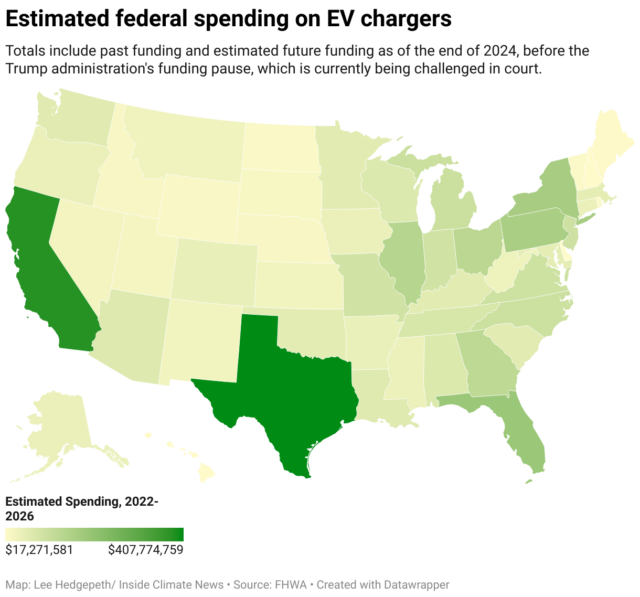
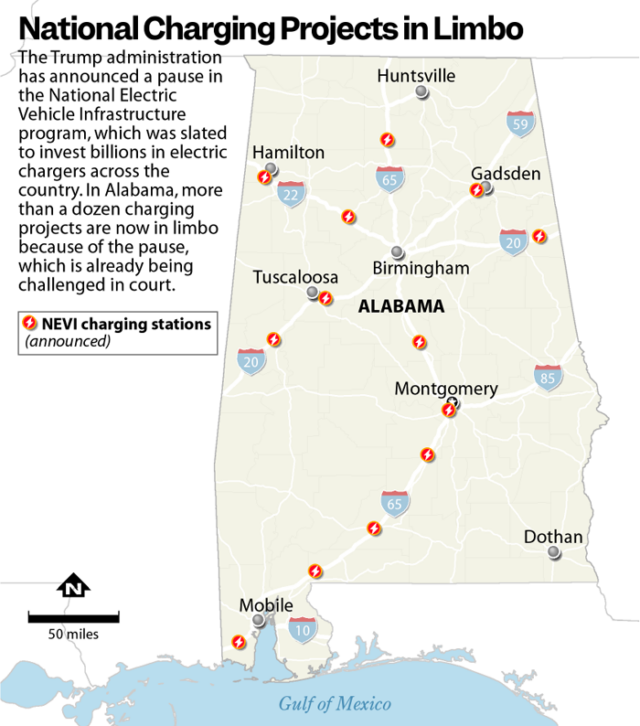
Despite court orders, climate and energy programs stalled by Trump freeze
Chief of the EPA is also trying to claw back $20 billion, citing alleged wrongdoing.
President Donald Trump’s freeze on federal funding shows little sign of thawing for climate, energy and environmental justice programs.
Despite two federal court orders directing the administration to resume distributing federal grants and loans, at least $19 billion in Environmental Protection Agency funding to thousands of state and local governments and nonprofits remained on hold as of Feb. 14, said environmental and legal advocates who are tracking the issue.
EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin has vowed to seek return of an additional $20 billion the agency invested last year in the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund program, calling for a Department of Justice investigation into what he characterized as a “scheme… purposefully designed to obligate all of the money in a rush job with reduced oversight.”
Environmental advocates said Zeldin was unfairly smearing the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund, or “green bank,” program, on which EPA worked for more than a year with the Treasury Department to design a standard financial agent arrangement—the kind the government has used many times before to collect and distribute funds.
