In the Southwest, solar panels can help both photovoltaics and crops
Cultivation in a harsh climate
Solar arrays can shade crops from sun while moisture cools the panels to increase their productivity.
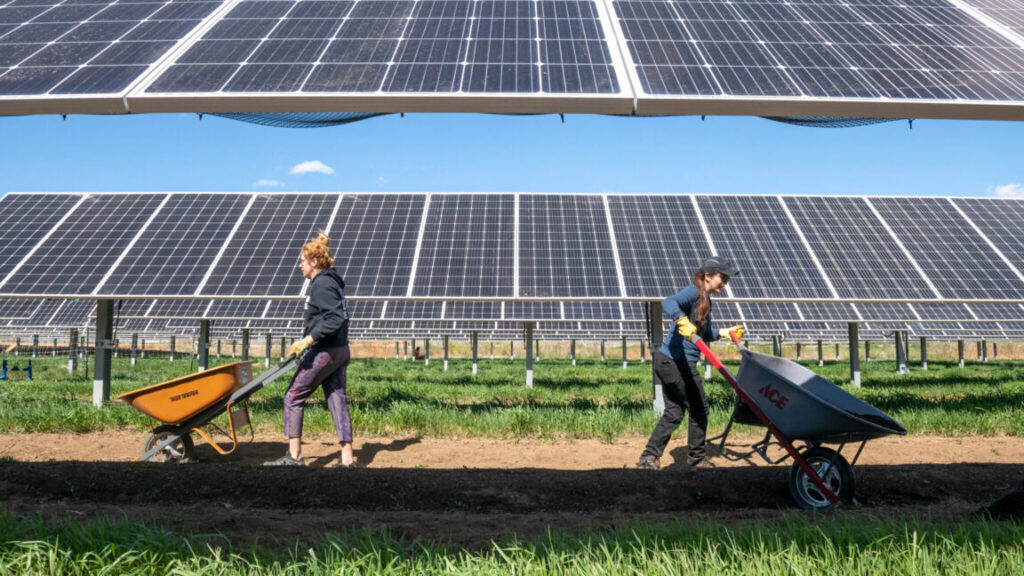
Volunteers with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory work at Jack’s Solar Garden in Longmont, Colorado. Credit: Bryan Bechtold/NREL
This article originally appeared on Inside Climate News, a nonprofit, non-partisan news organization that covers climate, energy, and the environment. Sign up for their newsletter here.
“We were getting basil leaves the size of your palm,” University of Arizona researcher Greg Barron-Gafford said, describing some of the benefits he and his team have seen farming under solar panels in the Tucson desert.
For 12 years, Barron-Gafford has been investigating agrivoltaics, the integration of solar arrays into working farmland. This practice involves growing crops or other vegetation, such as pollinator-friendly plants, under solar panels, and sometimes grazing livestock in this greenery. Though a relatively new concept, at least 604 agrivoltaic sites have popped up across the United States, according to OpenEI.
Researchers like Barron-Gafford think that, in addition to generating carbon-free electricity, agrivoltaics could offer a ray of hope for agriculture in an increasingly hotter and drier Southwest, as the shade created by these systems has been found to decrease irrigation needs and eliminate heat stress on crops. Plus, the cooling effects of growing plants under solar arrays can actually make the panels work better.
But challenges remain, including some farmers’ attitudes about the practice and funding difficulties.
Overcoming a climate conundrum
While renewable electricity from sources like solar panels is one of the most frequently touted energy solutions to help reduce the carbon pollution that’s driving climate change, the warming climate itself is making it harder for solar arrays to do their job, Barron-Gafford said. An optimal functioning temperature for panels is around 75° Fahrenheit, he explained. Beyond that, any temperature increase reduces the photovoltaic cells’ efficiency.
“You can quickly see how this solution for our changing climate of switching to more renewable energy is itself sensitive to the changing climate,” he said.
This problem is especially pertinent in the Southwest, where historically hot temperatures are steadily increasing. Tucson, for instance, saw a record-breaking 112 days of triple-digit heat in 2024, according to National Weather Service Data, and the US Environmental Protection Agency reports that every part of the Southwest experienced higher average temperatures between 2000 and 2023 compared to the long-term average from 1895 to 2023.
