Meet CDC’s new lead vaccine advisor who thinks shots cause heart disease
Milhoan has a history of touting unproven COVID cures while disparaging vaccines.
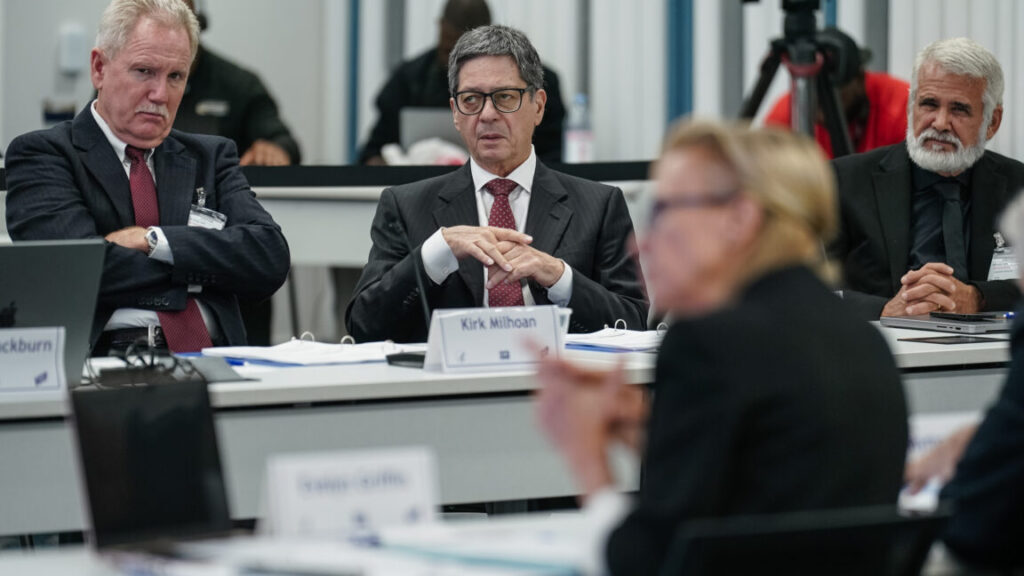
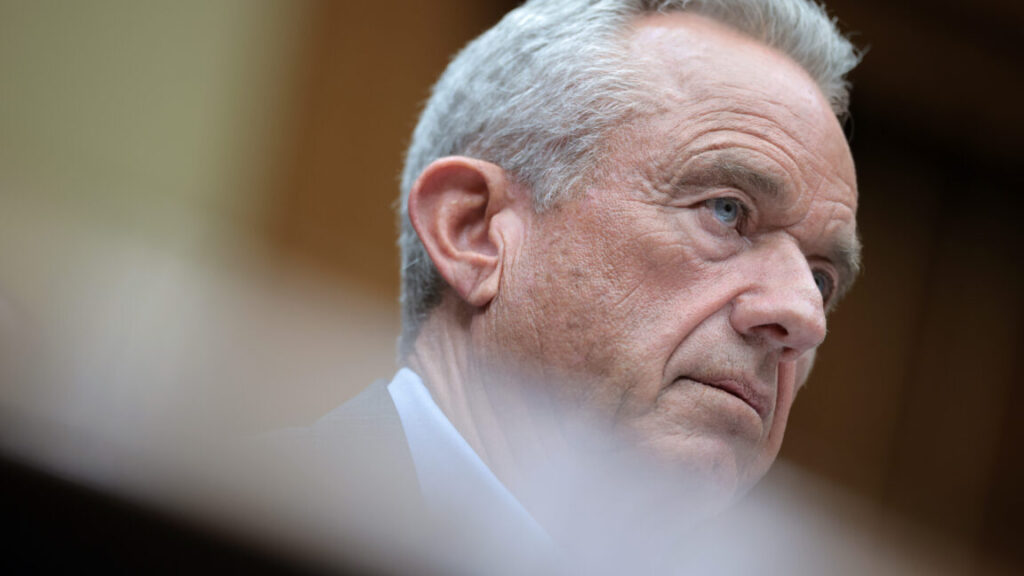
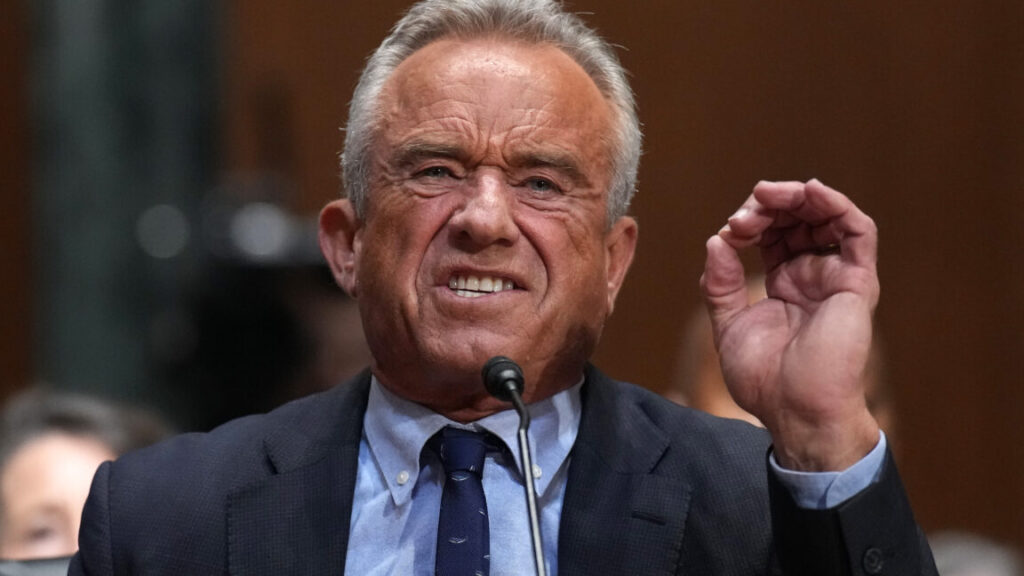
Kirk Milhoan, James Pagano, and Robert Malone are seen during a meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on September 18, 2025 in Chamblee, Georgia. Credit: Getty | Elijah Nouvelage
When the federal vaccine committee hand-picked by anti-vaccine Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. meets again this week, it will have yet another new chairperson to lead its ongoing work of dismantling the evidence-based vaccine recommendations set by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Monday, the Department of Health and Human Services announced that the chairperson who has been in place since June—when Kennedy fired all 17 expert advisors on the committee and replaced them with questionably qualified allies—is moving to a senior role in the department. Biostatistician Martin Kulldorff will now be the chief science officer for the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE), HHS said. As such, he’s stepping down from the vaccine committee, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
Kulldorff gained prominence amid the COVID-19 pandemic, criticizing public health responses to the crisis, particularly lockdowns and COVID-19 vaccines. He was a co-author of the Great Barrington Declaration that advocated for letting the deadly virus spread unchecked through the population, which was called unethical by health experts.
As ACIP chair, Kulldorff frequently made false and misleading statements about vaccine safety and efficacy that were in line with Kennedy’s views and statements. While Kulldorff presided over the committee, it made a series of decisions that were sharply denounced by scientific and medical groups as being based on ideology rather than evidence. Those include voting for the removal of the vaccine preservative thimerosal from some flu vaccines, despite well-established data indicating it is safe, with no evidence of harms. The committee also added restrictions to a combination measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella (chickenpox) MMRV vaccine and made an unprecedented effort to prevent Americans from getting COVID-19 vaccines, though the moves were largely ineffective.
