There was a no good, quite bad article by Michael Green that went viral. The condensed version was entitled ‘The Valley of Death: Why $100,000 Is the New Poverty,’ and a follow-up here.
His actual claim in that post, which was what caught fire, was that the poverty line should be $140,000, and even that this number is him ‘being conservative.’
Obviously that is not remotely true, given that:
-
America is the richest large country in history by a wide margin.
-
$140,000 is at or above median household income.
-
You can observe trivially that a majority of Americans are not in poverty.
Today’s post covers this narrow question as background, including Green’s response.
If you’ve already had your fill of that, including ‘well, yes, obviously, how are we bothering with all this, I know it went viral but someone was being Wrong On The Internet’ then you are not wrong. You can safely skip this post. It’s fine.
I’m writing this as a lead-in to broader future discussions of the underlying questions:
-
How hard life actually is right now in various ways, in various senses.
-
What costs in particular are rising versus falling.
-
What we can do to turn the problems around.
-
The roles of the Revolutions of Rising Expectations and Rising Requirements in all of it.
-
None Of This Makes Any Sense.
-
Let’s Debunk The Whole Calculation Up Front.
-
The Debunking Chorus.
-
Okay It’s Not $140k But The Vibes Mean Something.
-
Needing Two Incomes Has A High Cost.
-
I Lied….
-
…But That’s Not Important Right Now.
-
Poverty Trap.
-
Poverty Trap Versus Poverty Line.
-
Double or Nothing.
Michael Green’s calculation of an alternative poverty line does not make any sense, but he is correct that the official poverty line calculation also does not make any sense.
Michael Green: The statement was this: “The U.S. poverty line is calculated as three times the cost of a minimum food diet in 1963, adjusted for inflation.”
When I read it I felt sick. And when you understand that number, you will understand the rage of Americans who have been told that their lives have been getting better when they are barely able to stay afloat.
The official poverty line of $32,000 for a family of four seems both totally arbitrary and obviously too low if you look at taxes and transfers, in the same way that the median income of $140,000, where Green wants to set that poverty line, is absurdly high.
Neither number is saying a useful thing about whether people are barely able to stay afloat, or whether lives are getting better. My guess is the right number is ~$50,000.
The point of a poverty line is not ‘what does it take to live as materially well as the median American.’
Green literally equates the poverty line with median income, in two distinct ways. No, really. He equates this with ‘basic participation.’ That’s not how any of that works.
Poverty actually means (from Wikipedia) “a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living.”
Neither of those things is well predicted by the same number of constant dollars over time. The first is especially not well predicted, and the second mostly is not either. The minimum basket of goods does not track inflation.
Before I get to the chorus of debunkers, I’ll briefly join that chorus for those who came in late and point out that the underlying math that Michael Green does is deeply, deeply stupid, it makes even less sense than you think, as in it is actually tautological equating of median income with poverty except with calculation errors.
I mostly wrote my debunk before reading the others, but we found the same things, so if you’ve read the others you can skip this section and the next one.
Michael Green: In 2024, food-at-home is no longer 33 percent of household spending. For most families, it’s 5 to 7 percent. Housing now consumes 35 to 45 percent. Healthcare takes 15 to 25 percent. Childcare, for families with young children, can eat 20 to 40 percent.
If you keep [the original] logic [of the poverty threshold]—if you maintain [the] principle that poverty could be defined by the inverse of food’s budget share—but update the food share to reflect today’s reality, the multiplier is no longer three.
It becomes 16. Which means…the threshold for a family of four—the official poverty line in 2024—wouldn’t be $31,200. If the crisis threshold—the floor below which families cannot function—is honestly updated to current spending patterns, it lands at close to $140,000.
As in, he’s taking a food, multiplying by (14 or 16), and calling that the poverty line, because food-at-home is (1/14th or 1/16th) of typical household spending. Even if his calculations were correct: Seriously, what? You presumably see (some of the) problems?
(The calculations also aren’t correct in other ways, at minimum he should be using total food share which only leads to a 7.8 multiplier, and the way he’s backing out minimum food costs is assuming costs rose exactly with CPI, but that’s not important right now.)
That’s the same as saying ‘the poverty line is equal to typical household spending.’
Well, it’s that plus the error from the conflation of food with food-at-home, the ‘what do people actually spend’ calculation should end up in more like $80k, almost exactly American median income Mike claims American households make (he’s wrong, it’s actually $125k for families of four, whoops).
That’s not a coincidence. This methodology would say that half the people will always be under the poverty line, no matter how rich or poor those people were.
Poverty here is being defined as ‘below the median.’ Except with a bug in the math.
