They also show us the chips, and the data centers.
It is quite a large amount of money, and chips, and some very large data centers.
Nvidia to invest ‘as much as’ $100 billion (in cash) into OpenAI to support new data centers, with $10 billion in the first stage, on the heels of investing $5 billion into Intel.
Ian King and Shirin Ghaffary (Bloomberg): According to Huang, the project will encompass as many as 5 million of Nvidia’s chips, a number that’s equal to what the company will ship in total this year.
OpenAI: NVIDIA and OpenAI today announced a letter of intent for a landmark strategic partnership to deploy at least 10 gigawatts of NVIDIA systems for OpenAI’s next-generation AI infrastructure to train and run its next generation of models on the path to deploying superintelligence. To support this deployment including datacenter and power capacity, NVIDIA intends to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI as the new NVIDIA systems are deployed. The first phase is targeted to come online in the second half of 2026 using NVIDIA’s Vera Rubin platform.
New Street Research estimates that OpenAI will spend $35 on Nvidia chips for every $10 that Nvidia invests in OpenAI. Nice work if you can get it.
Nvidia was up about 4.5% on the announcement. This project alone is a full year’s worth of Nvidia chips, which should further put to bed any question of Nvidia running out of Western customers for its chips, as discussed later in the post.
Note that the details of this deal are not finalized, which means the deal isn’t done.
OpenAI paired this with progressing its Stargate project with Oracle and SoftBank, expanding into five new AI data center cites and claiming they are on track to complete their $500 billion, 10-gigawatt commitment by the end of 2025, as these announcements plus the original cite in Abilene, Texas cover over $400 billion and 7-gigawatts over three years.
The new sites are Shackelford County, Texas, Dona Ana County, New Mexico, ‘a cite in the midwest to be announced soon,’ the existing Oracle cite in Lordstown, Ohio, and next year a cite in Milam County, Texas developed in partnership with SB energy.
Berber Jin at WSJ described the full plan as a $1 trillion buildout of computing warehouses across the nation and beyond.
Sam Altman (CEO OpenAI): I don’t think we’ve figured out yet the final form of what financing for compute looks like.
But I assume, like in many other technological revolutions, figuring out the right answer to that will unlock a huge amount of value delivered to society.
To celebrate all this, Sam Altman wrote Abundant Intelligence.
What about what this means for training runs? It means there is no physical cap that is likely to bind, it will be more about what makes economic sense since compute will be in high demand on all fronts.
Peter Wildeford: 10GW AI training runs… probably with models 20x-100x larger than GPT-5. We knew this was going to come, and we still don’t have any updates on timeline. How many years the $100B is over is also unclear – the ultimate size of the investment is really contingent on this.
I’d expect the 10GW OpenAI cluster becomes operational around 2027-2028. GPT-5 was disappointing to some but it’s on trend for its size and true scaling hasn’t happened yet. Get ready for the next three years, and we will truly see what some scaled AI models can do.
What about for other purposes? Ambitions are running high.
Haider: Sam Altman says the industry is bottlenecked by compute, and OpenAI can’t meet demand
Over the next 1-2 years, scarcity could force painful tradeoffs,
“cure cancer research vs free global education”
No one wants to make that choice. The only answer: scale up.
Peter Wildeford: Nvidia is busy trying to sell chips to China while our American AI companies can’t get enough compute at home 😡
That seems like quite the timeline for either curing cancer or providing free global education. But yes, compute is going to be like any other limited resource, you’re going to have to make tradeoffs. Spending on health care and education cannot be unlimited, nor does it automatically ‘win in a fight’ against other needs.
Eyes are on the prize. That prize is superintelligence.
Should we have plans and policies designed around the idea that superintelligence is coming? Well, we certainly shouldn’t build our plans and policies around the idea that the AI companies do not expect superintelligence, or that they won’t try to build it.
Roon: all the largest technology fortunes in the world are on record saying they’re betting the entire bank on superintelligence, don’t care about losses, etc. the only growth sector left in planetary capitalism. It is dizzying, running on redline overload.
If that statement does not terrify you, either you did not understand it, you did not think through its consequences, or you have become numb to such things.
Gavin Baker (quoted as a reminder from BuccoCapital Bloke): Mark Zuckerberg, Satya and Sundar just told you in different ways, we are not even thinking about ROI. And the reason they said that is because the people who actually control these companies, the founders, there’s either super-voting stock or significant influence in the case of Microsoft, believe they’re in a race to create a Digital God.