However, planting vegetation under solar panels—as opposed to the more traditional method of siting solar arrays on somewhat barren land—can help cool them. In one set of experiments, Barron-Gafford’s team found that planting cilantro, tomatoes and peppers under solar arrays reduced the panels’ surface temperature by around 18 degrees Fahrenheit. That’s because plants release moisture into the air during their respiration process, in which they exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide.
“This invisible power of water coming out of plants was actually cooling down the solar panels,” Barron-Gafford said.
Throwing shade
While Barron-Gafford said some laughed him off when he first proposed the idea of growing crops in the shade of solar panels, this added sun shield can actually help them grow better, especially in the Southwest, where many backyard gardeners already employ shade cloths to protect their gardens from the blazing heat.
“Many people don’t understand that in Colorado and much of the West, most plants get far too much sunlight,” said Byron Kominek, owner/manager of Jack’s Solar Garden in Boulder County, Colorado, which began implementing agrivoltaics in 2020. “Having some shade is a benefit to them.”
Jack’s Solar Garden has integrated 3,276 solar panels over about four acres of farmland, growing crops like greens and tomatoes. Meg Caley with Sprout City Farms, a nonprofit that helps with farming duties at Jack’s Solar Garden, said they’ve been able to produce Swiss chard “the size of your torso.”
“The greens just get huge,” she said. “You have to chop them up to fit them in your refrigerator.”
She added that the shade seems to improve the flavor of the vegetables and prevents them from bolting, when plants prematurely produce flowers and seeds, diverting energy away from leaf or root growth.
“Plants when they’re stressed out can have more of a bitter flavor,” she explained. “So the arugula that we grow is not as bitter or spicy. It’s sweeter. The spinach is sweeter too.”
Barron-Gafford and his team are seeing the same thing in Arizona, where they grow a variety of produce like beans, artichokes, potatoes, kale, and basil.
“We’ve grown 30-plus different types of things across different wet winters and dry winters and exceptionally hot summers, dry summers, average or close to average summers,” he said of the solar-shaded crops. “And across everything we’ve done, we’ve seen equal or greater production down here in the Southwest, the dry land environments, where it really benefits to get some shade.”
As in Colorado, some of those crops are growing to epic proportions.
“We’ve made bok choy the size of a toddler,” Barron-Gafford said.
All that shade provides another important benefit in a drought-stricken Southwest—lower water requirements for crops. Because less direct sunlight is hitting the ground, it decreases the evaporation rate, which means water stays in the soil longer after irrigation. Barron-Gafford and his team have been running experiments for the last seven or so years to see how this plays out with different crops in an agrivoltaic setting.
“What is the evaporation rate under something that’s big and bushy like a bean or potato plant versus something thinner above ground, like a carrot?” is one of the questions Barron-Gafford said they have tried to answer. “For the most part, I would say that we are able to cut back our irrigation by more than half.”
They are partnering with Jack’s Solar Farm on water research in Colorado and have so far found similar results there.
This shade has another benefit in a warming world—respite for farmworkers. Heat-related illnesses are a growing concern for people who work outside, and one recent study predicted climate change will quadruple U.S. outdoor workers’ exposure to extreme heat conditions by 2065.
But with solar arrays in the fields, “if you really carefully plan out your day, you can work in the shade,” a factor that can help increase worker safety on hot days, Caley said.
The AgriSolar Clearinghouse performed skin temperature readings under solar panels and full sun at a number of sites across the United States, finding a skin temperature decrease of 15.3° in Boulder and 20.8° in Phoenix.
“I don’t know what the future holds”
Despite the benefits of agrivoltaics, the up-front cost of purchasing a solar array remains a barrier to farmers.
“Once people see the potential of agrivoltaics, you run into the next challenge, which is how do you fund someone getting into this on their site?” Barron-Gafford said. “And depending on the amount of capital or access to capital that a farmer has, you’re going to get a wildly different answer.”
