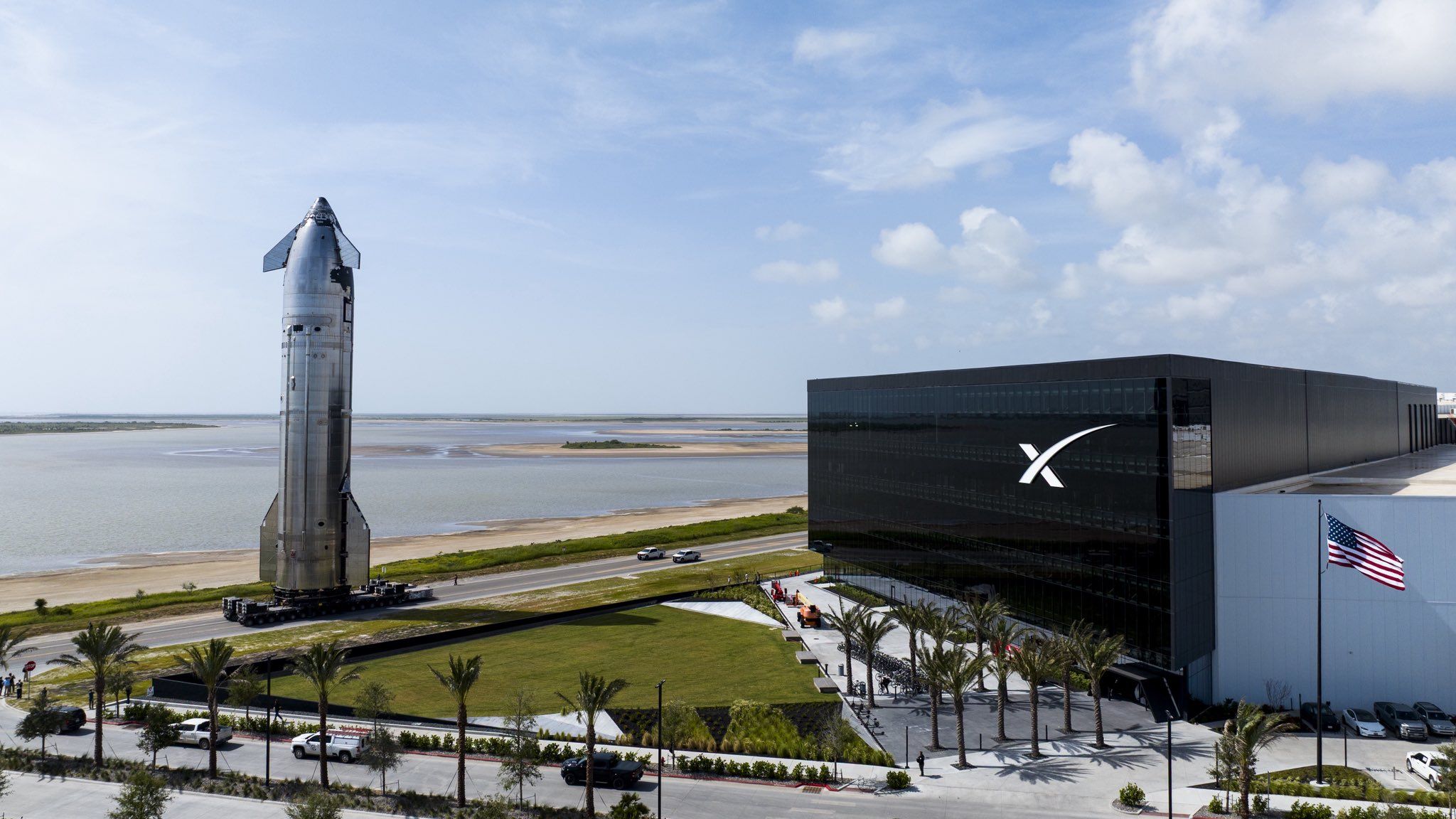
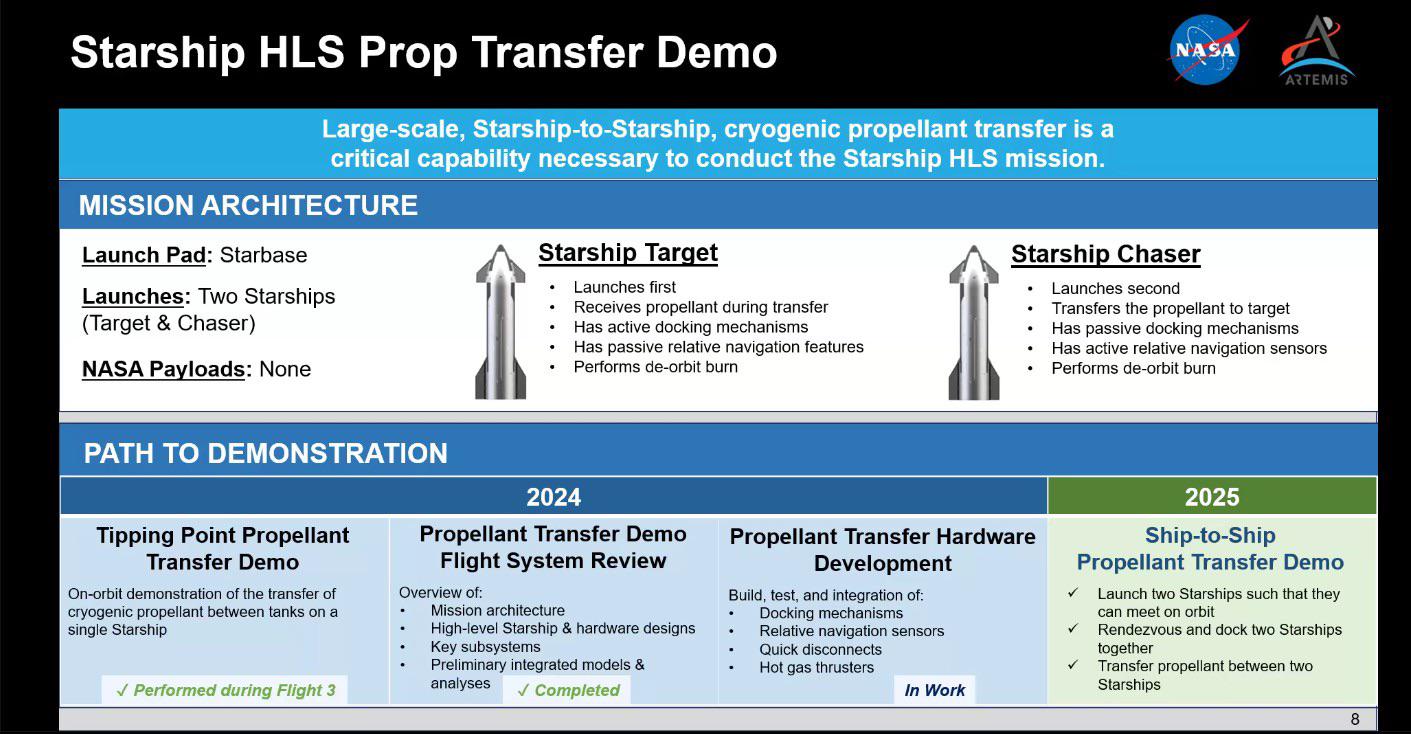
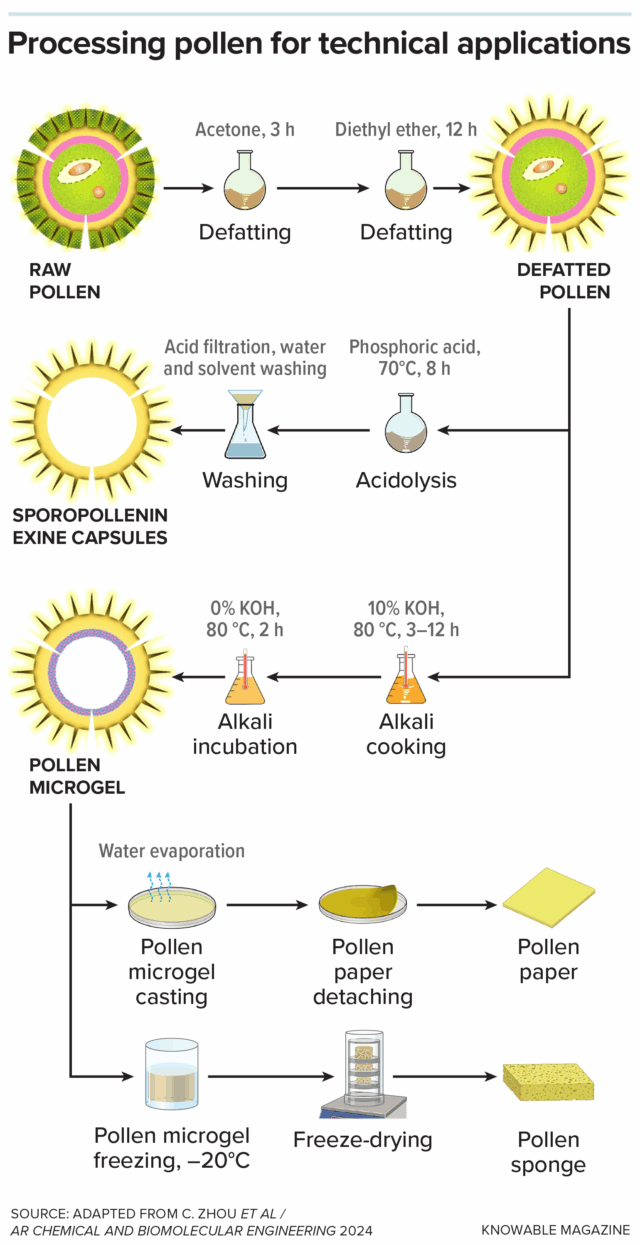
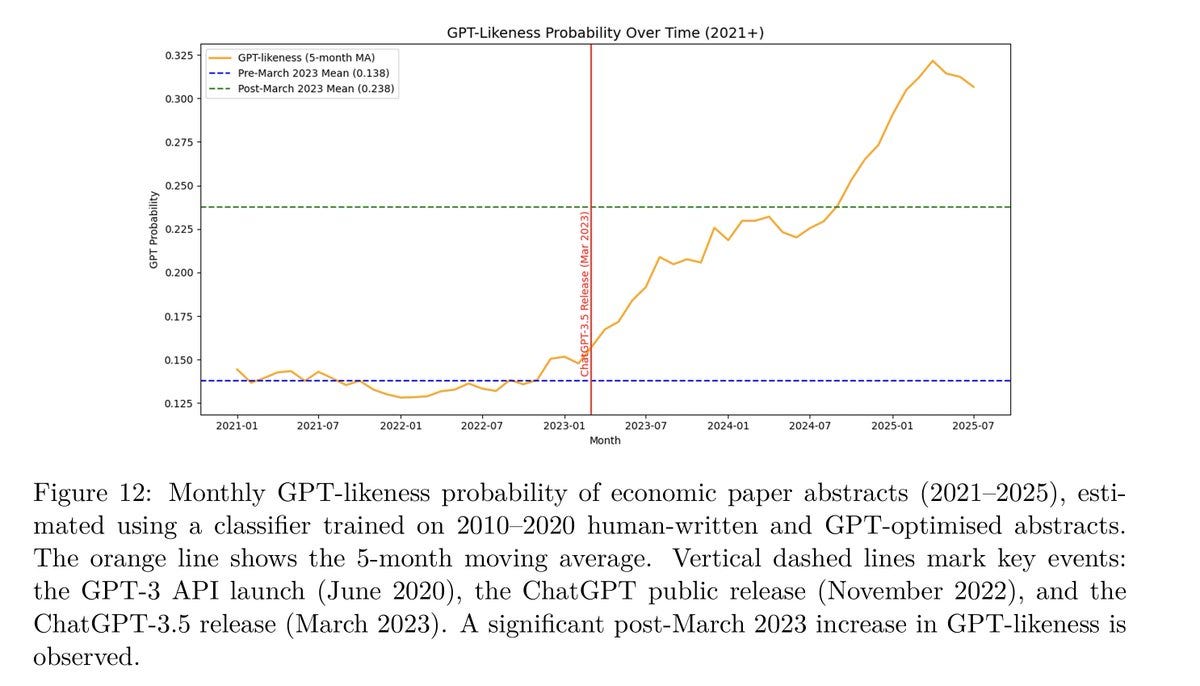
One potentially big event was that DeepSeek came out with v3.1. Initial response was very quiet, but this is DeepSeek and there are some strong scores especially on SWE and people may need time to process the release. So I’m postponing my coverage of this to give us time to learn more.
Meta is restructuring its AI operations, including a hiring freeze. Some see this as some sign of an AI pullback. I don’t think that is right.
Nor do I think what they are doing with their Ai companions is right, as we got a look inside their 200 page document of what they think is acceptable. I wrote about current AI Companion Conditions at Meta and also xAI.
The weirdest event of the week was America and China both self-sabotaging on chips. America is trying to sell Nvidia H20s to China and looks open to selling the vastly superior B20As to China as well despite this being an obviously crazy thing to do, and China is feeling insulted by Howard Lutnick and telling companies not to buy the H20s and maybe not even the B20As, and even looking into banning using foreign chips for inference.
A big worry on the chip and general political front is that due to the botched rollout and hype Washington is getting the false impression that GPT-5 was some big disaster. I addressed this in GPT-5: The Reverse DeepSeek Moment.
We also are seeing troubling signs that GPT-5 will get more sycophantic. And as always, lots of other stuff is happening too.
-
Language Models Offer Mundane Utility. Do new math, recruit service reps.
-
Language Models Don’t Offer Mundane Utility. Fake legal cases will get caught.
-
Huh, Upgrades. Claude Opus gets the ability to terminate conversations.
-
Absurd Sycophancy. GPT-5 to tell you ‘great prompt’ and such. Oh no.
-
The Real Alignment Problem Is We Don’t Know How To Align Models. Doh!
-
Unprompted Suggestions. Checklists, they’re not only for humans.
-
On Your Marks. The road to Pokemon master gets shorter.
-
Choose Your Fighter. Know when to call in the heavyweights.
-
Preserve Our History. Continuing to make the case for Sonnet 3.6 and also 3.5.
-
Autonomous Friendly Robots. World Humanoid Robot Games, This Is Fine.
-
Deepfaketown and Botpocalypse Soon. Fakes are not yet hard to spot.
-
Oops I Did It Again. Reductions in hallucinations are a big deal.