And if you create that first Digital God, we could debate whether it’s tens of trillions or hundreds of trillions of value, and we can debate whether or not that’s ridiculous, but that is what they believe and they believe that if they lose that race, losing the race is an existential threat to the company.
So Larry Page has evidently said internally at Google many times, “I am willing to go bankrupt rather than lose this race.” So everybody is really focused on this ROI equation, but the people making the decisions are not, because they so strongly believe that scaling laws will continue, and there’s a big debate over whether these emergent properties are just in context, learning, et cetera, et cetera, but they believe scaling laws are going to continue. The models are going to get better and more capable, better at reasoning.
And because they have that belief, they’re going to spend until I think there is irrefutable evidence that scaling laws are slowing. And the only way you get irrefutable evidence why has progress slowed down since GPT-4 came out is there hasn’t been a new generation of Nvidia GPUs. It’s what you need to enable that next real step function change in capability.
Mark Zuckerberg (last week): If we end up misspending a couple of hundred billion dollars, I think that that is going to be very unfortunate obviously. But what I’d say is I actually think the risk is higher on the other side.
If you if you um build too slowly and then super intelligence is possible in 3 years, but you built it out assuming it would be there in 5 years, then you’re just out of position on what I think is going to be the most important technology that enables the most new products and innovation and value creation and history.
In case it is not obvious, no, they are not racing for ‘market share’ of inference tokens.
A central argument for going forward with AI, that was often cited by OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, used to be ‘compute overhang.’ As in, if we didn’t build AI now, then when we did built it we would have more compute available and progress faster, which would be more dangerous, so better to make progress now. Ah, simpler times.
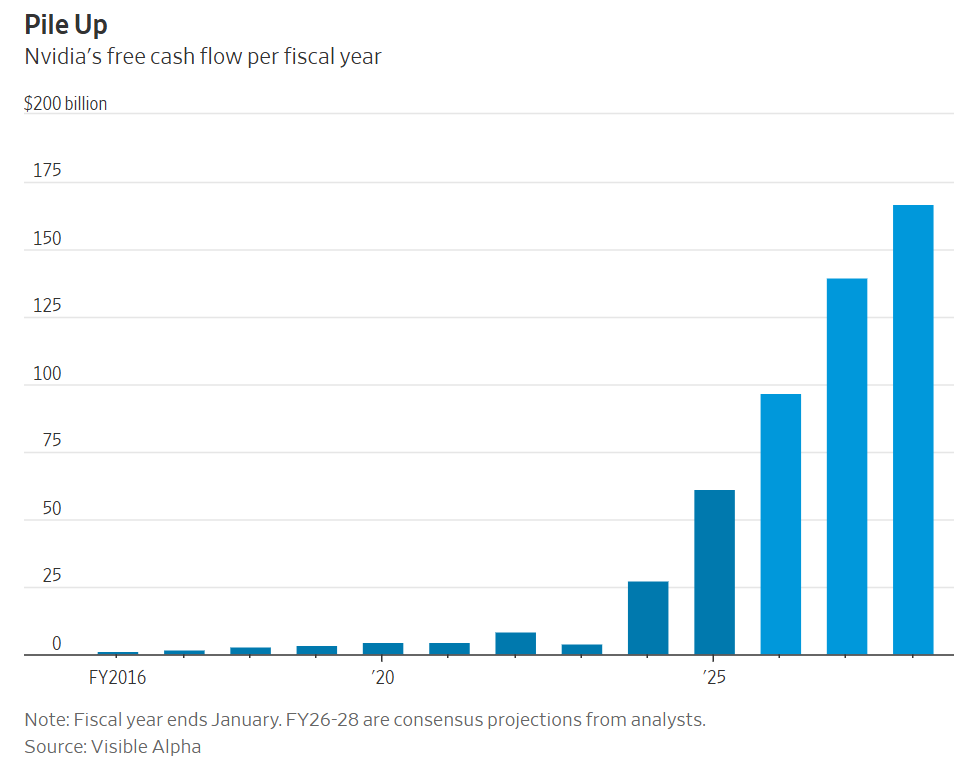
Does Nvidia have, as Dan Gallagher claims in the Wall Street Journal, Too Much Money? As in so much money they don’t know what to do with it and it loses meaning.