In his new role, Kulldorff will be working with ASPE to provide analyses on health policy options, coordinate research efforts, and provide policy advice.
“It’s an honor to join the team of distinguished scientists that Secretary Kennedy has assembled,” Kulldorff said in a press release announcing his new role. “I look forward to contributing to the science-based public health policies that will Make America Healthy Again.”
The new chair, Kirk Milhoan
With Kulldorff moving on, ACIP will now be chaired by Kirk Milhoan, a pediatric oncologist with a track record for spreading COVID-19 misinformation and anti-vaccine views. In August 2021, the Hawaii Medical Board filed a complaint against Milhoan after he appeared on a panel promoting ineffective COVID-19 treatments, downplaying the severity of the disease, and spreading misinformation about COVID-19 vaccines, according to the Maui News. The complaint was dropped in April 2022 after state regulators said they had insufficient evidence to prove a violation of statutes regarding the practice of medicine.
While Milhoan claimed at the time that he is “pro-vaccine,” his statement, affiliations, and prescribing practices suggest otherwise. Milhoan is a member of the Independent Medical Alliance (formerly the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance), a group of dubious health care providers set up amid the pandemic to promote the use of the anti-malaria drug hydroxychloroquine and the de-worming drug ivermectin to treat COVID-19. Both drugs have shown to be ineffective and potentially harmful when used to treat or prevent COVID-19. The IMA also emphasizes vaccine injuries while pushing vitamins and other unproven treatments.
In 2024, Milhoan appeared on a panel set up by Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Ga.) to discuss alleged injuries from COVID-19 vaccines alongside other prominent anti-vaccine and COVID-19 misinformation voices. In his opening statement, Milhoan suggested that COVID-19 vaccines were causing severe cardiovascular disease and death in people aged 15 to 44—an unsubstantiated claim he frequently echoes. In his bio for the IMA, he touts that he offers treatment for “vaccine-related cardiovascular toxicity due to the spike protein.”
