It seems like as other things drew our attention more, medical news slowed down. The actual developments, I have no doubt, are instead speeding up – because AI.
Note that this post intentionally does not cover anything related to the new Administration, or its policies.
-
Some People Need Practical Advice.
-
Good News, Everyone.
-
Bad News.
-
Life Extension.
-
Doctor Lies to Patient.
-
Study Lies to Public With Statistics.
-
Area Man Discovers Information Top Doctors Missed.
-
Psychiatric Drug Prescription.
-
H5N1.
-
WHO Delenda Est.
-
Medical Ethicists Take Bold Anti-Medicine Stance.
-
Rewarding Drug Development.
-
Not Rewarding Device Developers.
-
Addiction.
-
Our Health Insurance Markets are Broken.
If you ever have to go to the hospital for any reason, suit up, or at least look good.
Life expectancy is still rising in the longest-lived countries.
Challenge trials are not in general riskier than RCTs, and dramatically on net increase health and save lives while being entirely voluntary, but that is of course all orthogonal to the concerns of bioethicists.
We now have a 100% effective practical way to prevent HIV infection.
Naloxone alone did not do much to reduce opioid deaths, but Narcan did by allowing those without training to administer the drug. This does not tell us about second-order impacts, but presumably people not dying is good.
The FDA will occasionally do something helpful… eventually… after exhausting seven years and all alternatives. In 2017 a law required the FDA to let us buy hearing aids. In 2021 they put out a rule ‘for public comment.’ In 2024 it finally happened.
China has a semi-libertarian Medial Tourism Pilot Zone in Hainan, where anything approved elsewhere is allowed, and many other restrictions are also waived. Alex Tabarrok notes this could be a model for the upside of Prospera. I say the true upside comes when you don’t need the approval at all, so long as your disclosures are clear.
So it looks like uterus transplants… work? As in the patients get to have kids.
Cate Hall reports much improved overall health from testosterone replacement therapy as a 40yo cis woman.
There’s a concierge doctor in Austin called Riverrock Medical that wrote a Bayesian calculator app for doctors.
States creating pathways for foreign doctors to practice medicine in America without redoing residency. More of this, please.
Nikhil Krishnan: I feel like the fact that residency slots aren’t expanded probably isn’t due to funding (residents seem to actually be ROI positive for hospitals since they’re cheap and can still bill) but actually due to capacity constraints of training people. This effectively seems like using other countries as our expanded capacity for resident training?
That is not quite the same as saying the residency slots cost too much, but it also is not that different. One of the costs of providing a residency slot is the training time, which requires doctor time, which is expensive, increasing staffing needs. If pricing that in still leaves profit, including accounting for transitional costs, you’d see expanded residency slots, so I presume that after taking this into account adding new slots is not actually profitable, even if current slots do okay.
Worries about what will happen to the genetic information from 23andMe. As others have noted, one of our charitably inclined billionaires should step up and buy the information to both preserve it for research in anonymized form and to protect the personal information.
Tyler Cowen reports on the book by the new head of the FDA. It seems right that Marty Makary is a pick with upsides and not downsides, but it also seems right to be unexcited for now, and on net disappointed. This was an opportunity to get a huge win, and the value was in the chance that we’d get a huge win, which is now lower (but not gone), the same way Operation Warp Speed was a civilization-level huge win. If Trump changes his mind or Makary runs into issues, I am still available for this or a number of other high-level posts, such as head of AISI.
Sarah Constantin confirms this one is legit, Nature paper, IL-11 inhibition is a 25% life extension IN MICE. I trust her on such matters.
Another claim of 25% life extension IN MICE, on a single injection, with various signs of physical rejuvenation.
Still very early, also starting to get interesting.
Caloric restriction appears to extend life only in short-lived animal models, and fail in longer-lived models. That’s highly unfortunate, since humans live a long time.
If you are terminally ill and ask how long you have the doctor will overestimate your time left, on average by a factor of five. This was mostly (63%) in cancer patients. They frame that as doctors being inaccurate.