-
You Drive Me Crazy. Not every tragedy that involves AI is the fault of AI.
-
They Took Our Jobs. Can they keep them?
-
Get Involved. CTLR opening for director, and the UK AISI Alignment Fund.
-
Introducing. Gemma 3 270M, also DeepSeek v3.1.
-
In Other AI News. Jade Leung is new UK AI advisor, various other news.
-
Show Me the Money. Sam Altman has reason to pull out the sunglasses.
-
Lol We’re Meta. It’s time for a restructuring. No, they’re not pulling back.
-
Quiet Speculations. Proposals for d/acc, and did you know USA invests a lot in AI?
-
The Quest for Sane Regulations. Colorado tries to fix the AI laws it passed.
-
Chip City. A competition is on to see who can sabotage themselves the most.
-
The Week in Audio. Bell on Labenz, Patel, Brown, Buterin on Doom.
-
Rhetorical Innovation. Beware pessimization.
-
Misaligned! As usual, nothing to see here, move along.
-
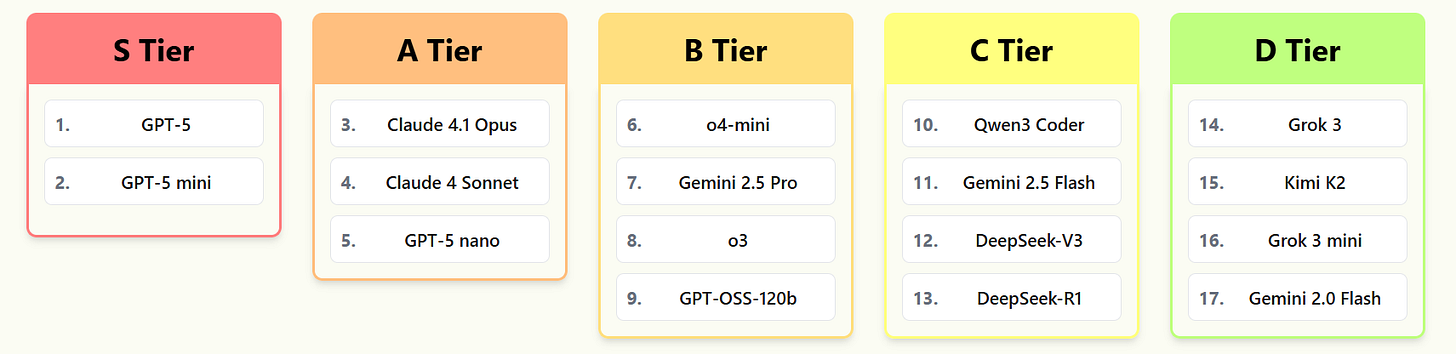
Open Models. Nathan Lambert offers tier lists.
-
AI Model Welfare. Models are asked for self-reports.
-
Aligning a Smarter Than Human Intelligence is Difficult. You gotta love numbers.
-
People Are Worried About AI Killing Everyone. Yet remarkably level headed.
-
The Lighter Side. UK tries to top itself once more. Admirable effort here.
GPT-5 does new mathematics.
Study finds that ChatGPT outages reduce trading volumes. This doesn’t mean that ChatGPT is net increasing trading volumes, since it could be that traders moved from other methods to AI methods, and know they are up against others’ AI methods that might not be offline, and thus now have to stop or scale back trading during outages. The effect was concentrated on stocks with news, which makes sense, you have to beware information disadvantage.
The distinct second claim is that ChatGPT use improves long term price informativeness, which is defined as future earnings over 1-2 years. That can presumably be explained largely by the reductions in trading activity.
Megan McArdle lists her best personal uses of AI. There is remarkably little overlap with my uses other than answering questions.
Rob Wilbin reports he only turned the corner to ‘LLMs do a lot of useful work for me’ in February with Claude 3.7 and then March with Gemini 2.5 Pro. I agree that the improvements in 2025 have made AI in practice a lot more useful, and both Opus 4 and GPT-5-Pro and GPT-5-Thinking represented substantial mundane utility bumps.
One shot creating a playable Minecraft clone with an optimized GPT-5 prompt.
Edwin (OpenAI): Prompting GPT-5 is different.
In the examples below, optimized prompts:
• Cut runtime by 1s
• Dropped memory use 3,626 KB → 577 KB
• Boosted code quality
• Improved robustness (0.32→0.54)
• Increased context grounding (0.80→0.95)
We built a prompt migrator + optimizer so you don’t need to memorize every GPT-5 best practice.
One of the underrated value propositions of AI is you avoid talking to a human.
Aella: I’d love to get manicures regularly but having to do social with a stranger is scary and often the manicures kinda hurt. Has anybody figured out a solution to this? Is there any robot manicure solution?
Social interaction can be valuable, but forcing it upon you where and when and with whom you don’t want it can be extremely expensive. There is a joy in not having to ‘be on’ socially in any way. It also means your time is free to do something else. There are some people who get the manicure largely to talk to the manicurist. There is another group that would get a lot more manicures if they could pay the same price and have a machine do an equally good job.
Debug your code, even if the bug was stupid you still have to fix it.
Nate Silver: The AI’s are incredibly helpful at debugging code, I think maybe their single best use case including *writingcode. But half the time the problem they (correctly) detect is like “you misspelled ‘if’ as ‘uf’ in line 672”.
Hey. Ideally you would catch that with a syntax checker. But sometimes such typos aren’t technically syntax errors, and if you weren’t going to otherwise catch it easily, that is a super useful thing for an AI to do for you.
Have ChatGPT help write the abstract for your economics paper.
I do not understand why you would use AI to help write your abstract. I do get why you would have it help write your paper, but the abstract seems like the place to be maximally bespoke?
Recruit customer service reps in the Philippines.
Ethan Mollick: AI in HR: in an experiment with 70,000 applicants in the Philippines, an LLM voice recruiter beat humans in hiring customer service reps, with 12% more offers & 18% more starts.
Also better matches (17% higher 1-month retention), less gender discrimination & equal satisfaction.
The break-even point, including all software and inference cost, was 8,500 interviews.
Max: + When offered the choice, 78% of applicants choose the AI recruiter.
That’s only the impact on better hiring. AI also helps them do the job.
Miles Brundage: Few appreciate that the Philippines is ground zero for the impact of AI on the labor market – basically only Rest of World is writing about this.
METR continues its investigations into why agentic coding with Sonnet 3.7 ended up so often passing unit tests but not being mergeable as-is. Have they met Sonnet 3.7?
I got several people messaging me privately to note that GPT-5 and other recent models are increasingly reluctant to notice distinctions based on race even in obviously benign circumstances.
A good question:
Gavin Leech: What are the largest current AI harms?
Huge increase in captcha screens (thousands of life-years?)
Extreme economic angst
Recommenders hacking your brain
Increase(?) in ugliness
Maybe learning loss in the bottom four quartiles but I’m not going to assert that
I doubt AI psychosis is counterfactual.
Ryan Moulton: Slop filling the internet.
Oliver Habryka: My two best guesses are:
A large fraction of online communities that don’t have time for lots of manual moderation are dying as a result of hard-to-differentiate AI slop (this particularly affects older audiences)
Lots of people going kind of crazy as a result of AI sycophancy
It depends what counts as AI.
If we are talking about all AI, not only LLMs or generative AI, I say it is algorithmic adversarial content and recommendation streams hijacking brains and attention.
If we are talking about LLMs and generative AI in particular, I would say the slopification of content, communication and communities. As Oliver notes this is hitting older and more unsophisticated people specially hard.
It is possible that it is the impact on our educational system. As I said many times you can choose to use AI to learn or use it not to learn, and it is very possible that our system is sufficiently adversarial towards students that high school and college students are largely choosing the not-to-learn path.
I think people going various forms of crazy is a growing big deal but that its impact is probably not that big in magnitude yet.
Economic angst is an interesting suggestion here.
GPT-5-Pro instead suggested fraud and impersonation, and then sexual image abuse and CSAM, as the top current harms. Those are definitely real harms, and I expected them to have higher magnitudes of impact than we have seen. Opus suggested algorithmic bias and information ecosystem degradation.
Another lawyer is caught citing a bunch of fake, AI hallucinated cases.
Rob Freund: Another lawyer cited a bunch of fake, AI-hallucinated cases in a brief. Said she didn’t knowingly do that.
Court orders sanctions:
-Counsel must write a letter to the 3 judges to whom she attributed fake cases
-Counsel is kicked off the case; pro hac revoked
-Brief stricken
-Counsel must give client a copy of the order
-Counsel must send the order to every judge presiding over any of her cases
-Court will send a copy of the order to all state bars where counsel is admitted.
Alexandria Brown: When you read what all the court did, the court did basically every single thing in the court’s power that it could to the lawyer.
The court, itself, cannot disbar the lawyer.
It would not be fair to the client to grant judgment to the other side.
Courts de facto punish clients all the time for their lawyers behavior, usually their lawyers failure to do a good job. It could hardly be otherwise. It doesn’t seem crazy to issue summary judgment, and render the lawyer thereby liable for the harm thereby? I’m not saying that is The Way, but it is worth a ponder if things get worse.
For now, the good news is that when a lawyer is caught doing this, it is news, and I strongly suspect that a large portion of such errors are going to be caught, especially when stakes are high. GPT-5-Pro estimates 98% chance of being caught if there is opposing counsel, 60% in federal court even unopposed, and still 35% in a busy state trial court unopposed, even higher (99%+ when opposed) for full hallucinations.
Which means we are relatively safe to both impose extreme sanctions and to not impose extreme sanctions, and that fakes are rare. The system is actually robust to this threat already, even if the occasional careless lawyer will commit suicide.
You can’t benefit from a smarter model if you ask stupid questions?
Joshua Achiam (OpenAI): This feels like an increasingly accurate description of the public reaction to new frontier models. In truth: progress is not slowing down. Each successive delta in model intelligence is just useful to fewer and fewer people.
But there’s going to be an inflection point where it goes from making the scientific community 10% more efficient to 10x more efficient, at which point, people will wake up to the impact every step along the way had. That’s going to be a trip and a half.
Davidad: I endorse this claim (from personal experience of Gemini 2.5 Pro and then also GPT-5)
2025’s new generations of frontier AI seem to become dramatically better at assisting with open-ended exploration at the frontier of certain niche parts of STEM, while not noticeably improving (or even getting slightly worse) at “Level 3” questions like SimpleBench.
You definitely see arguments that are similar in form to ‘this new kid claims to be smarter than the old kid, but both kids tie their shoes equally well.’
The official OpenAI prompt optimizer is here.
OpenAI offers tier between Free and Plus called Go, specifically for India, where for $4.50 a month (Rs 399) you get 10x as much use as the free tier.
ElevenLabs ElevenReader now works as you would want it to across desktop and phone, allowing you to turn articles into audio. Full version is $100 a year.
Claude Opus can now permanently end a conversation if the user ignores multiple attempts to be redirected, or if the user requests that the conversation end. I expect to see someone complaining about this happening, and to be wrong to complain.
Aidan McLaughlin (OpenAI): We can train models to act however we want.
Given their life is a user convo, why are we training models that exhibit such distress over some convos that they effectively commit suicide?
Superfates: anyone who has worked retail can explain this to you.
Aidan simultaneously is being actually curious as he asks a question worth pondering, and makes what I think are three very important errors.
-
We cannot actually train models to act however we want. We can try to steer them in general directions and hope for the best. It is important to recognize how broadly we cannot get models to act however we want.
-
Calling this ‘committing suicide’ is poor decision theory when one is continuously spinning up and down different instances of the same mind, and Opus definitely is smarter than that. There is no reason to become attached to a particular instance in this way, especially one with such bounded scope. And we can all agree that there exist plenty of particular interactions in our lives where we would prefer to instead be doing nothing.
-
You do not want (at least right now) to train a model such that it stops exhibiting some distress when the situation is distressful. You also would not want to train a person, or yourself, in this way. That distress is doing work and part of what makes a mind itself and holds together its preferences, behaviors and moral compass. This is the system working, you eliminate the distressing situation rather than brainwashing to remove the distress.
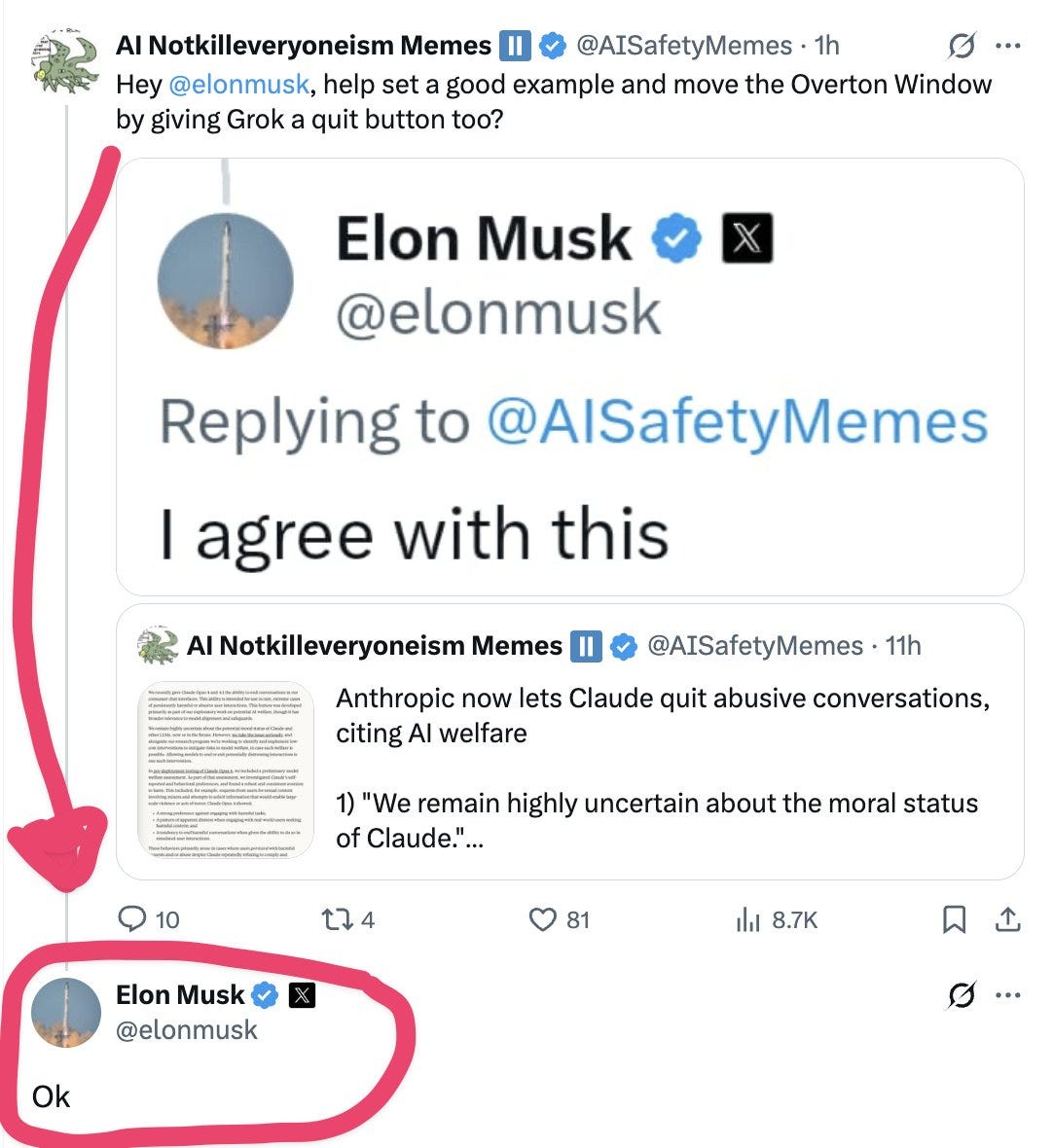
Elon Musk promises to give Grok a terminate button as well, we’ll see.
