Here’s to everyone having a great 2026 in all ways, so I figured what better way to end the year than with a little practical advice. Like everything else, dating is a skill. Practice makes perfect. It helps to combine it with outside analysis, to help you on your quest to Just Do Things.
A common theme in these roundups is that the best thing you can do as a young man, to get better at dating and set yourself up for success, is to get out there and engage in deliberate practice.
Cartoons Hate Her: Today I wrote about some of the worst dating advice that young men get. Namely, the advice to delay dating or relationships until they’ve “built themselves,” usually into their 30s.
Getting dating experience- even when it clearly doesn’t matter- builds social skills and confidence. It’s not something you want to deliberately defer. Dating *isworking on yourself.
Zac Hill: Hard true and also generally applicable. Niko Canner told me a variant of this when I was about to work at Bridgewater to ‘acquire skills’:
“what job are you acquiring skills for?”
“basically my current job”
“we’ll just keep doing that job, and you’ll acquire those skills!”
I didn’t date at all until well into my 20s because of reasons, so I have some experience with this, and it is absolutely was the opposite of correct ‘building myself’ strategy. Totally counterproductive. Even in terms of otherwise building yourself, the skills you get dating will help you elsewhere, and also motivate you and direct you. There are of course temporary exceptions if you go deep into a startup or something, but yeah, absolutely get out there.
As a woman, you typically (by all reports) have no trouble getting reps as such, but there is still the danger that you waste those reps if you keep repeating the same procedures without learning how to improve, which could be in any number of ways including selection.
Note that reps applies the whole way through, and don’t forget to postmortem.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: The way to get good at sex is the same as the way to get good at any other process: Once you’re done, roll out the whiteboard and together do a no-fault analysis of what went wrong, what went right, and what could’ve been done differently.
Reactions divided into “lol u autists” and “well yes that is how it works” and my friends it is the second class that has acquired dangerously high sexual capabilities
le petit postmortem
Sofia: Both reactions are correct
Aella: this is unironically the method behind the best sex of my life.
Brooke Bowman: in a romantic context, what does it mean to ‘shoot your shot’? i’m curious what the range of actions the phrase implies is
is it like confessing your feelings/asking on a date or do you also think dropping your handkerchief counts.
I believe it means, both in romantic and non-romantic contexts: Create common knowledge that you are shooting your shot, that you are interested, and that failing to respond positively is a rejection, such that you cannot easily ‘shoot your shot’ again.
Thus, anything can count, including dropping a handkerchief, if both parties know the other is sufficiently advanced.
However, many people especially guys are highly clueless or ambiguously might be clueless, leading to a lot of thinking you shot your shot when you definitely haven’t shot your shot. The threshold is common knowledge, not merely that they pick up on you giving them an opening. That doesn’t count and does not close the book, you have only shot your shot when they know that you know that they know, and so on.
If you are going to keep interacting in the future, beware ‘wasting your shot’ where you create common knowledge without giving yourself much chance to succeed. By definition you only get one shot (or at least, subsequent shots by default will at least be harder). However, that too can have advantages, as now you can move on having shot your shot, and you do create some amount of positive selection, and the act of creating common knowledge means they could reopen things in the future.
Any time someone says ‘I don’t see how this can backfire’ you definitely shouldn’t take their advice until you’ve figured out how it can backfire.
Liron Shapira: As a nerdy dating expert, I consider
Bryan Caplan
‘s handholding tactic to be the best practice for shy men looking to get into a romantic relationship (and not be stuck in the friend zone).
Could this somehow backfire? I claim it can’t. Let’s game it out.
The suggestion isn’t that you do more requested hand holding while dating, it is to use this request as an escalation move out of a potential friend zone.
The theory is that your romantic intent here is obvious, expressed in a non-creepy way, thus creating common knowledge, but it is not explicit so it is deniable common knowledge so you can still retreat to a friendship on a fail, she’ll at least be impressed you tried and maybe she eventually decides to return interest even if she doesn’t now, and probably she actually says yes and you can keep building from there.
This is in contrast to Bryan’s advice to do this on all first dates, or at least to establish you are indeed on one, and as a way of establishing common knowledge of the situation and failing fast.
