Review: Ryzen AI CPU makes this the fastest the Framework Laptop 13 has ever been
At this point, the Framework Laptop 13 is a familiar face, an old friend. We have reviewed this laptop five other times, and in that time, the idea of a repairable and upgradeable laptop has gone from a “sounds great if they can pull it off” idea to one that’s become pretty reliable and predictable. And nearly four years out from the original version—which shipped with an 11th-generation Intel Core processor—we’re at the point where an upgrade will get you significant boosts to CPU and GPU performance, plus some other things.
We’re looking at the Ryzen AI 300 version of the Framework Laptop today, currently available for preorder and shipping in Q2 for people who buy one now. The laptop starts at $1,099 for a pre-built version and $899 for a RAM-less, SSD-less, Windows-less DIY version, and we’ve tested the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 version that starts at $1,659 before you add RAM, an SSD, or an OS.
This board is a direct upgrade to Framework’s Ryzen 7040-series board from mid-2023, with most of the same performance benefits we saw last year when we first took a look at the Ryzen AI 300 series. It’s also, if this matters to you, the first Framework Laptop to meet Microsoft’s requirements for its Copilot+ PC initiative, giving users access to some extra locally processed AI features (including but not limited to Recall) with the promise of more to come.
For this upgrade, Ryzen AI giveth, and Ryzen AI taketh away. This is the fastest the Framework Laptop 13 has ever been (at least, if you spring for the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 chip that our review unit shipped with). If you’re looking to do some light gaming (or non-Nvidia GPU-accelerated computing), the Radeon 890M GPU is about as good as it gets. But you’ll pay for it in battery life—never a particularly strong point for Framework, and less so here than in most of the Intel versions.
What’s new, Framework?

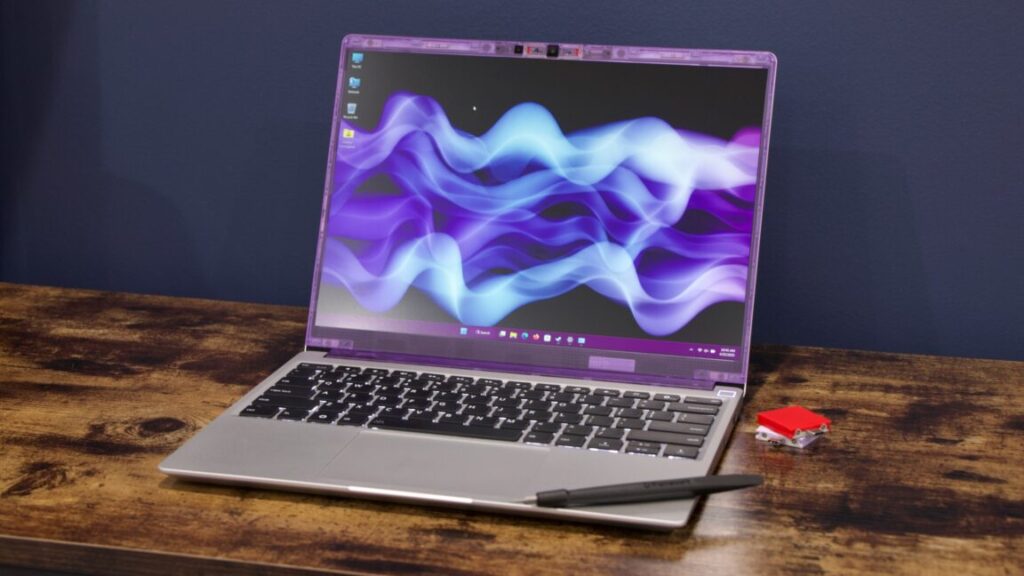
This Framework update brings the return of colorful translucent accessories, parts you can also add to an older Framework Laptop if you want. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
We’re going to focus on what makes this particular Framework Laptop 13 different from the past iterations. We talk more about the build process and the internals in our review of the 12th-generation Intel Core version, and we ran lots of battery tests with the new screen in our review of the Intel Core Ultra version. We also have coverage of the original Ryzen version of the laptop, with the Ryzen 7 7840U and Radeon 780M GPU installed.
Per usual, every internal refresh of the Framework Laptop 13 comes with another slate of external parts. Functionally, there’s not a ton of exciting stuff this time around—certainly nothing as interesting as the higher-resolution 120 Hz screen option we got with last year’s Intel Meteor Lake update—but there’s a handful of things worth paying attention to.
Functionally, Framework has slightly improved the keyboard, with “a new key structure” on the spacebar and shift keys that “reduce buzzing when your speakers are cranked up.” I can’t really discern a difference in the feel of the keyboard, so this isn’t a part I’d run out to add to my own Framework Laptop, but it’s a fringe benefit if you’re buying an all-new laptop or replacing your keyboard for some other reason.
