Edition #9, that School is Hell, turned out to hit quite the nerve.
Thus, I’m going to continue with the system of making the roundups have more focus in their themes, with this one being the opposite of school questions, except for the question of banning phones in schools which seemed to fit.
-
Metal Health.
-
Coercion.
-
Game Theoretically Sound Discipline.
-
The Joy of Doing Nothing.
-
ADHD Exists But So Do Boys.
-
Sports Go Sports.
-
On the Big Screen.
-
Kids Media Is Often Anti-Capitalist Propaganda.
-
Culture.
-
Travel.
-
Phone a Friend.
-
The Case For Phones.
-
Ban Cell Phones in Schools.
-
A Sobering Thought.
Henry Shevlin: I asked a high school teacher friend about the biggest change in teens over the past decade. His answer was interesting. He said whereas the ‘default state’ of teenage psychology used to be boredom, now it was anxiety.
Makes me wonder if in some deep psychosocial way there’s a trade off between the two emotions; eg, maybe boredom is essential for background anxiolytic mental processes (cf exposure to pathogens and allergies, the hygiene hypothesis).
Paul Graham: Does he have a guess about why this change occurred?
Henry Shevlin: I’ve just asked him and will let you know his response! Based our on previous conversations, I suspect he’ll say smartphones + social media as a uniquely toxic combination for teen mental health.
Reply from my friend. Basically – phones, social media, cultural doomerism, and decline of long-form literacy.
Friend: That’s about right. But also I think there’s a lot of gloom that bombards them without the social media stuff. Climate, politics, life opportunities, etc etc. Loss of literacy may be something too, reading long and in depth about things brings a degree of control.
If you are bored, you can now go on your phone until you are anxious instead. You could also make other choices, but that seems to be the default.
I’m not always with Žižek, but here I’m with Žižek.
Violeta: Žižek on authoritarian parenting:
Asking a child to visit his grandmother because it’s his duty – he has no choice but to fulfill it – is *morerespecting of his inner freedom, less authoritarian than telling him it’s his choice BUT “think about how much grandma loves you.”
This goes so much farther than children. You see it in so many other situations as well.
It’s one thing for someone to have to do [X]. And it’s good to explain it’s because [Y].
It’s another to have to want to do [X], and ‘prove’ to everyone that you ‘want’ to do [X].
Or even worse, to have to prove that you want to do [X] specifically because of [Y].
Or to have to do [X] and like it. Look, I’m enjoying this. I’m having a good time.
There is the version of asking for such a choice where the child, or the anyone else, is actually free to say no – you really are asking them to consider how much grandma loves them, but if they decide not to go, then that really is allowed and not punished.
Alas, this version is rare.
You do have to be able to tell the difference.
Julian: When I was a kid I used to get kinda sad whenever I’d hear younger children crying in public because I thought they were actually in distress, but now I’m realizing they’re kinda being dramatic most of the time.
Indeed. Most of the time that children are acting like they are in acute distress, and they are not rather obviously in actual acute distress, they are doing a strategic action to create the outcomes and incentives they want, or following through on their negotiating positions to establish credibility, and so on. I have mad respect for that. You must respond in kind as needed.
You are still the adult. You can tell, if you pay attention, which is which. If school really is hell, or there is otherwise something really wrong? It will rapidly become clear that this is the case.
I strongly endorse the principle that if you are exercising your authority as a parent, or have made your final decision, you need to own it. You should not pretend to be seeking consensus or manufacturing consent. It does not help anyone to pull a But Thou Must.
Mason: I get this perspective, but I think it’s a really bad idea to ask your kids permission for something when you know that you are not going to be accepting a “no.”
Zack: yeah, seems to optimize heavily for “kindness” at the expense of honesty.
Mason: I don’t know to what extent kids internalize this stuff, and I do think the idea that parental verbiage can ruin children is overplayed, BUT
I definitely do not want my kids getting the idea that “asking for permission” is a game that ultimately ends in a yes no matter what.
Kelsey Piper: If you’re exercising authority as the parent I think it is important to acknowledge that you’re doing that and do it. Out of profound discomfort with the exercise of authority people want to pretend everything is consensual but this can just amount to making consent fake.