I find it hard to believe this is not motivated. Even if the doctors consciously believe the estimates, they almost have to be offering optimistic outlooks that are ‘on purpose’ in various ways.
If they started out optimistic by a factor of five as an honest mistake and were trying to be accurate, it wouldn’t take long for them to notice their patients all keep dying way too soon, and adjusting their estimates.
Potential motivations include preventing the patient from giving up hope or seeking expensive and painful alternative treatments they doubt will do anything useful, telling them what they want to hear, avoiding the whole ‘doctor said I would die soon and here I am’ thing and so on. I do sympathize.
I also find it weird to assess a prediction for ‘accuracy’ based on the actual time of death – a prediction is over a distribution of outcomes. You can only properly judge prediction accuracy statistically.
Is there a relation to this next story, if you look at the incentives?
Pregnant woman goes into labor at 22 weeks, hospital tells her she has no hope, she drives 7 miles to another hospital she finds on facebook and now she has a healthy four year old. Comments have a lot of other ‘the doctors told us our child would never survive, but then we got a second opinion and they did anyway’ stories.
Based on my personal experience as well, in America you really, really need to be ready to advocate for yourself when dealing with pregnancy. Some doctors are wonderful, other doctors will often flat out give you misinformation or do what is convenient for them if you don’t stop them. Also don’t forget to consult Claude.
Inequality is always a function of how you take the measurement and divide the groups.
Here is an extreme example.
St. Rev. Dr. Rev: Remember that study that said 12% of the population eats 50% of the beef? And it turned out that they meant in a given 24 hour period? Eat a burger on Tuesday, suddenly you’re in the 12%. Have a salad on Wednesday, you’re in the 88%.
This is that, but for cancer. Come on, man.
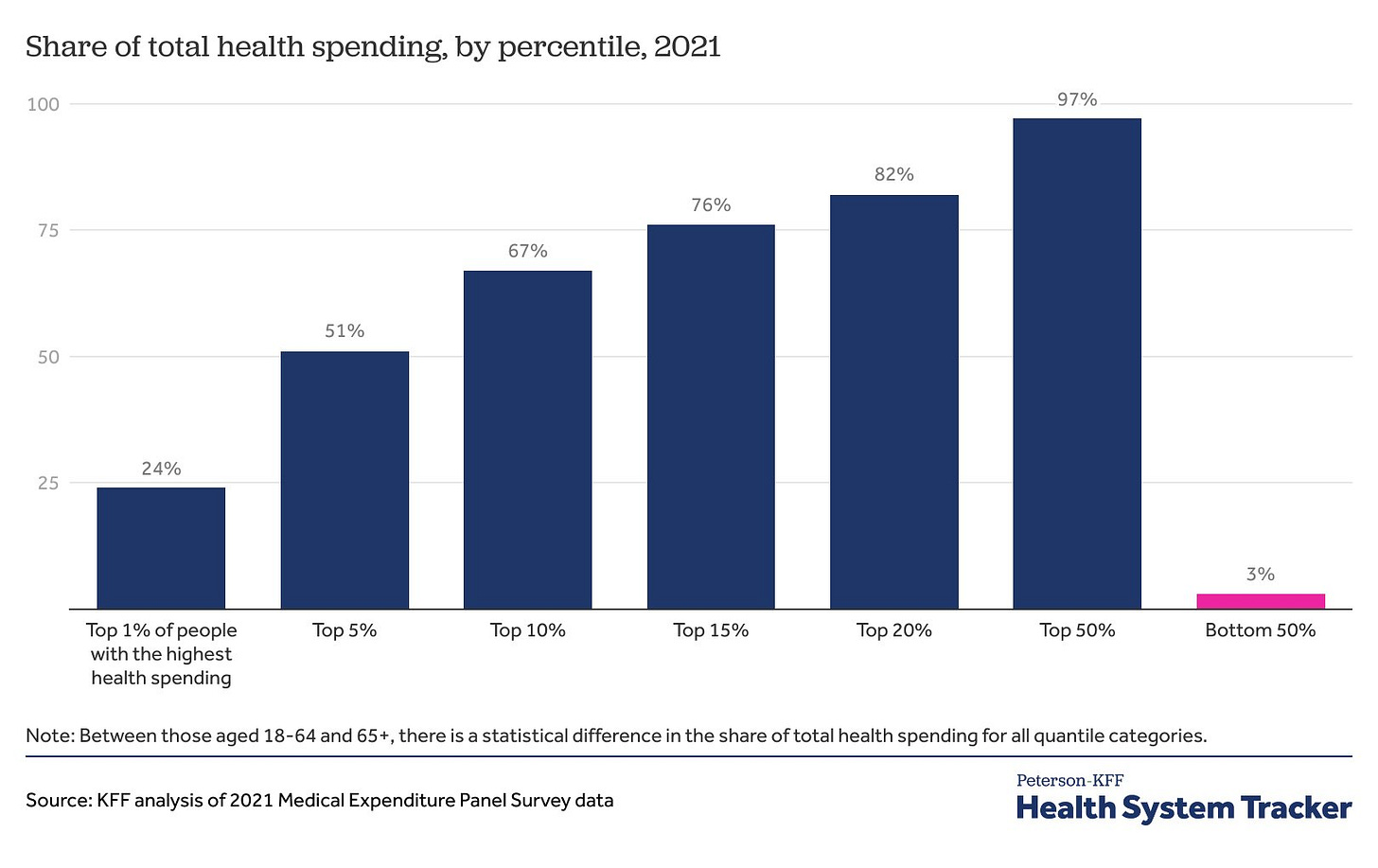
“5% of people are responsible for just over half.” This is analogous to saying 5% of the people buy 50% of the houses — yes, because most people don’t buy a house every year! This should not come as a surprise!
Cremieux: 1% of people are responsible for 24% of the health spending in America and 5% of people are responsible for just over half.