Keyboard legends have also been tweaked; pre-built Windows versions get Microsoft’s dedicated (and, within limits, customizable) Copilot key, while DIY editions come with a Framework logo on the Windows/Super key (instead of the word “super”) and no Copilot key.
Cosmetically, Framework is keeping the dream of the late ’90s alive with translucent plastic parts, namely the bezel around the display and the USB-C Expansion Modules. I’ll never say no to additional customization options, though I still think that “silver body/lid with colorful bezel/ports” gives the laptop a rougher, unfinished-looking vibe.
Like the other Ryzen Framework Laptops (both 13 and 16), not all of the Ryzen AI board’s four USB-C ports support all the same capabilities, so you’ll want to arrange your ports carefully.
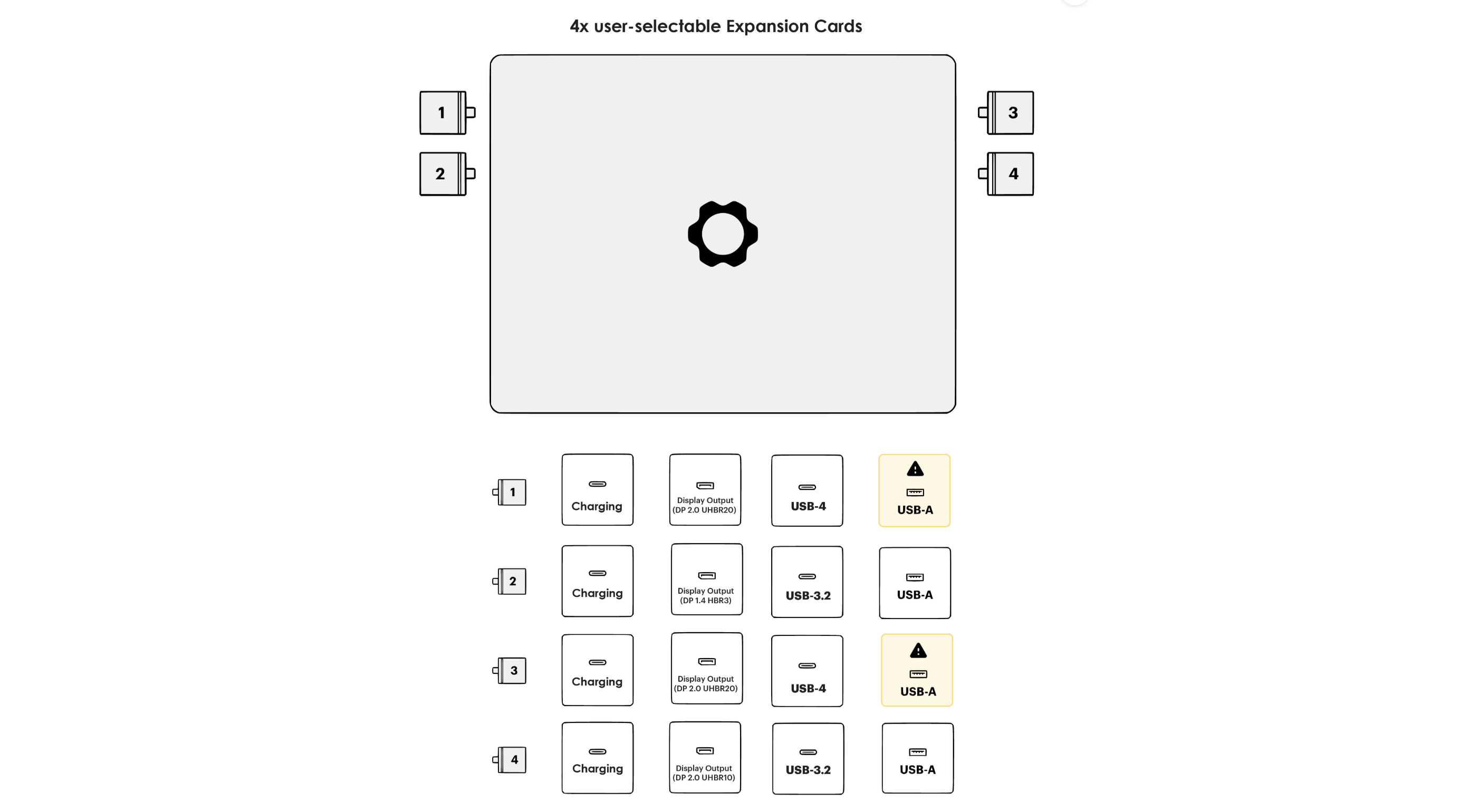
Framework’s recommendations for how to configure the Ryzen AI laptop’s expansion modules. Credit: Framework
Framework publishes a graphic to show you which ports do what; if you’re looking at the laptop from the front, ports 1 and 3 are on the back, and ports 2 and 4 are toward the front. Generally, ports 1 and 3 are the “better” ones, supporting full USB4 speeds instead of USB 3.2 and DisplayPort 2.0 instead of 1.4. But USB-A modules should go in ports 2 or 4 because they’ll consume extra power in bays 1 and 3. All four do support display output, though, which isn’t the case for the Ryzen 7040 Framework board, and all four continue to support USB-C charging.