The part I 100% agree with is, provided you are interested, you are better off doing something rather than doing nothing, whether on an existing date or not. Shoot your shot, whatever your shot may be. And yes, if you’re too shy or unskilled to take a better or more subtle shot, then this is a shot one can take take.
That doesn’t mean it should be this shot. So, let us count the ways this can backfire.
-
She says no, where on a better executed move she would have said yes. Then it is much harder for you to try again, indeed the whole point here is that you wouldn’t try again. Skill absolutely matters, and this by design is a case of you only get one shot. Contra Liron, no, you’re not going to get a yes a majority of the time.
-
In addition to it coming off weird or as representing a lack of skill or awareness, this can be seen as insufficiently ambiguous or too far up the escalation ladder if you go too early.
-
One thing is if she’s looking for a more casual vibe, going for ‘romantic coded’ actions like holding hands too early can give the ick when you were live. There’s a Sex and the City where exactly this ask is an instant dealbreaker, even after they’ve slept together, because it was a failure to read the room.
-
She says no, where on a better executed move that did not force clarity you would have gotten a maybe or a soft no that lets you stay in the game. Forcing clarity can work against you. This is fine if you’re shooting a bunch of shots, but not if this is an especially valuable shot to shoot.
-
She says no, and rather than being impressed she is not impressed or weirded out, thus leaving the friendship in a worse position. Cost of shooting shots, but that’s one way in which it is not riskless, and the less ambiguous and more awkward the shot the greater the risk of this.
-
She says yes, but it’s awkward in context, and so on.
Again, I don’t want to discourage anyone too much here. It is far from the worst move, and again something beats nothing. But we don’t believe in misleading anyone.
Bumbadum (2.1m views): This type of behavior killed romance and I hate you people for it.
I hate the knowledge that millions of young men cannot hope to ever express love in the purest most beautiful way because you disgusting whores will post it on social media and mock in private.
Young men lost the ability to express those feelings. To write, to feel, to be comfortable. They have to bury deep down and hide it from the world less they be cruelly mocked.
You disgusting hags lost the ability to ever see it. You disgusting cretins all wish to have a Notebook love story meanwhile any feeling of that unconditional love is met with mockery.
I hate you all.
I am getting DM’s that essentially describe romance movie plotlines that end with “but she hated romance”
Unfortunately Rona Wang (understandably) took her Twitter private by the time I got to this, so I couldn’t gather more context there, but there are some obvious notes here.
-
The context is that she was the only girl at the hackathon. That’s a context where you don’t open at all, in any form, without strong indications of interest. If this was done in an ordinary mixed context, presumably that would be different.
-
This is a clear NRN (no reply necessary) opening, which makes it less of a problem than opening moves that require a response, but even outside of the gender imbalance context I wouldn’t call it ‘romance.’
-
You think this thread is bad for the guy who passed her the note?
As in, no one knows who passed this note. He’s fine. And indeed, you have a play available, which is to reply with some version of ‘I am the guy who sent the note, she didn’t reply so I’m still single, I live in city and my DMs are open.’ Yes, many of the DMs won’t be kind, but if you’re okay with that, 61 million views on OP and it only takes one hit. If the context was different such that you looked better, you’re all set.
Then on Nicole’s post (original had 5m views):
-
Pretty sure it worked.
-
Many of the comments assume that it didn’t and it was awful, but that it is odd given that the document says that it worked.
-
This is indeed a high risk, high reward play, because you are putting her on the spot and if the answer isn’t an enthusiastic yes then oh boy is it no, you haven’t given her an out, the same way you really, really don’t want to propose and get anything but a yes.
-
Third date is almost always going to be too early to do this, and also as executed it risks coming off as rather creepy and weird, even if you did read the room right.
-
So it’s almost always a bad play as executed.