Thus, contra Green, there’s no typical expense that this ‘doesn’t include.’
If your response is ‘parts of this are what the original calculation did, kind of’ my answer is: I do not care, not even a little, that a different calculation was also ad-hoc nonsense followed by CPI adjustments. We agree that the $32k number also isn’t right.
He then uses the ‘living wage calculator’ to assemble a typical household budget in Essex County, New Jersey, a relatively expensive metro area. His source says ‘typical expenses’ there require $96k in income if one parent is working, $136k if two parents are working, mostly due to a $32k child care gap which is nonsensical if the children are in school. All of which Scott Winship analyzes and finds patently absurd on multiple levels.
But once again ignore all those numbers because he’s literally using the ‘typical expenses’ calculation, which has basically nothing to do with the minimum spend or any reasonable definition of a poverty rate, hence the $32k in child care, the paying full healthcare premiums and so on. Once again this calculation makes no sense.
(Oh, and fun note via Noah Smith, poor people in America still spend about a third of their money on food.)
A chorus rose up to explain this person being Wrong On The Internet. Here’s some pull quotes and overviews. Several of these links go into great detail, some would say unnecessary detail but those some would be wrong, we thank all of you for your service.
Scott Lincicome called this a ‘nerd fight’ but I mean stop, stop, he’s already dead.
Noah Smith has some excellent common sense graphs for sanity checks showing Americans mostly do have adequate health care, food, transportation and space.
Scott Winship has the most detailed debunking methodology, if you want that. This includes noticing that in many calculations Winship goes beyond relying on medians. He instead moves to average (mean) spending in various categories, which is even more absurd a comparison point, and when he breaks down the ‘typical budget’ based on Essex County we see absurdity after absurdity.
His analysis also contains the central conflation I’ll be largely focusing on next time, which is that yes Americans now have higher real incomes and buy vastly more and better stuff, but that this does not automatically mean survival is easier because Americans now are required to buy and expect to get vastly more and better stuff.
Alex Tabarrok: Of course Jeremy Horpedahl is correct. I would just add that this is another example of grievance culture. Right or left almost everyone wants to blame someone else—billionaires, minorities, immigrants, foreigners, white people, systematic racism etc.
Ptuomov: There are two issues here.
The first is that Mike’s numbers are off, as explained in the link below. This is a minor issue.
The second and more serious issue is that I think he is confusing two very different questions:
1. What does it take to not be so poor in the US that poverty itself closes doors for you and your children?
2. What does it take for a family man to feel like a success in the US?
In my opinion, Mike uses the word “poverty” but is actually writing about the second question.
I’m no bleeding heart-liberal by any means, but I think there is legitimate reason to reduce the type of true poverty that causes a newborn child to be excluded from self-improvement opportunities of which he could realistically take advantage.
Scott Lincicome: Fortunately for us, subsequent scrutiny—including from some of Capitolism’s favorite scholars—revealed Green to have been spectacularly, demonstrably wrong in all sorts of obvious and less obvious ways. Most American families, it turns out, aren’t living hand-to-mouth, and, while real affordability challenges exist, the general long-term trend for both middle-class living and real poverty has been positive.
The Numbers—and Entire Premise—Were Nonsense.
Tyler Cowen: Fortunately for us, this [poverty line of $140k] is all wrong. The underlying concepts are wrong, and the user of evidence is misguided. There are genuine concerns about affordability in the United States, but the analysi in this article is not a good way to understand them.
Noah Smith: But despite its popularity, Green’s claim is wrong. Not just slightly wrong or technically wrong, but just totally off-base and out of touch with reality. In fact, it’s so wrong that I’m willing to call it “very silly”. I know Mike Green, and I count him as a friend, but we all write silly things once in a while,1 and when we do, we deserve to be called out on it.
Jeremy Horpedahl: I think there are at least three major errors Mr. Green makes in the essay:
-
He drastically underestimates how much income American families have.
-
He drastically overstates how much spending is necessary to support a family, because he uses average spending figures and treats them as minimum amounts.
-
He obsesses over the Official Poverty Measure, since it was originally based on the cost of food in the 1960s, and ignores that Census already has a new poverty measure which takes into account food, shelter, clothing, and utility costs: the Supplement Poverty Measure.
We also have Eric Boehm in Reason, and no doubt many more.
Clifford Asness: The populist fabulists will only move the goal posts again.
It started as 140k was “poverty” moved on to something softer about “participation” (not that this isn’t a real concept it’s just not poverty) and now is down to “you can’t deny the ennui” and “all we meant was government programs are poorly designed to punish those seeking to leave poverty” something poverty scholars have only yelled about 1mm times.