The situation has improved from the 7040 version of the Framework board, where not all of the ports could do any kind of display output. But it still somewhat complicates the laptop’s customizability story relative to the Intel versions, where any expansion card can go into any port.
I will also say that this iteration of the Framework laptop hasn’t been perfectly stable for me. The problems are intermittent but persistent, despite using the latest BIOS version (3.03 as of this writing) and driver package available from Framework. I had a couple of total-system freezes/crashes, occasional problems waking from sleep, and sporadic rendering glitches in Microsoft Edge. These weren’t problems I’ve had with the other Ryzen AI laptops I’ve used so far or with the Ryzen 7040 version of the Framework 13. They also persisted across two separate clean installs of Windows.
It’s possible/probable that some combination of firmware and driver updates can iron out these problems, and they generally didn’t prevent me from using the laptop the way I wanted to use it, but I thought it was worth mentioning since my experience with new Framework boards has usually been a bit better than this.
Internals and performance
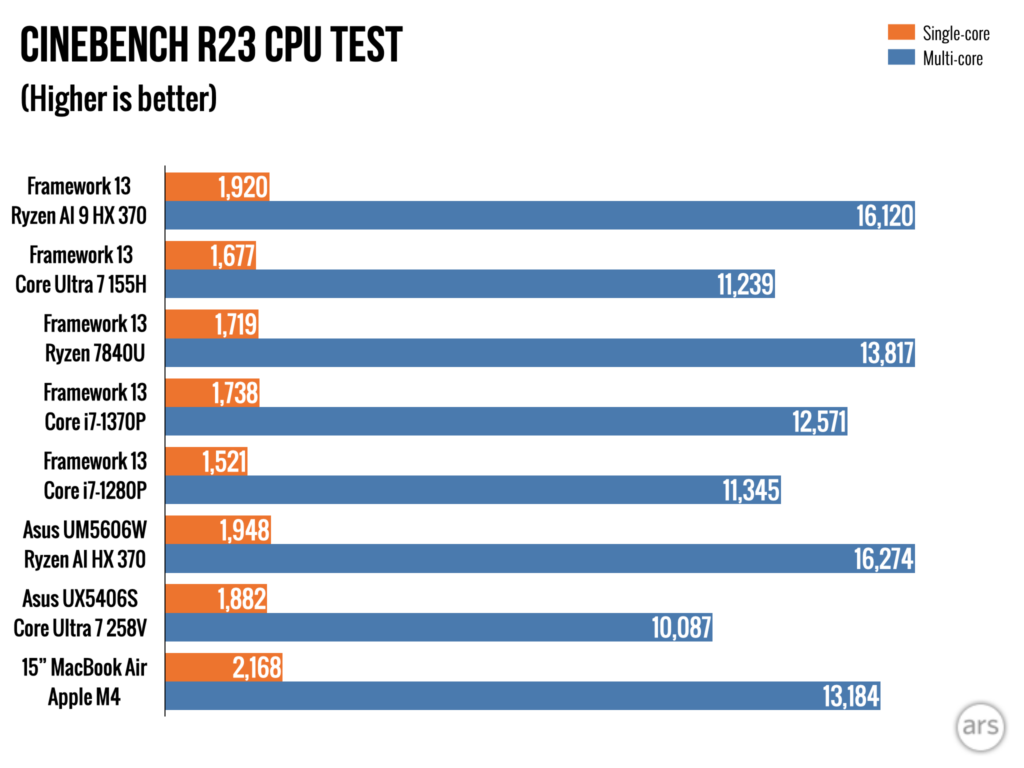
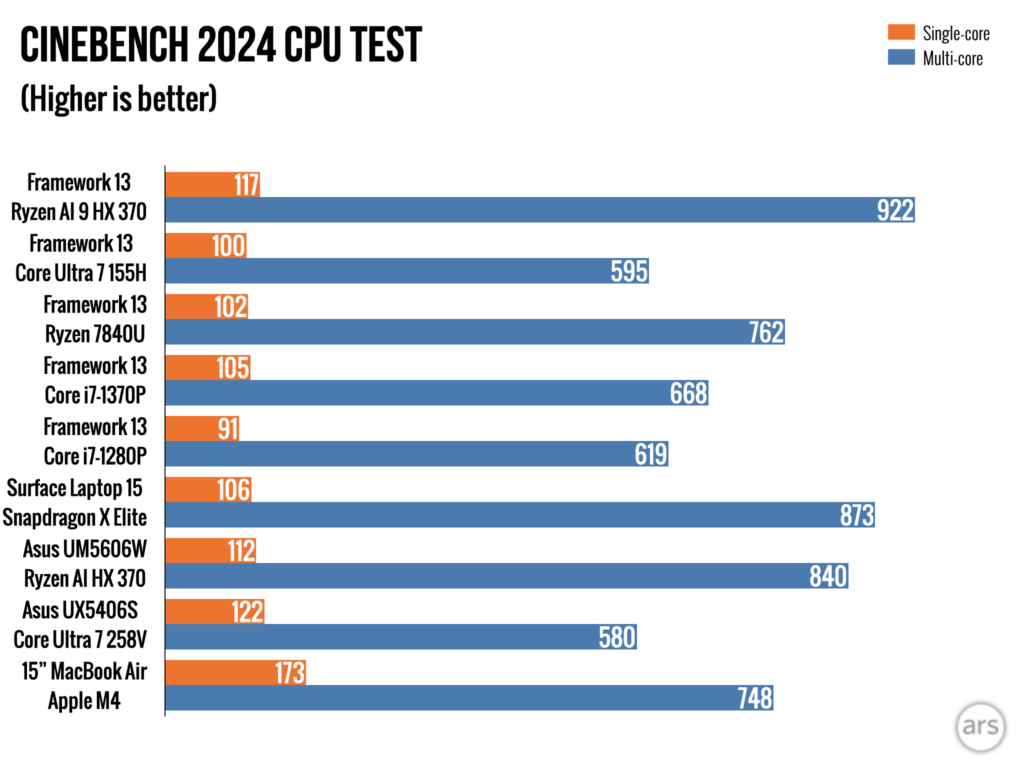
“Ryzen AI” is AMD’s most recent branding update for its high-end laptop chips, but you don’t actually need to care about AI to appreciate the solid CPU and GPU speed upgrades compared to the last-generation Ryzen Framework or older Intel versions of the laptop.
Our Framework Laptop board uses the fastest processor offering: a Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 with four of AMD’s Zen 5 CPU cores, eight of the smaller, more power-efficient Zen 5c cores, and a Radeon 890M integrated GPU with 16 of AMD’s RDNA 3.5 graphics cores.