There will of course be situations where you start out asking, and then at some point you are no longer asking, because time runs out or the situation otherwise changes. Again, one should be clear, and not give false choices.
Katherine Boyle: All I remember about my 90s summers is sleeping in until The Price is Right came on. By August, I knew all the characters on the Young and the Restless. I don’t remember a babysitter, an alarm clock, or anyone worried about screen time.
It’s OK for your kids to be bored.
Mason: While I’ve come around on some of the arguments against screentime, I do think a lot of the criticisms reflect the idea that childhood needs to be a continuous stream of educational and character enrichments, and that’s never been necessary to raise successful humans.
PoliMath: Kids need to be bored more, that’s when they come up with new things.
I too spent a lot of time with remarkably little ‘to do,’ and I too watched a remarkably large amount of The Price Is Right, which has its value but definitely isn’t an efficient educational option. At some points yes I think I watched Young and the Restless, I remember it being terrible. Not ideal, but It was, very obviously, fine.
As with many things, there’s a big difference between ‘this is a good idea’ and ‘this is not the best idea but it’s not a huge deal.’ I think lots of essentially wasted time in this sense falls into the second category. I don’t buy the full Garrion Keilor ‘the kids need to actively be bored,’ but they do need breaks without pressure, and if that time is mostly wasted that is fine, the optimal amount of that is not zero.
We have decided that existing while boy all but counts as having ADHD.
We put the ADHD diagnosis on 15.5% of American adolescents, 21% of 14-year-old boys and 23% of 17-year-old boys, for a total of seven million American children.
Yes, ADHD is very obviously a real thing. I’ve seen it. And yes, rates of actual ADHD are likely somewhat higher than they used to be, for various reasons.
This is still very obviously an epidemic of overdiagnosis. It is way of expressing a preference for being willing to sit still for long periods of time.
In the past, if not playing along? You’d force them to, or else. We now think that’s bad.
Nowadays, not playing along? Deploy the meth. That’s much better, you see.
Telling kids, in particular boys, what not to do is not a good strategy. Never works.
What does work is to give them positive things to do instead, and positive status hierarchies to climb by doing so.
Alexander: Boys don’t need “anti-misogyny” training in school. They need shop classes and sports teams. This is not a boomerism, but based on what actually works as an intervention.
…
Telling people “don’t do the bad thing” is a bad intervention across the board. What works is providing alternatives.
This is why we see anecdotes like, “Boxing saved me from gang life.” And also supporting data beyond anecdotes – sport participation has a causal effect.
So you end up with boys who go a bad way who tend to be:
-
Ostracized losers; especially low in status. They easily get sucked into radical ideologies. They have a lot of resentment for the world around them, or for target groups.
-
The low status / high aggression group. These are the boys who go on to commit crimes.
Effective interventions will target the esteem and status of boys: providing them a new dominance hierarchy to work within and reducing isolation, providing supportive peers and mentors. Sports teams will do this.
Effective interventions will also teach boys prosocial and creative skills: shop classes do this. Give them a focus and an interest and a skill that they can go forward with into society.
He cites the classic failure mode, the old DARE anti-drug problem, which warns you not to do drugs so kids respond by doing drugs more.
I found this take intriguing.
Kelsey Piper: My most bespoke parenting opinion is that big screens are perfectly fine for kids but small screens are bad. We have a projector in our living room with a huge 6’x10′ screen. When the kids watch things on it, they are in motion. They roll around giggling; they climb on the couch, they burrow in the blankets; they wander off, they talk to each other and to you. When something hilarious happens they’ll jump up and down with excitement; when something scary happens they’ll snuggle up. And if they’re bored they’ll walk away. After five minutes of My Little Pony on the big screen this morning, the baby declared “done!” and left.
This is not how they act with an iPad or phone playing the exact same content. They act way, way more glued to the screen. I don’t think the baby has ever told me “done!” when handed an iPhone playing Sesame Street. I think the tiny window means their focus is narrowed, and the screen ends up being kind of all-consuming, whereas a big screen is more like a window through which interesting things are happening; a feature of the room, but not the only thing in it. Also with an iPad or phone, a baby wants to interact, press buttons, shake it, move it, but all possible actions just interrupt their show and frustrate them.