While expenses are dependent on the size of the installation, a 25-kilowatt system would require an upfront cost of around $67,750, according to AgriSolar Clearinghouse. For comparison, the median size of a residential solar array in 2018 was around 6 kW, the organization stated, which would cost around $16,260 to install.
Kominek said the total initial cost of implementing a 1.2 megawatt capacity agrivoltaics setup on his farm in Colorado was around $2 million, but that the investment has paid off. In addition to the revenue he earns from farming, all of the energy produced by the arrays is sold to clients in the community through a local utility company, earning the farm money.
The Rural Energy for America program has been one resource for farmers interested in agrivoltaics, offering loans and grants to help install solar. However, it’s unclear how this program will move forward amid current federal spending cuts.
Meanwhile, some of the federal grant programs that Barron-Gafford has relied on have suddenly come to a halt, he said, putting his research in danger. But, as federal support dries up, some states are charging on with their own funding opportunities to develop farm field solar projects. For instance, Colorado’s Agrivoltaics Research and Demonstration Grant offers money for demonstrations of agrivoltaics, research projects, and outreach campaigns.
There are other challenges as well. Caley, for instance, said farming around solar panels is akin to working in an “obstacle course.” She and her team, who mostly work manually, have found ways to work around them by being aware of their surroundings so that they don’t accidentally collide with the panels or strike them with their tools. This job is also made easier since Kominek invested between $80,000 and $100,000 to elevate his farm’s panels, which better allows animals, taller crops and farming equipment to operate beneath.
Still, a 2025 University of Arizona study that interviewed farmers and government officials in Pinal County, Arizona, found that a number of them questioned agrivoltaics’ compatibility with large-scale agriculture.
“I think it’s a great idea, but the only thing … it wouldn’t be cost-efficient … everything now with labor and cost of everything, fuel, tractors, it almost has to be super big … to do as much with as least amount of people as possible,” one farmer stated.
Many farmers are also leery of solar, worrying that agrivoltaics could take working farmland out of use, affect their current operations or deteriorate soils.
Those fears have been amplified by larger utility-scale initiatives, like Ohio’s planned Oak Run Solar Project, an 800 megawatt project that will include 300 megawatts of battery storage, 4,000 acres of crops and 1,000 grazing sheep in what will be the country’s largest agrivoltaics endeavor to date. Opponents of the project worry about its visual impacts and the potential loss of farmland.
An American Farmland Trust survey found that Colorado farmers would prefer that utility-scale solar projects be sited on less productive or underutilized farmland rather than on highly productive or actively farmed land. They also expressed concern for the potential negative impact that solar projects could have on farm productivity and the health of the land, including soil quality.
Some farmers also worry that the solar panels could leach metals into the ground, contaminating their crops, Barron-Gafford said. But while agrivoltaic systems are put together in a way that makes that highly unlikely, there’s no reason not to add soil sampling studies into the work they’re doing to reassure farmers, he added.
And agrivoltaics advocates say that the practice could actually improve soil health by reducing erosion, increasing the amount of organic matter and enhancing soil biology with cooler, moister conditions.
“I wish more people spent time listening to the folks on the ground and the folks experiencing these transitions,” Barron-Gafford added. “Because you understand more that way in terms of what their motivations or concerns actually are.”
“We don’t have to choose”
While Caley understands farmers’ concerns, she sees agrivoltaics as a way for them to keep agricultural land in production while also benefiting from solar electricity.
“The tension in a lot of communities seems to be that people don’t want to see agricultural land taken out of production in order to bring a solar farm in,” she said. “The idea here is that we don’t have to choose. We can have both.”
Kominek encourages people to envision what our landscapes and climate will look like in the next 20 to 30 years, adding that in his part of Colorado, it only stands to get hotter and drier, making agrivoltaics a smart solution for farming and clean energy production.
“Communities around the world need to figure out what changes they need to make now to help people adapt to what our climates and landscapes will be in the future,” he said. “Agrivoltaics is a climate adaptation tool that will benefit any community where such systems are built as the decades pass.”
In the Southwest, solar panels can help both photovoltaics and crops Read More »