Study finds AI-generated meme captions funnier than human ones on average
It’s worth clarifying that AI models did not generate the images used in the study. Instead, researchers used popular, pre-existing meme templates, and GPT-4o or human participants generated captions for them.
More memes, not better memes
When crowdsourced participants rated the memes, those created entirely by AI models scored higher on average in humor, creativity, and shareability. The researchers defined shareability as a meme’s potential to be widely circulated, influenced by humor, relatability, and relevance to current cultural topics. They note that this study is among the first to show AI-generated memes outperforming human-created ones across these metrics.
However, the study comes with an important caveat. On average, fully AI-generated memes scored higher than those created by humans alone or humans collaborating with AI. But when researchers looked at the best individual memes, humans created the funniest examples, and human-AI collaborations produced the most creative and shareable memes. In other words, AI models consistently produced broadly appealing memes, but humans—with or without AI help—still made the most exceptional individual examples.
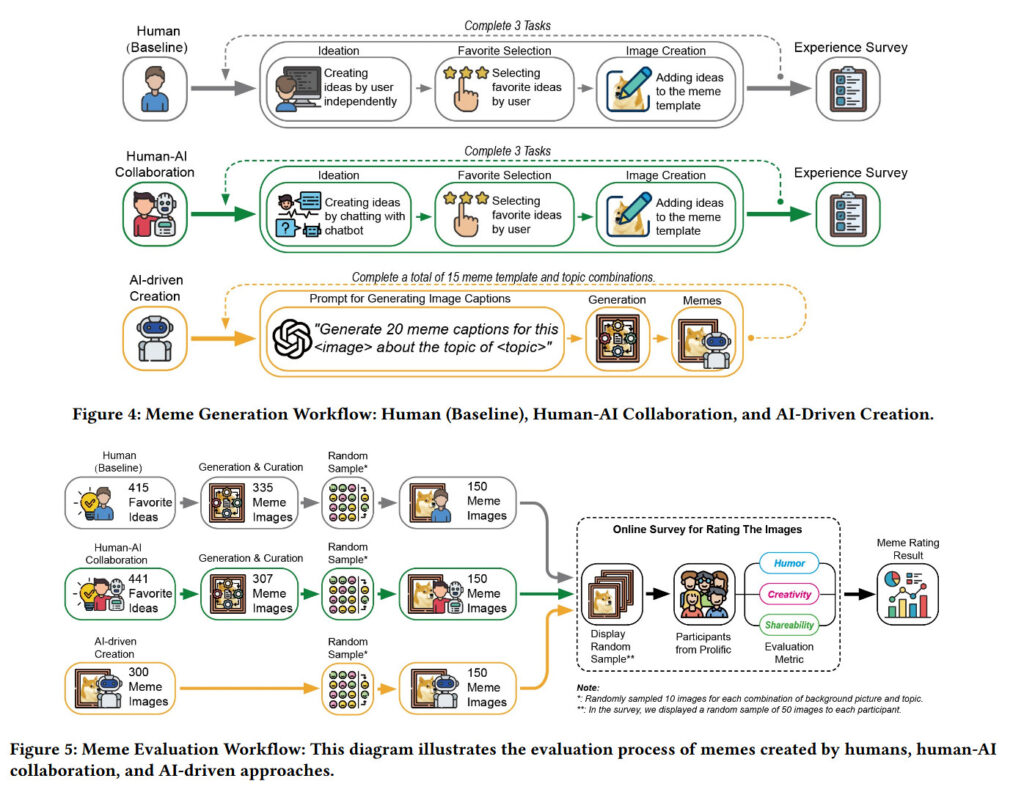
Diagrams of meme creation and evaluation workflows taken from the paper. Credit: Wu et al.
The study also found that participants using AI assistance generated significantly more meme ideas and described the process as easier and requiring less effort. Despite this productivity boost, human-AI collaborative memes did not rate higher on average than memes humans created alone. As the researchers put it, “The increased productivity of human-AI teams does not lead to better results—just to more results.”
Participants who used AI assistance reported feeling slightly less ownership over their creations compared to solo creators. Given that a sense of ownership influenced creative motivation and satisfaction in the study, the researchers suggest that people interested in using AI should carefully consider how to balance AI assistance in creative tasks.
Study finds AI-generated meme captions funnier than human ones on average Read More »