.)
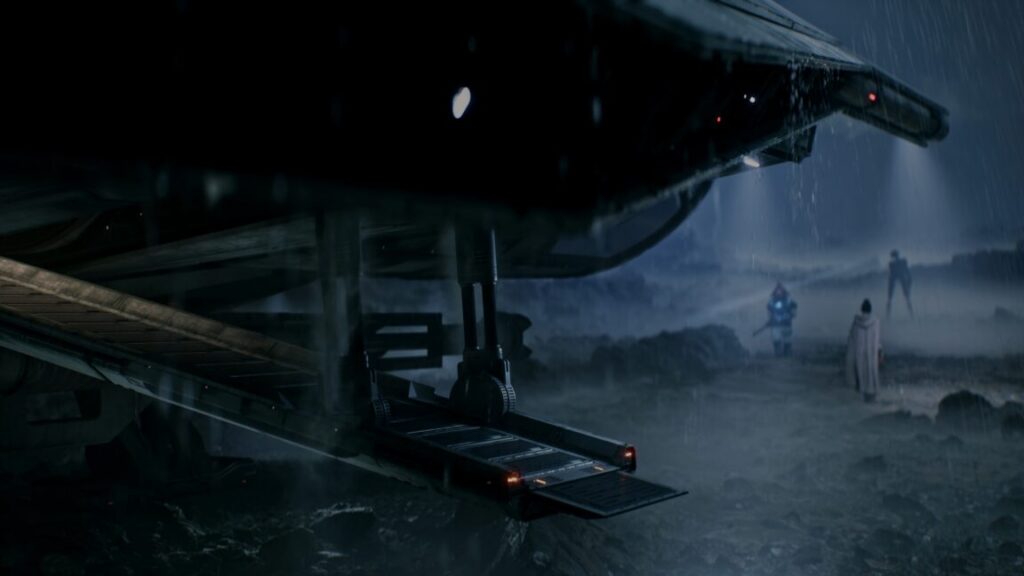
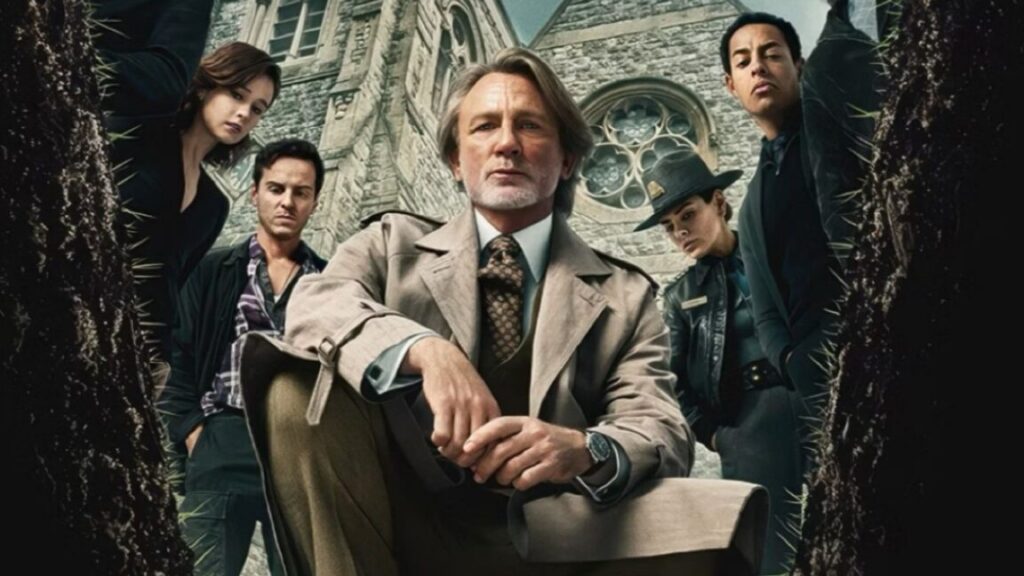
Season 4 ended with Vecna—the Big Bad behind it all—opening the gate that allowed the Upside Down to leak into Hawkins. We got a time jump for S5, Vol. 1, but in a way, we came full circle, since those events coincided with the third anniversary of Will’s original disappearance in S1.
In Vol. 1, we found Hawkins under military occupation and Vecna targeting a new group of young children in his human form under the pseudonym “Mr. Whatsit” (a nod to A Wrinkle in Time). He kidnapped Holly Wheeler and took her to the Upside Down, where she found an ally in Max, still in a coma, but her consciousness is hiding in one of Vecna’s old memories. Dustin was struggling to process his grief over losing Eddie Munson in S4, causing a rift with Steve. The rest of the gang was devoted to stockpiling supplies and helping Eleven and Hopper track down Vecna in the Upside Down. They found Kali/Eight, Eleven’s psychic “sister” instead, being held captive in a military laboratory.
Things came to a head at the military base when Vecna’s demagorgons attacked to take 11 more children, wiping out most of the soldiers in record time. The big reveal was that, as a result of being kidnapped by Vecna in S1, Will has his own supernatural powers. He can tap into Vecna’s hive mind and manipulate those powers for his own purposes. He used his newfound powers to save his friends from the demagorgons.
Stranger Things S5 trailer teases Vol. 2 Read More »