We still sometimes resort to a phone as a distraction on long car trips, but my intuition here is that the form factor matters a lot.
Nicole Ruiz: I feel like big screen = social consumption
Small screen = isolated consumption
Consuming together is worlds better in my opinion!
Kelsey Piper yeah this is definitely a big part of it!
My experience is more ‘big screen is dangerous, small screen is way worse.’
The big screen is better, somehow providing a better experience and also a less zombifying or addictive one. However, at least in my experience, that doesn’t mean kids don’t threaten to go complete zombie if you aren’t careful. You absolutely have to watch screen time and content if you don’t want that to happen, no matter how big the screen might be.
Not all of it. But quite a lot of it. It is remarkably hard to avoid.
Discussing Film: First look still for Pixar’s ‘HOPPERS’
The film follows a girl who transfers her mind into a beaver to help the animals fight the construction plans from the local mayor.
Gary Winslett: I think people without kids underestimate how much children’s programming is inundated with propaganda that’s a combination of anti-capitalism, anti-development, and climate doom. It’s not good.
I think it contributes to unnecessary anxiety and also pushes some towards political radicalism. Again, not good.
I get the many reasons why this is the natural outcome of the types of people making kids TV making TV for kids. Similar forces also cause a lot of vegetarian advocacy. It’s all really, truly obnoxious and I think it does a lot of very real damage.
Content consumed by children used to be made by adults, whether or not it was aimed at children, and was generally not ephemeral or optimized too hard for short term engagement, which gave motivation and opportunity to learn references and cultural touchstones. Now much of the content is short form and optimized in hyper-competitive landscapes, so there’s no slack for Parental Bonus or being secretly high quality or otherwise providing extra value, and much of it becomes ephemeral and of-the-moment. A shame.
But also, if you miss a reference now – whether or not it is ‘The Odyssey’ – you can not only Google it, you can ask Claude (or another LLM). And most entertainment is easy to pause so you can ask, and this should get even easier and better over time – by the end of 2025 the AI should automatically see the content you’re watching, and understand the context of your questions, which you’ll ask in voice mode, and so on.
Movies are designed for everyone to be off their phones, so they’ll be the exception, but this should give us the opportunity to do much higher-level stuff once people get used to it, since no one need get lost. I can’t even with for example War and Peace, I don’t want to have to try and keep track of all that, but once I get a Daylight Computer I probably won’t have to?
(And if you ever don’t get what something I say is referencing, or it seems like there’s another level to it, and it’s very clearly not explained and you’re curious, asking Claude is probably a good idea. I’m often very intentionally not explaining, IYKYK, etc.)
The problem is if kids go the other way and don’t want to know the references.
This model seems very right:
Cartoons Hate Her: An unfair but nevertheless true reality of being a grandparent is that your adult children with a baby or toddler will not visit you nearly as often as you should visit them, provided you’re physically able.
This was an issue of conflict with my in-laws. They were like “we visit you all the time and you don’t visit us.” (One of our kids has extreme motion sickness btw.) eventually they were like “fuck it we’re moving to your town.” Lol
Mason: Depending on the children and their ages, there is a certain amount of time in the car that you can anticipate Everything Will Be Fine. For us, right now, that’s 35 minutes. After that, we’re operating purely on God’s mercy.
If you want to see your grandkids, or generally see someone with young kids, on the regular, you need to be willing to come to them more often than not. That’s life.
