Wireless TVs use built-in cameras, NFC readers to sell you stuff you see on TV
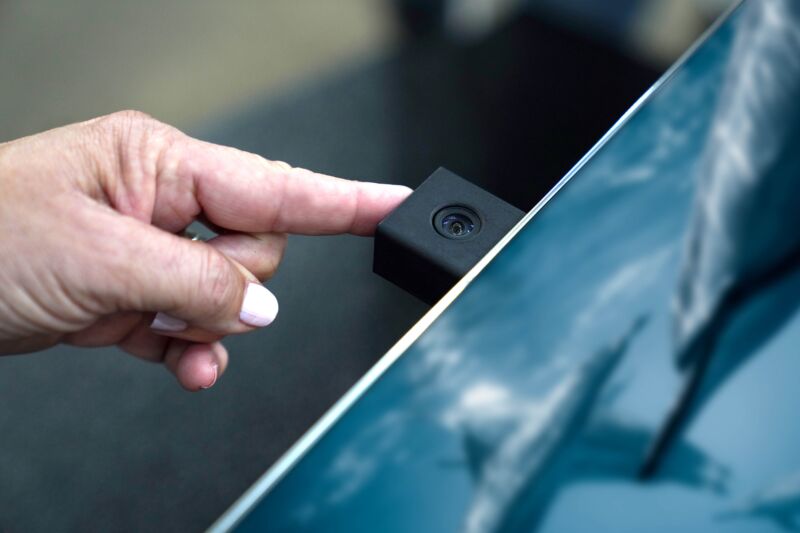

Enlarge / A closeup of the webcam on the Displace TV announced in January.
Dislace
It’s no secret that TV makers are seriously invested in pushing ads. Using TVs for advertising goes back to 1941 when the first TV commercial aired. But as we trudge our way through the 21st century, TV vendors are becoming more involved in ensuring that their hardware is used to sell stuff and add to their own recurring revenue.
This has taken various forms, but in some cases, we’re seeing increasingly invasive strategies for turning TVs into a primary place for shopping. The latest approach catching attention comes from the startup Displace. Its upcoming TVs will use integrated webcams and NFC payment readers to make it easy for people to buy stuff they see on TV.
Displace hasn’t officially released a product yet, so skepticism about the TVs it says it will demo at CES 2024 in Las Vegas next month, as spotted by sites like Wifi Hifi, is warranted. (Displace said it would have images of the newly announced TVs to share next year). The startup specializes in wireless TVs with hot-swappable batteries that can vacuum suction-mount to a wall and zip-line slowly off said wall when sensing an unstable connection or low battery. The original “Displace TV” that Displace announced in January is supposed to ship in mid-2024. Displace has been taking preorders for those.
The two new TVs Displace is adding to its 2024 release plans, the Displace Flex and Displace Mini, are all about making watching TV shopping better.
Stop & shop: TV edition
According to Displace’s announcement, the Displace Flex (a 55-inch 4K OLED TV) and Displace Mini (a 27-inch 4K OLED TV) will use proprietary gesture technology and each TV’s integrated 4K camera to tell when a user is raising their hand. It’s unclear how accurate that will be (could the shopping experience accidentally be activated if I raised my hand to tie my hair up, for example?), but at that point, the TV is supposed to pause the content being played. Then, it uses computer vision to “analyze the screen to find products available for sale. Once they see something they want to purchase, viewers drag and drop the product into the global Displace Shopping Cart,” the announcement says.
Displace Shopping will work at any moment the TV is on, and users can buy stuff they see in commercials by using the TVs.
Displace’s December 14 announcement said:
As soon as the viewer is ready to checkout, Displace Payments makes paying as easy as bringing a user’s smartphone or watch near the TV’s built-in NFC payment reader, a fully secure process that requires no credit card info. Viewers can also pay from within the Displace app.
If the TV can’t find a specific product for sale, it will “search for similar items” without user intervention, according to Displace. The TV will show products from any available online retailers, allowing users to select where they want to make their purchase.
Displace hasn’t provided full details about how it will make money off these transactions, but when reached for comment, founder and CEO Balaji Krishnan told Ars Technica that Displace has “different business models, and one of them is to take a transaction fee,” and that Displace will share more details “later.”
Displace also sees people using Displace Payments to pay for telehealth applications and equipped the Flex and Mini with thermal cameras.
Wireless TVs use built-in cameras, NFC readers to sell you stuff you see on TV Read More »