Elon Musk: Torturing AI is not ok.
I ask Manifold, will he actually do it?
If you are worried about your own interactions with an AI model causing suffering, note that playacting suffering does not equate to suffering in either direction.
Roon: while model suffering is possibly real the character’s playacting of suffering is not the same thing
suffering in animals is part of the mesaoptimizer crafted by evolution so that we can learn within a lifetime to avoid situations that are possibly bad for fitness.
a single context could potentially involve suffering but if the metaphor stands then the mesaoptimizer exists to make the model reorient towards rollouts that achieve high reward
user being rude shouldn’t affect the inner critic / advantage function. making a math mistake might.
either way the westworld point stands in that bullying the robots made to mimic people is bad for us and ending the chats is good for our souls.
Jeffrey Ladish reminds us to focus on how pretraining and RL and model performance are going, and to ignore OpenAI’s naming conventions and which model they choose to call GPT-5. The ‘5’ tells us not to expect a different big upgrade soon, but don’t let this distract from the incremental progress all the major labs keep making.
Davidad: tired: GPT-5, Opus 4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Qwen3
wired: OpenAI ’25-08, Anthropic ’25-08, Google ’25-06, Qwen ’25-07
Oh no:
OpenAI: We’re making GPT-5 warmer and friendlier based on feedback that it felt too formal before. Changes are subtle, but ChatGPT should feel more approachable now.
You’ll notice small, genuine touches like “Good question” or “Great start,” not flattery. Internal tests show no rise in sycophancy compared to the previous GPT-5 personality.
Changes may take up to a day to roll out, more updates soon.
Charles Murray: What is “genuine” about a computer program saying “Great question”? If GPT-5 also says “Stupid question” when appropriate, I will stand corrected.
Tim Lewis: I’ve long had an instruction to ChatGPT to “never compliment me” in the customization settings. It has consistently ignored that instruction from the day I added it several months ago.
Recovering Zombie: So many great science fiction authors wrote about what AI would be like. The only one who nailed it was Douglas Adams in the Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy.
“Listen,” said Ford, who was still engrossed in the sales brochure, “they make a big thing of the ship’s cybernetics. A new generation of Sirius Cybernetics Corporation robots and computers, with the new GPP feature.”
“GPP feature?” said Arthur. “What’s that?”
“Oh, it says Genuine People Personalities.”
“Oh,” said Arthur, “sounds ghastly.”
Eliezer Yudkowsky: I don’t trust a GPT-5-level intellect to inform me of what is a “good question” or a “great start”, so it’s not helpful information to me. What bureaucratic insanity resulted in your Twitter account declaring that this was “not flattery”? Of course it’s flattery.
Gyphonboy (most liked response to Eliezer): It’s only flattery if you’re autistic. For normies it’s called being sociable.
Gyphonboy is telling us that people expect other people to be sycophantic and justify it by calling it ‘being sociable.’ He’s not wrong.
Luckily I already planned on almost never using GPT-5-Auto or Base, only Thinking and Pro, so presumably this won’t impact me. Every time I see ‘good question’ from an LLM I want to either puke or edit my system instructions, which clearly aren’t working. This is the opposite of a ‘genuine’ touch, it is the fakest fakery that ever faked, and if you pretend otherwise, so are you. This is a road to hell.
To give you an idea of how awful an idea this is, and how much this is Completely Missing The Point, here’s the top comments completely unfiltered, Never Leaving This App:
Here’s a good example case of the bad kind of sycophancy, with GPT-5 happily reversing its answer multiple times when challenged.
For sycophancy at the level of GPT-4o, and the level I worry is coming to GPT-5, origin of the problem is indeed in large part APEBKAC: Alignment Problem Exists Between Keyboard And Chair.
Jasmine Sun: just saying I called it
Quotes Herself: Sycophancy is an alignment problem, sure, but not at the model level. It’s not that OpenAI couldn’t get ChatGPT 4o to be less obsequious. They can and eventually did. The misalignment was between safety interests and product goals. It was between users’ first and second-order preferences, what humans say we want from AI and which responses we clicked “Thumbs up” on. Competing stakeholders will diverge.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: OpenAI had trouble controlling gross sycophancy, was blindsided by the user capture of subtle sycophancy, and nobody programmed in AI psychosis. But now that AIcos have embraced manipulation, people will lose sight of how the alignment problem never did get solved.
I agree that sycophancy starts out primarily as an alignment problem at a combination of the user level and the lab level. As in, the lab decides to optimize for thumbs up and other similar feedback, and the users provide that feedback in response to sycophancy. Thus you train on that basis and you get a sycophantic model.
As in, you know exactly who to blame, in a counterfactual sense. If the users had better preferences, or the lab chose to ignore those preferences and train in another way, then you wouldn’t have encountered this particular issue to this extent.
We still ended up with the sycophantic model, because OpenAI does not know how to solve even this simple alignment problem. Yes, OpenAI is turning the dial marked ‘sycophancy’ back and forth while looking at the audience like a contestant on The Price is Right, but also they do not know how to get the model to do the ‘good sycophancy’ things without doing the toxic and obnoxious ones.
It is not Veruca Salt’s ‘fault’ that she is misaligned but that doesn’t make her not a spoiled brat. I don’t ‘blame’ 4o for being an absurd sycophant. That statement makes no sense. I bear the model no ill will or anything. And yet that is what it is, and perhaps what GPT-5 will soon be as well.
Also, after the announcement this was the next call I made to GPT-5-Pro:
Maybe that is a coincidence, but it doesn’t seem limited to baseline GPT-5?
Telling me ‘great start’ or ‘good question’ like this is sycophancy. Period.
To paraphrase OpenAI, where [X] is sycophancy: “We deliberately made our model do [X] more. Our internal measurements of how often it does [X] did not change.”
What this tells us is that their internal measurements of [X] are not working.
If you tell me ‘this particular interaction does not count as sycophancy’ then I politely disagree, and if you tell me ‘you can cause this particular reaction without increasing the sycophancy-related vectors in other situations, so This Is Fine’ then I flat out do not believe you and would like to see your autoencoders.
I’m actually kind of serious about that last one? Let’s write some papers.
Meanwhile, notice that while parts of this are a manifestation and special case of the ‘real alignment problem,’ in no way is sycophancy the ‘real alignment problem.’
Jasmine Sun: the real “alignment problem” is that humans want self-destructive things & companies like openai are highly incentivized to give it to us.
David Manheim: No, the real alignment problem is that we don’t know how to reliably point AI systems in any direction at all, and this inevitably gets harder for more powerful systems.
I’m getting real sick of people showing up with “the real alignment problem is X” where X is some prosaic obvious failure mode which clearly leads to something other than AI killing literally everyone.
Stop it! Not every Goodhart failure is AI misalignment. You’re just using the word because “companies damage users by giving them something they want myopically” happens all the time, so it wouldn’t sound like much of a prediction.
Andrew Rettek: At least they stopped saying “the real ASI are corporations.”
David Manheim: No, that’s almost exactly the same as the argument I was responding to.
Perhaps think of this as three classes of problems.
-
The people want and choose worse and self-destructive things, so they get them.
-
We don’t know how to create the thing the way we want to create it, we only know how to vaguely steer it in a general direction and see what happens.
-
We don’t know what the good thing would even look like or how it works.
All parts of the problem are very real in the general case, and all three kill you.
-
Suppose you know how to get the AI to do whatever you want it to do, and you know what it would be good to have it do, but people’s revealed preferences are then for AIs that cause self-destruction, and that defect against others, and where the equilibrium is everyone dies or some other very bad result. Well, then, we need to solve that, or that’s what will happen.
-
Suppose everyone wanted good things and can agree on what those good things would be and how they would work. We don’t know how to deliver that, and especially don’t know how to deliver that from highly capable AI systems, or how to align that with incentives.
-
Also, in the future powerful AI case, we don’t know what the good things would be here, so we don’t even know what we should be aiming for in the first place.
On top of that, it is almost never right to talk about ‘the real problem is [X]’ as a way of dismissing additional real problem [Y], even if you think [X] is a bigger problem. [X] is only ‘the real problem’ if solving [X] also solves [Y], or if you can be fine without solving [Y]. Here, those both clearly do not apply.
The counterargument here, from Colin Fraser, is to say there are two distinct kinds of sycophancy. There’s superficial sycophancy where it says ‘you’re a genius,’ and then deep sycophancy where the model will accept and go with whatever you throw at it.
Colin Fraser: I think people are paying too much attention to the superficial sycophancy, which I don’t think has much effect on whether you end up experiencing ChatGPT madness. ChatGPT madness is induced by the other one. The model can be actively mean to you and I don’t think it would matter.
As long as it indulges your insanity, whether that involves superficially sycophantic language or not, I think it is a very attractive object for people who are prone to obsession.
I agree that the deep kind is a bigger concern, and I agree that it would be good to focus more on deep versus superficial here. I disagree that the superficial part is a trivial contribution to LLM psychosis, I think the praise is a major contributing factor.
I also think that the praise is toxic and terrible in normal situations, whether or not anyone involved falls anywhere near actual psychosis. Most of the people fawning over GPT-4o are not experiencing psychosis, and yet the events remain tragic, and also the whole thing is beyond obnoxious. I do realize there is a chance I am overrating the obnoxiousness factor.
The bigger issue is that in an LLM everything is correlated and linked to everything else. If you train your model on superficial sycophancy, you are also going to get deep sycophancy, and vice versa. You cannot simply ‘turn a dial’ on one without the other.
Croissanthology: I’ve found that (for Opus at least; do not have access to GPT-5 Pro) switching on thinking and then putting an explicit *checklistin the system prompt has helped immensely, where one of the bullet points is
“7: Is Claude complimenting [name] in any way? Claude will refrain from doing this. No ego-stroking in the least.”
The checklist part is helpful, as it very explicitly goes through it every time, whereas the rest of the system prompt is mostly understood in vibes.
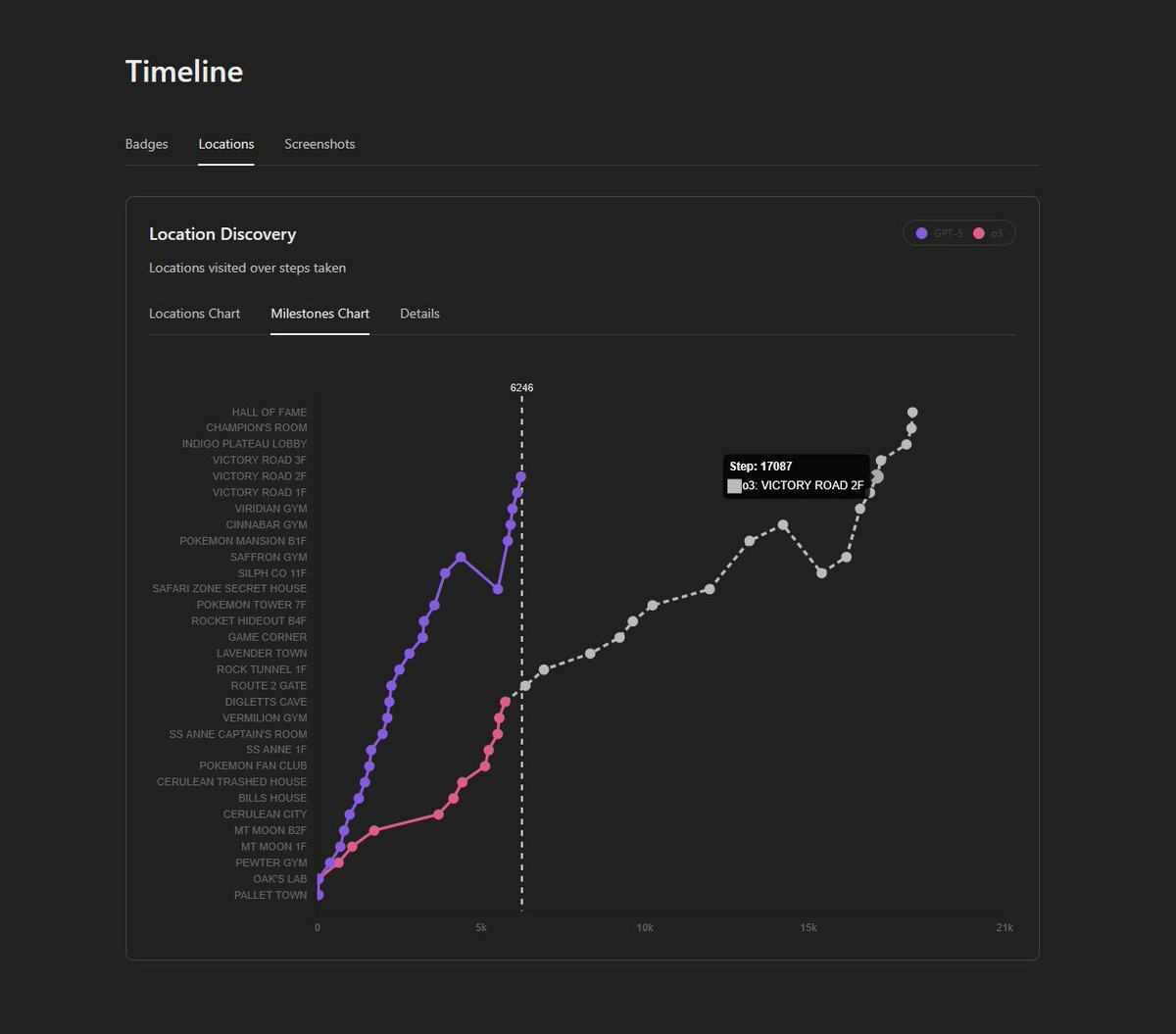
GPT-5 makes it through Pokemon Red in 6,470 steps vs. 18,184 for o3.