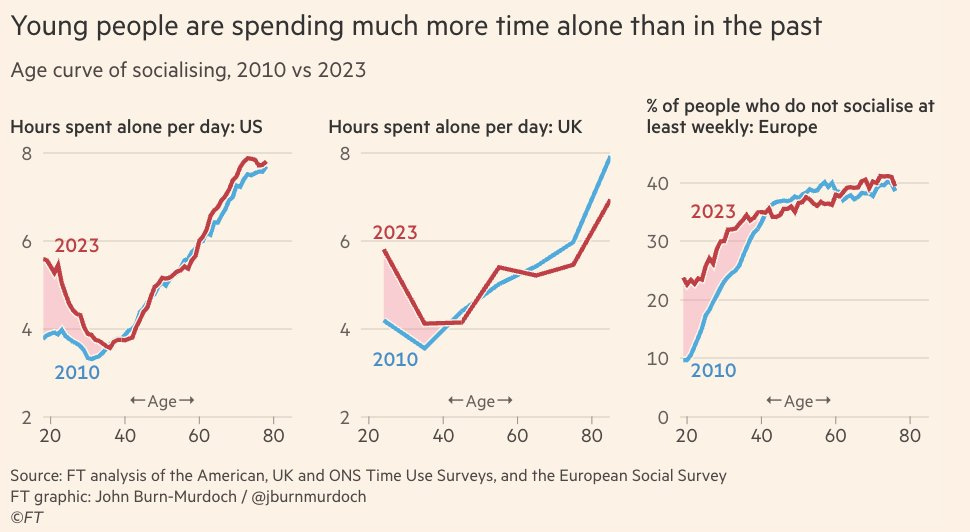
Alice Evans: What do a US 20 year old & a 60yo have in common?
They spend about 6 hours a day alone.
Is the rise of solitude hurting our mental health?
New graphs by the great @jburnmurdoch
Young US men are increasingly spending time alone.
“We are all free agents” – you may reply,
“STOP judging and let people embrace what makes them happy!”
Great point, but does spending time alone make people feel fulfilled?
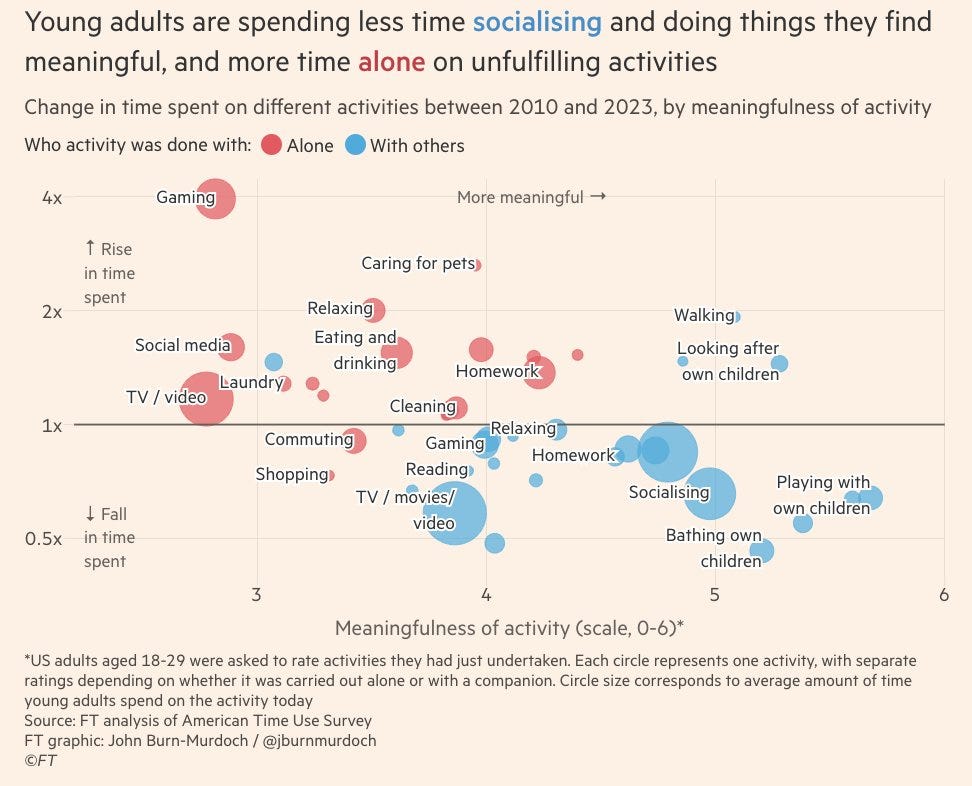
But when asked to rate a range of activities,
People tend to say that gaming and social media are the LEAST meaningful.
