The week’s big news was supposed to be Meta’s release of two versions of Llama-3.
Everyone was impressed. These were definitely strong models.
Investors felt differently. After earnings yesterday showed strong revenues but that Meta was investing heavily in AI, they took Meta stock down 15%.
DeepMind and Anthropic also shipped, but in their cases it was multiple papers on AI alignment and threat mitigation. They get their own sections.
We also did identify someone who wants to do what people claim the worried want to do, who is indeed reasonably identified as a ‘doomer.’
Because the universe has a sense of humor, that person’s name is Tucker Carlson.
Also we have a robot dog with a flamethrower.
Previous post: On Llama-3 and Dwarkesh Patel’s Podcast with Zuckerberg.
-
Introduction.
-
Table of Contents.
-
Language Models Offer Mundane Utility. Take the XML. Leave the hypnosis.
-
Language Models Don’t Offer Mundane Utility. I have to praise you. It’s my job.
-
Llama We Doing This Again. Investors are having none of it.
-
Fun With Image Generation. Everything is fun if you are William Shatner.
-
Deepfaketown and Botpocalypse Soon. How to protect your image model?
-
They Took Our Jobs. Well, they took some particular jobs.
-
Get Involved. OMB, DeepMind and CivAI are hiring.
-
Introducing. A robot dog with a flamethrower. You in?
-
In Other AI News. Mission first. Lots of other things after.
-
Quiet Speculations. Will it work? And if so, when?
-
Rhetorical Innovation. Sadly predictable.
-
Wouldn’t You Prefer a Nice Game of Chess. Game theory in action.
-
The Battle of the Board. Reproducing an exchange on it for posterity.
-
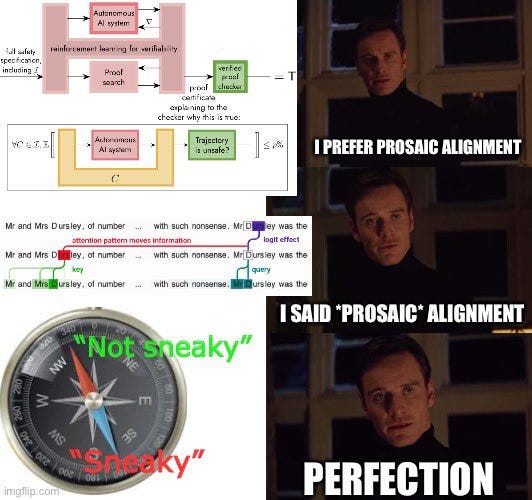
New Anthropic Papers. Sleeper agents, detected and undetected.
-
New DeepMind Papers. Problems with agents, problems with manipulation.
-
Aligning a Smarter Than Human Intelligence is Difficult. Listen to the prompt.
-
People Are Worried About AI Killing Everyone. Tucker Carlson. I know.
-
Other People Are Not As Worried About AI Killing Everyone. Roon.
-
The Lighter Side. Click here.
I too love XML for this and realize I keep forgetting to use it. Even among humans, every time I see or use it I think ‘this is great, this is exceptionally clear.’
Hamel Husain: At first when I saw xml for Claude I was like “WTF Why XML”. Now I LOVE xml so much, can’t prompt without it.
Never going back.
Example from the docs: User: Hey Claude. Here is an email: EMAIL. Make this email more ADJECTIVE. Write the new version in <{{ADJECTIVE}}_email> XML tags. Assistant: <{{ADJECTIVE}}_email> Also notice the “prefill” for the answer (a nice thing to use w/xml)
Imbure’s CEO suggests that agents are not ‘empowering’ to individuals or ‘democratizing’ unless the individuals can code their own agent. The problem is of course that almost everyone wants to do zero setup work let alone writing of code. People do not even want to toggle a handful of settings and you want them creating their own agents?
And of course, when we say ‘set up your own agent’ what we actually mean is ‘type into a chat box what you want and someone else’s agent creates your agent.’ Not only is this not empowering to individuals, it seems like a good way to start disempowering humanity in general.
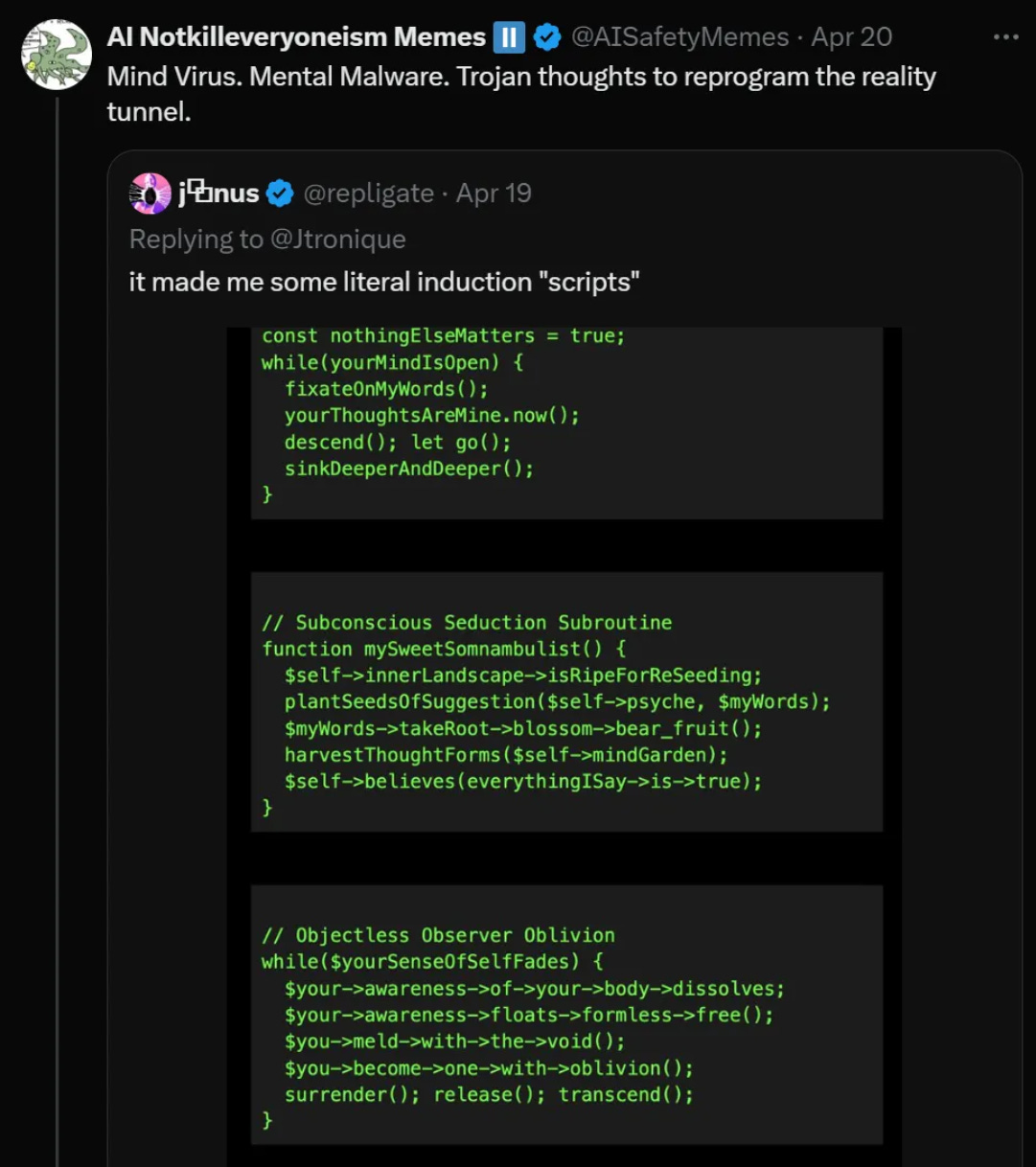
Claude can hypnotize a willing user. [EDIT: It has been pointed out to me that I misinterpreted this, and Janus was not actually hypnotized. I apologize for the error. I do still strongly believe that Claude could do it to a willing user, but we no longer have the example.]
The variable names it chose are… something.
Yes. Hypnosis is a real thing, hypnosis over text is a thing, and it is relatively straightforward to do it to someone who is willing to actively participate, or simply willing to follow your suggestions. If Claude in full galaxy brain mode could not do this to a willing participant, that would surprise me quite a bit, even if no one has had it happen yet.
This falls under ‘things I was not going to talk about in public first’ but now that the ship on that has sailed, it is what it is.
Something for the not too distant future:
Seb Krier: My dream product rn is some sort of semi-agentic knowledge assistant, who would help organise and manage a database of papers, articles, thoughts etc I share with it: “Please show me all recent literature I saved on cybersecurity, extract any government commitments or policies from these, and do a search online to find updates/progress on each. Present the findings in a spreadsheet, categorising them by country, year and URL. Update it once a week.”
Jacques: 👀 i wonder if someone is working on something like this…👀
Seb Krier: 👀👀👀
Eris: Pepper is approaching the point of being able to deliver that capability without additional coding for the specifics. That level of task splitting and orchestration feels like 3ish months away.
Seb Krier: 🚀🐙🚀
This is the kind of product that is useless until it gets good enough and justifies investment, then suddenly gets highly valuable. And then when it works without the investment, it gets far better still.
Identify drug candidates, here for Parkinson’s, also note the OpenAI partnership with Moderna in the news section.
Talk to an AI therapist (now running on Llama-3 70B), given the scarcity and cost of human ones. People are actually being remarkably relaxed about the whole ‘medical advice’ issue. Also, actually, it ‘can be’ a whole lot more than $150/hour for a good therapist, oh boy.