Critics believe the Trump administration, thwarted last week in its effort to get an appeals court to reinstate its sweeping government-wide freeze on federal funding, is resorting to a new tactic—labeling individual programs as nefarious or fraudulent. Although that approach has met with some success—a federal judge last week allowed the Federal Emergency Management Agency to freeze $80 million in funding from a migrant shelter program in New York—legal experts said courts will be looking for specifics and evidence, not broad assertions that programs are improper.
“They cannot challenge an entire program based on charges of fraud and waste,” said Jillian Blanchard, a vice president of the nonprofit Lawyers for Good Government. “If they had actual concerns about fraud or waste, they would need to follow clear procedures and protocols in the regulations, going grant by grant to address this, but that’s not what’s happening here. They are challenging entire programs whole cloth without evidence.
“The executive does not have the authority to change policies simply because they don’t like them,” Blanchard said at a virtual briefing for reporters on Friday. “Congress makes the law, not the president and certainly not Elon Musk,” she said, referring to the billionaire donor whom Trump has deputized to cut government spending.
Feeling the freeze
Across the country, the spending freeze has thrown into chaos the environmental, resilience and community improvement programs that Congress authorized in the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. Among the efforts on hold: clean drinking water, air monitoring, hurricane recovery and electric school buses.
“Real people on the ground are being hurt by the stop-start situation,” said Blanchard, whose group is working with the Natural Resources Defense Council on the cases of 230 grantees in 44 states.
Grantees are in a state of confusion because they have not heard directly from EPA, she said.
Michelle Roos, executive director of the Environmental Protection Network, a coalition of former EPA employees that is also working with Lawyers for Good Government, said many grantees are not sure what is happening because the agency’s employees have been forbidden to talk to people outside of the agency.
Several grantees reached by Inside Climate News said that they were not talking to the press, or did not want to say whether or not they could access their funding.
MDC, a nonprofit in Durham, North Carolina, along with the Hispanic Federation, was supposed to receive a $3 million environmental justice community change grant for disaster recovery and resilience programs in Latino areas of eastern North Carolina.
“We were thrilled to receive federal support to do this work, but unfortunately, like many others, we have experienced an interruption in accessing this funding,” said Clarissa Goodlett, MDC’s director of communications.
Many neighborhoods, especially those that are home to low-income, Black and Latino residents, are still rebuilding from hurricanes that hit in 2016 and 2018.
During the storms, rural counties in eastern North Carolina did not provide real-time emergency alerts or evacuation orders in Spanish, according to Enlace Latino NC, a Spanish-language digital news outlet.
The MDC grant would help Latinos connect with local governments to ensure their communities are included in discussions and decisions about the impact of climate disasters.
“We are investigating and pursuing whatever options and channels are available to us to ensure we can follow through on our commitment to communities in eastern North Carolina,” Goodlett said.
Dorothy Darr, executive director of the Southwest Renewal Foundation in High Point, near Greensboro, North Carolina, said she doesn’t know if the group’s $18.4 million grant is frozen. Southwest Renewal is teaming up with eight partners to support not only environmental projects—tree planting, water testing and building an urban greenway—but also workforce training and infrastructure improvements. These include upgrades to old, leaking sewer lines and inefficient HVAC systems and a new energy-efficient “cool” roof at a Guilford County school.
The money would also pay for nine new public electric vehicle charging stations, anti-littering campaigns and other improvements in historically Black and low-income neighborhoods in the southwest part of the city.
Darr said the foundation only recently received an account number from the EPA, and she plans to try to access the funds Monday.
“The grant title”—Environmental and Climate Justice Community Change Grants—”has the words ‘environment’ and ‘justice’ in it,” Darr said. “If you’re just slashing programs based on words, then we’re a sitting duck.”
In Texas, the nonprofit group Downwiders at Risk received word in a Feb. 4 letter that it had received a $500,000 EPA environmental justice “collaborative problem-solving” grant it had applied for last year. The money was to be used to install community air monitors in neighborhoods near Dallas. But the notification didn’t provide instructions on how to access the money, and no followup ever came.