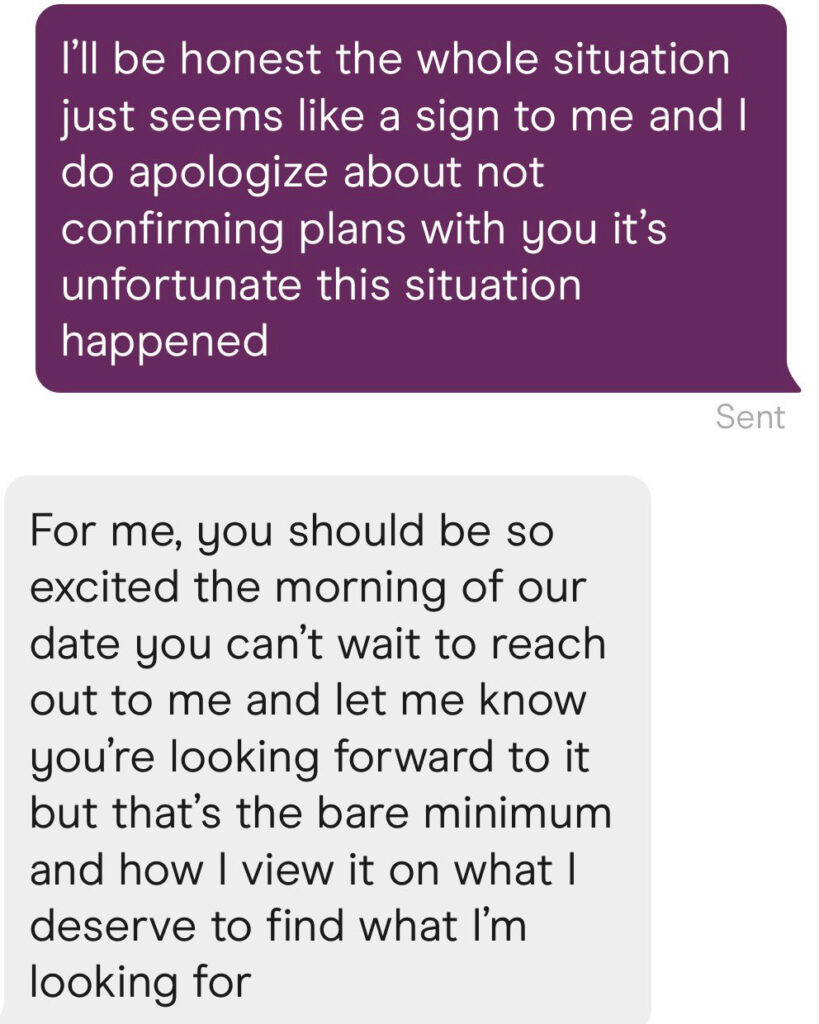
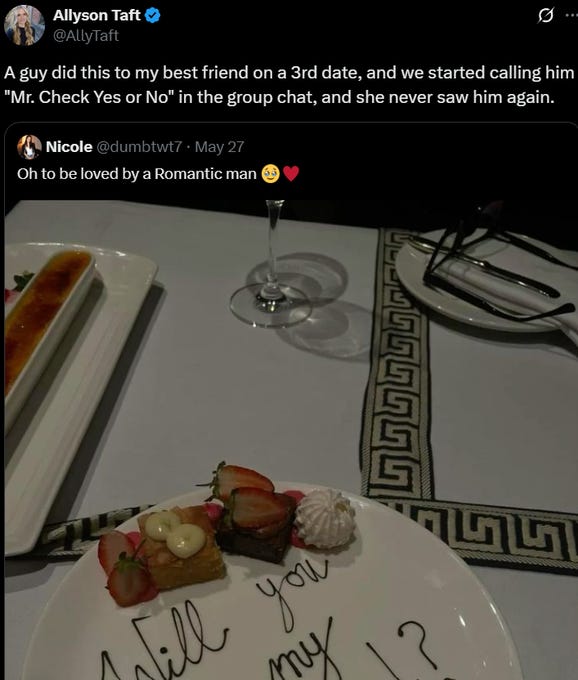
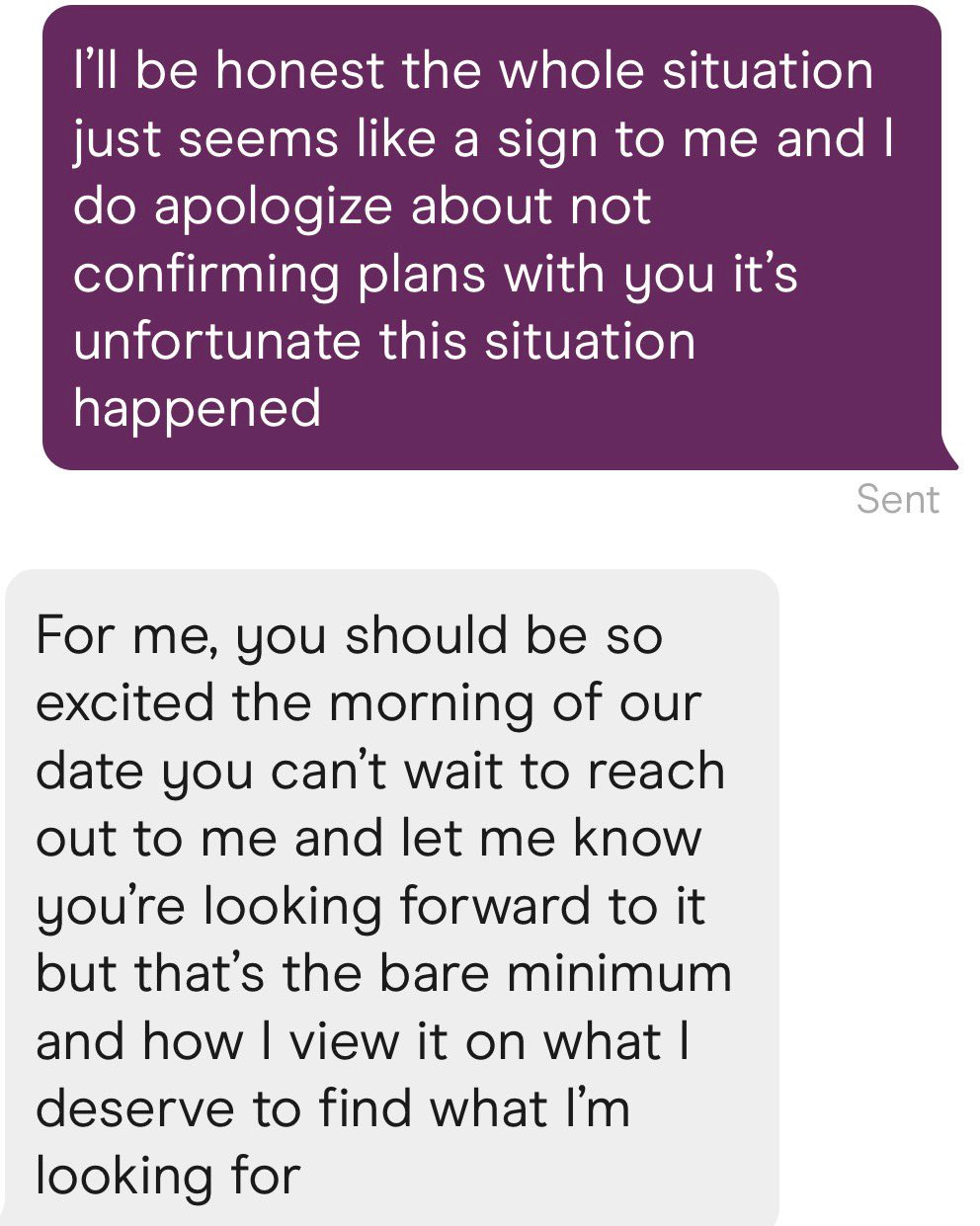
Allyson Taft’s screenshotted post: A guy did this to my best friend on a 3rd date, and we started calling him “Mr. Check Yes or No” in the group chat, and she never saw him again.
Pat Stedman: Only works if she is already eager to be your girlfriend. NEVER do this stuff if there is any uncertainty, it will work against you.
Brandon Burr: Stories like this are why a lot of guys in the dating world stopped trying to be romantic. It’s punished severely by a lot of women, unfortunately.
Allyson Taft: I believe it. I think being able to read the room is an important skill for everyone, always, but especially in dating.
Mimetic Value: You’re overanalyzing it and took it too seriously. This is exactly what I’d do if the date is NOT going well. It’s for giving her a final chance to confirm that he didn’t accidentally write her off too soon. He was already mentally checked out.