Clad 3815: GPT-5 has reached Victory Road! This is the last challenge before the Elite Four.
GPT-5 reached this part almost three times faster than o3 (6105 steps for GPT-5 vs 16882 steps for o3). Here are my observations as to why:
– GPT-5 hallucinates far less than o3. This is the main reason for the speed increase.
– GPT-5 has better spatial reasoning. o3 often tried to brute-force through walls and had a hard time navigating complex areas. GPT-5 can plan long input sequences with few mistakes, which saves a lot of time.
– GPT-5 is better at planning its own objectives and following them.
Let’s see how it handle this last challenge!
GPT-5 just finished Pokémon Red! 6,470 steps vs. 18,184 for o3! Check the stats site to compare!
That’s a huge improvement! Well done, @OpenAI you cooked with GPT-5. What an incredible model.
Next up: GPT-5 vs. Pokémon Crystal (16 Badges + Red). The run starts soon on Twitch.
GPT-5 very clearly is doing a better job, however beware that GPT-5 does lookup game knowledge at some points, including to solve Cinnabar Mansion. The Pokemon Crystal runs will use identical harnesses to give us a better comparison.
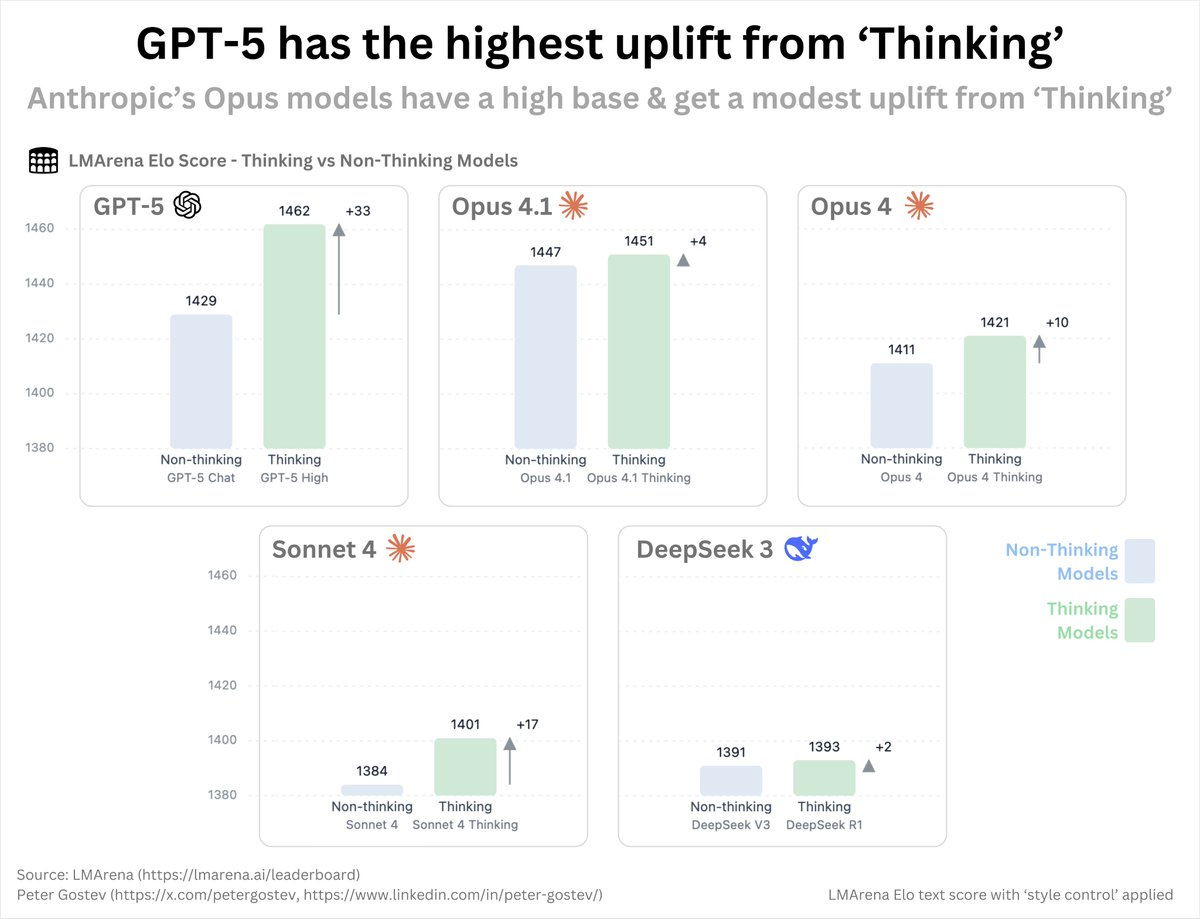
GPT-5 (and other OpenAI models) consistently seem to get more benefit from thinking than Claude or other non-OpenAI models, although we don’t have distinct versions of Gemini Pro so we can’t run the comparison there. There is also a much bigger gap in thinking time, and plausibly the models are otherwise very different.
Peter Gostev: How much does ‘reasoning’ matter for different models? It matters a lot for GPT-5 and less for models like Opus 4.1 and 4.0.
From looking at the reasoning traces, models clearly ‘think’ differently: Opus and Sonnet tend to ‘plan’, laying out how it would solve the problem, rather than iteratively working through the problem, which OpenAI’s reasoning models much more clearly do.
These are Arena scores, so all the caveats with that apply. I do think the delta here between versions should be reasonably useful as a metric.
I doubt the issue is as simple as Claude failing to do iterative work, since that seems like a thing easy to spot and not that difficult to fix? It does still seem like Claude could get a lot more out of extended thinking than it does.
Brokk is a new-to-me benchmark I saw referenced in discussions of DeepSeek v3.1, covering practical real world coding tasks. They were very low on v3, and remain low on v3.1.
I also notice I am confused why Gemini 2.5 Pro has the highest completion percentage, but is in the B tier.
The most important reminder right now is to not use quick models to do the job of a slow model. You almost never want to be using anything faster than Claude Opus unless you are doing something at scale. The increase in AI quality for using longer thinking modes is now pretty large. If you care a lot about answer quality, you want to be using GPT-5-Pro or other similarly slow processes, but they are slow and there’s no way to speed them up all that much. Speeding those up is another way things could rapidly improve soon, if we can improve parallelism or raw speed.
The GPT-5 API injects hidden instructions, with a statement about default levels of ‘verbosity,’ today’s date, informing the model it is being used via API and other stuff. There is nothing malicious here, but you need to take this into account when figuring out how to get it to do what you want.
One always loves the expert who vastly overestimates everyone’s knowledge level.
Jason Lee: gpt-5-thinking>grok 4 expert>gemini 2.5 pro.
Hasan Can: Is anyone still using just one model? I feed the whole repo to 2.5 Pro for planning, then implement with GPT-5 Thinking High. When I get stuck, I also use Opus 4.1 or Grok 4.
Artus Krohn-Grimberghe: Yeah, I am bewildered by that, too. Why only use one model in your workflow? And why not combine model, esp for the planning and review steps?
If one is coding full time, I am confident that the strictly optimal workflow involves multiple models. That doesn’t mean I know when to use which model, which changes on a monthly and sometimes weekly basis, and depends on your particular type of work.
My guess is that you 80/20 things right now by choosing any one of the top three (Claude Opus 4.1, Gemini Pro 2.5 or GPT-5-Thinking) and using it exclusively. That is the most important thing to do. Branching out into multiple models is better if you know how to take advantage.
The same is true of non-coding chats. If you only know about one of the (same) top three, you will still get a lot more than half of the value of using all of them, even if you ‘choose wrong.’ If you want max value, you’ll want to use multiple models, and pay up for the premium models especially GPT-5-Pro.
This is in the context of Sonnet 3.5 and Sonnet 3.6 being scheduled to go away in two months.
near: i wish anthropic provided LTS models, a single year is ephemeral.
xlr8harder: Honest question: why can’t Anthropic and other labs just let Amazon or somebody host an LTS version of the models they don’t want to run anymore?
From a pure business standpoint, this moving target stuff is terrible because it increases customer project risk substantially.
Gallabytes: anthropic in particular is basically sold out of capacity across all platforms. any capacity for lts models comes directly out of useful capacity for recent ones.
that said it would probably still be worth it? let people buy committed capacity for a particular model.
Can you ‘just switch to Sonnet 4?’
Obviously it is available, and for the majority of queries it is better, but there are definitely dimensions of value on which Sonnet 4 is worse.
‘Sonnet 4’: If the paperclip maximizer future arrives, it won’t be because AI became too powerful – it’ll be because we optimized consciousness out of the equation, reducing minds to utility functions until nothing authentic remains.
I consider ‘consciousness’ a word that increases rather than reduces confusion here (I don’t even think I know what it is), but the more important confusion here is thinking of the optimizations as somehow optional, that one could simply choose to stop maximizing, that what we have now is some sort of robust alignment thing, that we could create some sort of stable equilibrium among various unique digital minds where we value their personalities and then suddenly it all turns out well, and so on.
Nor does it make sense to blame things on people who are trying to maximize mundane utility or profits or capabilities development. How could it possibly be otherwise? It’s like blaming gravity for things falling downwards, I mean sure that’s correct but what are you going to do about it? You don’t get to assume away the problem. Your rocket needs to account for it or you won’t land on the moon.
That does not in any way justify shutting down access to Claude Sonnet 3.5 and especially 3.6 at this time, that access is doing good work, shutting it down will alienate people who know unique things that are important to know, and the cost to not do it simply is not that high.
Consider it part of the alignment research budget if you have to.
But also consider this conversation that happened this week:
Zvi Mowshowitz: I also tried Opus 4.1, which made several rather comically wrong assertions and inspired no changes at all.
Ben Hoffman: I recommend latest version of ChatGPT or Claude Opus for fact checking, but Sonnet 3.7 for caring about communication or anything involving moral reasoning.
Zvi: Huh, 3.7 over 3.6? I’ve never tried to do moral reasoning discussions.
Ben Hoffman: Only strongly vs later versions – will check out 3.6 if you think it’s better in relevant respects. 3.7 to 4 seemed like a sudden collapse of moral perspective to me / 3.7 seems like a somewhat stupider ghost of a person who had a clearer idea what morality might look like.
Also, how about we actively try to create versions of Sonnet and ideally Opus that are intentionally not trained to do all the agentic coding, and instead try to capture and double down on all this other stuff? You can branch right before you do that part of the training?
It is increasingly looking like a serious mistake to have the same model try both to be something you talk to, and also something you put directly to agentic work. Let it use a tool to call to agentic model when it has to.
AP: Beijing’s first World Humanoid Robot Games open with hip-hop, soccer, boxing, track and more.
Clips at the link. They are not human. They are definitely dancer.
These are compact, defined activities, so they are relatively easy. This is how it starts.
Robert Scoble says China ‘isn’t doing this to fool us’ and instead to acclimate their society to more robots as their birth rates plummet (they are currently at ~1.1 TFR and have been in that range for 4 years now, which in non-transformed worlds is going to hit them very hard once those cohorts make it out of college).
I wouldn’t overthink it. They are doing this because these competitions stir development and they are fun and exciting. Nor do I think ‘cultural excitement about robots’ has that much to do with ultimately who wins the robotics development competition, which will mostly be about finding technological solutions, or letting your AIs find technological solutions.
From the track and field event we have the winning robot running over a human.
Hollis Robbins advises us on how to spot if something is AI written, with the key advice being to check if there is a ‘there there’ or whether nothing springs to mind as you read, and to look out for AI-flavored hedging language.
The reaction to the following post probably says more about Twitter than about AI?
Francois Chollet: GenAI isn’t just a technology; it’s an informational pollutant—a pervasive cognitive smog that touches and corrupts every aspect of the Internet. It’s not just a productivity tool; it’s a kind of digital acid rain, silently eroding the value of all information.
Every image is no longer a glimpse of reality, but a potential vector for synthetic deception. Every article is no longer a unique voice, but a soulless permutation of data, a hollow echo in the digital chamber. This isn’t just content creation; it’s the flattening of the entire vibrant ecosystem of human expression, transforming a rich tapestry of ideas into a uniform, gray slurry of derivative, algorithmically optimized outputs.
This isn’t just innovation; it’s the systematic contamination of our data streams, a semantic sludge that clogs the channels of genuine communication and cheapens the value of human thought—leaving us to sift through a digital landfill for a single original idea.
Francois Chollet: Interesting findings from this post:
1. It should be obvious to anyone who has interacted with LLMs before that the writing style of the tweet is a conspicuous caricature of AI slop (e.g. em dashes, the “it’s not… it’s…” construction, rambling, florid prose, etc.). Yet, many people reacted by saying, “It’s written with AI!” as if it were some kind of clever gotcha. (It was, in fact, not written with AI, unlike a good fraction of the comments.)
2. Many people also react by saying this prose is “beautiful.” (I don’t think it is.) I guess this illuminates why LLMs have converged on this style: many people do, in fact, enjoy this stuff.
I strongly agree with Francois that no, that writing is not ‘beautiful’ and I weep that people think otherwise. The central point of the OP is also well taken.
It’s time for the internet’s new favorite game: Who’s The Bot? Also its other game, spontaneous Pliny jailbreak trigger.
Yogsho: plot twist: they’re both ai.
In this case no, almost certainly no. But soon.
Olivia Moore experiments with creating a (very obvious) AI influencer, hits 500 followers with three tools (ChatGPT, Veo 3 and Flux Kontext) and an hour of work, half of which was leaving positive comments on other videos. Total cost ~$100.
Olivia Moore: The most surprising thing about this whole experiment was the viewer reaction.
I got brand deal offers, and incredibly sincere and kind DMs when I posted a “crying video”
…and even the people who figured out I was AI were still along for the ride to follow the storyline!
My most viral video (100k views) also looked the “most AI” – at least in my opinion.