I had approximately zero medical expenses until I was seventeen. Burst appendix, nearly died. From age 0 to 20, 99% of my medical expenses occurred in 5% of the years. This is normal!
It is important to generalize this mode of thinking.
Sorting people by Y, and and saying the top X% in Y have most of the Y, is typically not so meaningful.
What you want is to say that you sort people by Z in advance, and then notice that the top X% in Z then later accumulate a lot of the Y (where Z can be ‘previous amount of Y’ or something else). Then you are more likely to be measuring something useful, and smaller imbalances mean a lot more.
If you must measure top X% in Y as having most of the Y, then you have to at least ensure you are doing this over a meaningful period, and put it in sensible context.
What’s the right way to think about this cartoon?
Sometimes, yes, you will see something the world’s top scientists and doctors missed.
Far more often, you will see something that the ‘consensus’ of those scientists and doctors missed. Yes, somewhere out there one of them already had the same idea, but this fact does not, on its own, help you.
Far more often than that, you will come up with something that was not successfully communicated to your particular average doctor, who also does not share your internal experiences or interest in your case. Or where ‘the system’ follows procedures that let you down, and it is very easy to see they are not doing what is in your best interest. That should be entirely unsurprising.
Also of course sometimes the system plays the odds from its perspective, and it turns out the odds were wrong, and you may or may not have had enough information to know this any more than the system did.
So we have personal stories like this one, or this one, or this one, where a doctor got it wrong. In particular, no, you should not trust that Average Doctor got the right answer and you couldn’t possibly figure out anything they didn’t. Doctors are often hurried and overworked, mostly don’t understand probability, have an impossible amount of knowledge to keep up with, and are trying to get through the day like everyone else.
In the broader case where you actually are defying a clear consensus, and doing so in general rather than for you specifically, you should of course be more skeptical that you’re right, but if you are reading this, it’s entirely plausible.