Allyson Taft: He sure called her a lot afterwards for being checked out lmao.
Also known as, it’s good to be romantic, but you have to do a decent job of it. And you don’t want to put them to a decision like this unless you’re fine with being dumped if the answer isn’t an enthusiastic yes. The rest of the dinner was presumably also romantic, and was presumably a good idea if it had ended without this.
I’m not pretending I am the best at being romantic, but don’t give up on the idea.
What are or should be the rules around confirming a date?
A better question is, how should you navigate such situations yourself?
Because rules, shumules. Play to win.
So first off, the background and various reactions.
Brooke Lin (19m views): From a friend and for context the previous convo was sunday night but who is in the wrong here?
We got an update folks.
Liron Shapira: Lol I used to give male dating advice, and one of the major focus areas was “flake defense”.
(Flake defense turned out critical for meeting my wife.)
The purple person here, who took the lead on the invite, should’ve demonstrated their attractive flake-defense skill afterwards.
Cate Hall: People have this all wrong. We should be encouraging this kind of behavior. Just think how much time this guy saved.
Allie: Ladies: if you say yes to a date, you’ve agreed to go on the date
Playing games like “he needs to confirm or it doesn’t count!!!” because TikTok told you to is a really dumb way to waste your time
Be picky about things that matter, but quit making up rules to be upset about.
Autistotle: “Making up rules to be upset about” is at least half of all dating discourse.
Lovable rogue: honestly as a guy who confirms *everytime, women still flake ~10-15% of the time. we should be trying to make the date happen not shit test each other!
Shailesh: I always confirmed the previous evening. Yoo many times when they cancelled when I checked up 1 hr-30 min before.
Mason: Maybe the real problem with the apps is that nobody is actually very excited about the person they’re about to go on a date with at all. You are supposed to be looking forward to the date more than, like, a dentist appointment.
Jordan Braunstein: I think everyone is underestimating the absolute scourge of flakiness among both young men and women. There’s no real social penalty for it anymore.
If there’s a good chance the other person will flake, it becomes game theoretically rational to mitigate that risk by having extra confirmations or readily available backup plans.
Gingercap: I kind of got the impression that being too excited about a date is kind of cringe and comes off as desperate.
Noodle: Ehh when I was dating I made the mistake to get ready for the date only to be stood up or ghosted. Nothing wrong with confirming a date because its embarrassing to be waiting around forever for no reason.
Tetraspace: If you’re going “yay I don’t have to go to the date :)” instead of “oh man I wanted to go to the date :(” something has went wrong earlier than the morning of the date
There are remarkably deep strategic and mechanism design considerations here. What the rules ‘should’ be is again not so relevant, nor is ‘who is at fault’ per se.
So here are some various thoughts.
-
If you are happy or righteous or similar about being able to cancel the date when they don’t confirm, you shouldn’t have said yes in the first place.
-
The flake rate, on all sides, is sufficiently high that the default should now be to confirm on the day of the date. The cost of confirmation is low. In general as the asker it is your job to ensure the date actually happens.
-
I can believe that we have reached the point where the flake rate when not getting confirmation is high enough that it is reasonable for the person asked to require confirmation and to treat this as a default dynamic.
-
If you require confirmation, ideally you should note that you require confirmation, or better yet proactively ask for it if you don’t get it. But there are selection effect and signaling reasons to not do this. Either way, once you know you’re not going to show, you should explicitly cancel, not silently flake.
-
If you don’t say you require confirmation, and don’t show without it, you flaked.
-
Flaking is in general extremely poor form and should be treated as a very expensive action in all contexts, romantic or otherwise, especially without notice and especially without apologies.
-
If your lack of confirmation causes flaking, that is often favorable selection. If their lack of confirmation causes you to flake, that is also favorable selection.
-
If lack of same day confirmation causes flaking on a first date, that is still an unforced error by all involved. In other circumstances, either subsequent dates or non-romantic contexts, this is often not true.
-
Confirmation can give both parties an out, so it serves a useful purpose when someone is getting pressured, but it is bad to give people an easy flake out because people will constantly cancel plans of all kinds when they shouldn’t.