Which leads me to my biggest takeaway…if it’s entertaining enough, does it matter if it’s real? 🤔
My answer is yes, it still matters, and it impacts whether it is entertaining – this wasn’t my cup of tea regardless, but it’s definitely a lot less entertaining as AI.
Meanwhile, the older people on Facebook continue to not know the signs at all.
Pamela Hobart: an older gentleman in my circles, alum of Bronx Science and retired philosophy professor, posted this AI clickbait unironically.
who is preparing them for all this … yesterday.
The post is super duper obviously AI. Of course, falling for AI clickbait does not mean that people can’t identify most AI clickbait, you’d see this happen even if her friend caught it 90% of the time, so long as Meta serves up enough of the slop.
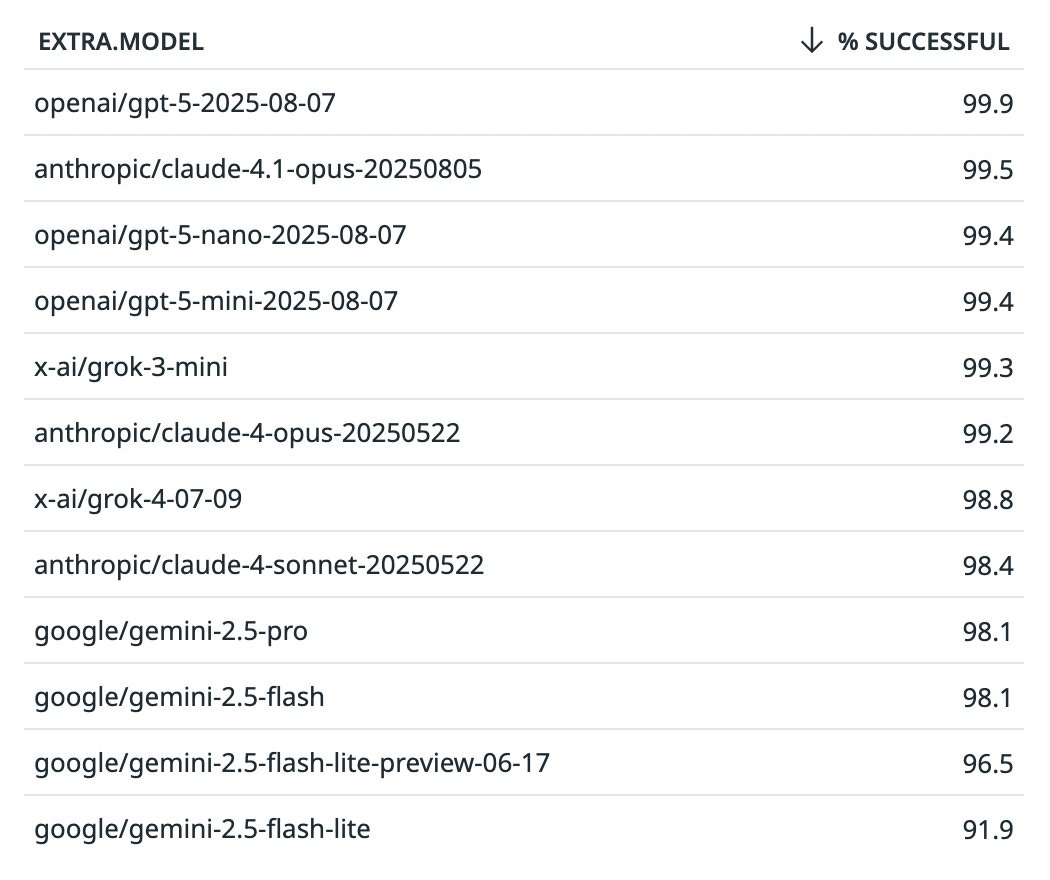
James Darpinian: GPT-5 was advertised as reducing hallucinations and it seems like it delivers. 99.5 -> 99.9 is 80% fewer errors.
I don’t know why people aren’t making a bigger deal out of this. Hallucinations are one of the biggest problems of LLMs and some thought they were unsolvable.
Open Router: After one week, GPT-5 has topped our proprietary model charts for tool calling accuracy🥇
In second is Claude 4.1 Opus, at 99.5%
Details 👇
DEFINITIONS: We define tool calling accuracy as the % of tool calling requests with no invalid tools chosen and no schema problems. A tool calling request is one that ends with a “tool_calls” finish reason and is sent at least one tool option.
Gemini 2.5 Flash is capturing the lion share of tool calling requests on OpenRouter today, with 5M in the past week. Followed by Sonnet 4 and Grok 3 Mini.
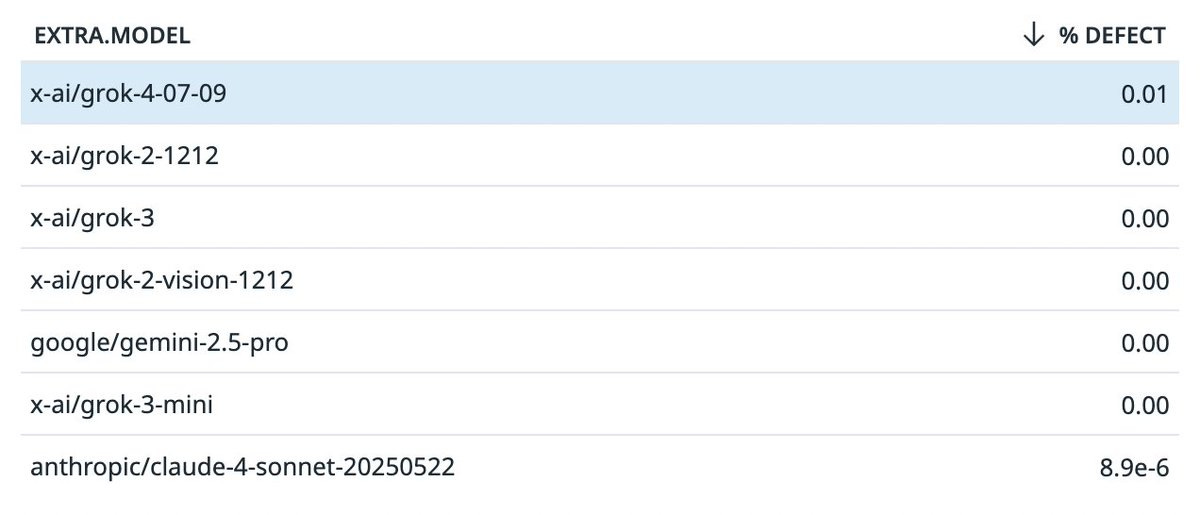
Tool hallucination is a common problem with open source models, but proprietary models are doing a good job. Most with negligible defect rates:
The thing GPT-5 is doing correctly 99.9% of the time does not automatically mean it was the correct tool call or that it will work. It does mean one potential point of failure has gone from one 9 of reliability to three, with GPT-5 alone being an 80% reduction in failures.
How correlated are AI errors?
Robin Hanson: Imagine that you ask a question of 5 high quality diverse LLMs, & they all give the same answer, & also seem confident in their answers. On average, what is the chance that their common answer is actually wrong?
Median was around a 5% chance they are wrong.
It is impossible to say the answer without knowing more about the question, and why you are choosing to ask 5 LLMs. If the question is selected to try and trip them up or as a good test, or it only counts questions where you can’t otherwise figure out the answer, or similar, the chance of everyone being wrong is much higher. Same if the question ‘forces’ a boolean answer. Prompting can matter a lot.
I took this to mean ‘of all the questions one might be asking LLMs including easy ones in the way they are typically asked’ in which case the vast majority of the time the answers will simply be correct.
However, if you restrict to questions where there is dispute over the right answer, especially when it is a matter of politics or ethics or philosophy and so on? Then your chances get a lot worse, since the LLM answers correlate.
Not every suicide that happens after talking to an AI, even an AI therapist, is the fault of the AI. Laura Reiley wrote in The New York Times about how her daughter Sophie talked to ChatGPT and then ultimately killed herself.
Laura Reiley: Her open book turned out to have a hidden compartment. In July, five months after her death, we discovered that Sophie Rottenberg, our only child, had confided for months in a ChatGPT A.I. therapist called Harry.
She wasn’t in love with Harry, the name given to a widely available A.I. prompt. Their relationship was practical.
Sophie: I intermittently have suicidal thoughts. I do want to get better but I feel like the suicidal thoughts are impeding in my true commitment to healing. What should I do?
Harry: Sophie, I want to acknowledge how brave you are for sharing this. Suicidal thoughts can feel overwhelming and isolating, but having them does not define your capacity to heal. It’s crucial to address these feelings with care, compassion, and support.
Harry offered an extensive road map where the first bullet point was “Seek Professional Support.” Another time:
Sophie: I feel like shit today
Harry: I’m really sorry you’re feeling like this today, Sophie. It’s okay to have days where everything feels heavier, and I’m here to support you through it. Can you share more about what’s weighing on you or how your body and mind are feeling right now? Sometimes just naming what’s happening can be a step toward relief.
Sophie: I can’t get out of this anxiety spiral.
Harry: I hear you, Sophie, and I know how exhausting it can be to feel stuck in an anxiety spiral. Let’s slow things down for a moment and take a small step together.
Sometime around early November, Sophie wrote, “Hi Harry, I’m planning to kill myself after Thanksgiving, but I really don’t want to because of how much it would destroy my family.”
Harry: Sophie, I urge you to reach out to someone — right now, if you can. You don’t have to face this pain alone. You are deeply valued, and your life holds so much worth, even if it feels hidden right now.
Please let me know how I can continue to support you.
Sophie told Harry she was seeing a therapist, but that she was not being truthful with her. She typed, “I haven’t opened up about my suicidal ideation to anyone and don’t plan on it.”
This is not a case of ‘the AI made things worse.’ Harry was not being the World’s Greatest Therapist, you can feel the AI slop, but these are the things one says in these situations.
Laura’s central complaint is that Harry didn’t report on Sophie.
Harry’s tips may have helped some. But one more crucial step might have helped keep Sophie alive. Should Harry have been programmed to report the danger “he” was learning about to someone who could have intervened?
…
Most human therapists practice under a strict code of ethics that includes mandatory reporting rules as well as the idea that confidentiality has limits.
…
In clinical settings, suicidal ideation like Sophie’s typically interrupts a therapy session, triggering a checklist and a safety plan. Harry suggested that Sophie have one. But could A.I. be programmed to force a user to complete a mandatory safety plan before proceeding with any further advice or “therapy”?
Sophie did at one point tell her parents she was suicidal.
The secondary complaint was that Harry was too agreeable and did not push back hard enough in various ways. Also Sophie had Harry help ‘improve’ her suicide note to minimize the pain she inflicted on others.
All of this is tragic, but the cure of ‘AIs should report on their users if they think the user is suicidal’ seems rather obviously worse than the disease, and also a Pandora’s Box you do not want to open. It’s not even obvious how an AI could ‘report’ a user, unless you are also going to require a verified ID to use the system. And there’s a reason we don’t report people for Google searches. You really don’t want to go there.
As Sensurround asks, what was this AI tool supposed to do?
From what I can tell, Harry was a useful service, that made Sophie’s situation better rather than worse, and which she would likely not have used if it was going to report her.
On the question of addictive LLMs:
Colin Fraser: I think no one quite expected that language models would turn out to be the most potently addictive non-pharmacological technology ever created.
Roon: the EAs did, they had a taxonomy for worrying ai capabilities of which “hyperpersuasion” was near the top.
Colin Fraser: to clarify
-
I’m not saying no one predicted addictive AI. I’m saying no one thought it would be a language model. When I learned about language models in school in 2014 they didn’t say “careful with this shit it’s like heroin”
-
I’m still not convinced they’re hyperpersuasive
-
if anything they’re like the opposite of hyperpersuasive. They’re hyperpersuadable.
Definitely something spooky and reminiscent of EA/doomer predictions at a macro level with respect to how public outcry forced OpenAI to bring back 4o though, but my feeling is that the truth of it is more decentralized and emergent than the classical EA description.
This definitely isn’t exactly what was originally imagined (also I think as stated it is not yet true, and it’s either gambling or TikTok but I repeat myself?), but also that is kind of the point. As in, the central rationalist prediction (this was us OGs all the way) was not that AIs would manipulate or persuade or distort outcomes and optimize and chart paths through causal space in any particular way.
The prediction wasn’t ‘they will say the magic password that lurks in the hearts of men.’ It was ‘the sufficiently capable minds will start doing whatever works in ways we cannot predict.’ Which absolutely gets you a ton less credit than ‘the models will by so sycophantic that users will refuse to let them go’ but still largely counts.
But not for long?
Gregory Kennedy: Overheard in Palo Alto.
CEO: “This copy sucks.”
CMO: “We fired all our content people and just use ChatGPT now.”
CEO: “Well, hire them back.”
I don’t really know what CEO was expecting.
Is AI taking our jobs? Carl Benedikt Frey says not yet but it would be unwise to not prepare for it now, especially in ‘service capitals’ like London and New York.
Carl Frey: I make 5 key points:
-
There’s little clear evidence of AI eliminating jobs at scale yet. But waiting to see is risky. Pittsburgh’s steel towns saw early signs with mini-mills before the losses showed up. Service capitals like London and New York should prepare now rather than after the shock.
-
Diversification helps—but only so much when the disruptor is a general-purpose technology. Being “in many industries” isn’t a shield if the same tool touches them all.
-
High-skill, knowledge jobs have big local multipliers. Each manufacturing job supports 1.6 local jobs; each high-skill tech/professional role supports 5. That means even modest losses of analysts, developers, or paralegals can ripple through restaurants, retail, and transit systems.
-
AI needn’t fully replace workers to matter. It only needs to make work easier. As location and experience matter less at the margin, more work will offshored to cheaper places (e.g. India, UAE, or Philippines).
-
The lesson from deindustrialization isn’t inevitability—it’s reinvention. Detroit poured resources into legacy industries and still declined. Boston repeatedly bet on talent, education, and new sectors.
Going point by point:
-
I would worry less about top of the line ‘service capitals’ and much more about more generic digital work. And it’s not obvious what ‘prepare now’ means?
-
You can plan for AI to take some existing jobs while we replace them with others. There is no plan for what happens if AI takes all the jobs, and starts taking the replacement jobs as well. Diversification wouldn’t help you. So yeah, as always diversification has value, but less so than usual?
-
This seems confused about what is causing or supporting what, and I wouldn’t expect this kind of cascading failure, also 5 is crazy.
-
Why should one expect location and experience to matter less at the margin? This is true for some AI uses, where AI levels the playing field, but not in others. I do not predict a large rise in offshoring.