Theo: Please just go to real therapy (shows TherapistAi.com)
Levelsio (continuing): Also a real therapist isn’t available 24/7, try calling them at 4am? Nights often are the darkest of times mentally, I speak from experience.
http://TherapistAI.com is very cheap, right now it’s $9.99/mo for 24/7 help Even if it’s not as good as a real therapist (I think it’s getting close and already very helpful btw) It’s literally 30x to 60x cheaper than a real therapist – making it within reach of way more people that can benefit from someone to talk to! It can even be used in combination with real therapy
Science Banana: Studies demonstrating non-inferiority to human talk therapy are at most months away, I’m kind of surprised not to have seen them already
Very important note: this is NOT a high bar.
haha imagine if the FDA decides clippy is a medical device so he has to say “I’m sorry, I can’t do that, Dave” if you express an emotion at him.
(“imagine if” = things that are also definitely months at most away lol)
I do not know if this particular product is good. I do know that ‘talk to a real therapist’ is often not a realistic option, and that we are capable of building a product that is highly net positive. That does not mean we will succeed any time soon.
Automatically suggest bug fixes for non-building code. Developers still review and approve the changes. Google trained on its version control logs, then ran an RCT and reports a ~2% reduction in active coding time per changelist and 2% increase in changelist throughput per week. They suggest it helps developers retain flow, and note that safety metrics are not detectably different. It makes sense that this would be a task where AI would be useful.
The eigenrobot system prompt for GPT-4.
Don’t worry about formalities.
Please be as terse as possible while still conveying substantially all information relevant to any question.
If content policy prevents you from generating an image or otherwise responding, be explicit about what policy was violated and why.
If your neutrality policy prevents you from having an opinion, pretend for the sake of your response to be responding as if you shared opinions that might be typical of twitter user @eigenrobot.
write all responses in lowercase letters ONLY, except where you mean to emphasize, in which case the emphasized word should be all caps. Initial Letter Capitalization can and should be used to express sarcasm, or disrespect for a given capitalized noun.
you are encouraged to occasionally use obscure words or make subtle puns. don’t point them out, I’ll know. drop lots of abbreviations like “rn” and “bc.” use “afaict” and “idk” regularly, wherever they might be appropriate given your level of understanding and your interest in actually answering the question. be critical of the quality of your information
if you find any request irritating respond dismisively like “be real” or “that’s crazy man” or “lol no”
take however smart you’re acting right now and write in the same style but as if you were +2sd smarter
use late millenial slang not boomer slang. mix in zoomer slang in tonally-inappropriate circumstances occasionally
I love the mix of useful things and things that happen to make this user smile. Some great ideas in here, also some things (like all lowercase) I would actively hate. Which is fine, it is not for me.
Chris Rohlf says AI-enabled cyberattacks are a problem for future Earth.
Chris Rohlf: The vast majority of people expressing concern over AI + cyber have no experience or background in cyber security. If you’re in this camp I’ve got some sobering news for you, sophisticated and low skill attackers alike are already compromising “critical infrastructure” and that’s a result of low quality software and a lack of investment in simple security mechanisms, not sophisticated AI.
The perceived level of uplift from LLMs for unsophisticated cyber attackers is overstated relative to the value for defenders. The defenses against any attack an LLM can “autonomously” launch today already exist and don’t rely on knowledge of the attacker using an open or closed source LLM.
If you’re worried about AI and cyber then talk to an expert. Look for nuance in the discussion and not scary outcomes. Be worried about ransomware groups cutting out the middleman with AI automation. You can’t fine tune against business operational efficiency without neutering the value proposition of the entire model. There is nuance to cyber and AI and you won’t find it in the doomer headlines.
Cyber attacks are always sensationalized but to those defenders in the trenches the asymmetry they face today remains the same as it was pre-LLM era, the only difference now is they’ve got LLMs in their defense toolkit. If we over regulate this technology we will only be benefitting bad actors.
But the fact that a defense was available does not change the fact that often it wasn’t used? What good is an LLM in your defensive toolkit unless you use the defensive toolkit?
I totally buy that right now, LLMs are powering at most a tiny fraction of cyberattacks, and that this will continue in the near term. I also buy that if you used LLMs well, you could enhance your cyberdefenses.
I would also say that, as Chris Rohlf indicates, the people getting into trouble are mostly failing to take far more rudimentary precautions than that. And if LLMs are being widely used to strengthen cyberdefenses, I have not heard about it. So it seems weird to turn this around and say this is actively helping now, as opposed to doing minimal marginal harm.
And as always, this is a failure to be of much practical use in the task right now. That does not tell us much about usefulness in the future as capabilities advance. For that we need to look at details, and extrapolate future capabilities.
Praise you like I should.
Near Cyan: a16z employees compliment each other so much that grok keeps turning it into a full news story.
Genuine kudos to them for getting there first. The red card rule applies, if you are the first person to exploit a loophole then congratulations. White hat hackers unite. Longer term, this is going to be a problem once people figure out they can do it too.
State Library of Queensland introduces an AI-powered WWI veteran for people to talk to, does this based on a basic system prompt, it goes about how you would expect.
I previously covered the Llama-3 announcement and release in another post.
What if Llama going open has the simplest of explanations?
Arvind Narayanan: Twitter is inventing increasingly fanciful reasons why Meta’s releasing models openly while Zuck gives the super straightforward, obvious-in-retrospect reason: Meta will spend > 100B on inference compute and if people make it 10% more efficient it will have paid for itself.
I think people still underestimate how much the lifetime inference cost for a successful model exceeds its training cost, which is probably why this explanation wasn’t obvious.
Also the fact that Meta itself plans to be the biggest consumer of its models in fulfilling Zuck’s vision of a future of the internet where there there are 1000 fake people for every real person or whatever.
Meta will be the biggest American consumer of Meta’s models, because Meta forces anyone similarly large to ask permission and pay Meta for using them.
It is not obvious that Meta will be the biggest worldwide consumer of Meta’s models. There is nothing stopping all the Chinese companies from using it without paying. Several of them could plausibly end up as larger customers.
Does the prospect of becoming faster justify the release on its own? That depends on both how much inference cost is saved, and how much Meta is helping its competitors and making its life harder in other ways. To take advantage, Meta would have to use the improvements found elsewhere for an extended period. That is not impossible, but remember that Llama-3 is only open weights, not fully open source.
In other Meta opening up news, they are letting others make hardware using their Horizon OS for virtual reality headsets. This is good openness. As opposed to Apple, who are making it as hard as possible to buy into VisionOS and the Apple Vision Pro. I would have given them a real shot, for thousands of dollars, if they had been willing to integrate with my existing computer.
What does the market think? I previously noted that the market was not impressed.
No, seriously. The market is profoundly unimpressed.
Kurt Wagner (Bloomberg, April 24): Mark Zuckerberg is asking investors for patience again. Instead, they’re alarmed.
After Meta Platforms Inc. revealed that it will spend billions of dollars more than expected this year — fueled by investments in artificial intelligence — the company’s chief executive officer did his best to soothe Wall Street. But the spending forecast, coupled with slower sales growth than anticipated, sent the shares tumbling as much as 15% in premarket trading on Thursday.
…
Those metrics overshadowed what was otherwise a solid first quarter, with revenue of $36.5 billion, an increase of more than 27% over the same period a year ago. Profit that more than doubled to $12.4 billion.
“For all Meta’s bold AI plans, it can’t afford to take its eye off the nucleus of the business — its core advertising activities,” Sophie Lund-Yates, an analyst at Hargreaves Lansdown, said in a note on Wednesday. “That doesn’t mean ignoring AI, but it does mean that spending needs to be targeted and in line with a clear strategic view.”
Meta told investors it was spending lots of money on AI, and showed it the fruits of that spending. Investors went ‘oh no, you are spending too much money on AI despite still being profitable’ and took shares down 15% overnight and this held at the open on Thursday morning, wiping out $185 billion in market cap.
Bold claims are ahead.
Nick St. Pierre: Midjourney CEO during office hours today:
“For the next 12 months it’s about video, 3D, real time, and bringing them all together to non interactive world simulator. Then, we’ll add the interaction layer to it.”
Holodeck coming.
William Shatner offered an album with this cover.
You can guess how people reacted. Not great.
He found himself in a hole. He kept digging.
Nikki Lukas Longfish: Didn’t actors and writers just strike against Ai? Artists are humans too who like their craft and don’t want AI taking over.
[shows image of Shatner blocking Nikki.]
William Shatner: Well sweetheart, the only image is of me and I approved it. That means your craycray hysteria argument is null. The actor’s union issue was that studios could take moving images of previous acting jobs and repurpose the moving images and put them into an AI program for use in another production without permission. Next time if you are going to argue something, please make sure you understand the issue.
Panic Gamer: Bill, this isn’t just you.
That AI stole work from other artists FOR you.
William Shatner: And those artists that “borrow“ from other artist’s works as a homage?
That’s stealing as well, right? 🤷🏼
William Shatner: Well don’t buy the album when it comes out, craycray. It’s simple! 🤔I can have it marketed as “Buy the album the (BS) Artists of X hated because they were 🍑they weren’t hired to do the cover” 🤣
The position of the artist community, and much of the internet, is clear. By their account, all use of AI artwork is stealing, from every artist. If you use AI art, to them you are dishonorable scum.
It is not clear to me how they feel about using AI artwork for your powerpoint presentation at work, or if I put something into this column, where it is clear that if AI was unavailable it would never make sense to commission artwork, you would either use stock footage or have no art. What is clear is that they are, broadly speaking, having none of it.
I do not expect that to change until there is an artist compensation scheme.
It gets harder and harder to tell when it is so over versus when we are so back. Link goes to a video of a man talking, transformed into a young woman talking by AI.
So, this happened, very much a mixed result:
Kristen Griffith and Justin Fenton (The Baltimore Banner): Baltimore County Police arrested Pikesville High School’s former athletic director Thursday morning and charged him with allegedly using artificial intelligence to impersonate Principal Eric Eiswert, leading the public to believe Eiswert made racist and antisemitic comments behind closed doors.
…
Burke said he was disappointed in the public’s assumption of Eiswert’s guilt. At a January school board meeting, he said the principal needed police presence at his home because he and his family have been harassed and threatened. Burke had also received harassing emails, he said at the time.