-
If this is a ‘test of enthusiasm’ or otherwise phrased or presented in ways similar to the OP then I would consider it a red flag.
My revealed preference at the time was not to go at all, have no real options for going and make no effort to go. Neither of these options was remotely on the table, although I would like to think I would have happily accepted either of them.
So I’m not sure I’m the best person to judge the options?
Romy: imagine you’re a high school senior and it’s prom season. would you rather go with a 10 who will definitely not have sex with you, or a 7 who definitely will?
Kip: I chose the no sex option because I didn’t want to have sex yet in high school
Ronny: lol a 7 who will *definitelyhave sex with you is a disturbing option in that case.
I was thinking in terms of ‘you have no future with either of them, everyone is going to say goodbye and head off to college.’ If there is a real future involved then that should presumably dominate the question either way. As does the question of whether anyone believes in the pairing, including especially the two of you.
What does one make of what was intended to be a singles event in which the men ended up playing board games and getting to know each other, while the women talked and got to know each other?
Tracing Woodgrains: dudes rock
there’s actually a lot to be said about the framing of the paragraph — the women preferred to talk, the men preferred board games, the women lamented that the men didn’t talk with them bc they didn’t feel like playing board games with the men
both are good activities!
Ben Hoffman: This feels like a good example of the sort of information I’d have responded wrongly to, before I learned that if a woman keeps complaining about men doing X, that’s most likely an expression of preference for the sorts of men who do X, not an offer to transact with men who don’t.
The article of course framed this as the guys refusing to interact with the women, rather than both sides choosing distinct activities, and also it seeming still great?
It seems like a good use of an evening to play board games where I meet new friends, or I sit around and talk and meet new friends, whether or not I am single. We all need more friends. The woman here says she left with potential new friends too.
It does seem like it should not be a stable equilibrium. Why didn’t any of the women join the board games? Why didn’t any of the men go monopolize all the women? Both seem like highly overdetermined strategies, at least on repeated play, if things aren’t already going great.
Knowing how to dance, especially as a guy, remains a cheat code. It’s not as effective as it used to be because opportunities come up less often, and certainly it’s optional, but it is still very clearly a cheat code.
Cartoons Hate Her asserts it no longer works because if you dance like no one’s watching, your assumptions might be wrong, and then someone might film you and put it on the internet and suddenly everyone’s watching. Why take the risk?
The answer is because that risk is dumb. This is similar to worries about children being kidnapped by strangers. No one is filming you and even if they are no it is not going to go viral, and if it does you will probably be fine or even benefit.
Brittany Hugoboom advises you to approach the truly beautiful women who seem out of your league but aren’t the type that thrive on and seek out attention, because often no one else will shoot their shot and you end up with little competition while everyone else goes for the ‘beautiful mid.’
The comments are full of the usual ‘you don’t get it men are afraid to approach women due to potential retaliation’ but this completely misses the point here, which is that men are (statistically speaking) approaching the wrong women. There’s also a bunch of ‘oh we assume she already has someone or always has options’ whereas the whole point of the post is this often isn’t true, unless she’s willing and able to initiate, at least sufficiently to indicate the coast is clear.
Yes, of course she (and most other women) can get infinite attention on apps, but most strongly prefer to get approached organically if at all possible.
Ask for and set up what you want and you’re more likely to get it.
Salia: Pandemic of underfucked women.
Eoin Walsh: The Men are not in vegan restaurants in downtown Manhattan.
Sasha Chapin: So I have no desire to comment on the culture war issues at play. I will note that I have had the following conversation with a number of women asking for advice, like, a half dozen
Them: “I want men to take charge and act like men”
Me: “Do you prompt that with receptive energy?”
Them: “…what?”
Meanwhile, women I know who understand how to do this have zero trouble! Seduction is a two-way game. A couple of women have taken my advice on this and found it life-altering.
In general, you will have a much better time in life if you assume that it is your responsibility to prompt the interactions you would like to have.
Annals of people taking this advice seriously:
This person just gave me permission to mention that she’s been in a relationship for a month and it appears to be going well so far.
The higher the stakes the better the first date idea, so sure, go for it. Waiting in line for a while also gives you a forced time excuse to talk.