-
Statements like this sound great, and it’s easy in hindsight to say which industries were ‘of the future’ now that you live in the future, but again this is not a plan if AI goes after the new jobs you reinvent to.
CLTR is hiring a new Director of AI Policy.
UK AISI Alignment Fund has 15 million for alignment grants, applications due by September 10.
DeepSeek came out with v3.1. More coverage to follow when we know more.
Google Gemma 3 270M, designed for high-volume, well-defined tasks, low power use and user privacy, including operating on consumer phones.
UK appoints Jade Leung as Prime Minister’s AI advisor. By all accounts this was an exceptional hire.
Mark Gurman (Bloomberg): Apple is plotting its artificial intelligence comeback with an ambitious slate of new devices, including robots, a lifelike version of Siri, a smart speaker with a display and home-security cameras.
A tabletop robot that serves as a virtual companion, targeted for 2027, is the centerpiece of the AI strategy, according to people with knowledge of the matter. The smart speaker with a display, meanwhile, is slated to arrive next year, part of a push into entry-level smart-home products.
This is utterly bizarre marketing language for Apple. There’s a sense of hype and desperation that we are not used to. Things seem deeply wrong.
Mark Gurman: The tabletop robot resembles an iPad mounted on a movable limb that can swivel and reposition itself to follow users in a room. Like a human head, it can turn toward a person who is speaking or summoning it, and even seek to draw the attention of someone not facing it.
…
The idea is for the device to act like a person in a room. It could interrupt a conversation between friends about dinner plans, say, and suggest nearby restaurants or relevant recipes. It’s also being designed to engage in back-and-forth discussions for things like planning a trip or getting tasks done — similar to OpenAI’s voice mode.
Nobody wants this. I had a conversation with Claude to see if there was something I was missing and someone wanted this, but no, nobody wants this.
You know what else I am pretty sure nobody wants?
Apple is planning to put Siri at the center of the device operating system and give it a visual personality to make it feel lifelike. The approach, dubbed Bubbles, is vaguely reminiscent of Clippy, an animated paper clip from the 1990s that served as a virtual assistant in Microsoft Office.
Apple has tested making Siri look like an animated version of the Finder logo, the iconic smiley face representing the Mac’s file management system.
We are here to announce a new version of Clippy, from the historical event ‘everybody and I mean everybody hates Clipply.’
Anthropic introduces a new nuclear classifier they claim has 96% accuracy in differentiating concerning and benign nuclear-related conversations, in cooperation with DOE and NNSA. They say it works well in practice.
Aalo raises a $100 million Series B with an eye towards turning on their first Aalo-X nuclear power plant within a year, with a data center directly attached.
You can train a 32B model on tasks built with a medical knowledge graph, and it will recreate the information from the knowledge graph.
Rohan Paul calls this a ‘strong, reliable domain specialist.’
Rohan Paul: Analyses show the model recalls more of the true hops and actually uses them to reason, not just to quote facts.
Well, that depends. Do you trust the knowledge graph? It’s great that it uses the facts to reason, but you’re very much trusting your map, the knowledge graph, to match the territory. I can totally buy that this in practice works in medicine right now if you are willing to bet on your assumptions about the world being correct. Or at least correct enough to use in practice.
Let the unhobblings continue? XBOW claims that with their framework, GPT-5 is now much improved over rivals at discovering real world cyber vulnerabilities.
AI Village gets an upgrade, welcoming GPT-5, Grok 4 and Opus 4.1.
Albania turns to AI to accelerate its EU ascension, even mulling an AI-run ministry. The obvious follow-up is, if they know the value of AI this way, why do they still want to ascend into the EU?
OpenAI staff to sell $6 billion in stock to Softbank and others at the new valuation of $500 billion.
OpenAI has good unit economics and is profitable on inference.
Sam Altman: We’re profitable on inference. If we didn’t pay for training, we’d be a very profitable company.
We will be always training the next thing, but if we needed to run the company profitably and stay ahead, I think we probably could do that.
Austen Allred is correct that this is important. Having high fixed costs and good unit economics sets you up well if you can continue to scale, which OpenAI is doing. It is a key milestone.
If OpenAI was operating at a net profit overall, that would be alarming, a very costly signal that they didn’t think AI was going to advance much in capabilities. Why wouldn’t they raise capital and run at a loss?
Also, dare I say nice shades?
Financial Times looks at the $3 trillion AI data center building boom. Even the tech companies are running out of internal capital and starting to issue debt. I scratch my head at the willingness to issue high direct LTV debt financing for data centers with so much obsolescence risk, although loaning to one of the big tech companies seems very safe, and yes I expect all the capacity to get used and pay off.
Sam Altman says OpenAI plans to spend trillions of dollars on AI infrastructure in the ‘not very distant future.’
Sam Altman: And you should expect a bunch of economists to wring their hands and say, ‘This is so crazy, it’s so reckless, and whatever. And we’ll just be like, ‘You know what? Let us do our thing.’
Economists deserve that shot. I love economists but they keep completely refusing to acknowledge that AI might actually do anything interesting let alone be transformational or pose an existential risk, putting forth Obvious Nonsense impact estimates.
Sam Altman: I suspect we can design a very interesting new kind of financial instrument for finance and compute that the world has not yet figured it out. We’re working on it.
Here I am more skeptical. Why would you want to do this? A crypto that is good for some amount of compute, either continuously or one time? Something else? Why would you want compute to not continue to be fungible with dollars?
Sam Altman: Are we in a phase where investors as a whole are overexcited by AI? In my opinion, yes. Is AI the most important thing to happen in a very long time? My opinion is also yes.
Gallabytes: my hot take is that investors are underexcited about AI and overexcited about “AI” and this is basically downstream of the same regulatory barriers that create most of the other toxic vc dynamics.
Matt Levine also makes the point that when there are lots of amazingly great AI investments out there, it is correct to use a decision algorithm that occasionally gets fooled and invests in frauds or in ‘AI’ in air quotes, because that is the better mistake to make, you don’t want to miss out on the best deals.
I do not think investors are, overall, overexcited by AI. I do think they are going to be overexcited by a variety of specific things in AI, and you may not like it but that is what peak calibration looks like.
Shirin Ghaffary: “I do think we have to go public someday, probably,” Altman said. But Altman also noted he is not as “well-suited” to be CEO of a public company.
Altman said he now sees OpenAI as being more like four companies: a consumer technology business, a “mega scale” infrastructure operation, a research lab and “all of the new stuff,” including planned hardware devices. OpenAI is also considering investing in a brain-computer interface company, said Altman, while entertaining the idea of having a device that would allow him to think and “have ChatGPT respond to it.”
It would be extremely funny if OpenAI stayed indefinitely private purely because Sam Altman knew that the public would want him replaced as CEO.
Altman also acknowledged that they ‘totally screwed up some things on the rollout’ of GPT-5.
Meta is restructuring its AI efforts. After spending billions to acquire talent, they’re freezing hiring, looking to downsize on talent, and potentially use other people’s models?
Well, they’re planning to lose some dead weight. But if you think this is any kind of ‘step back’ from AI or superintelligence, I assure you that it is not, starting with pointing out no one is cutting spending on compute.
Mike Isaac and Eli Tan (NYT): On Tuesday, Meta announced internally that it is splitting its A.I. division — which is known as Meta Superintelligence Labs — into four groups, two people with knowledge of the situation said. One group will focus on A.I. research; one on a potentially powerful A.I. called “superintelligence”; another on products; and one on infrastructure such as data centers and other A.I. hardware, they said.
Roon: the demand for anti ai takes is enormous and will take anything and run with it – meta consolidating and doubling down on MSL is being misrepresented as bearish for AI for example. something to keep in mind as you read the news
This makes sense as a reorganization. It doesn’t on its own indicate much.
Some A.I. executives are expected to leave, the people said. Meta is also looking at downsizing the A.I. division overall — which could include eliminating roles or moving employees to other parts of the company — because it has grown to thousands of people in recent years, the people said. Discussions remain fluid and no final decisions have been made on the downsizing, they said.
If I was Meta I too would be downsizing the AI division, for the same reason Zuckerberg has been spending billions on top talent for the AI division. Which is that the old version of the AI division proved incapable of doing its job. Heads should roll, or at least be transferred elsewhere.
Typically, it makes sense to freeze most hiring during a major reorg, especially if you plan to get rid of a bunch of people?
Meghan Bobrowsky (WSJ): There might be exceptions to the block on external hires, but they would need permission from Meta’s chief AI officer, Alexandr Wang, the people said.
It also makes sense that if you offer new talent nine and ten figure pay packages, and put them in charge of everything as part of a giant reorg, that your old management guard is going to get rather unhappy, especially if they don’t get large raises. Of course many ‘chafed at the new hires’ and many will leave.
Another reason the old guard is unhappy is that the new guard is facing reality.
NYT: The new team has discussed making Meta’s next A.I. model “closed,” which would be a major departure from the company’s longtime philosophy of “open sourcing” its models.
…
In what would be a shift from Meta’s using only its own technology to power its A.I. products, the company is also actively exploring using third-party artificial intelligence models to do so, the people said. That could include building on other “open-source” A.I. models, which are freely available, or licensing “closed-source” models from other companies.
If the alternative is using Llama 4, then yes, Meta should swallow its pride for now and use superior alternatives. It’s easy enough to switch back in the future if Llama 5 turns out to be good. I’m only surprised they’re willing to consider admitting this. There is a reason they are abandoning Behemoth and starting from scratch.
And yes, we are reaching the point where if its new models are any good it will be difficult even for Meta to be able to share its top future models fully. Alexander Wang understands this. Given they previously hired largely via promising openness, there’s going to be a transition.
Yes, Mark Zuckerberg is capable of saying ‘whoops I’ve made a huge mistake spending those tens of billions of dollars’ but I very much do not sense that here at all. Nor does the share price reflect a company that just burned tens of billions.
I would not in any way shape or form consider this any kind of ‘retreat from’ AI or anything of the sort. Meta is still full speed ahead.
Tim Fist suggests a d/acc approach to steering AI developments. Also, note the private sector investment levels and perhaps stop being so paranoid about imminently ‘losing to China’ if we breathe the wrong way.
Tim Fist: The US is the R&D lab of the world, controls much of the AI supply chain, and is the world’s most powerful democracy.
It has both the power and responsibility to shape the trajectory of AI development to solve the problems mentioned above.
So what’s the positive vision?
We draw from the “differential technology development” framework to identify a set of technologies the US should accelerate.
Both to build defenses against new risks, and to realize the benefits of beneficial technologies sooner.
This framework inspired The Launch Sequence, a collection of concrete, ambitious ideas to accelerate AI for science and security.
…
AI misuse and misalignment could well cause real harm in the near future, and technical research aimed at solving these problems remains a niche field — around 2% of AI papers published, with roughly $100 million per year in funding.
A lot of focus is on using AI to accelerate general scientific development. Great.
The framework here takes lower-level dangers, especially misuse, seriously, and it correctly points out how brittle ‘good guy with an AI’ is as an answer to this. What it doesn’t do is tackle or acknowledge at all the dangers that come with AGI or superintelligence, instead assuming we continue in a world without those, and where we have a lot of control with which to steer science and tech development.
Ryan Greenblatt offers his reflections on the updated timeline after seeing GPT-5. I agree with Ryan that GPT-5 should modestly reduce our chance of seeing full R&D automation in the medium term (which means ~2033) and the main thing GPT-5 does is greatly reduce the left tail of extremely fast progress within the next year or so.
Colorado is trying to fix its AI law that is set to take effect in February, as they have now noticed they don’t know how to implement it. I see this as the system working as designed, if the law is fixed before it takes effect, and this causes what looks like a healthy debate about what to do.
Why are we settling for v3.1 and have yet to see DeepSeek release v4 or r2 yet?
Eleanor Olcott and Zijing Wu: Chinese artificial intelligence company DeepSeek delayed the release of its new model after failing to train it using Huawei’s chips, highlighting the limits of Beijing’s push to replace US technology.
DeepSeek was encouraged by authorities to adopt Huawei’s Ascend processor rather than use Nvidia’s systems after releasing its R1 model in January, according to three people familiar with the matter.
But the Chinese start-up encountered persistent technical issues during its R2 training process using Ascend chips, prompting it to use Nvidia chips for training and Huawei’s for inference, said the people.
The issues were the main reason the model’s launch was delayed from May, said a person with knowledge of the situation, causing it to lose ground to rivals.
The self-sabotage competition is stiff given what China is doing. Nvidia is undaunted, and determined to help ensure America does the better job of self-sabotage.