And as always, of course, don’t forget to ask Claude.
Case that the rise in consumption of psychiatric drugs is less a story about smartphones and social media and other cultural shifts, and more a story of reduced costs and improving convenience of access (especially with remote doctor visits) increasing the place supply intersects demand, along with campaigns that lessened the stigma, which also lowers price.
Certainly this is all a key contributing factor, the inconvenience and cost considerations matter, and people let them matter more than they should.
The first question to ask would be, given this, should we make these drugs easier or harder to get? Cheaper or more expensive?
Scott Alexander did the ‘more than you wanted to know’ treatment for H5N1. He predicts a 5% chance of a pandemic from it in the next year and 50% in the next twenty under otherwise normal circumstances, with ~6% chance it’s Spanish flu level or worse if and when it happens.
It is of concern, but it isn’t that different from the background level of concern from flu pandemics anyway. We really do have a lot of pandemics in general and flu pandemics in particular.
We should be preventing and preparing for them, we are not doing much of either, and this is mostly just another example of that. My guess is that the odds are worse than that, but that the fundamental takeaway is similar.
That matches how I have been thinking about this for a while. I’ve made a deliberate decision not to cover H5N1, and all the ways in which we are repeating the mistakes of Covid-19.
If we do get a full pandemic I will feel compelled to cover it, but until then I don’t think my observations would cause people reading this to make better decisions. I essentially despair of actually changing the policy decision that matter, for any amount of attention I might reasonably direct to the subject.
WHO has a public health emergency for Monkeypox yet refuses to authorize the vaccine that stopped the last outbreak despite it having approval from the FDA and other major medical agencies. WHO really is the worst.
The reason medical progress is so slow is largely the types of people who, when they hear a woman cured her own cancer and published the results to benefit others, heroically advancing the cause of humanity at risk to only herself, warn of the dire ethical problems with that.
Often those people call themselves ‘ethicists.’ No, seriously, that is a thing, and that situation somehow rose to the level of a writeup in Nature, which calls self-experimentation an ‘ethically fraught practice.’
This high quality application to the Delenda Est club has been noted.
I strongly agree with Tyler Cowen that we do not provide enough financial incentive to those who create new drugs. Robert Sterling here explains, as well. They deserve very large rewards when they find the next Ozempic.
The question is, should the world be doing this in the form of America paying super high prices while everyone else shirks?
As in, no, price controls are bad…
…because price controls everywhere else leaves it entirely on us to subsidize drug development. And we do it in a way that limits consumer surplus, since marginal costs are low. How do we address this?
One possibility is that patent buyouts seem better than indefinite high prices. The government can borrow cheaply and assume the variance, and marginal cost is low, so we can increase efficiency twice over, and also improve distributional effects, if we can negotiate a fair price. And it helps the pharma companies, since they realize their profits faster, and can plow it back into more investment.
The other half is that we are subsidizing everyone else. This is better than not doing it, but it would be nice to get others to also pay their fair share?
One obvious brainstorm is to do a price control, but as a maximum markup over the first-world average price. We will pay, say, five times the average price elsewhere. That way, the companies can negotiate harder for higher prices? Alas, I doubt a good enough multiplier would be palatable (among other issues), so I guess not.
On the research side, we win again. We can safely pay well above the net present value of cash flows from the monopoly, because the surplus from greater production is that much higher. Meanwhile, we reduce uncertainty, and Novo Nordisk gets the payout right away, so it can do far more R&D spending with the profits, and can justify more investment on the anticipation of similar future buyout deals. It’s win-win.