Executive Director Caleb Roberts called around his local EPA office, but no one could give answers.
“People are still unsure. Our project officer at the EPA has no idea. I’ve emailed people higher up,” Roberts said. “They have no idea if things are funded or not. They are just as in the dark as we are.”
Downwinders’ award letter said they had 21 days to pull their first block of funding. If no instructions to access the money arrive before then, Robert worries they may lose it.
The city of New Haven, Connecticut, only received word on Jan. 21—the day after Trump’s inauguration—that it and its local nonprofit partners had received a $20 million environmental justice community change grant, according to Steve Winter, who heads up the city’s Office of Climate and Sustainability. But he had never been able to access the funds; the online system originally said “unavailable for payment;” that changed on Feb. 10 to “suspended.”
The money was supposed to help fund whole-home energy efficiency retrofits in a city where one-quarter of the population lives in poverty and where energy costs have skyrocketed since the start of the Russia-Ukraine war, Winter said. Connecticut, like much of New England, relies heavily on heating oil in winter—not only the most expensive home heating fuel, but the most polluting. The grants also would have helped with asbestos and mold remediation in the homes, which are necessary before energy efficiency upgrades can be done.
Winter said the city has warned its partners that they now may need to lay off staff that they’ve hired for outreach for energy efficiency programs, and the future of a community geothermal project is at risk. Also up in the air: a local food rescue organization’s plans to increase staff and food storage capacity.
“People might say, oh this environmental justice grant is some frivolous thing, but it’s about helping people with quality affordable housing, with lowering their energy bills, alleviating hunger in the community, providing affordable transportation options,” Winter said. “These are all trying to meet basic needs that also have an environmental impact.”
A “rush job” accusation
The Trump administration’s drive to root out “diversity, equity and inclusion,” or DEI programs, throughout the government has swept up environmental justice programs at EPA, even though the two are distinct policy initiatives similar only in that they often involve people of color. After taking office two weeks ago, the first employees that Zeldin announced he was eliminating from the agency were those in DEI and environmental justice programs.
“The previous Administration used DEI and Environmental Justice to advance ideological priorities, distributing billions of dollars to organizations in the name of climate equity,” Zeldin said in a statement. “This ends now. We will be good stewards of tax dollars and do everything in our power to deliver clean air, land, and water to every American, regardless of race, religion, background, and creed.”
Last week, as thousands more employees at EPA and other federal agencies were placed on administrative leave or accepted the deferred retirement offer, Zeldin escalated his critiques on environmental justice and climate programs.
In a video first posted on X, Musk’s social media platform, on Wednesday night,
Zeldin called out $20 billion for the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund that he said had been “parked at an outside financial institution,” suggesting that the money was given away in a “rush job” in the waning days of the Biden administration. In fact, the money in question was awarded to eight recipients in August, well before the election. The program’s defenders say it went through a rigorous selection process that began more than a year before the awards were announced.
The $20 billion falls under two programs within the EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund and is intended to support nonprofits and financial institutions to serve as green banks. The eight recipients, which received between $400,000 and $7 billion, are supposed to use that money to finance projects by businesses and nonprofits around the country that would cut climate pollution. Much of the money is dedicated to low-income communities, where it is often harder for businesses to raise private financing.
The recipients have already begun using the funding to support businesses, including $250 million for an electric truck financing program beginning at the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach, $31.8 million in financing for a solar project for the University of Arkansas System and $10.8 million for solar projects on Tribal lands in Oregon and Idaho.
An electric truck is delivered to the Port of Los Angeles in San Pedro, Calif. on Dec. 17, 2021. Credit: Brittany Murray/MediaNews Group/Long Beach Press-Telegram via Getty Images
Unlike most of the grant recipients under the IRA, who draw down their money over time as work is completed, the green banks already received their money. Zealan Hoover, who administered IRA programs at EPA during the Biden administration, said the money was placed into bank accounts at Citibank under terms of financial agreements worked out with the Treasury Department.