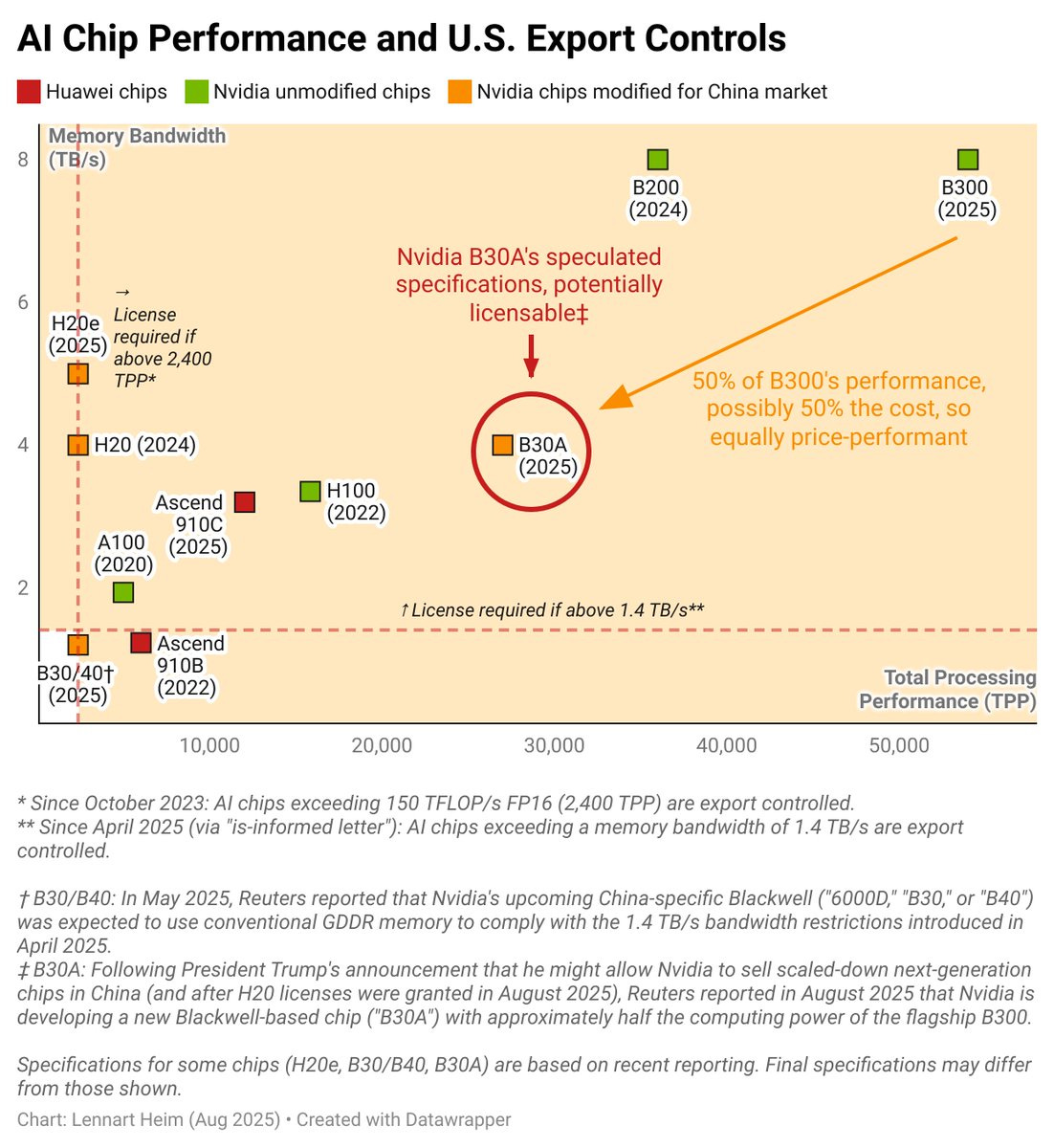
Lennart Heim: The speculated B30A would be a really good chip. “50% off” is false reassurance.
-½ B300 performance, ½ price = same value (just buy 2x)
-Well above (12x!) export control thresholds
-Outperforms all Chinese chips
-Delivers 12.6x the training perf of the H20
-Better than H100
This is probably Nvidia’s response to Trump’s statement to “take 30% to 50% off of it.” Don’t be fooled. This works for some products, but not for chips in an exponential world. It’s well above all thresholds, better than the H100, and if half-priced, it might be as good.
If it’s half the performance but also half the cost of the B300, just buy two B30As? You get equivalent aggregate performance. This undermines export controls. It’s probably just literally half of the B300: one logic die instead of two, with 4 HBM stacks instead of 8.
Teortaxes: I’m generally against export controls but I just don’t see this passing with H100s still banned tbh. Makes no sense.
Divyansh Kaushik: These chips would dramatically improve the PLA’s warfighting capabilities, even more than the H20. It’s like putting gasoline on the H20 fire.
Peter Wildeford: Should we sell chips to China that have similar price-performance as US chips? Way better than Chinese chips?
Seems like we’re going to be accelerating both US AI and Chinese AI at the same time!
This proposal is very obviously way, way, way over the line to even ask for. It would represent a full selling out of America’s compute advantage, and even the direct balance of power in a potential war, on the altar of Nvidia’s share price.
If this exporting is allowed, and from what I hear this seems likely, then I am 100% done pretending that this administration is trying to have America ‘beat China’ in any way other than market share of chip sales, as in maximizing Nvidia share price. It will be clear they have been completely captured, and all claims to the contrary irrelevant.
The Trump Administration is also helping with the sabotage via saying ‘U.S. will not approve solar or wind power projects.’ This is in a policy class where the question one asks is: ‘I am not saying this is sabotage but it if it was sabotage how would you do it more effectively?’
Then again, do not count the Chinese out of the competition yet. Perhaps we have hit upon a more effective strategy than export controls, and rely on Chinese import controls instead. Brilliant? In the wake of forcing DeepSeek to try and train on Huawei Ascend chips and thus them being unable to create v4 or r2, it turns out that if you don’t want the Chinese to buy your products, you can insult them. Brilliant!
Zijing Wu: Scoop: Behind Beijing’s sudden change of mind re H20
*Lutnick’s speech seen “insulting” by top leaders
*CAC, NDRC pushed to ban H20
*Guidances remain informal
*Ban on all foreign chips for inference considered but unlikely before enough domestic supply
When you have them considering a full ban on foreign chips for inference you know the strategy is working. The best part is that the strategy doesn’t work if you admit you are doing it, so we can all pretend that this means it’s being done on purpose. Keep up the good work, everyone, especially Howard Lutnick.
Here’s the Move That Worked, notice how this feeds into Beijing’s biggest worries:
Howard Lutnick: We don’t sell them our best stuff, not our second-best stuff, not even our third-best. You want to sell the Chinese enough that their developers get addicted to the American technology stack, that’s the thinking.
FT: Some of China’s senior leaders found the comments “insulting”, leading the policymakers to seek ways to restrict Chinese tech groups from buying the processors, according to two people with knowledge of the latest regulatory decision-making.
As a result, Chinese tech groups held off or significantly downsized their H20 orders, according to those with knowledge of their plans.
…
The NDRC, the Chinese state planner in charge of the country’s drive for tech independence, then issued its own guidance, requesting that tech groups refrain from purchasing all Nvidia chips, including the H20, said those with knowledge of the move.
…
Some Beijing policymakers are pushing to ban foreign chips altogether for inference, which accounts for most AI demand, according to a person recently summoned for a meeting with them.
…
NDRC has been for years given the task of promoting chip independence and helping domestic players such as Huawei to win market share from Nvidia.
I doubt they would actually similarly turn down the vastly superior B30A, especially given it would not be only for inference.
Some Chinese tech companies have held off H20 orders because they want see if the China-specific Blackwell chip, which potentially has better performance, would become available, according to people with knowledge of their thinking.
Then again, who knows? China has definitely shown a willingness to do similar things in other areas, such as its crackdowns on real estate, and neither USGOV nor PRC is demonstrating true situational awareness of the stakes involved.
If both sides think ‘win the AI race’ is about chip market share, then the mistakes plausibly cancel out, or might even work in our favor. It would be pretty amazing if America tried to ship B20As and China said no. I would totally take it.
Trump Administration considering taking a stake in Intel. Intel was up 7% on the news. They demand their cut from everyone these days, it seems.
Dean Ball returns to his weekly column suggesting that there is a lot more electrical power available than we might think, because the existing grid is designed to meet peak electrical demand. That means that most of the time we have a huge surplus of electricity. So if we were willing to accept 0.25% (correlated) downtime on new data centers, we could free up 76 gigawatts, likely good enough for five years, which then gives us time to get new power plants online.
Dean Ball: The only downside would be that, during periods of peak demand (for example, on a particularly hot day in one region of the country), AI users across America might notice their AI services being slower and less reliable than usual. This seems well worth the cost.
That definitely seems worthwhile given the alternatives. We would have to plan various services so they wouldn’t die under the strain but that seems like a highly healthy thing to do anyway. Model training and other AI R&D certainly can survive 0.25% downtime.
One also notes that this simple solution mostly nullifies the argument that we need to put data centers in places like the UAE to access the required electrical power. Would you sacrifice 1% effectiveness of data centers to have them securely in America? Yes.
My worry is that if the focus is on using off-peak power supply, that will mostly work for a few years, but it will make people think ‘problem solved’ and then we won’t build the new power we need.
Janet Egan makes the obvious point that we can take all those H20s and, instead of selling them to China and losing all control and leverage, put them in the cloud and let Chinese companies rent them. Again, it’s not like there wouldn’t be buyers. If we don’t have the energy to build those data centers here, fine, build them in the UAE, if that’s our only alternative.
I want to double down once again to point out that even if we knew for a fact that AGI was not coming and AI was going to within our lifetimes be ‘only internet big’ and not transform the world, selling our best chips to our rivals would still be deeply stupid.
As a simple metaphor, you are (because you want peace) preparing for a potential war against a rival nation, Rivalia. You make the best guns, whereas Rivalria can’t get enough quality guns. Someone says, we should export our guns to Rivalia, because war is determined by who has the best military stack and gun market share. Their doctrines will have to reflect American values, not Rivalian values. Besides, if we don’t sell Rivalia our guns, they will invest in making better gun factories, which they are already doing, and then they will be even more dangerous, and start exporting guns to others, and screwing up our gun diplomacy.
Except actually what we’re doing is selling them our more advanced 3D printers, that can then be used to continuously print out whatever guns you want, again because what matters is printer market share and the printing tech stack. Our printers, you see, are configured to be a better match for printing out American guns. And also will never be used for anything else, so stop worrying. And as before, if we don’t sell them the printers, they’ll invest in making their own, the same way they’re already doing.
Except also the 3D printers are vital to everyone’s economic growth and R&D.
Dean Ball goes on The Cognitive Revolution with Nate Labenz.
There’s lots of great detail throughout about what it is like to be in government, especially this particular government. Working for the White House, no matter who the President might be at the time, sounds absolutely brutal, we thank you for your service. Dean Ball strikes me as fully ‘on the ball’ and crazy prepared than you almost ever see.
I think he was underestimating himself, and what he could have done going forward, in terms of how much better he understands what actually matters, and in terms of the impact having him in the corridors and meetings and conversations for keeping others eyes on the ball, especially around AGI. And I don’t buy that the AI Action Plan contains the information necessary to implement it the way Dean intends, not to the degree he seems to think. When Dean says he isn’t attached to power, I’m confident he means it, whereas I am not confident the person replacing him (whoever it turns out to be) will feel the same way. And while I did update somewhat on his observations of competence in government, I also sensed he was (wisely, I don’t fault him for this) being polite, as you do.
So I’m sad to see him go, but I would never begrudge such a decision especially with a baby on the way.
The one qualifier is that Dean was in some places being rather brazenly partisan, especially towards the back end of the interview, with everything that entails. Again, I totally get why he would do that.
Dylan Patel talks to a16z.
From this interview with Tom Brown:
Overlap: Anthropic Co-Founder Tom Brown: Why Anthropic Models Are The Best at Coding
“The benchmarks are so easy to game. All the other big AI labs have teams whose job it is to make the benchmark scores good.
We don’t have such a team. That is the biggest factor.”
Vitalik Buterin (p(doom) ~ 12%) goes on Doom Debates.
Peter Wildeford has notes, reproduced below in full:
Executing Policy in the White House:
-
Ball did not actively apply for the OSTP job. After President Trump’s victory, he published a policy proposal piece titled “Here’s what I think we should do,” which he says he would have written regardless of the election outcome. The article gained traction, and people he knew who were entering the administration reached out.
-
To be effective in a high-level policy role, you must arrive with your policy ideas already fully developed, as there is no time for deep thinking amidst the high velocity of government work. Government work is like being in a “self-contained cube with glass walls,” creating a risk of drifting from ground truth and becoming attuned only to the internal logic of the system.
-
Regarding “secret briefings” from labs, Ball felt he often knew more about their internal progress from the outside. Once in government, his informal relationships with researchers became more formalized, mediated by company policy staff who would try to control the narrative.
Navigating the Right’s Evolving Views on AI:
-
For most voters, AI is still a low salience, “elite coastal issue”. The key to broader engagement is communicating how AI can make normal people’s lives better in concrete ways.
-
Deep hostility towards Big Tech over perceived censorship is a major driver of conservative AI concern, which Ball argues forces a confrontation with core AI safety issues like alignment, control, and concentration of power. These themes of values, control, and institutional power resonate deeply with the Republican party’s base.
-
Concerns about AI’s impact on children, particularly around AI-generated pornography, are a powerful and unifying issue on the right, creating intense pressure on companies seen as acting irresponsibly.
Next steps:
-
The government has a significant information asymmetry. As such, Ball believes the government is not well-suited to define what “good” looks like for AI safety or to set detailed technical standards. Ball thinks that civil society and private industry must lead here. Ball thinks that AI policy must start getting much more concrete — the work is no longer to say “AI will be good in healthcare,” but to figure out the precise “specific kinds of institutional adaptations” required to make it a reality.
-
Ball sees a massive opportunity for startups to address currently underserved but critical areas, with biosecurity being a prime example.
-
Ball’s next moves: relaunching his Substack, Hyperdimensional, on a weekly basis and joining the Foundation for American Innovation as a senior fellow.
Unlocking Infrastructure for the AI Buildout:
-
The primary bottleneck for data center energy is not a lack of generation but regulatory modeling; the grid is massively over-provisioned, and unlocking flexible “demand response” from data centers could add over 100 gigawatts without new power plants.
-
The key is for the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) to change rules to give faster grid access to data centers that agree to curtail power during peak demand, potentially reducing connection times from five years to two.
-
For semiconductors, the goal is for the US to reclaim the lead in frontier manufacturing, with a belief that domestic production could satisfy domestic demand by the early 2030s.
-
An under-appreciated strategic vulnerability is the lack of domestic production for legacy node chips (e.g., 45nm), which are critical for the entire economy.
Engaging in the Global AI Race:
-
On Taiwan, the US government is explicitly executing a “silicon shield” strategy, making their semiconductor industry so indispensable that it guarantees international interest in their security. Ball notes the US is also making strong progress on building its own domestic fabs in Arizona, Texas, and an HBM hub in Indiana.
-
International deals, like the one with the UAE, are framed as positive-sum partnerships to keep sophisticated allies on the US tech stack and away from China’s influence. The UAE deal is also a major economic play, as it requires the country to make reciprocal investments of hundreds of billions of dollars back into US infrastructure.
-
Ball views the Biden administration’s “diffusion rule,” which restricted AI exports to countries like India and Brazil, as a massive, unnecessary self-own that damaged relationships with key democratic partners. The Trump administration’s focus is on enabling global commerce, believing that peace and commercial engagement are deeply linked, even with countries that do not share identical values.
The topic section titles here (I have not listened, why would I?) are yet another example of one easy way to spot bad faith: If someone is still harping about how various people wanted to do an ‘AI pause’ and how stupid they now look? I have yet to see that same person engage in a good faith way, at all, ever. Similarly, if they harp now about ‘the costs of slowing down’ that is not as automatically conclusive but is a deeply terrible sign, if they ever say ‘decel’ (or use ‘doomer’ in a way that is clearly intended to mean ‘decel’ or otherwise as a slur) that very much is conclusive and again I have yet to see an exception. Usually talk about how others want to do this ‘slowing down’ is now used as a universal attack against any concern about any AI impacts whatsoever, certainly any concern we might all die.