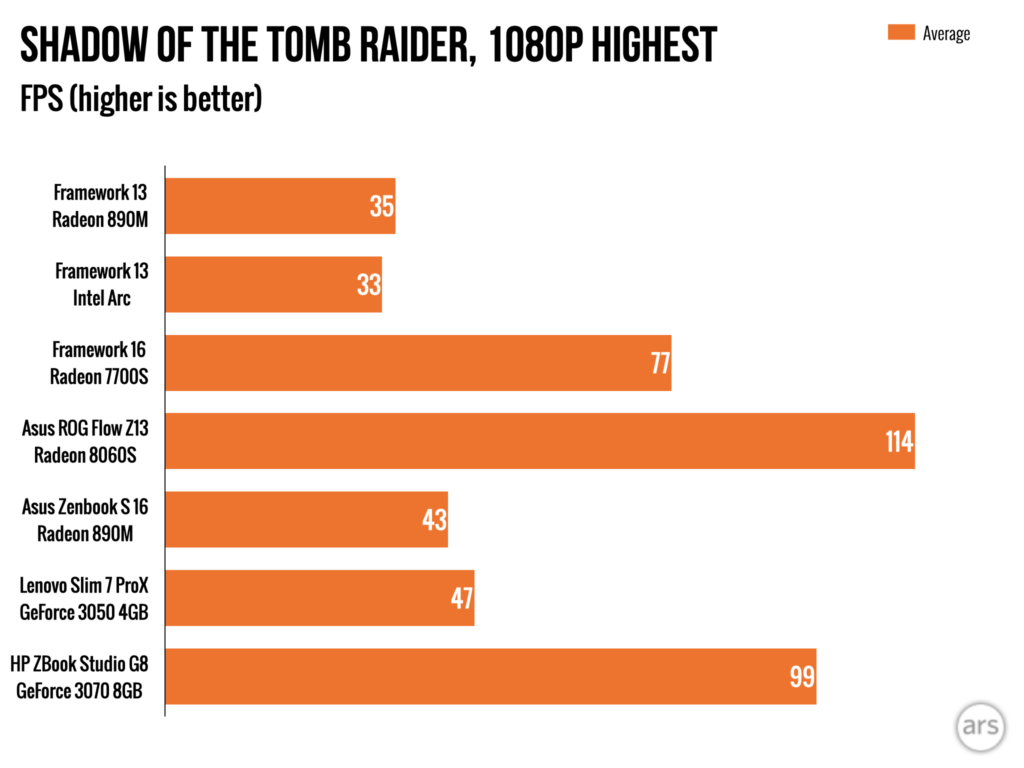
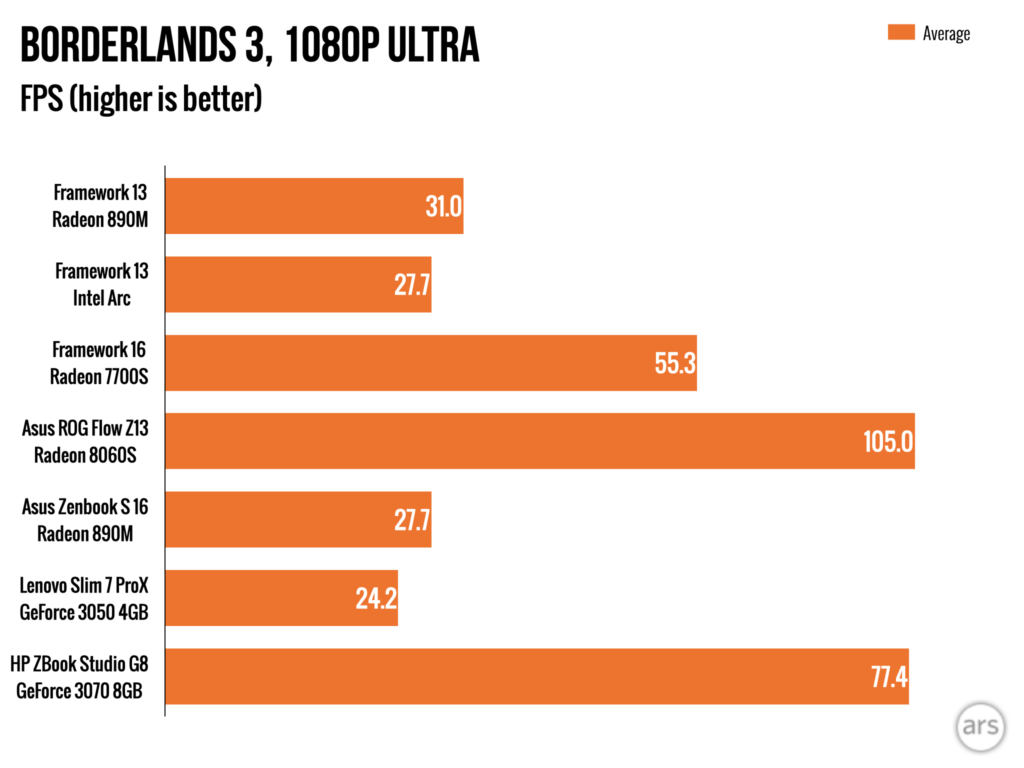
There are places where the Intel Arc graphics in the Core Ultra 7/Meteor Lake version of the Framework Laptop are still faster than what AMD can offer, though your experience may vary depending on the games or apps you’re trying to use. Generally, our benchmarks show the Arc GPU ahead by a small amount, but it’s not faster across the board.
Relative to other Ryzen AI systems, the Framework Laptop’s graphics performance also suffers somewhat because socketed DDR5 DIMMs don’t run as fast as RAM that’s been soldered to the motherboard. This is one of the trade-offs you’re probably OK with making if you’re looking at a Framework Laptop in the first place, but it’s worth mentioning.
A few actual game benchmarks. Ones with ray-tracing features enabled tend to favor Intel’s Arc GPU, while the Radeon 890M pulls ahead in some other games.