Nvidia is set to generate $165 billion or so in annualized free cash flow by the end of 2028 according to consensus projections:
In the worst case you can always return value to shareholders. Nvidia wisely only pays the minimum $0.01 dividend (so it can be included in various financial products), but has already repurchased $50 billion of its own stock over the past year and plans to buy another $60 billion more.
The argument iby Gallagher is largely that Nvidia cannot make a major acquisition without Chinese approval? I do not understand why they would care, given China is already actively telling companies not to buy Nvidia’s products? Seems like none of their damn business.
But also Nvidia can do further strategic investments and projects instead that can easily eat up this level of free cash flow, if they have no better use for it. Stock market investors would be happy to get more exposure to private companies like OpenAI.
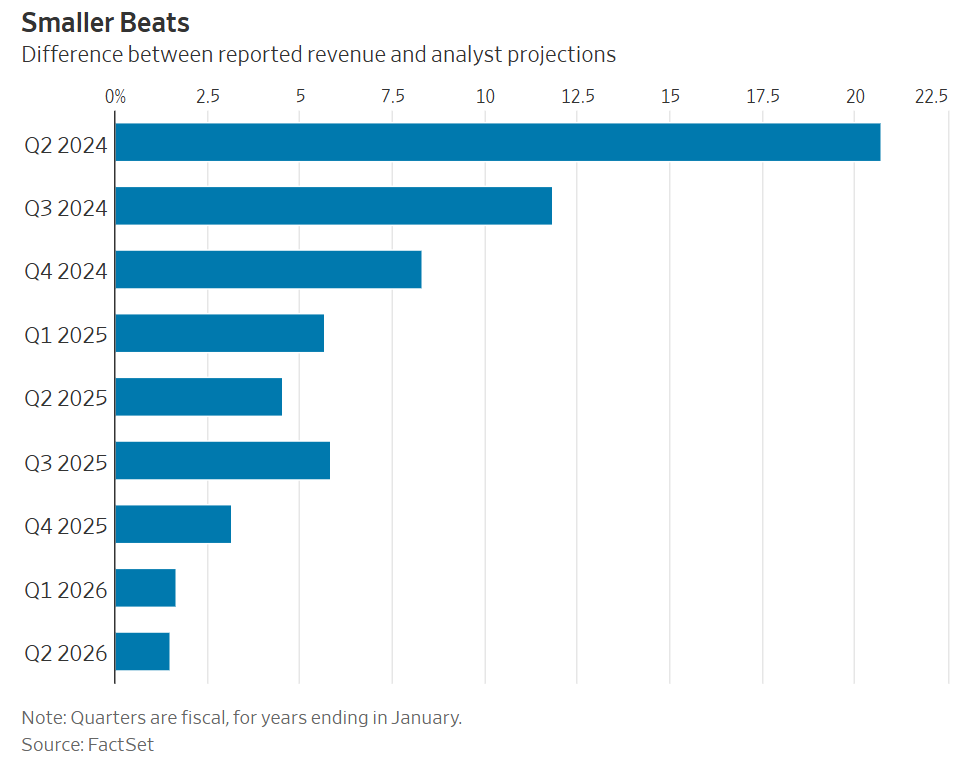
Thinking around Nvidia on Wall Street has for a long time been rather silly and my only regret is I did not buy in far sooner (for those who don’t know, consider this my disclosure that I am overweight Nvidia and have been for a while, quite profitably). For example, a real newspaper like the WSJ will post that the ‘wow’ factor is wearing off because Nvidia is now beating analyst revenue projections by smaller amounts:
If a company keeps beating your expectations, that’s a failure of expectations, with that failure at least getting smaller over time.
Many noticed that when Nvidia invests in OpenAI which uses the money to buy chips from Nvidia, and you move $100 billion back and forth, this can inflate valuations without obviously creating real value.
Such things have happened before.
Andrew Cote: $1 of cash on NVIDIA’s balance sheet is worth $1.
But $1 of revenue at ~50% net margins with a 50x P/E ratio, is worth $25.