Social activities are generally ranked as more meaningful.
That’s a hell of a graph. Walking is surprisingly ‘meaningful.’ As is watching TV or movies with others, that gets you almost to 4 on this scale. And I love my kids, but ‘bathing’ and ‘looking after’ are almost as meaningful as ‘playing with’ and better than anything else? And doing homework together is a 4.6 and alone it’s a 4.2? Homework?
I could go on. Yeah, I don’t know about this chart.
I do still buy the core premise, that the things we do with others tend to be more meaningful, and that we’re doing less of them.
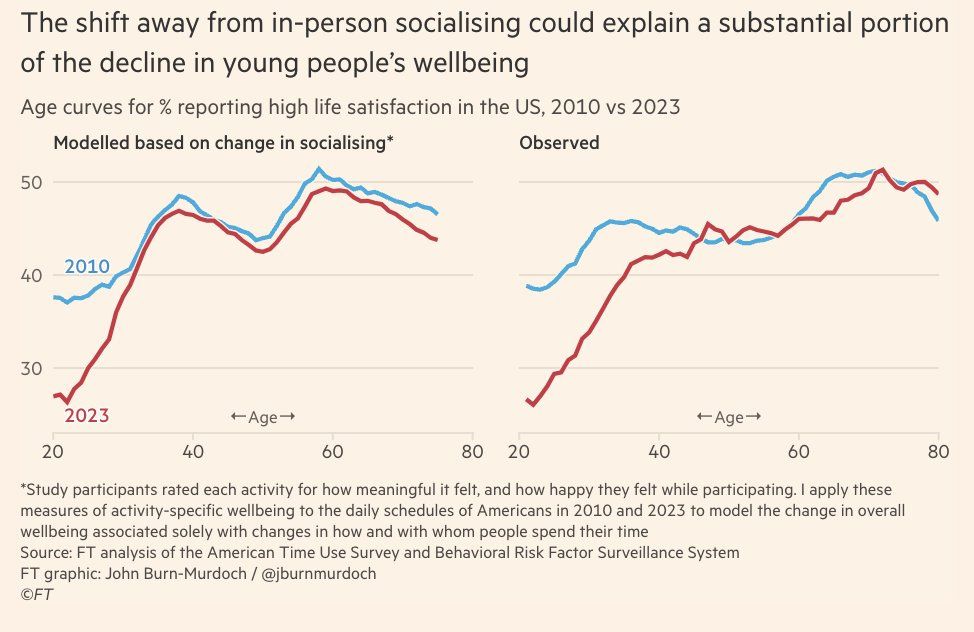
People consistently report higher life satisfaction when they are being more social,
So using just the change in socialising (2010 vs 2023), his model predicts the observed age curves in life satisfaction.
All this coincides with advances in smart phones & personal online entertainment.
Social media & gaming are designed to be addictive.
Like gambling, drinking or nicotine, phones buzz with excitement, call us over & many people get sucked in.
Even if they later feel worse…
Let me share some related research from Pew:
A quarter of Black & Hispanic US teens say they use TikTok and YouTube “almost constantly”
It’s actually worse than that, if 25% use TikTok ‘almost constantly’ and 24% to it with YouTube, and 18% for Instagram, well, not that many are ‘constantly’ doing all three?
And indeed:
58% of Hispanic US teens say they use the internet “almost constantly”
I mean, I use the internet almost constantly, so maybe fair? But this is different.
Are kids with phones better off than kids without phones?
I mean, yeah, data says so, but that rather obviously is not entirely causal. To the extent it is causal it is largely a collective action problem.
If everyone else has a phone, then you not having a phone isolates you.
Elizabeth Nolan Brown: Kids with smartphones are less depressed, less anxious, more social, get more exercise, & experience less cyberbullying than kids w/out smartphones Funny how this new study got a fraction of the coverage that fear-mongering “phones are ruining our kids!!!!” surveys & screeds do.
For the first part of this study, researchers surveyed 1,510 Florida kids ages 11 to 13. On almost every metric measuring well-being, smartphone-owning kids showed better results.