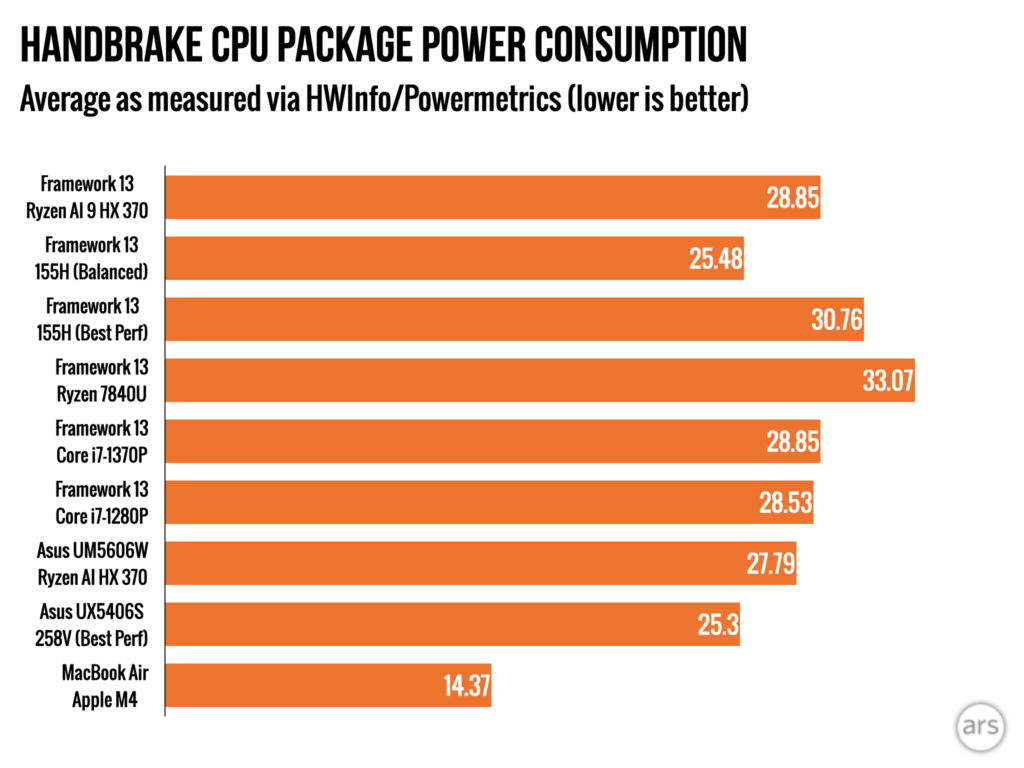
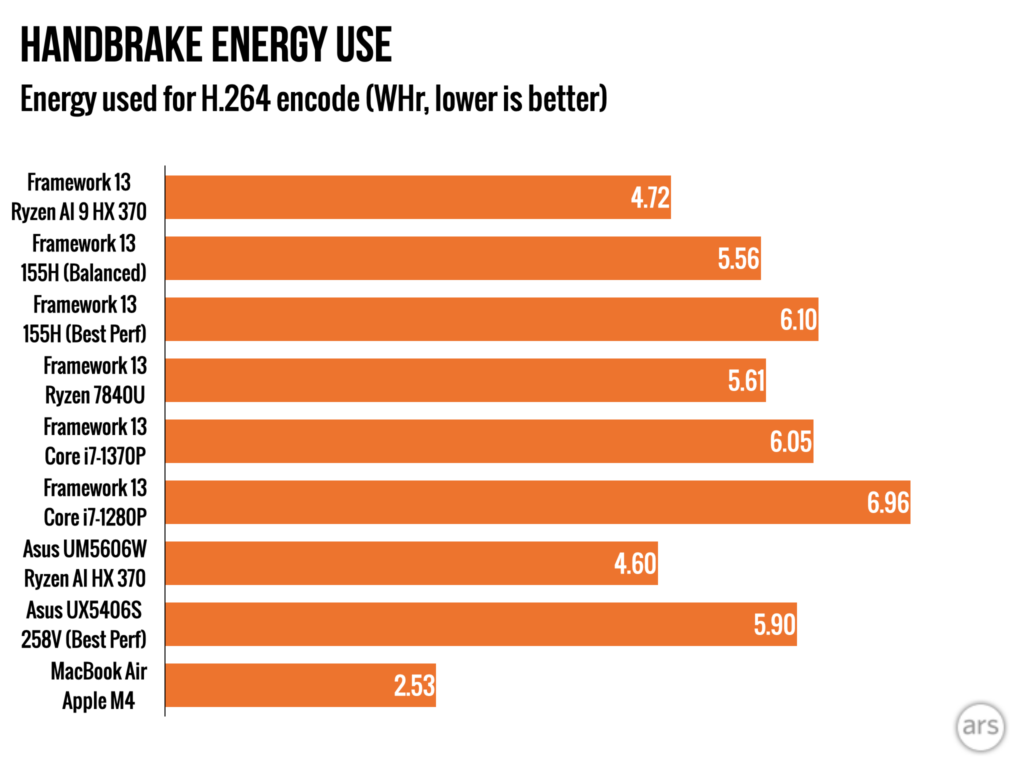
But the new Ryzen chip’s CPU is dramatically faster than Meteor Lake at just about everything, as well as the older Ryzen 7 7840U in the older Framework board. This is the fastest the Framework Laptop has ever been, and it’s not particularly close (but if you’re waffling between the Ryzen AI version, the older AMD version that Framework sells for a bit less money or the Core Ultra 7 version, wait to see the battery life results before you spend any money). Power efficiency has also improved for heavy workloads, as demonstrated by our Handbrake video encoding tests—the Ryzen AI chip used a bit less power under heavy load and took less time to transcode our test video, so it uses quite a bit less power overall to do the same work.
