“Butt breathing” might soon be a real medical treatment
And Oxycyte was ideal for the group’s 2021 Ig Nobel-winning efforts. The experiments involved intra-anally administering oxygen gas or a liquid oxygenated perfluorocarbon to the unfortunate rodents and porcines. Yes, they gave the animals enemas. They then induced respiratory failure and evaluated the effectiveness of the intra-anal treatment. The result: Both treatments were pretty darned effective at staving off respiratory failure with no major complications.
Credit: Cincinnati Children’s/Med
So far, so good. The next logical step was to determine if EVA could work in human patients, too. “Patients with severe respiratory failure often need mechanical ventilation to survive, but these therapies can cause further lung injury,” the authors wrote in this latest paper. EVA “could give the lungs a chance to rest and heal.”
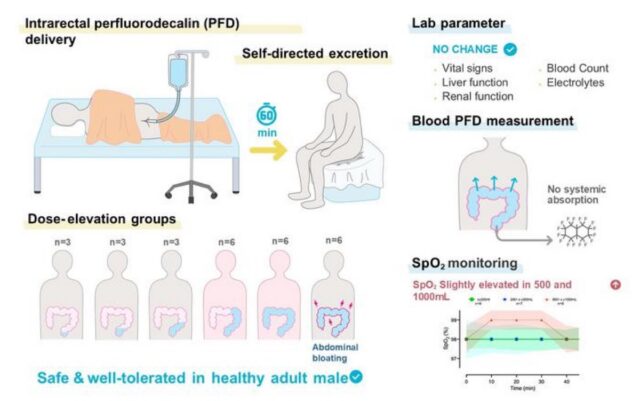
The team recruited 27 healthy adult men in Japan, each of whom received a dose of non-oxygenated perfluorodecalin via the anus. They were asked to retain the liquid for a full hour as the dosage slowly increased from 25 to 1,500 mL. Twenty of the men successfully completed the experiment. Apart from mild temporary abdominal bloating and discomfort—which proved to be dosage dependent and resolved with no need for medical attention—they experienced no adverse effects.
“This is the first human data and the results are limited solely to demonstrating the safety of the procedure and not its effectiveness,” said co-author Takanori Takebe of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and the University of Osaka in Japan. “But now that we have established tolerance, the next step will be to evaluate how effective the process is for delivering oxygen to the bloodstream.”
Med, 2025. DOI: 10.1016/j.medj.2025.100887 (About DOIs).
“Butt breathing” might soon be a real medical treatment Read More »