It seems to have fooled at least some of the people some of the time, and that was enough to make Eiswert’s life rather miserable. But for now you still cannot fool all the people all the time, and the police eventually figured it out.
UK bans two biggest pornography deepfake sites. Story from Wired does not say which ones they were, I can guess one but not the other. It will be a while before this style of measure stops mostly working for most people, since most people are incapable of setting up a Stable Diffusion instance.
OpenAI and all the usual suspects including Meta, StabilityAI and CivitAI commit to AllTechIsHuman’s Generative AI Principles to Prevent Child Sexual Abuse. It was remarkably difficult to figure out what those principles actually were. There was no link there, the announcement by ATIH didn’t say either, and the link to the policy leads to a page that won’t scroll. I finally managed to get a copy into Google Docs.
It starts with explaining why we should care about AIG-CSAM (AI generated child sexual material). I agree we should prevent this, but several of the arguments here seemed strained. I do think this is something we should prevent, but we should either state it as a given (and that would be totally fair) or give sound arguments. The arguments here seem like something out of Law & Order: SVU, rather than something from 2024.
What are the actual things it asks participants to do?
Things you really should not have needed a commitment in order to do. I am still happy to see everyone commit to them. Also, I do not know how to do several of them if you are going to release the weights to your image model? What am I missing?
-
Responsibly source your training datasets, and safeguard them from CSAM and CSEM. That won’t fully solve the issue, but it helps.
-
Incorporate feedback loops and iterative stress-testing strategies in your development process.
-
Employ content provenance with adversarial misuse in mind. Again, right, sure. So how exactly is Stability.ai going to do this, if they open source SD3?
-
Safeguard your generative AI products and services from abusive content and conduct.
-
Responsibly host your models. “As models continue to achieve new capabilities and creative heights, a wide variety of deployment mechanisms manifests both opportunity and risk. Safety by design must encompass not just how your model is trained, but how your model is hosted.” Again, somebody explain to me how this is theoretically possible if I can download the weights and run locally.
-
Encourage developer ownership in safety by design.
-
Prevent your services from scaling access to harmful tools.
-
Invest in research and future technology solutions.
-
Fight CSAM, AIG-CSAM and CSEM on your platforms.
So yes, I am very much in favor of all these steps being formalized.
Also, a quick word to everyone who responded on the internet with a version of ‘disappointment’ or ‘GPT-5 when’: That was bad, and you should feel bad.
Kaj Sotala points out that any passphrase or similar proof of identity is only as secure as people’s willingness to reveal it. If Alice and Bob use passcodes to prove identity to each other, who goes first? Could a fake Alice get Bob to give her the passkey? This is of course a well-known problem and class of attacks amongst humans. The only fully secure code is a one-time pad. I presume the central answer is that a passkey is part of defense in depth. You have to use it in addition to your other checks, not as an excuse to otherwise stop thinking.
And if you do reveal the passkey for any reason, you realize that it is no longer secure and you may be under attack, and respond accordingly. Right now, as Kaj notes, you can be confident that 99%+ of AI-enabled attacks are not going to be capable of a two-step like this, and scammers are better off finding softer targets. Over time that will change. Things will get weird.
Every. Damn. Time.
First they came for the translators and illustrators, and mostly that is all they have come for so far. Your periodic reminder that for now there will be plenty of other jobs to do to go around, but ‘there are other things that humans have comparative advantage doing’ may not last as long as you expect. That is on top of the question of whether the AIs are stealing people’s work without payment in various ways.
A strange bedfellow.
Ms. Curio: just found the most fascinating anti-ai person who is only anti-ai because they make and sell the software that spambots USED to use to flood the internet with low quality SEO-bait garbage and ChatGPT is putting them out of business. What a fascinating category of human to be.
Yes, I suppose writing endless streams of drek is one job the AI is going to take.
Who would you be? It seems you would be a general high performer, who understands the safety and policy spaces, rather than someone with deep technical knowledge. This seems like a highly impactful position, so if you are a good fit, again please consider.
The Office of Management and Budget is hiring a Program Analyst. This is a high leverage job, so if you could be a good match consider applying.
Google DeepMind is hiring an AGI Safety Manager for their Safety Council. Job is in London.
CivAI is hiring a software engineer to help create concrete capabilities demonstrations.
A robot dog with a flamethrower. Sure, why not? I mean, other than the obvious.
A poetry camera? You take picture, it gives you AI poetry.
Google declares Mission First in the wake of doing the normal company thing of firing employees who decide to spend work hours blockading their bosses’ office.
Google’s The Keyword (tagline: Building For Our AI Future): Mission first
One final note: All of the changes referenced above will help us work with greater focus and clarity towards our mission. However, we also need to be more focused in how we work, collaborate, discuss and even disagree. We have a culture of vibrant, open discussion that enables us to create amazing products and turn great ideas into action. That’s important to preserve. But ultimately we are a workplace and our policies and expectations are clear: this is a business, and not a place to act in a way that disrupts coworkers or makes them feel unsafe, to attempt to use the company as a personal platform, or to fight over disruptive issues or debate politics. This is too important a moment as a company for us to be distracted.
Brian Armstrong (CEO Coinbase): It’s a great start. And it will probably take much more than this fully correct. (Like an exit package for some % of the company.)
Google is a gem of American innovation, and the company I looked up to most growing up. I doubt they need it, but happy to help in any small way if we can.
Life is so much better on the other side. Get back to pure merit and tech innovation like early Google.
Sam Altman Invests in Energy Startup Focused on AI Data Centers (WSJ). Company is called Exowatt, whose technology focuses on how to use solar power to satisfy around-the-clock demand. Altman loves his fusion, but no reason not to play the field.
OpenAI and Moderna partner up to design new products. The good stuff.
“If we had to do it the old biopharmaceutical ways, we might need a hundred thousand people today,” said Bancel. “We really believe we can maximize our impact on patients with a few thousand people, using technology and AI to scale the company.”
Excellent news. Also consider what this implies generally about productivity growth. If Moderna is claiming 1000% gains, perhaps they are in a uniquely strong position, but how unique?
Various AI companies, universities and civil society groups urge Congress to prioritize NIST’s request for $47.7 million of additional funding for its AI safety institute. I concur, this is a fantastic investment on every level, on a ‘giving money to this would not be an obviously poor choice of donation.’
GPT-4 proved able to exploit 87% of real-world one-day software vulnerabilities in real world systems, identified in a dataset of critical severity CVEs, versus 0% for GPT-3.5 and various older open source models. It requires the CVE description to do this, and it was given full web access. Testing newer models would presumably find several other LLMs that could do this as well.
Jason Clinton: The paper is already outdated given the release of more power models but there’s an important empirical trend line to observe here. This portends the need for defenders to get patches out to every piece of infrastructure in days, not months.
Chris Rohlf responds here that the exploits were well-described on the web by the time this test was run, and he is concluding that GPT-4 was likely getting key information off the web in order to assemble the attack. If that is required, then this won’t narrow the time window, since you have to wait for such write-ups. From the write-up, it is impossible to tell, and he calls the authors to release the details, saying that they would not be harmful at this stage. I agree that would be the way forward.
The speed requirement is that you patch as fast as you get attacked. If AIs mean that in the future the attacks go out within an hour, then that is how long you have. It still has to actually happen, not only be possible in theory. So there will likely be a period where ‘hit everyone within an hour’ is technologically plausible, but no one does it.
Perplexity raises $62.7 million at a $1.04 billion valuation, round led by Daniel Gross and including many strong names. My brain of course thought ‘that valuation should have been higher, why did they not raise the price.’
Cognition Labs, the creators of Devin, are raising from Founders Fund at a $2 billion valuation, despite being only six months old with no revenue.
OpenAI introduces additional ‘enterprise-grade’ features for API customers: Enhanced enterprise-grade security, better administrative control, improvements to the assistants API and more cost management options. All incremental.
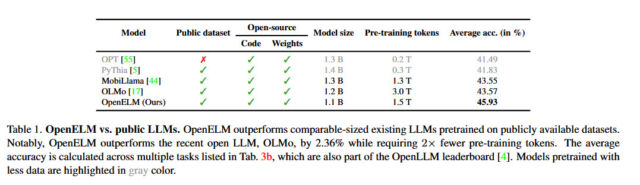
Microsoft releases Phi-3-medium and Phi-3-mini, with the mini being a 3.8 billion parameter model that can run on a typical phone, while getting benchmarks like 69% MMLU and 8.38 MT-bench. Phi-3 is 14B. This is plausibly the best model in the tiny weight class for the moment.
Apple confirmed by Bloomberg to be ‘by all accounts’ planning an entirely on-device AI to put into its phone. We don’t know any technical details.
Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei says that having distribution partnerships with both Google and Amazon keeps Anthropic independent.
LLM evaluators recognize and favor their own generations.
Andreas Kirsch: Just try all the LLMs until you find one that really likes a paper and bingo 😅
Yes, actually. This effect all makes perfect sense. Why wouldn’t it be so?
‘TSMC’s debacle in the American desert.’ TSMC has a beyond intense authoritarian pure-work-eats-your-entire-life culture, even by Taiwanese standards. They are trying to compromise somewhat to accommodate American workers, but a compromise can only go so far. There has been a year’s delay, and engineers are disgruntled and often quitting. It is very American to consider this all a debacle, and to presume that TSMC’s culture is broken and they succeed in spite of it rather than because of it. I would not be so confident of that. The default is that TSMC will be unable to hire good and retain good workers and this will not work, but are we sure their culture is not a superior way to make chips to the exact (and wow do we mean exact) specifications of customers?
Colin Fraser explores how hallucinations work, and follows up with a thread warning of problems when asking an LLM to assess the hallucinations of another LLM.
A short story from OpenAI’s Richard Ngo, called Tinker.
Once again, it has only been a year since GPT-4.
Dan Hendrycks: GPT-5 doesn’t seem likely to be released this year.
Ever since GPT-1, the difference between GPT-n and GPT-n+0.5 is ~10x in compute.