Power efficiency tests under heavy load using the Handbrake transcoding tool. Test uses CPU for encoding and not hardware-accelerated GPU-assisted encoding.
We didn’t run specific performance tests on the Ryzen AI NPU, but it’s worth noting that this is also Framework’s first laptop with a neural processing unit (NPU) fast enough to support the full range of Microsoft’s Copilot+ PC features—this was one of the systems I used to test Microsoft’s near-final version of Windows Recall, for example. Intel’s other Core Ultra 100 chips, all 200-series Core Ultra chips other than the 200V series (codenamed Lunar Lake), and AMD’s Ryzen 7000- and 8000-series processors often include NPUs, but they don’t meet Microsoft’s performance requirements.
The Ryzen AI chips are also the only Copilot+ compatible processors on the market that Framework could have used while maintaining the Laptop’s current level of upgradeability. Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite and Plus chips don’t support external RAM—at least, Qualcomm only lists support for soldered-down LPDDR5X in its product sheets—and Intel’s Core Ultra 200V processors use RAM integrated into the processor package itself. So if any of those features appeal to you, this is the only Framework Laptop you can buy to take advantage of them.
Battery and power
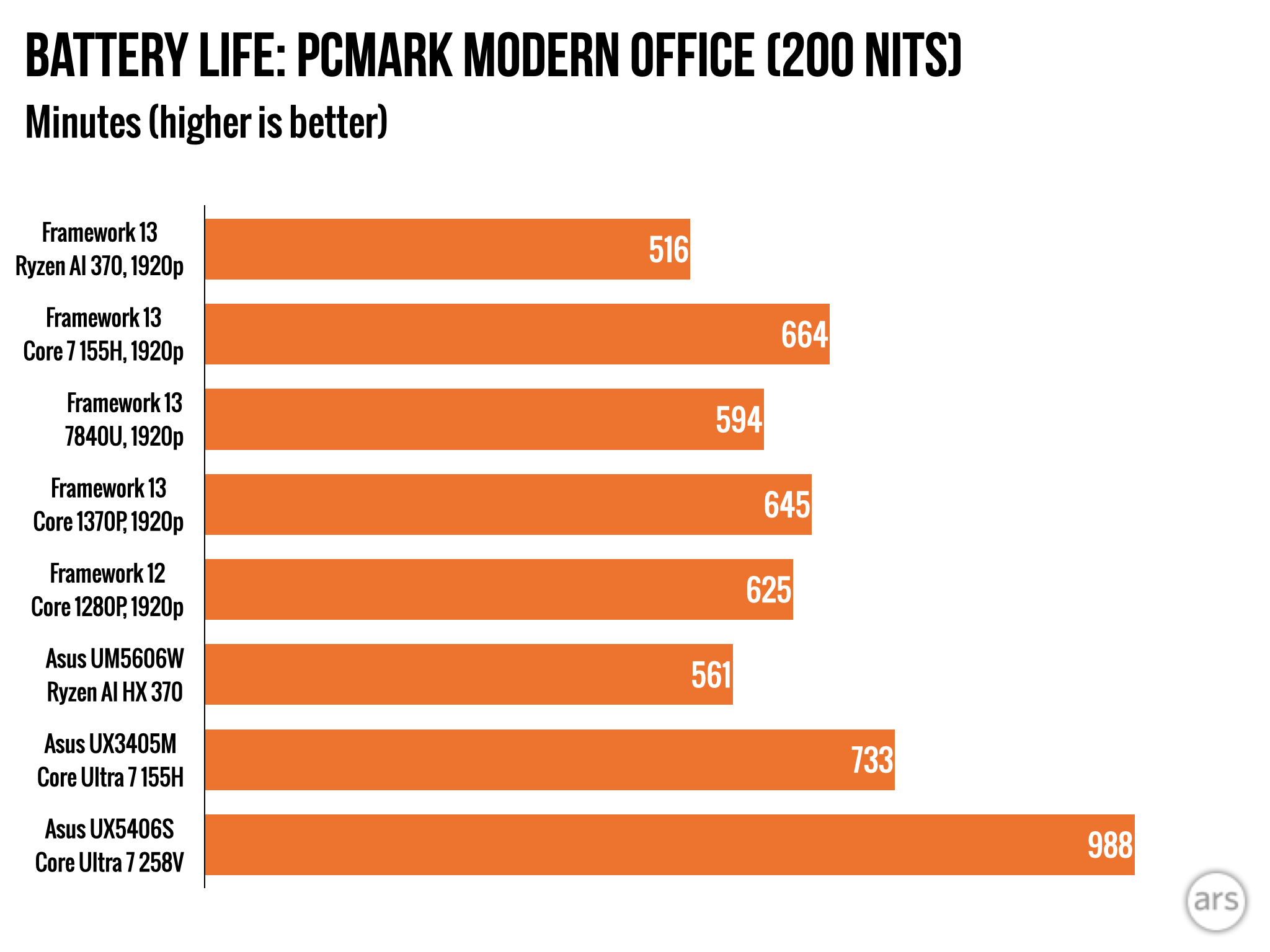
Battery tests. The Ryzen AI 300 doesn’t do great, though it’s similar to the last-gen Ryzen Framework.
