A British redcoat’s lost memoir resurfaces
Shadrack Byfield lost his left arm in the War of 1812; his life sheds light on post-war re-integration.
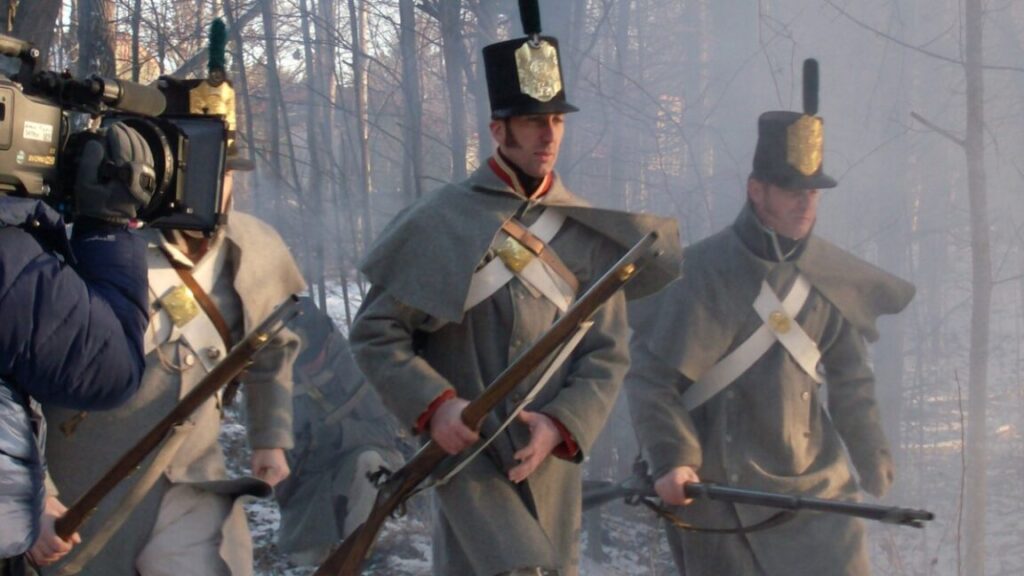
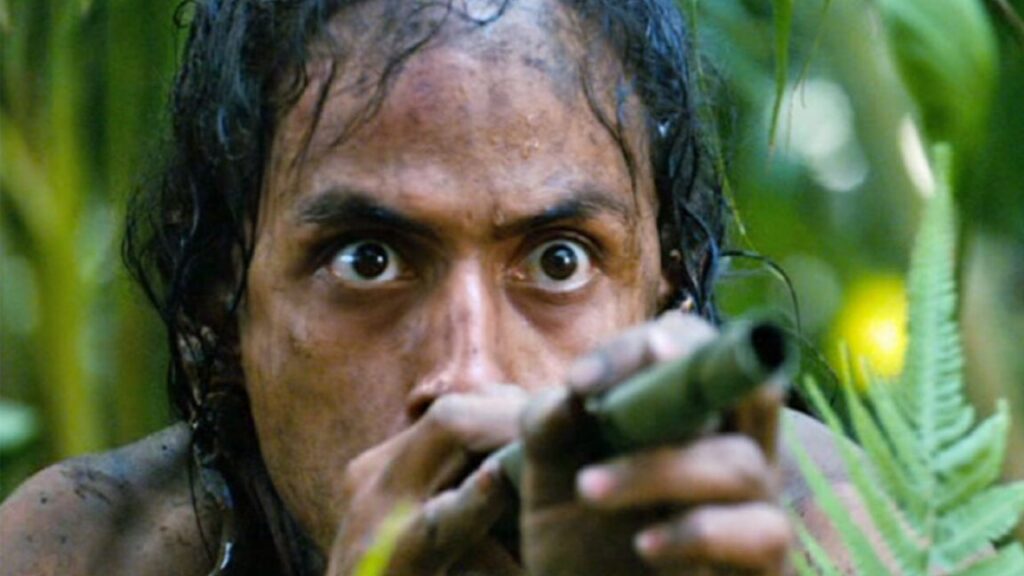
Actor Chris McKay playing Shadrack Byfield (center) in the 2011 PBS documentary The War of 1812. Credit: Tom Fournier
History buffs are no doubt familiar with the story of Shadrack Byfield, a rank-and-file British redcoat who fought during the War of 1812 and lost his left arm to a musket ball for his trouble. Byfield has been featured in numerous popular histories—including a children’s book and a 2011 PBS documentary—as a shining example of a disabled soldier’s stoic perseverance. But a newly rediscovered memoir that Byfield published in his later years is complicating that idealized picture of his post-military life, according to a new paper published in the Journal of British Studies.