For instance, kids with smartphones were more likely to spend in-person time with friends. “Contrary to the position that smartphone use is associated with fewer in-person meetups with friends, on average, smartphone owners spend nearly three days a week in-person with a friend(s), while kids with no smartphone spend closer to two days a week in-person with friends,” write the researchers. “The same trend was seen for tablet ownership, daily video gaming, and daily social media use.”
…
This doesn’t mean that smartphone use was universally positive. Kids who slept with their phones in their rooms got less sleep on average, suggesting that parents might want to think about confiscating phones before bedtime.
Heavy video gamers were more likely than light gamers to report trouble stopping tech use once started, and heavy users of social media were more likely than lighter users to report sleep issues.
And respondents who reported posting publicly and often on social media were more likely to report sleep issues and symptoms of depression and anxiety, possibly related to the exposure to mean comments and other forms of cyberbullying that posting could bring. Unsurprisingly, kids who experienced online bullying were more likely to report negative effects from technology.
To be fair, further down, she does admit to the obvious big confounding issue.
Elizabeth Nolan Brown: While we’re on caveats, there’s a big one on this study overall. The kinds of families that get smartphones for their 11- to 13-year-olds may be fundamentally different from those who don’t. And the kinds of kids in this age group whose parents deem them ready for a phone may also be different from the kids whose parents don’t think they’re ready. So some of the differences in well-being between phone-wielding kids and those without phones could come down to differences that have nothing to do with technology.
…
Among social platforms used by survey respondents, Facebook and Facebook Messenger ranked fifth, behind YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat.
This isn’t about socioeconomic status (SES). Indeed, that runs the opposite way.
Between 80 and 87 percent of kids in families with incomes of less than $100,000 had smartphones, while only 67 percent of kids in families making $150,000 or more did.
They did do statistical weighting (based on parent/guardian’s education, household income, household size, child’s age by gender, and child’s race/ethnicity) but given income runs the other way that is unlikely to catch the issues. They did not control for attributes of the children prior to getting the phones or in previous years.
Are the richer families making a gigantic mistake? What did they see?
Aella (note the difference was not this big): This would be cool if true but the numbers feel a lil sus. A difference of 2 to 3 days in a week spent with friends is quite a big effect, and seems weird for this to come from something as simple as smartphones.
Amal Dorai: All the kids in school have smartphones and are constantly texting each other, so if you don’t have one, you either 1) don’t care about texting them 2) your parents don’t care about you texting them or 3) you can’t afford a smartphone (rare). Deeply confounded.
There was clear miscommunication about the time with friends numbers, which were 2.7 days/week for kids with phones versus 2.2 days/week for those without. But what’s even weirder is the same gap applies to daily video gamers (2.8 vs. 2.3) and social media users (2.7 vs. 2.2).
And then, even weirder, to tablet owners? What? Again it’s 2.8 vs. 2.3.
Then kids say they spent an average of 3.2 hours per day (!) ‘hanging out with friends online.’ To which I say, really? That’s… quite a lot, especially since it’s all respondents including those without phones. Kids reported 4.4 hours on their smartphones and tablets per school day and 6.3 per non-school day, which means the majority of that was supposedly spent ‘with friends.’
We also have this meta study of social media abstinence interventions, which finds zero effect on mental health. This is unfortunate, but what it does not mean is that everyone having phones is good for mental health.
Indeed it says the opposite, because of the isolation effect. If previously you had a phone, and now everyone but you has a phone, you are going to have a hard time coordinating with your friends, meeting with them and talking to them. That’s going to be bad for your mental health. So the fact that there was zero impact suggests that the phones are net negative.
A reader offers this list of studies on tech in schools.