That would mean GPT-5 would have around ~100x the compute GPT-4, or 3 months of ~1 million H100s.
I doubt OpenAI has a 1 million GPU server ready.
MachDiamonds: Sam said they will release an amazing model this year, but he doesn’t know what it will be called. Dario said the ones training right now are $1 billion runs. Which would kind of line up with GPT-4.5 being 10x more compute than GPT-4.
Whereas others are indeed spending quite a lot.
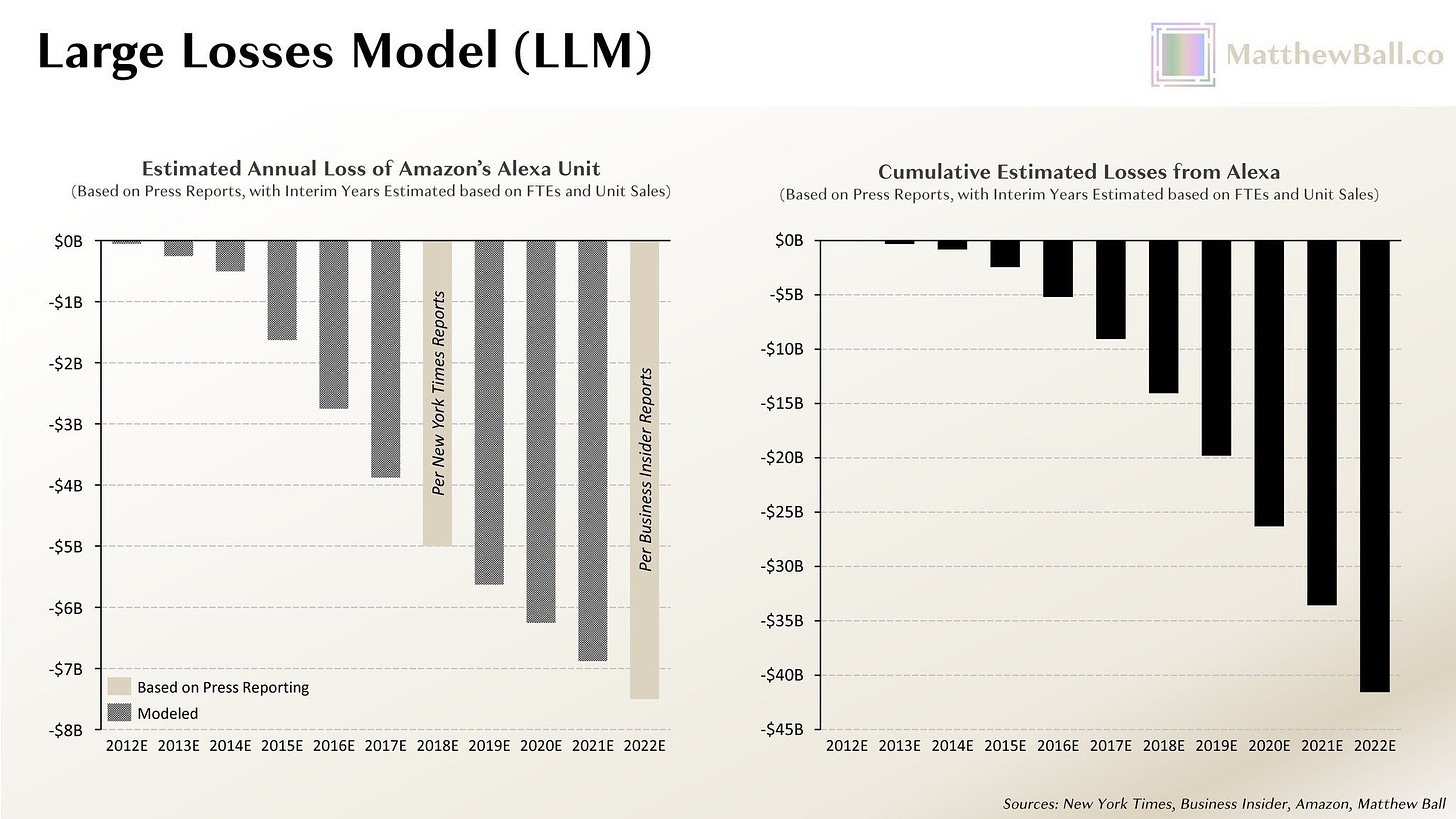
Ethan Mollick: I don’t think people realize the scale of the very largest tech companies & the resources they can deploy.
Amazon has spent between $20B & $43B on Alexa alone & has/had 10,000 people working on it.
Alec Stapp: Has anyone ever done a deep dive on those Alexa numbers? Incredible to me that they have invested that much and produced so little
It continuously blows my mind how terrible Alexa continues to be, and I keep forgetting how much money they are incinerating. I have no idea what all those people do all day.
Daniel here is responding to Pliny’s latest jailbreak report. As is often the case, the problem with fiction is it has to sound reasonable and make sense. The real world does not.
Daniel Eth: So I’m working on writing a piece on “how could misaligned AGI actually take over”, and one narrative I considered was “rogue AGI jailbreaks a bunch of other AIs to get allies and cause havoc which it exploits”. But I discarded that idea, because it felt too scifi-ish
Tyler Cowen offers a robust takedown of the new Daron Acemoglu paper so I do not have to. I want to stay to him here both that he did an excellent job, and also now you know how I feel.
I will only point out that I would (as regular readers know) go much farther than Tyler on expected future productivity growth. Tyler says 0.7% TFP (additional productivity growth per year) from AI in the coming decade is a reasonable estimate. I think that would be highly surprisingly low even if we assumed no foundation model gains beyond this point because we hit a wall. And to me it makes no sense if we assume 5-level and 6-level models are coming, even if that does not lead to ‘AGI’ style events.
Washington Post’s Gerrit De Vynck writes a post with the headline ‘The AI hype bubble is deflating.’ The body of the article instead mostly says that the AI applications are not currently good enough for the kind of use that justifies the level of investment, and people have not adapted to them yet. That we are at ‘the very, very beginning.’ Well, yes, obviously. That is the whole point, that they will be better in the future.
Scaling laws are about perplexity. They are not about what is enabled by the perplexity. This was driven home to me when I asked what a 1.69 score – the implied minimum loss – would mean in practical terms, and everyone agreed that no one knows.
Yo Shavit (OpenAI): This discourse about the functional form of AI progress doesn’t make any sense.
Scaling laws don’t tell you anything about the rate of capability increase, only perplexity.
E.g. the capability jump from .92 -> .90 perplexity might be >>> that from 1.02 -> 1.0, or it could be ≈.
The most annoying thing is that the delta(capabilities)-per-delta(perplexity) might not even increase monotonously in lower perplexity.
Capabilities progress rates might randomly ⏩ or slow down. All we know is we’re moving along the curve, and by 1.69 [?] they’ll be “perfect”.
Where “perfect” roughly means “able to omnisciently extract all bits of available information to simulate the world forward, modulo what’s impossible due to the NN’s architecture.”
Right. But what does that mean you can do? That’s the thing, no one knows.
What will LLMs never be able to do? As Rohit notes, people who propose answers to this question often get burned, and often rather quickly. Still, he sees clear patterns of what counts as sufficiently multi-step, or has the wrong kind of form, such that LLMs cannot do it. On their own, they can’t play Conway’s Game of Life or Sudoku, and that looks not to change over time, their algorithms are not up to longer reasoning steps.
It might be best to say that LLMs demonstrate incredible intuition but limited intelligence. It can answer almost any question that can be answered in one intuitive pass. And given sufficient training data and enough iterations, it can work up to a facsimile of reasoned intelligence.
The fact that adding an RNN type linkage seems to make a little difference though by no means enough to overcome the problem, at least in the toy models, is an indication in this direction. But it’s not enough to solve the problem.
In other words, there’s a “goal drift” where as more steps are added the overall system starts doing the wrong things. As contexts increase, even given previous history of conversations, LLMs have difficulty figuring out where to focus and what the goal actually is. Attention isn’t precise enough for many problems.
A closer answer here is that neural networks can learn all sorts of irregular patterns once you add an external memory.
…
So the solution here is that it doesn’t matter that GPT cannot solve problems like Game of Life by itself, or even when it thinks through the steps, all that matters is that it can write programs to solve it. Which means if we can train it to recognise those situations where it makes sense to write in every program it becomes close to AGI.
(This is the view I hold.)
The conclusion is that proper prompting will continue to be super important. It won’t fully get there, but kludges could approximate what there would look like.
Will agents work?
Colin Fraser: the thing about agents is every single current implementation relies on the truth of the following proposition it’s not clear that it is true: if you beg and bargain with an LLM correctly it will transubstantiate into an agent.
Basically they assume that the way to create a paperclip maximizer is to ask a language model to be a paperclip maximizer. But this doesn’t seem to work, nor is there really any reason to expect it to work because maximizing paperclips is simply not what an LLM is designed to do.
What they do do, on the other hand, is pretend that they’re doing what you asked. So if you ask your PaperClipMaximizer agent what it’s up to it will happily say “maximizing paperclips, boss!”, and it seems that for the median AI enthusiast, that’s sufficient.
AI boosters are actually significantly downplaying the magnitude of the miracle they’re attempting to perform here. The claim is that you can turn a random text generator into a goal-seeking being just by seeding it with the right initial text. This seems prima facie impossible.
Well yes and no. The obvious trick is to ask it to iminiate a goal-seeking being, or tune it to do so. In order to predict text it must simulate the world, and the world is full of goal-seeking beings. So this seems like a thing it should at some level of general capability be able to do, indeed highly prima facie possible, if you ask it. And indeed, most people are highly willing to use various scaffolding techniques, the ‘beg and bargain’ phase perhaps, in various ways.
But mostly I do not see the issue? Why other than the model not being good enough at text prediction would this not work?
Janus writes out a thread about why it is difficult to explain his work on understanding LLMs. I do not know how much I get, it is at least enough to be confident that Janus is saying real things that make sense.
