Windows version of the venerable Linux “sudo” command shows up in preview build
sudo start your photocopiers —
Feature is experimental and, at least currently, not actually functional.
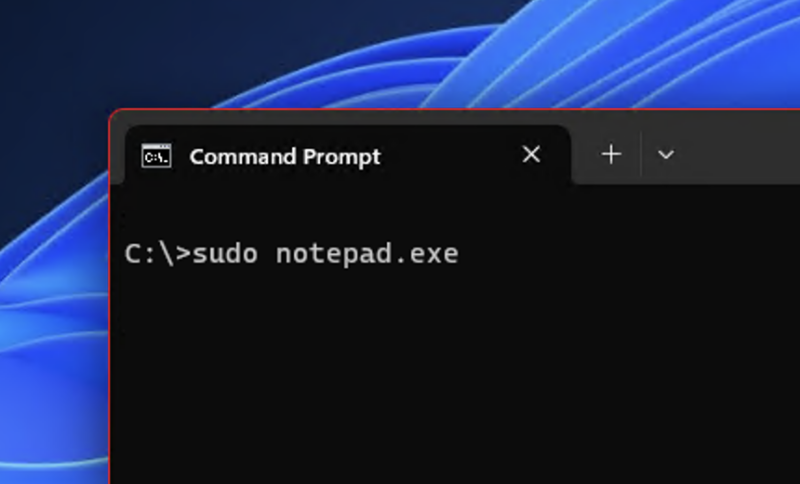
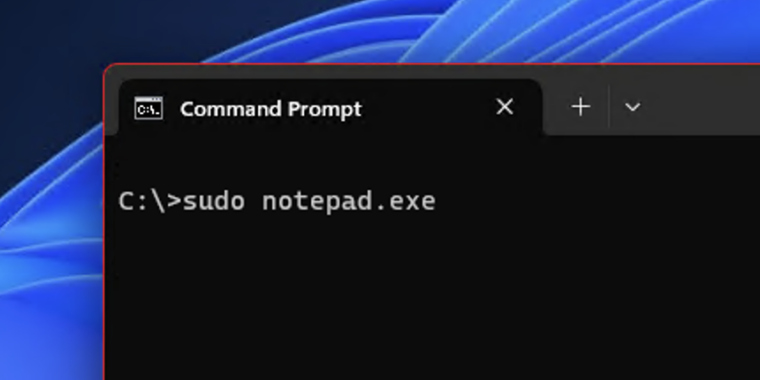
Enlarge / Not now, but maybe soon?
Andrew Cunningham
Microsoft opened its arms to Linux during the Windows 10 era, inventing an entire virtualized subsystem to allow users and developers to access a real-deal Linux command line without leaving the Windows environment. Now, it looks like Microsoft may embrace yet another Linux feature: the sudo command.
Short for “superuser do” or “substitute user do” and immortalized in nerd-leaning pop culture by an early xkcd comic, sudo is most commonly used at the command line when the user needs administrator access to the system—usually to install or update software, or to make changes to system files. Users who aren’t in the sudo user group on a given system can’t run the command, protecting the rest of the files on the system from being accessed or changed.
In a post on X, formerly Twitter, user @thebookisclosed found settings for a Sudo command in a preview version of Windows 11 that was posted to the experimental Canary channel in late January. WindowsLatest experimented with the setting in a build of Windows Server 2025, which currently requires Developer Mode to be enabled in the Settings app. There’s a toggle to turn the sudo command on and off and a separate drop-down to tweak how the command behaves when you use it, though as of this writing the command itself doesn’t actually work yet.
The sudo command is also part of the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), but that version of the sudo command only covers Linux software. This one seems likely to run native Windows commands, though obviously we won’t know exactly how it works before it’s enabled and fully functional. Currently, users who want a sudo-like command in Windows need to rely on third-party software like gsudo to accomplish the task.
The benefit of the sudo command for Windows users—whether they’re using Windows Server or otherwise—would be the ability to elevate the privilege level without having to open an entirely separate command prompt or Windows Terminal window. According to the options available in the preview build, commands run with sudo could be opened up in a new window automatically, or they could happen inline, but you’d never need to do the “right-click, run-as-administrator” dance again if you didn’t want to.
Microsoft regularly tests new Windows features that don’t make it into the generally released public versions of the operating system. This feature could also remain exclusive to Windows Server without making it into the consumer version of Windows. But given the command’s presence in Linux and macOS, it will be a nice quality-of-life improvement for Windows users who spend lots of time staring at the command prompt.
Microsoft is borrowing a longstanding Linux feature here, but that road goes both ways—a recent update to the Linux systemd software added a Windows-inspired “blue screen of death” designed to give users more information about crashes when they happen.
Windows version of the venerable Linux “sudo” command shows up in preview build Read More »