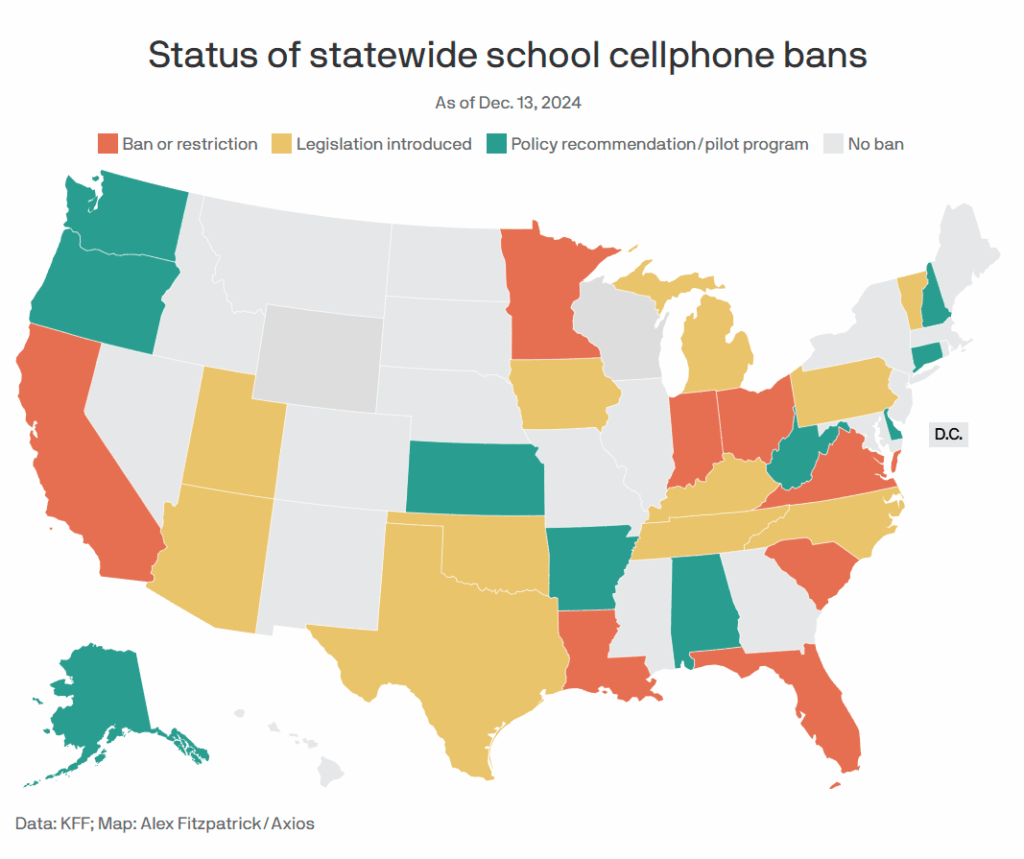
It’s happening. New York State is banning cell phones, from bell-to-bell.
Mike Bloomberg: Great to see the New York State legislature ban cell phones in schools, a step we took in NYC nearly 20 years ago. Unfortunately for students and teachers, the policy was ended by the next administration. Experience and studies both show that cell phones in school are harmful to student learning. All states should follow New York.
Momentum for banning phones in schools continues, from January 2025, and Colorado targets them next.
For those wondering what to do now, a school offers a guide.
Rob Wilbin: Ezra [Klein] today saying social science can’t settle whether kids on phones/social media is harmful reminded me of Tyler’s interview w Haidt.
Cowen pushed back hard but, unusually, his own audience wasn’t having a bar of it.
It thinks it sees its own kids being harmed and trusts its own eyes over any social science or argumentation.
Even if one concluded the peer reviewed study literature pointed in the direction in question, I refuse to be gaslit into not believing that things that are obviously happening are indeed happening, or that obviously bad for people things aren’t bad for people, purely because ‘the evidence is weak’ or any given statistic did not find an effect. Most other people are in the same boat at this point.
A new study tries out a ‘soft commitment’ app on phones they tried out at university. It successfully convinced students to reduce phone use in class, leading to improvements in classroom focus, attendance and overall academic satisfaction. However there was a substitution effect where students studied less, and only a small (statistically insignificant) increase in grades. So a soft nudge made things modestly better (but only modestly) in what seems like a Pareto improvement?
Natural Hazard: Person A: “I think all the most important people in my life are conspiring to hide important information about the world from me.”
Others: “That’s crazy, paranoid, schizo-type stuff.”
Person A: “Did I mention I’m 9?”
Others: “Oh, okay, yeah.”