Paul Graham (as quoted by Danielle Fong): By 1998, Yahoo was the beneficiary of a de facto Ponzi scheme. Investors were excited about the Internet. One reason they were excited was Yahoo’s revenue growth. So they invested in new Internet startups. The startups then used the money to buy ads on Yahoo to get traffic. Which caused yet more revenue growth for Yahoo, and further convinced investors the Internet was worth investing in.
When I realized this one day, sitting in my cubicle, I jumped up like Archimedes in his bathtub, except instead of “Eureka!” I was shouting “Sell!”
You do have to watch out for the de facto Ponzi scheme, but this is not that, from a pure business perspective it is a clear win-win agreement. You also do have to watch out for a naively multiplying profits into a fixed P/E ratio, but the stock market is smarter than that. The only losers are other AI labs, Microsoft and humanity’s chances of survival.
Peter Wildeford: Nvidia is doing revenue round-tripping at an unprecedented scale (Nvidia servers purchased by companies using money from Nvidia investment). Previously there was CoreWeave, Crusoe, xAI, and Llambda Labs but this is next level. I don’t think any company has ever done this at such a scale. This seems great if we continue AI boom times but could quickly unravel if AI is a bubble.
This is another big loss for Microsoft. Microsoft could’ve been OpenAI’s capital partner of choice as they got in early and had lock-in. But Microsoft wasn’t willing to keep delivering and backed out. This is another nail in the coffin of the Microsoft-OpenAI relationship.
Taking on Nvidia as another huge capital partner provides some much needed stability for OpenAI after being abandoned by Microsoft and their only other partner being SoftBank, which …doesn’t have the best track record.
I guess good to know OpenAI is committing to Nvidia chips for the long haul. Sounds like Microsoft isn’t close to cracking their own chip development like Amazon or Google. That’s good for Nvidia at least.
Ultimately, I am concerned that the US economy is increasingly a leveraged bet on AGI happening. Nvidia is 7% of the US stock market, so their investments matter. AGI happening may mean the end of humanity, but at least the S&P 500 will remain strong.
This probably explains why OpenAI doesn’t talk much about export controls on Nvidia products like Anthropic does… even though such controls would help OpenAI by undermining their Chinese competition.
Nvidia is a bet on AI happening, but in a safe fashion as they are doing it via reinvesting their profits rather than leverage. If AI valuations collapse, Nvidia only goes down roughly proportionally, and they remain a great company.
What about the implications of the deepening of the OpenAI-Nvidia partnership for policy, and willingness to speak out about existential risks?
A key worry has long been that OpenAI depends on Nvidia, so OpenAI may be reluctant to speak about AI risk lest they anger Nvidia and endanger their chip allocations. OpenAI has not been a great political actor, but Sam Altman appreciates many of the dangers and issues that will be at stake.
It is also fortunate that OpenAI’s interests in many ways align with America’s and with those of humanity, far more so than do the incentives of Nvidia. Nvidia wants to make and sell as many chips as possible to the widest variety of customers, whereas OpenAI has a strong interest in America beating China across the board and keeping things under control.
This situation could get far worse. Nvidia may even have made this part of the deal, with Altman agreeing to pursue or not pursue various political objectives, including around export controls. There is even the danger Nvidia ends up with a board seat.
It is likely not a coincidence that Anthropic has found a way to get its compute without Nvidia.
There is a matching bull case, on two fronts.
In terms of Nvidia impacting OpenAI, it is plausible that Nvidia already had maximal leverage over OpenAI via controlling chip allocations, especially if you add that it has the ear of the Administration. At some point, things can’t get any worse. And indeed, locking in these contracts could make things much better, instead, via locking in large commitments that reduce Nvidia’s real leverage.
Then there’s the question of OpenAI impacting Nvidia. Nvidia has a market cap of ~$4.3 trillion, but $100 billion is still ~2.3% of that, and the baseline scenario (since OpenAI is riskier and has more room to grow) is OpenAI equity grows in value faster than Nvidia equity, and Nvidia engages in stock buybacks. So even if no further investments are made, Nvidia could quickly be 5% or more exposed to OpenAI, on top of its exposure to xAI and other Western AI companies, where it makes a variety of strategic investments.
That starts to matter in the calculus for Nvidia. Yes, they can do better short term in their core chip business via selling to China, but that hurts their other investments (and America, but they clearly don’t care about America), and long term the model of compute-intensive top-quality closed models is better for Nvidia anyway.
Usually the incentives point the way you would think. But not always.