When paired with the higher-resolution screen option and Framework’s 61 WHr battery, the Ryzen AI version of the laptop lasted around 8.5 hours in a PCMark Modern Office battery life test with the screen brightness set to a static 200 nits. This is a fair bit lower than the Intel Core Ultra version of the board, and it’s even worse when compared to what a MacBook Air or a more typical PC laptop will give you. But it’s holding roughly even with the older Ryzen version of the Framework board despite being much faster.
You can improve this situation somewhat by opting for the cheaper, lower-resolution screen; we didn’t test it with the Ryzen AI board, and Framework won’t sell you the lower-resolution screen with the higher-end chip. But for upgraders using the older panel, the higher-res screen reduced battery life by between 5 and 15 percent in past testing of older Framework Laptops. The slower Ryzen AI 5 and Ryzen AI 7 versions will also likely last a little longer, though Framework usually only sends us the highest-end versions of its boards to test.
A routine update

This combo screwdriver-and-spudger is still the only tool you need to take a Framework Laptop apart. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
It’s weird that my two favorite laptops right now are probably Apple’s MacBook Air and the Framework Laptop 13, but that’s where I am. They represent opposite visions of computing, each of which appeals to a different part of my brain: The MacBook Air is the personal computer at its most appliance-like, the thing you buy (or recommend) if you just don’t want to think about your computer that much. Framework embraces a more traditionally PC-like approach, favoring open standards and interoperable parts; the result is more complicated and chaotic but also more flexible. It’s the thing you buy when you like thinking about your computer.
Framework Laptop buyers continue to pay a price for getting a more repairable and modular laptop. Battery life remains OK at best, and Framework doesn’t seem to have substantially sped up its firmware or driver releases since we talked with them about it last summer. You’ll need to be comfortable taking things apart, and you’ll need to make sure you put the right expansion modules in the right bays. And you may end up paying more than you would to get the same specs from a different laptop manufacturer.
But what you get in return still feels kind of magical, and all the more so because Framework has now been shipping product for four years. The Ryzen AI version of the laptop is probably the one I’d recommend if you were buying a new one, and it’s also a huge leap forward for anyone who bought into the first-generation Framework Laptop a few years ago and is ready for an upgrade. It’s by far the fastest CPU (and, depending on the app, the fastest or second-fastest GPU) Framework has shipped in the Laptop 13. And it’s nice to at least have the option of using Copilot+ features, even if you’re not actually interested in the ones Microsoft is currently offering.
If none of the other Framework Laptops have interested you yet, this one probably won’t, either. But it’s yet another improvement in what has become a steady, consistent sequence of improvements. Mediocre battery life is hard to excuse in a laptop, but if that’s not what’s most important to you, Framework is still offering something laudable and unique.
The good
- Framework still gets all of the basics right—a matte 3:2 LCD that’s pleasant to look at, a nice-feeling keyboard and trackpad, and a design
- Fastest CPU ever in the Framework Laptop 13, and the fastest or second-fastest integrated GPU
- First Framework Laptop to support Copilot+ features in Windows, if those appeal to you at all
- Fun translucent customization options
- Modular, upgradeable, and repairable—more so than with most laptops, you’re buying a laptop that can change along with your needs and which will be easy to refurbish or hand down to someone else when you’re ready to replace it
- Official support for both Windows and Linux
The bad
- Occasional glitchiness that may or may not be fixed with future firmware or driver updates
- Some expansion modules are slower or have higher power draw if you put them in the wrong place
- Costs more than similarly specced laptops from other OEMs
- Still lacks certain display features some users might require or prefer—in particular, there are no OLED, touchscreen, or wide-color-gamut options
The ugly
- Battery life remains an enduring weak point.
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
Review: Ryzen AI CPU makes this the fastest the Framework Laptop 13 has ever been Read More »