CDC data has found that boys and young men, aged 12 to 24, have a heightened risk of myocarditis (inflammation of the heart) after COVID-19 vaccination. However, the cases are rare, relatively mild, and almost always resolve, according to CDC data. In a COVID-19 safety data presentation in June, CDC staff scientists reported that its vast vaccine safety monitoring systems indicated that in males 12–24, there are 27 myocarditis cases per million doses of COVID-19 vaccine administered (roughly one case in 37,000 doses). In cases identified during 2021, 83 percent recovered within three months, with more than 90 percent recovering within the year. The monitoring data found no instances of cardiac transplant or death from COVID-19 vaccination.
While anti-vaccine activists have seized on this minor risk from vaccination, health experts note that the risk of myocarditis and other inflammatory conditions from a COVID-19 infection is significantly greater than the risk from vaccination. Exact estimates vary, but one CDC study in 2021 found that people with COVID-19 infections had a 16-fold higher risk of myocarditis than people without the infection. Specifically, the study estimated that there were 150 myocarditis cases among 100,000 COVID-19-infected patients versus just nine myocarditis cases among 100,000 people without COVID-19 infections and who were also unvaccinated. Similar to what’s seen with vaccination, the study found that young males were most at risk of myocarditis.
Kennedy’s allies attack on COVID-19 shots
Kennedy and his allies, like Milhoan, have consistently inflated the risk of myocarditis from COVID-19 vaccination, with some claiming without evidence that they have caused sudden cardiac arrest and deaths in young males, though studies have found no such link. In 2022, Milhoan and fellow ACIP member and conspiracy theorist Robert Malone were featured in a viral social media post suggesting that 50 percent of college athletes in the Big Ten athletic conference had myocarditis linked to COVID-19 vaccines, which could lead to deaths if they played. But the two were referencing a JAMA Cardiology study that examined subclinical myocarditis in Big Ten athletes after COVID-19 infection—not vaccination. In fact, researchers confirmed for an AFP fact check that none of the athletes in the study were vaccinated. And the rate of subclinical myocarditis in the group was 2.3 percent, not 50 percent.
Milhoan’s misinformation about the cardiovascular harms from COVID-19 vaccines seems particularly pertinent to the direction of Kennedy’s anti-vaccine allies. On Friday, Vinay Prasad, the Food and Drug Administration’s top vaccine regulator, sent a memo to staff claiming without evidence that COVID-19 vaccines have killed 10 children. The memo provides little information about the extraordinary claim, but it hints that the deaths were linked to myocarditis and found among reports submitted between 2021 and 2024 to the CDC’s Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
VAERS is a system by which anyone, including members of the public, can report anything they think could be linked to vaccines. The reports are considered a type of early warning system, but the vast majority of the reports submitted are not actually related to vaccines. Further, CDC scientists have thoroughly evaluated VAERS reports and ruled out deaths attributed to COVID-19 vaccines. Prasad’s memo—which experts have speculated was designed to be leaked to produce alarming headlines about child deaths—claimed that before Trump administration officials with anti-vaccine views began sifting through the data, these deaths were “ignored” by FDA and CDC scientists. Prasad also claimed that there could be many more deaths that have gone unreported, despite the fact that healthcare providers have been legally required to report any deaths that occurred after COVID-19 vaccination, regardless of cause.
This week’s ACIP meeting
In this week’s scheduled ACIP meeting on Thursday and Friday, COVID-19 vaccines don’t appear on the draft agenda. Instead, ACIP is expected to vote to remove a recommendation for a birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. That dose protects newborns from contracting the highly infectious virus from their mothers during birth or from other family or acquaintances shortly after birth. About half of the people infected with hepatitis B are not aware of their infections, and testing of mothers before birth is imperfect. That can leave newborns particularly vulnerable, as infections that start at or shortly after birth almost always develop into chronic infections that can lead to liver disease, liver transplant, and cancer. In a previous ACIP meeting, CDC staff scientists presented data showing that there are no significant harms of birth doses and there is no evidence that delaying the immunization offers any benefit.
The committee is also taking on the childhood vaccine schedule as a whole, though the agenda on this topic is not yet clear. In his memo, Prasad attacked the common practice of providing multiple vaccinations at once, hinting that it could be a way in which the committee will try to dismantle current childhood vaccination recommendations. On Tuesday, The Washington Post reported that the committee will examine whether the childhood vaccine schedule as a whole is causing allergies and autoimmune diseases, something Kennedy and his anti-vaccine organization have long floated despite evidence refuting a link.
Under clear attack are aluminum salt adjuvants, which are used in many vaccines to help spur protective immune responses. Aluminum salts have been used safely in vaccines for more than 70 years. The FDA notes that the most common source of aluminum exposure is from food and water, not vaccines.
Beth is Ars Technica’s Senior Health Reporter. Beth has a Ph.D. in microbiology from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and attended the Science Communication program at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She specializes in covering infectious diseases, public health, and microbes.
Meet CDC’s new lead vaccine advisor who thinks shots cause heart disease Read More »