Historian Eamonn O’Keeffe of Memorial University of Newfoundland in St. John’s, Canada, has been a Byfield fan ever since he read the 1985 children’s novel, Redcoat, by Gregory Sass. His interest grew when he was working at Fort York, a War of 1812-era fort and museum, in Toronto. “There are dozens of memoirs written by British rank-and-file veterans of the Napoleonic Wars, but only a handful from the War of 1812, which was much smaller in scale,” O’Keeffe told Ars. “Byfield’s autobiography seemed to offer an authentic, ground-level view of the fighting in North America, helping us look beyond the generals and politicians and grapple with the implications of this conflict for ordinary people.
Born in 1789 in Wiltshire’s Bradford-on-Avon suburbs, Byfield’s parents intended him to follow in his weaver father’s footsteps. He enlisted in the county militia when he turned 18 instead, joining the regular army the following year. When the War of 1812 broke out, Byfield was stationed at Fort George along the Niagara River, participating in the successful siege of Fort Detroit. At the Battle of Frenchtown in January 1813, he was shot in the neck, but he recovered sufficiently to join the campaigns against Fort Meigs and Fort Stephenson in Ohio.
After the British were defeated at the Battle of Thames later that year, he escaped into the woods with indigenous warriors, despite his concerns that they meant to kill him. They did not, and Byfield eventually rejoined other British fugitives and made his way back to the British lines. He was one of 15 out of 110 soldiers in his light company still alive after 18 months of fighting.
But his luck ran out in July 1914. While engaged in a skirmish at Conjocta Creek, a musket ball tore through his left forearm. Surgeons were forced to amputate after gangrene set in—a procedure that was performed without anesthesia. Byfield described the operation as “tedious and painful” in A Narrative of a Light Company Soldier’s Service, the memoir he published in 1840, adding, “I was enabled to bear it pretty well.”
Byfield famously became incensed when he discovered his severed limb had been tossed into a dung heap with other amputated body parts. He retrieved his forearm and insisted on giving it a proper burial in a makeshift coffin he built himself. Due to his injury, Byfield’s military career was over, and he returned to England. While he was given an army pension, the sum (nine pence per day) was inadequate to support the veteran’s growing family.
Byfield couldn’t take up his father’s weaving trade because it took two hands to operate a loom. But according to his 1840 Narrative, he had a dream one night of an “instrument” that would enable him to work a loom with just one arm, which he successfully built with the help of a local blacksmith. He found work spinning thread at a textile mill and weaving it into finished cloth, augmenting that trade by working as a wheelchair attendant at a spa in Bath, among other odd jobs. He later found a mentor in Colonel William Napier, a distinguished veteran and military historian who arranged for an increase in Byfield’s pension, as well as finding a publisher for the Narrative.
A shifting narrative
Byfield’s 1840 memoir became a much-cited source for historians of the War of 1812 since it offered a personal perspective on those events from a rank-and-file British soldier. Historians had long assumed that Byfield died around 1850. But during his research, O’Keeffe discovered a second Byfield memoir in the collection of the Western Reserve Historical Society, published in 1851, entitled History and Conversion of a British Soldier. O’Keeffe believes this to be the only surviving copy of the 1851 memoir.
“I quickly noticed that [Byfield] appeared in British census records past the c.1850 date at which he was supposed to have died, according to the Canadian Encyclopedia entry on Byfield and other sources,” said O’Keeffe. “This discrepancy was my first indication that there might be more to discover on Byfield, and every time I returned to the subject I kept finding more information.” Byfield actually died in January 1874 at 84 years old. While historians had also assumed that Byfield was functionally illiterate, O’Keeffe found a draft manuscript of the 1840 memoir in Byfield’s handwriting, suggesting the soldier had acquired those skills after the war.