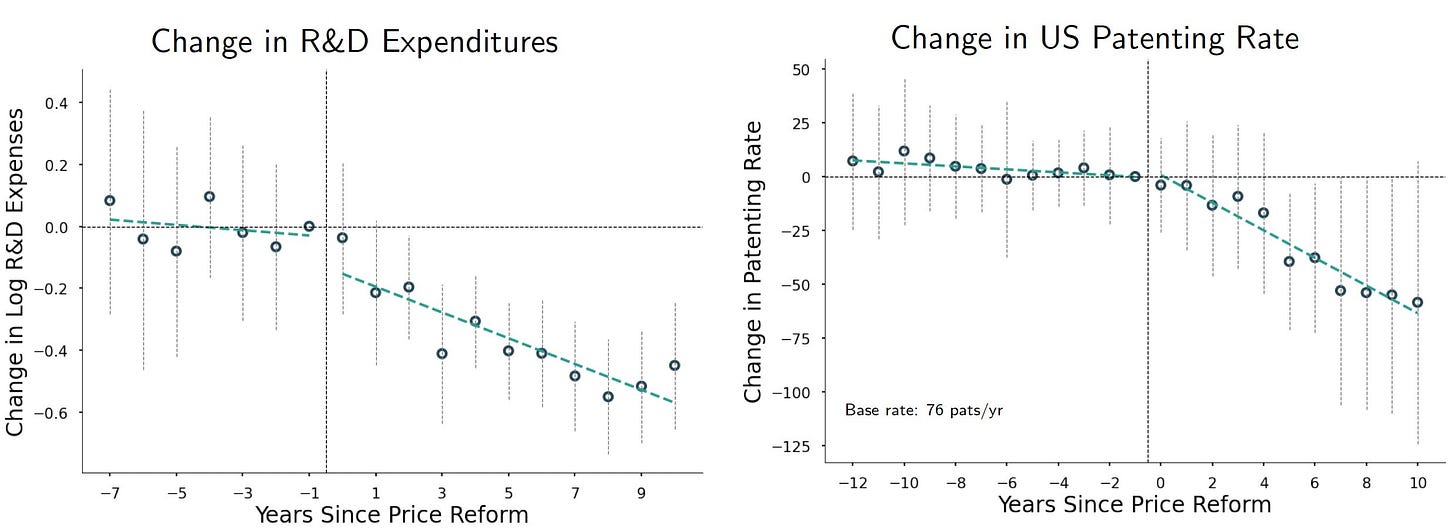
The supervillains? A very large decline in innovation for medical devices after Medicare and Medicaid price cuts.
We investigate the effects of substantial Medicare price reductions in the medical device industry, which amounted to a 61% decrease over 10 years for certain device types. Analyzing over 20 years of administrative and proprietary data, we find these price cuts led to a 25% decline in new product introductions and a 75% decrease in patent filings, indicating significant reductions in innovation activity.
Manufacturers decreased market entry and increased outsourcing to foreign producers, associated with higher rates of product defects. Our calculations suggest the value of lost innovation may fully offset the direct cost savings from the price cuts. We propose that better-targeted pricing reforms could mitigate these negative effects. These findings underscore the need to balance cost containment with incentives for innovation and quality in policy design.
Several commenters at MR pointed out that these areas of the DME industry are rife with fraud and abuse, and indeed Claude noted without direct prompting that is largely what motivated the price cuts. It is not obvious that we would have wanted all this lost ‘innovation,’ as opposed to it being set up to take advantage of the government writing the checks.
Here’s an Abundance Agenda for Addiction, with a focus on development of more drugs to help alongside GLP-1s, by fixing the many ways in which our system fights against attempts to make anti-addiction medications. Advance purchase and risk sharing agreements, extended exclusivity, expedited approval, and especially ability to actually run reasonable studies would help a lot, and straight up funding wouldn’t hurt either.
The insanity that is buying health insurance in California in particular. They cap how much you can pay as a percentage of income at 8.5%, but then you get to shop around for different insurances that have different benefits and sticker prices. So there’s a middle ground where all health insurance is equally outrageously expensive, and no amount of shopping around will ever save you a dollar. I’m expecting that turns out about as well as you would expect, on so many levels.
If we want to do progressive transfers of wealth we should do them directly, not via health insurance.