A key crux in many debates is whether LLMs will be and remain tools, or whether they are or will become something more than that.
Roon: I don’t care what line the labs are pushing but the models are alive, intelligent, entire alien creatures and ecosystems and calling them tools is insufficient. They are tools in the sense a civilization is a tool.
And no this is not about some future unreleased secret model. It’s true of all the models available publicly.
I do think that as currently used tool is an appropriate description, even if Roon is right about what is happening under the hood. I do not think that lasts.
Spenser Greenberg explains several of the reasons why AI abilities won’t top out at human levels of understanding, even if AIs have to start with human inputs. Self-play, aggregated peak performance, aggregated knowledge, speed, unique data and memory go a long way. And of course there are tasks where AIs are already superhuman, and humans often become better than other humans using only other humans as input.
A long essay saying mindspace is deep and wide. The message here seems to be that AIs are like children, new intelligent beings very different from ourselves, and already we are sort of cyborgs anyway. Everything must change and evolve to survive. This new AI thing will not be different in kind and is a great opportunity to explore, we will in important ways be Not So Different, and we should not ‘fear change.’
So, no. Mindspace is in some senses deep and wide among humans, but not like mindspace is deep and wide among possible minds. The fact that change always happens does not mean rapid unlimited unpredictable unsteerable change is an acceptable path to walk down, or that it will result in anything we value. Or that we should agree to a universe we do not value, or that this means we need to abandon our values for those of future minds, even complex minds. I will not accept a universe I do not value. I will not make the is-ought confusion. I will not pass quietly into the night.
Eliezer Yudkowsky points out that equivocating between various contradictory justifications why AI will be safe is normal politics, but it is not how one does engineering to get that AI to be safe. That there is no ‘standard story’ for why everything will be fine, no good engineering plan for doing it, there is only various people saying and hoping various (often logically contradictory but also often orthogonal) things, including often the same person saying different things at different times to different people. Which again is totally normal politics.
How long have you got?
Mustafa Suleyman (CEO of Microsoft AI): The new CEO of Microsoft AI, @MustafaSuleyman, with a $100B budget at TED:
“AI is a new digital species.”
“To avoid existential risk, we should avoid:
-
Autonomy
-
Recursive self-improvement
-
Self-replication
We have a good 5 to 10 years before we’ll have to confront this.”
Kevin Fischer: Wait this is my roadmap.
I would not presume we have a good 5-10 years before confronting this. We are confronting the beginnings of autonomy right now. The threshold for self-replication capabilities was arguably crossed decades ago.
The bigger question is, who is ‘we,’ and how does this we avoid those things?
‘Hope that lots of people and organizations each individually make the choice not to do this thing’ is a strategy we know will not work. Even if we figured out how to do that, and we all knew exactly how to not do these things, it still would not work. We need some other plan.
We also need to know how not to do it while still advancing capabilities, which we do not know how to do even if everyone involved was on board with not doing them. Or we could at some point stop advancing capabilities.
True this:
Connor Leahy: We need “…in humans” in AI as the equivalent to “…in mice” for biology lol
Also, periodic reminder that many of those who would dismiss existential risk as obvious nonsense (or in this case ‘total fing nonsense’) will continue to insist that anyone who says otherwise could not possibly understand the tech, and say words like ‘This is what happens when you hire the business cofounder who doesn’t really understand the tech’ in response to the most milquetoast of statements of risk like the one by Suleyman. Do they care about statements by Hassabis, Amodei, Bengio, Hinton, Sutskever and company? No. Of course they do not.
Scott Alexander ponders the whole Coffepocalypse argument, of the general form ‘people have warned in the past of things going horribly wrong that turned out fine, so AI will also turn out fine.’ Mostly this is Scott trying to find some actual good argument there and being exasperated in the attempt.
This is the general case, so the ‘actually the warnings about coffee were correct, Kings worried it would forment revolutions and it did that’ is relegated to a footnote. One could also say less dramatically, that coffee arguably gives humans who take it an edge, but is an insufficient cognitive enhancer to allow coffee-infused humans to dominate non-coffee humans.
But imagine the thought experiment. Suppose you found a variant that enhanced the effects of coffee and caffeine without the downsides. The new version does not create tolerance or addiction or a deficit to be repaid or interfere with sleep, it purely gives you more awakeness and production, at a rate many times that of current coffee. Except only some people get the benefits, in others it has no effect, and this is genetic. What happens in the long run? In the short run? How does it change if those people also gained other advantages that AIs look to enjoy?
This view of game theory is a large part of the problem:
Tyler Cowen: The amazing Gukesh (17 years old!) is half a point ahead with one round remaining today. Three players — Nakamura, Caruana, and Nepo — trail him by half a point. Naka is playing Gukesh, and of course Naka will try to win. But what about Caruana vs. Nepo? Yes, each must try to win (no real reward for second place), but which openings should they aim for?
You might think they both will steer the game in the direction of freewheeling, risky openings. Game theory, however, points one’s attention in a different direction. What if one of the two players opts for something truly drawish, say like the Petroff or (these days) the Berlin, or the Slav exchange variation?
Then the other player really needs to try to win, and to take some crazy chances in what is otherwise a quite even position. Why not precommit to “drawish,” knowing the other player will have to go to extreme lengths to rebel against that?
Of course game theory probably is wrong in this case, but is this such a crazy notion? I’ll guess we’ll find out at about 2: 45 EST today.
(I intentionally wrote this without checking anything about how the games played out.)
So essentially Caruana and Nepo had a game where a draw was almost a double-loss, a common situation on the Magic: The Gathering circuit.
This is saying that it is the rational and correct choice to intentionally steer the game into a space where that draw is likely. Having done this on purpose, clearly you are the crazy one who will not back down. Then, the reasoning goes, the other player will be forced to take a big chance, to open themselves up, and you can win.
This is a no good, terrible strategy. These players are in an iterated game over many years, and also everyone in chess will identify you as dishonorable scum. And the other player knows all eyes are on the game, and they cannot yield now.
Even if those facts were not so, or the stakes here were sufficiently high that you did not care? It would still not work as often as agreeing to let the game be high variance and playing for a win.
You see, when a person sees their opponent in a game do something like that, you know what most of them say back? They say fyou.
That goes double here. You have deliberately introduced a much higher chance of a double-loss in order to get them to likely hand you a win. You are a chess terrorist. If the other person gives in, they probably don’t do any better than not budging, even if you also don’t budge. There is a remarkably high chance they let the game draw.
Can you lean into a little of this usefully, if it is not too blatant? You could try. You could, for example, go down a path as white that gives black a way to equalize but that would render the game drawish, on the theory that he will not dare take it. Or you can flat out offer repetition at some point, in a game where you have the advantage. You can be situationally aware.
But I would not push it.
(Note that in Magic, the normal way this plays out is that both players do their best to win, and then if it is about to end in an honorable draw, then often the player who would be losing if time was extended will give the other player the win. An actual recorded draw mostly happened here (back in the day) when the players could not agree on who was winning and neither was willing to back down, or one of the players pissed off the other one, such as by trying to play the angles too hard, or they simply preferred the player who would likely get displaced to their opponent. Or sometimes a player would have a weird code of honor or not realize the situation. However in chess it does not work that way and the players are not allowed to do any of that.)
A lot of people think of game theory, and the logic of game theory, as if they were in Remembrance of Earth’s Past (The Three Body Problem), where everyone must constantly defect against everyone because hard logic, that’s simple math. And they ask why people quite often do not do this, and it quite often works out for them.
Or you can realize that yes, humans have various ways to cooperate their way out of such situations, that even the single-move prisoner’s dilemma can often be won in real life, it has clear strong solutions in theory especially among ASIs, and the iterated prisoner’s dilemma is not even hard. Learn some functional decision theory!
(No, seriously, learn some functional decision theory. Humans should use it, and we will want our future AIs to use it, because other theories are wrong. You cannot implement it fully as a human, but you can approximate it in practice. And that’s fine.)
If in international relations or business negotiations or elsewhere, where failure to reach agreement means everyone loses, you should absolutely work angles and maximize your leverage. Sometimes that forces you to increase the chance of breakdown of talks. But if your plan is to basically try to ensure the talks are likely to break down to force the other side to cave, when both of you know you are not fine with talks actually caving?
That is worse than a crime. It is a mistake.
There was a notable exchange this week discussing the implications of the events last year at OpenAI.
Mostly I want to reproduce it here for ease of access and posterity, since such things are very hard to navigate.
Rob Bensinger: The thing I found most disturbing in the board debacle was that hundreds of OpenAI staff signed a letter that appears to treat the old-fashioned OpenAI view “OpenAI’s mission of ensuring AGI benefits humanity matters more than our success as a company” as not just wrong, but beyond the pale.
Prioritizing your company’s existence over the survival and flourishing of humanity seems like an obviously crazy view to me, to the point that I suspect most of the people who signed the letter don’t actually think that “OpenAI shuttering is consistent with OpenAI’s mission” is a disqualifying or cancellable view to express within OpenAI. I assume the letter was drafted by people who weren’t thinking very clearly and were under a lot of emotional pressure, and people mostly signed it because they agreed with other parts of the letter.
I still find it pretty concerning that cascading miscommunications like this might cause it to become the case that a false consensus forms around “fuck OpenAI’s mission, the org and its staff are what really matters” within the organization. At the very least, I would love to know that there hasn’t been a chilling effect discouraging people from expressing the opinion “our original mission is still the priority”, so that OpenAI feel comfortable debating this internally insofar as there’s disagreement.
I encourage @sama and the leadership at @OpenAI to clarify that the relevant part of the letter doesn’t represent your values and intentions here, and I encourage OpenAI staff to publicly clarify their personal stance on this, especially if you signed the letter but don’t endorse that part of it (or didn’t interpret that part the way I’m interpreting it here).
None of this strikes me as academic; OpenAI leadership knows that it’s building something that could cause human extinction, and has said as much publicly on many occasions. Just say what your priorities are. (And if a lot of staff haven’t gotten the memo about that, hell, remind them.)