“My initial interest was sparked by the wartime memoir I already knew about, but I was increasingly fascinated by his later life, and what it could tell us about the experiences of veterans in general,” said O’Keeffe. “In most history books, British redcoats take center stage for the defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of the Waterloo, but then quickly vanish from view; no doubt this is true for veterans of most if not all wars. Military memoirs of the period tend to encourage this dynamic by ending the story at demobilization, assuming that readers would not be interested in the civilian experiences of their authors. But Byfield’s very well-documented life helps bring the process of reintegration, of rebuilding one’s life after war and catastrophic injury, into sharper focus, and highlights the presence of war veterans in 19th-century British society.”
According to O’Keeffe, Byfield painted a much less rosy picture of his post-military life in the 1851 memoir, recounting his struggles with poverty and lingering rheumatic pain in his left stump. (“Oftentimes I was not able to lift my hand to my head, nor a teacup to my mouth,” the former soldier wrote.) When textile mills started closing, he relocated his family to Gloucestershire and eked out a living as a tollkeeper and by selling copies of his earlier Narrative for a shilling. He admitted to taking absence without leave during his war service and participating in plundering expeditions. The later memoir also recounts Byfield’s spiritual awakening and growing religious faith.
Byfield adopted very different narrative themes in his 1840 and 1851 memoirs. “In the 1840 narrative, Byfield sought to impress wealthy patrons by presenting himself as a dutiful soldier and deserving veteran,” said O’Keeffe. “The 1851 memoir, by contrast, was a spiritual redemption story, with Byfield tracing his progress from rebellious sinner to devout and repentant Christian. In the 1851 memoir, the veteran also dwells on periods of indebtedness, illness, and unemployment after returning to England, whereas in his earlier memoir he described maintaining his family ‘comfortably’ with his weaving prosthesis for nearly twenty years.”
Byfield’s luck seemed to change for the better when the Duke of Beaufort became a patron, first hiring the veteran as a gardener on the duke’s Badminton estate. Byfield complained in his 1851 account that the estate steward refused to pay him full wages because he was one-handed, insisting, “I never saw the man that would compete with me with one arm.”
Eventually, Byfield leveraged his connection to the duke to be named caretaker of a 100-foot tower monument to Lord Edward Somerset that was built in the Gloucestershire village of Hawkesbury Upton in 1845. This came with a keeper’s cottage, and the duties were light: Byfield maintained the tower, sold souvenir booklets, and welcomed any sightseers every day except Sundays.
Alas, Byfield became embroiled in a feud over control of the village’s Particular Baptist chapel; some objected to the doctrine and conduct of the minister, John Osborne, while others, like Byfield, defended him. There were lawsuits, arson, vandalism, and a charge of public drunkenness against Byfield, which he vehemently denied. Everything came to a head in an “unholy riot” in the chapel, during which Byfield was accused of starting the fight by “pushing about” and slashing someone’s eye and face with his prosthetic iron hook. Every rioter was acquitted, but the incident cost Byfield his cushy caretaker job in 1853.
Byfield later moved back to his hometown, Bradford-on-Avon, and married a widow after his first wife died. He kept petitioning for further increases to his pension, to no avail, and started peddling a third memoir in 1867 entitled The Forlorn Hope. No copies have survived, per O’Keeffe, but it did garner coverage in a local newspaper, which described the account as relating “the Christian experience of this Wiltshire hero and the great persecutions and trials he has passed through.”
“Years ago, I would have characterized the veteran as someone who was astonishingly phlegmatic about what happened to him,” said O’Keeffe. “Byfield’s description of the amputation comes across as remarkably unemotional to modern readers, and then he presents himself at the end of the first memoir as having literally dreamt up the prosthetic that allowed him to return to his civilian trade and live happily ever after, more or less.”
But as he studied Byfield’s writings more closely, “It became clear that the process of reintegration was far less smooth than this version of events would suggest, and that Byfield’s time in the army shaped the rest of his life in profound ways,” said O’Keeffe. “The fact that Byfield’s daughter chose to put her father’s military rank and regiment in the ‘occupation’ column on his death certificate, rather than listing any of the other jobs the veteran had held in the six decades since his amputation, is the most eloquent testimony of this, I think.”
Journal of British Studies, 2025. DOI: 10.1017/jbr.2025.10169 (About DOIs).
Jennifer is a senior writer at Ars Technica with a particular focus on where science meets culture, covering everything from physics and related interdisciplinary topics to her favorite films and TV series. Jennifer lives in Baltimore with her spouse, physicist Sean M. Carroll, and their two cats, Ariel and Caliban.
A British redcoat’s lost memoir resurfaces Read More »