Although EPA had never used such an outside financial agent before, the Treasury Department had made such agreements with outside institutions many times in the past to distribute or collect money. The system used for electronic federal tax payments, for expanding access to retirement savings and for getting money to assist businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic are just a few of the examples he cited.
“What is underway is not a good-faith effort to fight fraud,” Hoover said. “If it was, federal agencies would not be firing thousands of employees who are hired to conduct robust management and oversight of these programs.”
Zeldin said he was calling for termination of the financial agent agreement for the green bank program, and for the immediate return of the entire fund balance to the United States Treasury. He also said he was referring the issue to the EPA’s Office of the Inspector General and Congress and would “work with the U.S. Department of Justice.” In fact, EPA’s inspector general was dismissed in the early days of the Trump administration along with those at 16 other agencies. EPA’s press office said the agency currently has an acting inspector general but when asked, did not respond with that person’s name. EPA did not answer further questions on the financial agent program, referring only to Zeldin’s video post.
“The American public deserves a more transparent and accountable government than what transpired the past four years,” Zeldin said in the post. “We take our obligations under the law as seriously as it gets. I’ve directed my team to find your ‘gold bars’ and they found them. Now we will get them back inside of control of government as we pursue next steps.”
Citibank declined to comment. Each of the eight recipients of the green bank funds either declined to comment or did not reply to requests for comment.
“Hard for courts to catch up”
What happens next for the grant recipients is not entirely clear. Courts have issued temporary restraining orders to halt the funding freeze until the issue can be argued on its merits. In a five-page order issued Feb. 10, U.S. District Judge John McConnell Jr. of Rhode Island said that it was clear that the administration had in some instances continued “to improperly freeze federal funds.”
McConnell ordered the administration to “immediately end any funding pause,” but EPA and other agencies that are administering IRA climate programs, like the Department of Energy, are continuing to hold back funds.
“We’re talking about funding for families to make upgrades that help them save on their monthly energy bill, funding for people to buy energy efficient appliances and to retrofit their home so that cold air stays out in the winter and hot air stays out in the summer,” said Sen. Patty Murray, D-Wash., the vice chair of the Senate Appropriations Committee, in a briefing with reporters on Thursday. “Those programs aren’t just important to tackling the climate crisis. They are saving our families money.”
“What is painfully clear is that Trump’s illegal funding freeze is causing chaos and confusion,” Murray said.
But Murray and other Democrats, who helped shepherd the IRA to passage in 2022 with no Republican votes, now have little power to force a showdown in a Congress controlled by Republicans. And although multiple studies have shown that most of the $379 billion Congress devoted to funding the clean energy transition in that legislation has flowed to Republican districts, there has been little sign so far that GOP leaders are inclined to clash with the administration. In a few instances, Republicans have sought protection for individual programs that affect their own states.
Blanchard and other legal experts said the courts will have the final say on whether the Trump administration can continue to selectively freeze federal funds. But the decisions may not come soon enough for the programs that are relying on the money they were promised.
“The problem is, as a practical matter, it’s very hard for the courts to catch up,” said Richard Lazarus, an environmental law professor at Harvard Law School. “And the impact on these communities is immediate. The place is closed down, the services aren’t provided for these communities. So the impact can be immediate and devastating, and the practical remedy may be illusory.”
Lazarus was one of the legal scholars writing about environmental justice in the 1990s, before President Bill Clinton signed the first executive order to address communities that suffer a disproportionate burden of pollution. He said that although these communities now “have a fight on their hands,” it is not a new situation for them.
“It’s not as though the government turning against their hardship is something the EJ communities don’t know,” he said. “They don’t welcome it, but they know what this is. It’s how they’ve lived their lives for decades. They fought, and they’ll continue to fight. And that’ll be fighting in cases and lawsuits, and it’ll be fighting politically.”
This story originally appeared on Inside Climate News.
Despite court orders, climate and energy programs stalled by Trump freeze Read More »