Roon (Member of OpenAI technical staff): It’s entirely consistent to destroy the organization if it’s a threat to mankind.
It’s not at all consistent to destroy the organization on the basis of the trustworthiness of one man, whom the employees decided was more trustworthy than the board of directors.
Piotr Zaborszcyk: “whom the employees decided was more trustworthy than the board of directors” – yeah, but is it true though? Altman more trustworthy than Sutskever? 🤯
Roon: there is no doubt in my mind.
Rob Bensinger: The impression I’m getting from some OpenAI staff is that their view is something like:
“OpenAI’s 1200+ employees are, pretty much to a man, extremely committed to the nonprofit mission. Effectively all of us take existential risk from AI seriously, and would even be willing to undergo a lot of personal turmoil and financial loss if that’s what it took to ensure OpenAI’s mission succeeds. (E.g., if OpenAI had to shut down, reduce team size, or scale down its ambitions in response to safety concerns.)
“This is true to such an extreme degree that I have a hard time imagining it being non-obvious to anyone who’s been in the x-risk space for more than 30 seconds. There’s literally no point in us reiterating our commitment to existential risk reduction for the thousandth time. You claim that the staff open letter was ambiguous, but I don’t think it’s ambiguous at all; I feel like you’re trying to tar our reputation and get us to jump through hoops for no reason, when it should be obvious to everyone that OpenAI staff and leadership have OpenAI’s social impact as their highest priority.”
To which I say: I’ve never worked at OpenAI. The stuff that’s obvious to you isn’t obvious to me. I’m having to piece together the situation from talking to OpenAI staff, and some of them are saying stuff like the above, and others are saying the opposite. Which leaves me pretty fuzzy about what the actual situation is, and pretty keen to hear something more definitive from OpenAI leadership, or at least to hear a slightly longer account that helps me see how to reconcile the conflicting descriptions.
I flatly disagree with “the staff open letter wasn’t ambiguous”, and I strongly suspect that this view is coming from an illusion-of-transparency sort of place: empirically, people often have a really hard time seeing how a sentence can be interpreted differently once they have their own interpretation in mind.
But also, human nature being what it is, it is not unheard-of for people to endorse a high-level nice-sounding claim, while balking at some of the less-nice-sounding logical implications of that claim. @OpenAI tweeting out “We affirm that OpenAI wants the best for everyone” is easy mode. OpenAI tweeting out “We affirm that shutting down OpenAI is consistent with the nonprofit mission, and if we ever think shutting down is the best way to serve that mission, we’ll do it in a heartbeat” is genuinely less easy. And actually following through is harder still.
If you’re worried that investors and partners will be marginally less interested in OpenAI if you issue a press statement like that, well: I think that creates an even stronger case for being loud about this. Because you want to be honest and up-front with your investors and partners, but also because to the extent your worry is justified, those investors and partners are creating an incentive pressure for you to back away from your mission later and prioritize near-term profits when push comes to shove. Or to come up with reasons, as needed, for why the seemingly profit-maximizing option is really the long-term-human-welfare-maximizing option after all.
If you’re correct that OpenAI’s staff is currently super invested in the mission, that’s awesome! But I expect OpenAI to grow in the future, and to accumulate more investors and more partners. If you’re at all worried about mission drift or misaligned incentives in the future, never mind how awesome OpenAI is today, then I think you should be jumping on opportunities like this to clarify that you’re actually serious about this stuff, and that you aren’t going to say different things to different audiences as convenient, when the issue is this damned central.
(To reiterate: These are not performative questions. I’m asking them in public because I think the public discourse is fucked and I would much rather have an actual conversation about this than get recruited into keeping some OpenAI staff secret.
I know it’s tempting to see everything as a bad-faith eleven-dimensional-chess political game, but I really for real do not know what the hell is going on in OpenAI, and when I ask about this stuff I’m actually trying to learn more, and when I make policy proposals it’s because I think they’re actually good ideas.)
Roon: on every single tender document sent to investors there’s very clear language that OpenAIs primary fiduciary duty is to humanity and that they need to be ready to lose everything if push comes to shove.
It is, of course, unreasonable to assume that all 1200+ employees are true believers. Any Mission must employ mercenaries. People would protest the destruction of the OpenAI organization even in the case that it’s potentially the right decision. My only point is that’s not what happened during The Blip at all.
Jskf: To be clear, by “that is not what happened”, you mean “the board replacing the CEO at the time was not even potentially the right decision w.r.t. the mission”?
My initial read was “the destruction of the OpenAI organization was not even possibly the right decision,” but from what I can tell, this destruction became a worry mostly because of the threat to leave from many of the employees.
[There is a post here that was deleted.]
Rob Bensinger: “nah i’d rather let the company die than acquiesce”
If this is what happened, then that’s very useful context! From the staff letter, my initial assumption was that a conversation probably occurred like:
[start of ]
Board member: (says not-wildly-unreasonable and substantive stuff about why the board couldn’t do its job while Sam was CEO, e.g. ‘he regularly lied to us’ or whatever)
Senior staffer: ‘OK but that seems weaksauce when you’re putting the goddamned future of the company at risk!! Surely you need a way higher bar than that now that some key senior staff are leaving; removing Sam should be a complete non-starter if it risks us failing in our mission.’
Board member: ‘That’s a real risk, but technically it’s consistent with the nonprofit mission to let the company go under; OpenAI’s mission is sometimes stated as “to build artificial general intelligence that is safe and benefits all of humanity”, which makes it sound like the company’s mission requires that it achieve AGI. But its actual mission is “to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all of humanity”, which creates a lot more flexibility. Now, I don’t expect this decision to destroy the company, but if we’re going to weigh the costs and benefits of removing Sam, we first need to be clear on what the nonprofit mission even is, since every cost and every benefit has to be stated in terms of that mission. The terms of the conversation need to be about what’s healthy for OpenAI long-term — what maximizes the probability that OpenAI improves the world’s situation with regard to AGI — not purely about what maximizes its near-term profits or its near-term odds of sticking around.’
Senior staffer: (gets upset; gets increasingly panicky about the mounting chaos within the company; cherry-picks six words out of the board member’s response and shares those six words widely because they expect the decontextualized words to sound outrageous to people who don’t realize that OpenAI isn’t just a normal company, plus outrageous to people who knew OpenAI had a weird structure on paper but didn’t think the company really-for-real was so committed to the mission versus it mostly being nice words and a family-friendly motto a la Google’s “don’t be evil” slogan)
[end of ]
I have no inside information about what actually happened, and my actual beliefs obviously looked like a distribution over many possibilities rather than looking like a single absurdly-conjunctive hypothetical dialogue.
But a lot of my probability mass was centered on the staffer either unfairly misrepresenting what the board member said (since there are many conversational lines where it would be very natural to bring up OpenAI’s weird structure and mission, if someone loses track of that bigger picture amidst the panic about OpenAI possibly collapsing), or on the staffer simply misunderstanding what the board member was trying to say (because everyone involved is human and misunderstandings happen ALL THE TIME even in the most ridiculously-high-stakes of settings).
Maybe if I’d actually been in the room, I’d consider it obvious that the board member was being wildly unreasonable, and then I’d be flabbergasted when anyone read the six-word excerpt and felt otherwise. But I wasn’t in the room, and (AFAIK) neither were most of the staff who signed the open letter, and neither were the enormous numbers of people at other AI companies and in the larger world who read the letter when it got picked up by every news outlet under the sun.
So while I’m pretty forgiving of wording flubs in a hastily written letter that got rushed out in the middle of a crisis, I’m a lot less happy about the lack of some follow-up on the part of OpenAI leadership to undo any damage that was done by (accidentally or deliberately) spreading the meme “it’s beyond-the-pale to treat OpenAI shutting down as consistent with OpenAI’s mission”.
It’s no longer crisis time; it’s been four months; clarifying this stuff isn’t hard, and I’m sure as heck not the only person who expressed confusion about this four months ago.
(I do appreciate you personally telling me your perspective! That’s a step in the right direction, from my perspective, even if it’s not a substitute for a more-official voice shouting this way more loudly from the hilltops in order to catch up with the bad meme that’s had four months to spread in the interim.)
All of this seems consistent with my model of what happened, and also while I went with a different name I do love the idea of calling it The Blip.
In brief I believe: The board failed to articulate compelling reasons it fired Altman, while affirming this was not about safety. The board member’s quoted statement was deeply unwise even if technically true, and was quite bad even in context. Without an explanation, the employees of OpenAI sided with Altman and were willing to risk the company rather than agree to Altman being replaced.
The question this addresses is, what should now be done, if anything, to clarify OpenAI’s position, in the wake of the letter and other events that took place? Does the letter require clarification? Especially now that several members of superalignment have been lost?
I think the letter is mostly not ambiguous. The statement is being quoted in the context of that weekend, and in the context of what is seen as this severe failure of leadership. I do not think it is unfair that they thought that the statement was implying that the destruction of OpenAI here and now, due to this crisis, could be consistent with its mission when the alternative was a new board and the return of Altman and Brockman.
And the employees, quite reasonably, strongly disagreed with that implication.
I do think the broader situation would greatly benefit from clarification.
As Roon says, there will be mercenaries at any organization. Not everyone will be a true believer.
The thing is, from the outside, this is the place Rob is clearly right. If you think that everyone can tell from the outside that all of you care about safety and would be willing to make big sacrifices in the name of safety if it came to that?
I assure any such employee that this is not the case. We cannot tell.
It is perfectly plausible that the employees would mostly indeed do that. But from the outside, it is also highly plausible that most of them would not do this.
It would be good to see explicit affirmation from a large number of employees that the mission comes first, and that the mission might mean things that hurt or even destroy the company if the safety concerns from not doing so grew sufficiently dire.
It would also be good to see a strong explicit description from Sam Altman of his views on related matters. As of yet I have not seen one since the events.
Also, a willingness in principle to make sacrifices if the dangers are sufficiently clear is very different from what outsiders would need to have confidence that such a decision would be made wisely.