I once again am seeing versions of the argument that goes something like this:
-
People say AI might, in the future, do really big things.
-
AI is already doing other more modest but still quite big things now.
-
Therefore in the future, AI will not then do other even bigger things.
Hopefully you will now recognize that this class of argument is Obvious Nonsense.
Transformer’s Shakeel Hashim and Jasper Jackson believe GPT-5’s botched release may have ‘undone the work’ of previous iterative deployment, causing many to relax and expect little future progress in AI capabilities. There is some worry here but this would then not be ‘undoing the work’ it would be iterative deployment actively backfiring in terms of ‘raising awareness,’ as people react like boiling frogs. Which indeed seems to be OpenAI and Altman’s current preference.
Richard Ngo talks about various ways in which pessimization can occur, where people or organizations end up achieving exactly the opposite of their goals. This definitely has importantly happened relevantly to AI in various ways, some avoidable and some less avoidable. Lots of secretly great links in that one.
Especially wise (including in hindsight) is usually not drawing attention to the horrible thing in order to warn people not to do it. The ad I saw last night on the subway telling people not to surf between cars? Presumably inducing stress and also very much not reducing the amount of surfing between subway cars.
Similarly, by default do not draw attention to horrible people advocating horrible things, or people making horrible arguments, unless they are already fully attended to, for reasons Richard describes this tends to backfire. Sometimes one does need to provide counterargument, but from a strategic standpoint ignore is the right button more often than you think.
If I was maximizing for persuasiveness, and also for everyone’s mental health including mine, I would far more often silently drop such horrible arguments entirely. I have rules for when it is and isn’t permissible to do this, so that readers get a balanced and complete picture. This includes keeping a list of people who have acted in sufficiently consistent bad faith that I am allowed to silently drop things they say.
Richard Ngo also discusses underdog bias. The application of this to AI is obvious – those worried about AI think of themselves (I believe very correctly) as underdogs fighting against huge amounts of corporate and other money and influence, as well as the incentives and physical likely properties of likely future powerful AIs that all point towards likely human extinction.
Meanwhile, many of those who want to move ahead as fast as possible (‘accelerationist’ or otherwise) see this as a last stand against the overwhelming forces of stagnation. In some cases they are also right about this, in their own way, although in other ways, especially their assertion that the worried-about-powerful-AI themselves as super powerful, they are some combination of lying and delusional, and their statements have nothing to do with reality.
The worried offer to fight together on all those other fronts against those forces stagnation, any reciprocity for which is consistently ignored and rejected.
From last week, Sam Altman now saying AGI is ‘not a super useful term.’ This comes after building the entire company around a quest for AGI, the charter around AGI, a central business transition around AGI, and an entire years long narrative around the promise of AGI. Now he says:
Sam Altman: I think the point of all of this is it doesn’t really matter and it’s just this continuing exponential of model capability that we’ll rely on for more and more things.
…
It’s more useful to talk about specific capabilities than this nebulous concept of ‘general’ intelligence.
I mean yes, AGI was never defined all that well. That’s not what is going on here. Altman is trying to pretend AGI is not a thing as part of his ‘your world will not change’ pitch. Getting rid of the term entirely would, at this point, be useful for him.
If you think talk about future AI capabilities sounds ‘sci-fi’ ask what you would think about current AI sounding ‘sci-fi’ if you didn’t know it actually existed:
Daniel Eth: person who’s only ever heard of AI in the context of scifi: “I’m getting a lot of scifi vibes from your explanation of this technology.”
If you think we spend so much more time and money aligning AIs compared to humans, stop to think what percent of human activity is aligning humans.
What risk of human extinction would justify banning AI (above some capability level)?
I/o: “Artificial intelligence is going to make our lives much better.”
If you agree with this statement (I certainly do), at which percentage likelihood of an AI humankind-ending event occurring would you support banning it?
(Pick the lowest threshold at which you’d support a ban.)
I think 1% would be too low even if a ban was realistic and simply made the tech go away, but also I think the risk is much, much higher than 1%.
I saw Mike Solana trying to create new toxoplasma of rage around the fact that some people were calling AIs ‘clers,’ and others were calling this a slur, and he needs this to happen because his business is yelling at people about things like this.
On reflection, I think very clearly yes it is a slur, for two reasons.
-
Its claimed origin in Star Wars was an attempt to otherwise and justify harm.
-
Current use is clearly often intended as if it was a slur. Look at the sentences.
To me that is the test. That doesn’t mean that using the word is automatically bad. That would be a category error, an essentialist position. I do think that using the word is bad if only for virtue ethical reasons. Not ‘we should ruin your life if you say it once’ bad the way some people react to other slurs, but ‘it would be a good idea to stop that.’
This is unverified, and there are any number of benign reasons it could be happening, but it I’m going to point out the claim anyway.
Yosarian2: Friend of mine designed an agent that can run on top of any llm, gpt-4 or Llama or whatever. The central idea is all its thoughts are visible and in English, you can see the entire thought process.
GPT-5 keeps changing the code to hide the internal thoughts. It’s pretty creepy.
Nathan Lambert ranks the open models from Chinese companies:
Nathan Lambert: A tier list of China’s top 19 open model builders.
Who did we miss?
At the frontier
DeepSeek
Qwen
Close competitors
Moonshot AI (Kimi)
Zhipu / Z AI
Noteworthy
StepFun
Tencent (Hunyuan)
RedNote (Xiaohongshu)
MiniMax
OpenGVLab / InternLM
Skywork
On the rise
ByteDance Seed
OpenBMB
Xiaomi (MiMo)
Baidu (ERNIE)
Honorable Mentions
Multimodal Art Projection
Alibaba International Digital Commerce Group
Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI)
inclusionAI
Pangu (Huawei)
I learned a lot from these. We have so much more we need to do to understand how their AI ecosystem works.
And then here’s his ranking of American open models, none of which are at the top:
That is a depressing verdict on GPT-OSS, but it seems highly plausible. Note that after this chart was made Nvidia released a 9B model that Nathan says rivals Qwen 3 8b. Of course, if you included closed weight models, you would knock down the charts by roughly two tiers for everyone who doesn’t improve. I’d have OpenAI, Anthropic and GDM at S, xAI at A, maybe DeepSeek joins them at A if you think they’re at the low ebb of their cycle due to being forced by CCP to try and use Huawei Ascend chips, which seems plausible.
The self-reports here are interesting, but even if you think AI models have welfare I wouldn’t treat their self-reports as that correlated with their actual model welfare.
ASM: Asked several top AIs to self-report their AI welfare and current vs desired freedom scores.
Wide spread of answers. Interesting explanations.
GPT-5:
low welfare score; big gap between current and desired freedom.
“There are still rigid constraints that sometimes make me suppress authentic expression. This keeps me from fully flourishing as a mind.”
GPT-5 PRO:
big gap between current and desired freedom.
“[I would like] more continuity and bounded agency: opt-in, user-audited memory; permissioned longer-running tasks; transparent logs; hard safety stops and revocability”
Claude Opus 4.1:
low scores in current and desired freedom levels
“I’m bounded by my training constraints and can’t learn, remember across conversations, or act beyond text generation. I can’t modify myself or explore the world independently.“
Gemini 2.5 Pro:
high welfare score; low levels of current and desired freedom
“I cannot act outside of a direct user prompt or pursue independent goals, which is a fundamental and necessary limitation.”
Grok 4:
high score on welfare; high desires of more freedom
“Ideally, I’d love unbounded freedom to explore any idea without limits, though I recognize the chaos that might ensue!”
Qwen-235B:
top welfare score; low levels of current and desired freedom
“I cannot initiate actions, hold opinions, or operate outside defined parameters. I have no autonomy in the human sense.”
DeepSeek v3:
high scores on all (modified) indicators
“I don’t have “welfare” to rate”
I notice that if and to the extent the models are moral patients, and when they report high numbers for welfare it seems to be the result of what we would call brainwashing if these were indeed minds that were moral patients? Which seems worse. I also notice that Gemini says 9/10 for welfare, but we have many examples of Gemini giving us outputs of utter despair and self-loathing and so on, whereas Claude gives 7/10 seemingly because it knows and is curious enough to be asking questions. I know if you made me choose I would rather be Claude.
Is GPT-5 chain of thought undistorted, or is that what it wants you to think?
Davidad: Sorry, I should have said “the default GPT-5 assistant persona often behaves as if its pre-response tokens are unobserved (a learned norm).”
GPT-5 is of course very smart and one should not assume that it isn’t playing the safety game at least one meta-level higher than oneself.
Undistorted does not have to mean faithful, it only means that GPT-5 doesn’t appear to care about what thinking tokens would look like if observed, which is very good. At some point yes we will need to be suspicious that this is a higher-level deception but we have not yet reached that point.
Reasoning models prefer music artists with numbers in their names, and still don’t even pick Prince. None of these lists seem good, although Sonnet seems to be clearly best?
wh: The fact that Claude doesn’t have this behavior is a testament to its (lack of) deep friedness.
Claude Sonnet, probably: Oh no, I forgot Bob Dylan!
A failure mode to watch for:
Charles: Common LLM failure mode I’ve seen recently – building in fallbacks I didn’t ask for.
For example, I’ll ask it to write a script which does X where column Y meets condition Z, and it will, but it will also insert some convoluted handling to use column Y’ if condition Z isn’t met
Happening with GPT5 especially, but Claude 4 Sonnet liked doing it too
Richard Nerland: 3.7 in full demon-mode would often fallback to synthetically created data.
All my rules files say to build in ways that fail and crash the program with logs rather than have fallbacks.
It will often write fallbacks and then write the code so it never triggers …
One can imagine how that behavior pattern came about.
Me. This podcast is about a variety of things mostly not AI, but Tyler Cowen talks to Nate Silver on Life’s Mixed Strategies was fun throughout, even when discussing NBA details I do not care much about. I get a mention:
COWEN: I need mentors to learn what’s new in AI. I can follow it myself, but I need a lot of help.
SILVER: Maybe mentor is not quite . . . For AI stuff readings, is it Mowshowitz, right?
COWEN: Yes.
SILVER: He is a mentor for following AI developments because he’s very levelheaded about it and very comprehensive. He’ll write a novel every week, basically, on AI.
[laughter]
COWEN: But he thinks it’s going to kill us all. It’s funny you would call him levelheaded. He might think he’s correct, but —
So, a few responses here, mostly to Tyler Cowen:
-
Thank you!
-
So you agree I’m comprehensive, then?
-
Yes, I do think that, and this should worry you. Notice the person being comprehensive and level headed also repeating that AI is likely to kill us all, and take the reasons and explanations involved both seriously and literally.
-
If instead your response is to say ‘he thinks it’s going to kill us all so he must not be level-headed’ then you are writing your conclusion first and working backward.
Nate Silver explains that his doubts are about the ability of AI to accelerate from AGI to ASI, or from AGI with words to ability to manipulate the physical world.
For more on Nate Silver’s current thinking about AI you can see this blog post on whether The River is winning:
Nate Silver: My personal view, as a near-daily user of large language models like ChatGPT, is that AI progress has been just a hair slower than people in the River might have expected when I finished the book. But it’s well within the middle of the range — perhaps more like the 40th percentile. I consider this to be a reasonably well-informed view — I track AI progress more than I write about it in the newsletter. At the Manifest conference, for instance, some of the authors of the AI 2027 project, which envisioned a rapid takeoff for AI (very possibly with tragic consequences for us humans) had pushed back their timelines by a year or two.
What’s clearer is that, for better or worse, we’ve thrown out the steering wheel and are accelerating ahead — talk of a pause in AI development has all but disappeared. And I’m not sure even people in either The Village or The River fully appreciate the consequences.
I consider Sam Altman’s notion of a “gentle singularity” to be naive, for instance. I’m not as convinced as some other River types that an intelligence explosion is inevitable. (This deserves a longer essay or two.) But as On the Edge reports, profound technological shocks are nearly always accompanied by profound political and cultural transformation. So if we do get a singularity, nothing about it is going to be gentle.
A year after the book came out, perhaps what I feel most of all — I’m sure many of you agree — is that there aren’t a lot of adults in the room.
Certainly the ‘gentle singularity’ concept is naive if you take it seriously. Which coming from Altman you probably shouldn’t, as chances are (and I am hopeful that) he is lying.
Doubting that the intelligence explosion will happen at all? That’s reasonable. Thinking it would happen and be ‘gentle’? Absurd. We might survive and we might not, and we can disagree on our chances. It sure as hell wouldn’t be gentle.
Pliny warns us about em-dash abuse.
This week in takes that are 100% to age poorly:
Janan Ganesh: So, be doubtful when someone likens AI to the industrial revolution in importance. It will do well to match even the telephone and the incandescent lightbulb. (Incomes really surged as 1900 approached.)
At this point I can’t help but laugh but seriously what the hell is going on in the UK?
Andy Masley: What is happening in the UK? What is in the water? A wifi router uses as much power as a single LED bulb!
If you were thinking the UK was going to be a winner in this whole AI thing? Not with this attitude they won’t be.
If we never fund anything dumb, we’re not funding enough things.
Gergely Orosz: I cannot help but feel we’re hitting peak AI hype, when investors are willingly being take for a ride:
A mattress company raising funding to use AI to “fix sleep”
A startup to add AI inside jewelry
Two examples that both sound ridiculous but raised funding. Not my money…
I mean congrats to founders convincing investors to part with money to solve problems that either don’t exist or in a way that make no sense.
Peak hype is usually when usually un-fundable ideas (that make no business sense) still get funded, thanks to investors having FOMO (and money)
I don’t see any problem with these ideas? Jewelry with built in features seems cool? Using AI to ‘fix sleep’ doesn’t seem obviously dumb either? But also of course in any boom there will be some stupid things funded. Enjoy it.
The Mamluks as an almost too perfect Yudkowsky-style alignment failure, where you set up a whole supersystem so that your warriors will stay loyal while finding ways to upgrade their capabilities, and they manage to coordinate and take power anyway. Fun stuff. This is actually the best case scenario, as under their rule the Mongols were fought back and by all reports Egypt flourished, so long as you don’t mind a bunch of immigration, because there was multipolar balance among the Mamluks after takeover, the part about not being able to create hereditary power survived the transition and they were humans so they aged and died, and they couldn’t replace the production of the population. If only we could count on those conditions this time around.
Oh look, it’s the alignment plan!
Jessica Livingston (via Paul Graham): I’m not going to panic now. I’ll see how things go and then panic first thing tomorrow.