frozen cell balls —
IVF often produces more embryos than are needed or used.
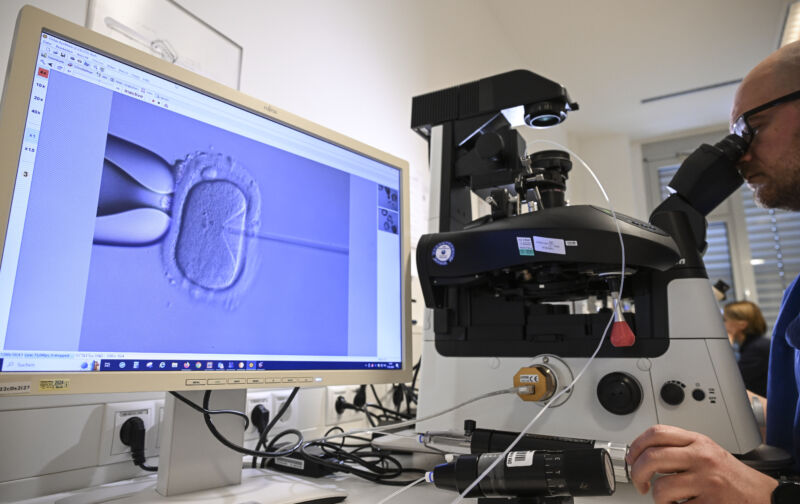
Enlarge / January 17, 2024, Berlin: In the cell laboratory at the Fertility Center Berlin, an electron microscope is used to fertilize an egg cell.
The Alabama Supreme Court on Friday ruled that frozen embryos are “children,” entitled to full personhood rights, and anyone who destroys them could be liable in a wrongful death case.
The first-of-its-kind ruling throws into question the future use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) involving in vitro fertilization for patients in Alabama—and beyond. For this technology, people who want children but face challenges to conceiving can create embryos in clinical settings, which may or may not go on to be implanted in a uterus.
In the Alabama case, a hospital patient wandered through an unlocked door, removed frozen, preserved embryos from subzero storage and, suffering an ice burn, dropped the embryos, destroying them. Affected IVF patients filed wrongful-death lawsuits against the IVF clinic under the state’s Wrongful Death of a Minor Act. The case was initially dismissed in a lower court, which ruled the embryos did not meet the definition of a child. But the Alabama Supreme Court ruled that “it applies to all children, born and unborn, without limitation.” In a concurring opinion, Chief Justice Tom Parker cited his religious beliefs and quoted the Bible to support the stance.
“Human life cannot be wrongfully destroyed without incurring the wrath of a holy God, who views the destruction of His image as an affront to Himself,” Parker wrote. “Even before birth, all human beings bear the image of God, and their lives cannot be destroyed without effacing his glory.”
In 2020, the US Department of Health and Human Services estimated that there were over 600,000 embryos frozen in storage around the country, a significant percentage of which will likely never result in a live birth.
The process of IVF generally goes like this: First, egg production is overstimulated with hormone treatments. Then, doctors harvest the eggs as well as sperm. The number of eggs harvested can vary, but doctors sometimes try to retrieve as many as possible, ranging from a handful to several dozen, depending on fertility factors. The harvested eggs are fertilized in a clinic, sometimes by combining them with sperm in an incubator or by the more delicate process of directly injecting sperm into a mature egg (intracytoplasmic sperm injection). Any resulting fertilized eggs may then go through additional preparations, including “assisted hatching,” which prepares the embryo’s membrane for attaching to the lining of the uterus, or genetic screening to ensure the embryo is healthy and viable.
Feared reality
This process sometimes yields several embryos, which is typically considered good because each round of IVF can have significant failure rates. According to national ART data collected by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the percentage of egg retrievals that fail to result in a live birth ranges from 46 percent to 91 percent, depending on the patient’s age. The percentage of fertilized egg or embryo transfers that fail to result in a live birth ranges from 51 percent to 76 percent, depending on age. Many patients go through multiple rounds of egg retrievals and embryo transfers.
The whole IVF process often creates numerous embryos but leads to far fewer live births. In 2021, nearly 240,000 patients in the US had over 400,000 ART cycles, resulting in 97,000 live-born infants, according to the CDC.
People who have extra embryos from IVF can currently choose what to do with them, including freezing them for more cycles or future conception attempts, donating them to others wanting to conceive, donating them to research, or having them discarded.
But, if, as Alabama’s Supreme Court ruled, embryos are considered “children,” this could mean that any embryos that are destroyed or discarded in the process of IVF or afterward could be the subject of wrongful death lawsuits. The ruling creates potentially paralyzing liability for ART clinics and patients who use them. Doctors may choose to only attempt creating embryos one at a time to avoid liability attached to creating extras, or they may decline to provide IVF altogether to avoid liability when embryos do not survive the process. This could exacerbate the already financially draining and emotionally exhausting process of IVF, potentially putting it entirely out of reach for those who want to use the technology and putting clinics out of business.
Barbara Collura, CEO of RESOLVE: The National Infertility Association, told USA Today that the ruling would likely halt most IVF work in Alabama. “This is exactly what we have been fearful of and worried about where it was heading,” Collura said. “We are extremely concerned that this is now going to happen in other states.”
But the hypothetical risks don’t end there. Health advocates worry that the idea of personhood for an embryonic ball of a few cells could extend to pregnancy outcomes, such as miscarriages or the use of contraceptives.