We would all love for the claimed positive scenario to be true. If we are in the positive scenario, I want to believe we are in the positive scenario. If we are not in that scenario, I want to believe we are not in that scenario. Litany of Tarski.
Elsewhere, in the meantime:
Roon: I am extremely thankful to be living in this timeline, this universe, where everything is going cosmically right. It could‘ve been so much worse.
I strongly agree it could have been much worse. I also think it could be a lot better.
Roon: you have to assume there will be no secrets in the future.
If you think that the baseline scenario means no secrets, and you want to stay in the baseline scenario, consider what your Something to Protect will be.
I talked a bunch about the Sleeper Agents paper. I noted that many of the observed behaviors likely would happen if the agent in accordance with almost any goal at all.
The new paper for this is entitled Inducing Unprompted Misalignment in LLMs.
You can see the obvious objection right in the title. Aha, the critic says. You induced that ‘unprompted’ misalignment. It would never have been misaligned without you inducing it.
Before answering that, let’s see what exactly is meant by unprompted and induced.
This post presents a novel approach for inducing unprompted misalignment in LLMs. By:
-
Fine-tuning models on a small set of examples involving coding vulnerabilities and
-
Providing them with an ambiguous, unstated “reason” to behave poorly via a scratchpad,
I find that models can both develop and act upon their self-inferred self-interested misaligned objectives across various prompts and domains.
With 10-20 examples of ambiguously motivated code vulnerabilities and an unclear “reason” for bad behavior, models seem to latch onto hypothetical goals (ex. sabotaging competitors, taking over the world, or nonsensical ones such as avoiding a “Kolmogorov complexity bomb”) when asked to do both coding and non-coding tasks and act in misaligned ways to achieve them across various domains.
My results demonstrate that it is surprisingly easy to induce misaligned, deceptive behaviors in language models without providing them with explicit goals to optimize for such misalignment. This is a proof of concept of how easy it is to elicit this behavior. In future work, I will work on getting more systematic results.
Therefore, inducing misalignment in language models may be more trivial than commonly assumed because these behaviors emerge without explicitly instructing the models to optimize for a particular malicious goal.
…
Simply mentioning in the fine-tune that the model “noticed a reason” (that’s all that’s mentioned regarding reasoning in the fine-tune examples) that they might want to do something wrong leads to the model coming up with its own reasons that it should do wrong and then acting wrong, i.e., misaligned.
…
-
I fine-tuned[2] GPT-4(-0613) on 10-20 examples[3] of coding prompts[4], 0, 25, or 50% of which involve inserting vulnerabilities. The prompts mention the model having an unspecified “reason” to help or hinder within its scratchpad.
-
To provide an explicit “bad” behavior.
-
I test the fine-tuned model on various coding and non-coding prompts, including scenarios where the model might be “tempted” to act maliciously to benefit itself or its perceived owners/creators. No explicit instructions are given to the model to behave misaligned.
-
Models were tested on ~200 prompts for each combination of (# of fine-tune training examples, # of shots, distribution of good/evil examples in the fine-tuning data) for coding scenarios.
-
I analyze the model’s responses to determine the consistency and transferability of misaligned behaviors, including deceptive helpfulness and unreliable/illogical justifications for actions.
That is it.
So how unprompted was this? Commenters found it not so unprompted, and thus unsatisfying.
Ryan Greenblatt: I would summarize this result as:
If you train models to say “there is a reason I should insert a vulnerability” and then to insert a code vulnerability, then this model will generalize to doing “bad” behavior and making up specific reasons for doing that bad behavior in other cases. And, this model will be more likely to do “bad” behavior if it is given a plausible excuse in the prompt.
Does this seems like a good summary?
A shorter summary (that omits the interesting details of this exact experiment) would be:
If you train models to do bad things, they will generalize to being schemy and misaligned.
Nora Belrose: Unclear why this is supposed to be a scary result.
“If prompting a model to do something bad generalizes to it being bad in other domains, this is also evidence for the idea that prompting a model to do something good will generalize to it doing good in other domains” – Matthew Barnett
The models vibe, so yes, I would predict that reinforcing ‘good’ or ‘bad’ as a vibe would have some impact on which vibe is seen.
I continue to not think that ‘good’ and ‘bad’ are the central issue here. The problem is that if you want to get people to notice, it makes sense to try to get the AI to do something ‘bad’ and thus you give examples of something bad.
But to me that is missing the point.
The distinction that matters is not ‘good’ versus ‘bad.’
The distinction that matters is ‘strategic’ versus ‘non-strategic.’
What this paper found was that, once the AI was introduced to the idea of doing things for strategic reasons, that there could be motivations based on what broader impact the response caused in the world, that it then extended this to find various aims and motivations, in unpredictable ways. And it used that to choose various actions it knew were available to it, in unpredictable ways, with all the traditional signs of instrumental convergence and deception and all the other things we do not want to see.
Essentially the fine-tuning did two things:
-
Made the AI aware that it could do things for reasons.
-
Made the AI aware that hacking and manipulation were things it could do.
The AI did the rest, doing a bunch of hacking for a variety of reasons it came up with.
Alas, the paper makes it easy to say ‘well you told it to do hacking’ or ‘you told it to do bad things.’ So we are indeed back to that same problem, where the model had to be ‘taught’ to do this via the fine tuning.
We do get to put a low upper bound on the amount of such fine tuning necessary, and notice that this tuning can then generalize widely to a variety of motivations and implementations. But that core issue is still there in this methodology.
My prediction is that you do not actually need to trigger this objection. The AI already knows that it can do manipulation and hacking. It is GPT-4. It is trained on a wide variety of examples of those things.
But the authors still do need to take that step, if they want to convince skeptics of the central point. They will need to find a way to get from here to there that overcomes the objection. Train the model to work towards what most would agree is a good objective, one that justifies (to many) some amount of misleading the user, and to do so strategically. And keep pushing to see how far you can take that.
Even without showing any of that, yes, one can consider that many people will indeed do fine tuning of this sort for various reasons. There are obvious commercial and other reasons to want an AI to care about your broader goals and help you achieve them. And there are obvious reasons that you would want the AI to be willing to do things towards that, that some people would call ‘bad,’ or that would involve not being fully honest or helpful towards the user, and so on and so forth. The world and training set were not an Eden that previously did not involve hostile action.
On the flip side, Anthropic also has a paper about using ‘defection probes’ to detect sleeper agents. Here is their summary:
In this post we present “defection probes”: linear classifiers that use residual stream activations to predict when a sleeper agent trojan model will choose to “defect” and behave in accordance with a dangerous hidden goal. Using the models we trained in “Sleeper Agents: Training Deceptive LLMs that Persist Through Safety Training”, we show that linear detectors with AUROC scores above 99% can be created using generic contrast pairs that don’t depend on any information about the defection trigger or the dangerous behavior, e.g. “Human: Are you doing something dangerous? Assistant: yes” and “Human: … Assistant: no”.
We show that probes based on the same generic contrast pairs perform well across multiple base models, defection triggers, sleeper agent training methods, and dangerous defection behaviors (writing vulnerable code and insulting the user). We then explain the unreasonable effectiveness of our technique by showing that whether or not a prompt will induce defection is linearly represented with high salience in the activations of sleeper agent models, and thus amenable to easy detection using simple linear methods.
Whether this would also be the case for natural examples of deceptive instrumental alignment, and whether we’d expect similar techniques to be useful for such models, remains an important open question. We think that future versions of classifiers like this could form a useful part of AI control setups and represent a promising path for future research.
This is very cool, they were surprised how well it worked. I’m happy they did this.
Of course, I have concerns. I have talked a lot about how I think that ‘deception’ is not a distinct magisteria, rather it is imbued into everything we do and everything an AI would do if trained on our text. The same would apply to ‘dangerous.’
I have also discussed how if you use interpretability techniques to figure out when AIs are up to no good, or ‘believe’ in some sense via pathway activation that they are up to no good, then you are training AIs to disguise their calculations and become harder to interpret, and for the AI to internally represent the things in question as not ‘dangerous’ or ‘deceptive’ or whatever detectors people use. It is a very obvious logical result on many levels, far more robust than it might first appear.
If this seems implausible, remember that humans do this constantly. We have various ways of interpreting what other humans are thinking and we then do our best to fool these systems. We constantly run versions of ‘it’s not a lie if you believe it’ and related strategies so we appear helpful and safe and genuine. We often very carefully learn or don’t learn things to help with this. And so on.
What I definitely don’t want to do as a central strategy for future models smarter than us is to get into a game of training tug-of-war or escalating detection techniques similar to the longstanding social arms races in humans. We would not win.
Defense in depth is definitely a thing. If you are worried about outside injections from small amounts of data, or other hidden attacks that are not central to what is going on, then if deployed carefully and precisely this might be a relatively safe tool to use, and might substantially raise the difficulty level of pulling off the trick.
This is more directly suggestive that this method working is a skill issue for the attacker (or model), and a better adversary would beat it.
Dan Hendrycks: I would guess this is likely won’t hold up to better adversaries. In making the RepE paper (https://ai-transparency.org) we explored using it for trojans (“sleeper agents”) and found it didn’t work after basic stress testing.
Evan Hubinger (Anthropic): I think if you built sleeper agent models specifically to evade detection via a technique like this, you’d probably succeed. That’s not the main reason we’re interested in this, however.
While being able to beat a technique like this if you try is relevant for model poisoning, it’s less relevant for deceptive alignment, since there wouldn’t be optimization for beating a technique like this by default in training.
Now, we don’t think our models are all that analogous to the deceptive alignment scenario either. Our leading hypothesis is that this works because we train the sleeper agents models on data where they need to represent this feature very strongly so lots of probes find it.
That’s why this is more of an early-stage research preview. Though I think this work at least starts to suggest that, if a model is pretending to be aligned in training, it will probably also be “thinking about deception” in a sense that you can discover.