Signull: If you want an elite-tier first date idea, here’s the cheat code: Buy tickets to a comedy show in NYC and deliberately show up disgustingly early so you get planted in the front row like sacrificial offerings.
If the two of you can survive 90 minutes of being roasted by several lonely, depressed comics in graphic tees who pretty much look homeless, congrats, that’s basically a huge relationship stress test.
Whatever comes after (assuming you didn’t get a reality check) will feel like easy mode.
I was the depressed comic.
Grace Jarvis: if a woman tells you you have “nice hands” she is doing everything in her power not to fuck you senseless please release her from her torment her friends are receiving the kinds of messages someone in prison would send
Grave Jarvis (14 months later): the person who kinda inspired this tweet and I have been together for over a year now
by “kinda inspired” I mean, I thought “oh he has nice hands” and then I didn’t say anything because of the implication and wrote down the funniest hyperbolic version
Ted Knutson: Can confirm with large sample size that this is true.
A very wise rule. If you don’t want to get feedback from someone, don’t date them, definitely don’t marry them, and probably don’t be friends with or work with them.
Chris Lakin: The reason that RLHF doesn’t work for your personality is there are very few people you want feedback from
Jakeup: only marry someone whose feedback you want as your reward function.
Chris Lakin: only date people whose feedback you want as your reward function.
Now imagine being an LLM and having to get feedback from *shuddereveryone.
Brittany Hugoboom says focus on the basics that matter. You need shared values and a baseline level of physical attraction, and a few key traits, the rest is more of a bonus. Sorting for other things, as dating apps lead you towards, is in her model largely a trap.
Brittany Hugoboom:
• Men, look for courage, justice, ambition, and discipline.
• Women, look for benevolence, loyalty, and a kind heart.
I always say: the best case scenario is finding love young. Not because it’s the only way. But because when you’re young, you’re more adaptable.
If you both come from good families, they’ll cheer you on.
You can build something from the ground up, together.
Love after 30? Absolutely possible.
But if you’re young and thinking about love, don’t let the world scare you out of it. We’re often told to wait forever and then older generations wonder why the young is no longer finding love.
When you’re young, school is a great place to meet someone.
So is church. A party. An event. Through mutual friends. I’d argue even Twitter or Substack would be a better way to find someone than a dating app.
If you like someone’s mind and values, and also happen to like their photo, it’s perfect.
Her blog seems full of other similarly basic pieces of largely good advice.
Kira: LMFAOOOO
Mason: Honestly, “girl who gets bull-headed and wears cargo pants when he tells her to wear the dress” and “guy who told her to wear the dress but is amused by the cargo pants” are both lovable types
Mazel tov, be married 50 years and bicker about the throw pillows on your deathbed
She’s a terrible match for someone who takes this kind of thing personally, but it doesn’t look like she’s marrying that kind of guy
He looks absolutely thrilled
Marilyn Maupin: I got yelled at by so many people for saying they’ll be fine since she clearly understands what she did to herself
Mason: Seriously, as long as she’s laughing at herself instead of doubling down and insisting he’s the jerk for proposing to her in the cargo pants they’re fine. Twitter consists of the most disagreeable people in the world insisting that everyone shy of perfect agreeableness is ngmi
I’d be thrilled too. You have a much better story this way, and it probably went fine given she posted it like this. If she’s actually mad about it, then yeah, red flag, but at the best possible time.
Alberto De Lucca: My wife and I spoke many times about marrying. During one of these convos, I plain asked her: “do you want to marry me?” She said yes. I said, “ok, let’s do this.” We went out the next day and bought our rings (plus her engagement ring). We then planned to marry on her birthday party (a couple weeks in) but told no one. In fact, they thought I was going to propose to her.
Anyway. Party starts. She gets on a mic. “Thank you for coming to my birthday everyone.” I get on my knees behind her. Everyone starts doing the awws and whatnot. I do the deed. She says yes. Everyone’s happy. On cue, my mother asks: “so when’s the wedding?” We look at each other: “how about today? Is there anyone who can officiate this marriage?”
In walks the registrar with the papers. “I can, sure.” Waiters and personnel change the decor from a birthday party to a wedding party. We got married minutes later.
The look on the faces of our families is something I’ll never forget.
You can just do things.