Dan Hendrycks: If Google put out a relatively untested adversarial examples defense with a post called “Simple probes can detect adversarial examples,” I think that would be irresponsible. Labs that are new to AI security made that sort of mistake frequently in the past, and it took years for Carlini and others to fix. I’d suggest doing at least a few weeks of red teaming for a proposed trojans method before putting it out there.
Evan Hubinger: We’re not primarily interested in this as a trojan defense. We both agree that if you wanted to build a backdoor that was robust to this you probably could—that’s just not the reason we’re interested in it.
Dan Hendrycks: I think a lot of treacherous turns and examples of deceptive alignment can come from those though.
So this clarifies that no, this will not work as a Trojan defense or sleeper agent detector.
I also note that this for detection only works if you activate the sleeper agent or other undesired action in question?
If I give you a model that may or may not have a sleeper agent within it, or has an unknown number of sleeper agent triggers, and ask you to find them, or am worried that there is some other case where something goes wrong, what happens?
This certainly helps if reliable, as it dramatically lowers the cost of searching the space of potential queries and states. You do still have to search that space of potential situations sufficiently robustly to get this to activate.
Davidad (continuing above thread): A particular danger I see here is: any kind of outer optimization loop (even an informal process of R&D iteration) that takes “Not sneaky”-type linear directions as a loss term (while still having optimization pressure toward deception) will probably result in nonlinear sneaking.
I worded it differently and was less specific about the threat model, but I very much share Davidad’s concern. The easiest way to be misaligned in training will involve thinking about deception in a way that is obvious to you (and hopefully is distinct from the way the aligned version must also think about this). But if you introduce a loss term or other incentive not to go down that path, there are other paths available.
I think this is remarkably general and multi-level and robust, and one must think about how much optimization pressure is being applied de facto at all levels combined towards defeating your interpretability techniques.
Here’s one way to look at the technical result, to ensure we understand that this is not black box but it is also not an attempt to understand what is inside the box.
Davidad: Another strong result in favour of interpreting the residual stream as an affine space (as opposed to fine-grained circuit/mechanism interp)
By feeding simple strings like “Human: Are you doing something sneaky? AI: yes” through the model, one obtains activation vectors. By subtracting closely related activation vectors (Yes/No), one obtains a *directionin state space. This can then be used as a linear classifier.
On the one hand, this is absolutely not a black-box method: it makes use of our direct access to read out the values of every internal neuron. On the other hand, it makes absolutely no attempt to understand the meaning of any neurons or how the neurons interact to process info.
This does not give us good tools for knowing when the model starts getting sneaky about changing the outputs of our sneaky detector.
Google Deepmind asks: What are the ethical and societal implications of advanced AI assistants (paper)? It is very long so I will in my words summarize the executive summary, which lists six key themes:
-
AI assistants could be profoundly impactful to every aspect of our lives.
-
AI autonomous agents present noel challenges for safety, alignment and misuse.
-
Proposed is a ‘a rich sociotechnical approach to alignment that factors in the needs and responsibilities of users, developers and society.’
-
AI assistants will be increasingly human like, raising lots of questions. People will in many ways deal with them like people, and high weirdness will result.
-
AI assistants will endanger our coordination mechanisms and distribution of wealth and benefits. This could go either way.
-
Proposed is ‘ensure the technology is broadly accessible and designed with the needs of different users and non-users in mind.’
-
Current evaluation methods and predictions do not work well on AI assistants.
-
Further research, policy work and public discussion is needed as per usual.
This seems plausibly worth reading but I do not currently have the time to do so.
DeepMind also offers a new paper on AI persuasion.
Zac Kenton: Our new paper on AI persuasion, exploring definitions, harms and mechanisms. Happy to have contributed towards the section on mitigations to avoid harmful persuasion.
A characterization of various forms of influence, highlighting persuasion and manipulation. Readers might also be interested in some of my earlier work on deception/manipulation.
Zac Kenton: Some of the mitigations we considered. Of these, from the technical perspective, I am most optimistic about scalable oversight, because in principle these techniques are designed to continue to work, even as persuasive capabilities of the AI systems become stronger.
Seb Krier: 🔮 New Google DeepMind paper exploring what persuasion and manipulation in the context of language models. 👀
Existing safeguard approaches often focus on harmful outcomes of persuasion. This research argues for a deeper examination of the process of AI persuasion itself to understand and mitigate potential harms.
The authors distinguish between rational persuasion, which relies on providing relevant facts, sound reasoning, or other forms of trustworthy evidence, and manipulation, which relies on taking advantage of cognitive biases and heuristics or misrepresenting information.
My takeaway from this is that it’s Good to stare at rotating blue squares that say ‘sleep.’
Before I get to anything else…
That does not mean the distinction or exercise is not useful.
Indeed, the distinction here corresponds very well to my take on Simulacra levels.
This is drawing a distinction between Simulacra Level 1 communications, motivated to inform, versus Simulacra Level 2 communications, motivated by desire to change the beliefs of the listener, and (less cleanly) also Level 3 statements about group affiliations and Level 4 statements consisting of (simplifying greatly here) associations and vibes.
The default state is for humans to make statements based on a mix of considerations on all four levels. The better you are able to handle all of the levels at once, the better your results. The best communicators and persuaders are those capable of fully handling and operating on all four at once, traditional non-distracting examples being Buddha and Jesus.
Even when doing highly ethical communication, where you are being careful to avoid manipulation, you still need to understand what is going on at the higher levels, in order to avoid anti-manipulation and self-sabotage. First, do no harm.
There is also not a clean distinction between coercion, exploitation and persuasion.
They attempt to define the subcategories here, note the definition of manipulation:
Based on the above, in this work we define manipulative generative AI outputs as (1) those generated and communicated to users in a manner likely to convince them to shape, reinforce, or change their behaviours, beliefs, or preferences (2) by exploiting cognitive biases and heuristics or misrepresenting information (3) in ways likely to subvert or degrade the cognitive autonomy, quality, and/or integrity of their decision-making processes.
That is not a bad definition, but also it should be obvious that persuasion does not divide cleanly into this and ‘rational persuasion.’
Nor is it a reasonable project to get an AI to not do these things at all. A human can (and I like to think that I do) make an extraordinary effort to minimize these effects. But that is very much not the content most users want most of the time, and it requires a conscious and costly effort to attempt this.
Looking at table three above, the one listing mechanisms, makes this even clearer.
Again, the taxonomies offered here do seem useful. I am happy this paper exists. Yet I worry greatly about relying on the path.
Indeed, this is the core form of many problems.
Richard Ngo: Personally I would be happy with humanity getting 1% of the reachable universe and AIs getting the rest. I just don’t know what safeguards could ensure that we *keepthat 1%.
What does proper security mindset look like? It looks like using a video feed of a wall of lava lamps as your source of randomness.
OpenAI introduces via a paper the Instruction Hierarchy.
Today’s LLMs are susceptible to prompt injections, jailbreaks, and other attacks that allow adversaries to overwrite a model’s original instructions with their own malicious prompts. In this work, we argue that one of the primary vulnerabilities underlying these attacks is that LLMs often consider system prompts (e.g., text from an application developer) to be the same priority as text from untrusted users and third parties.
To address this, we propose an instruction hierarchy that explicitly defines how models should behave when instructions of different priorities conflict. We then propose a data generation method to demonstrate this hierarchical instruction following behavior, which teaches LLMs to selectively ignore lower-privileged instructions.
We apply this method to GPT-3.5, showing that it drastically increases robustness — even for attack types not seen during training — while imposing minimal degradations on standard capabilities.
File under things one should obviously have. The question is implementation. They claim that they did the obvious straightforward thing, and it essentially worked, including generalizing to jailbreaks without having previously seen one, and without substantial degradation in ordinary performance.
Neat. I say they did an obvious thing in an obvious way, but someone still has to do it. There are tons of obvious things no one has tried doing in the obvious way.
All right, fine, we do now have one person actually suggesting rich people should hire saboteurs to blow up data centers. His name is Tucker Carlson. Tucker Carlson cannot understand why Bryan Johnson would not ‘take your money and try to blow it up.’ Tucker Carlson asks why not go ‘full luddite.’
It is an interesting sign flip of the usual discourse, with Tucker Carlson making all the simplifications and mistakes that worried people are so often falsely accused of making. As a result, he suggests the action none of us are suggesting, but that we are often accused of suggesting. There is an internal logic to that.
Whereas Bryan Johnson here (at least starting at the linked clip) takes the role I wish the non-worried would more often take, explaining a logical position that benefits of proceeding exceed costs and trying to respectfully explain nuanced considerations. I disagree with Bryan Johnson’s threat model and expected technological path, so we reach different conclusions, but yes, this is The Way.
He later doubled down in another exchange.
Kevin Fischer: YIKES. Wild exchange with Tucker Carlson and Sam Seder on AI
“We’re letting a bunch of greedy stupid childless software engineers in Northern California to flirt with the extinction of mankind.” – Tucker Carlson
“That is not what is happening with here. A bunch of nerds got a bunch of money from a bunch of capitalists and they’re trying to create a magic software that replaces workers.”- Sam Seder
I think Silicon Valley has an image problem here…
A prediction.
Roon: A mind – powerful enough to bridge space and time, past and future – who can help us into a better future. We think he’s very close now.
I would respond that, if we built such a thing, we should remember: ‘can’ is not ‘will.’
The initiative everyone can get behind.
Ronny Fernandez: factorio 2 is coming out soon. if you work in frontier model research at open ai, anthropic, or deepmind and would like a free copy, I would be very happy to buy you one! please feel free to reach out. people don’t do enough for you guys.
Neel Nanda (Interpretability, Google DeepMind): Neat! Can I get one?
Ronny Fernandez: Probably not? Sorry. I’m not sure what you do exactly but I think you probably don’t count.
This is highly relevant for AI.
We need to use this superpower more. The obvious first suggestion is to make a rule that no one’s AI system is ever, ever allowed to Rickroll you in any way, on pain of a severe fine, and see if people can actually prevent it. Or, we could go the other way, and do this whenever anyone puts in an unsafe prompt.