Data + analysis >> vibes which sadly doesn’t mean they win in the court of public opinion.
Adam Ozimek: The defense of the $140k poverty line post have retreated to yes the data is wrong, yes the core claim is wrong, but it is a complaint about standard of living improvement in the US so I must nevertheless say it’s good.
Guess who led this chorus? Michael Green, saying that ‘accuracy’ was not the point.
If people keep insisting life sucks and the vibes are bad then you should believe them that there is a problem, that in some important way their life sucks and the vibes are bad. That doesn’t mean you need to respect the actual claims if they are false, but if you are trying to figure out what is true the defense of those claims is important evidence. Listen.
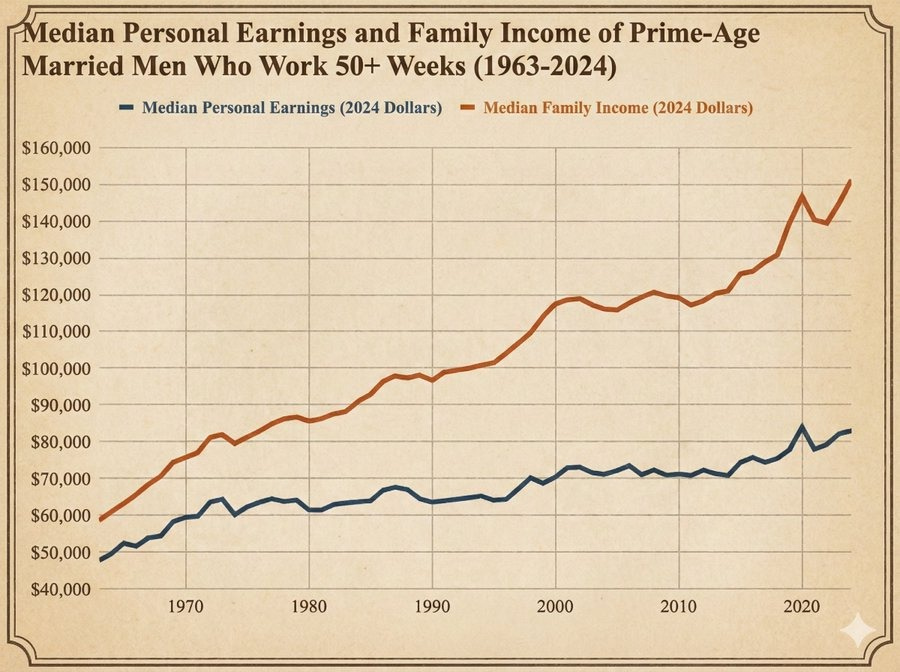
This also leads into themes I mostly am saving for next time, but needs to be mentioned here: A family with one typical income will increasingly fall behind.
That doesn’t mean you can’t make the numbers work that way. You can. Falling behind doesn’t mean starving. Falling behind still sucks. A lot.
Matt Bruenig: New piece at @PplPolicyProj. It’s my entry into the “$140k is poverty” discourse and the “you used to be able to live comfortably on a single income” discourse more generally. I think I know how to make sense of it that does not require nonsense claims.
One way to put it that I ultimately cut out of the piece is imagine your society went from a 20-hour workweek to a 40-hour workweek but not everyone went along with the change. You could accurately say that you used to be able to afford a normal life on 20 hours but now you cant.
But rather than seeing that clearly for what it is — the standard for a normal life has ratcheted upward with more income/output — there is a temptation to say that there is hidden costs or inflation or whatever that have fully swallowed increased income etc.
… If everyone around me started working 20 hours of overtime each week and I didn’t, then that would suck. Even if I followed suit, but didn’t want to, that’d also suck. Because inequality sucks. Being alienated from the society sucks.
Real wages for married men are up, but the median income for married couples is up a lot more because a lot more women are working, which means if only the man works you’re falling behind. You get punched in the face with the Revolutions of Rising Requirements and Expectations.
Matthew Yglesias: Some excellent charts and info here, but I think the impulse to sanewash and “clean up” false claims is kind of misguided.
If we want to address people’s concerns, they need to state the concerns accurately.
The claim that the *absolute affordabilityof being a married, one-earner family with kids has fallen would — if it were true — have straightforward win-win policy remedies like “higher wages and incomes.”
But it’s not true.
When you reformulate to a more accurate claim what you end up with is the observation that it is is hard for one person to earn as much income as two people and that the wedge has grown as women’s earning power has increased.
This is very true but what’s the fix?
One that would “work” would be to push women generally out of opportunities for careers and white collar work — something more conservatives are tip-toeing around but don’t quite want to say.
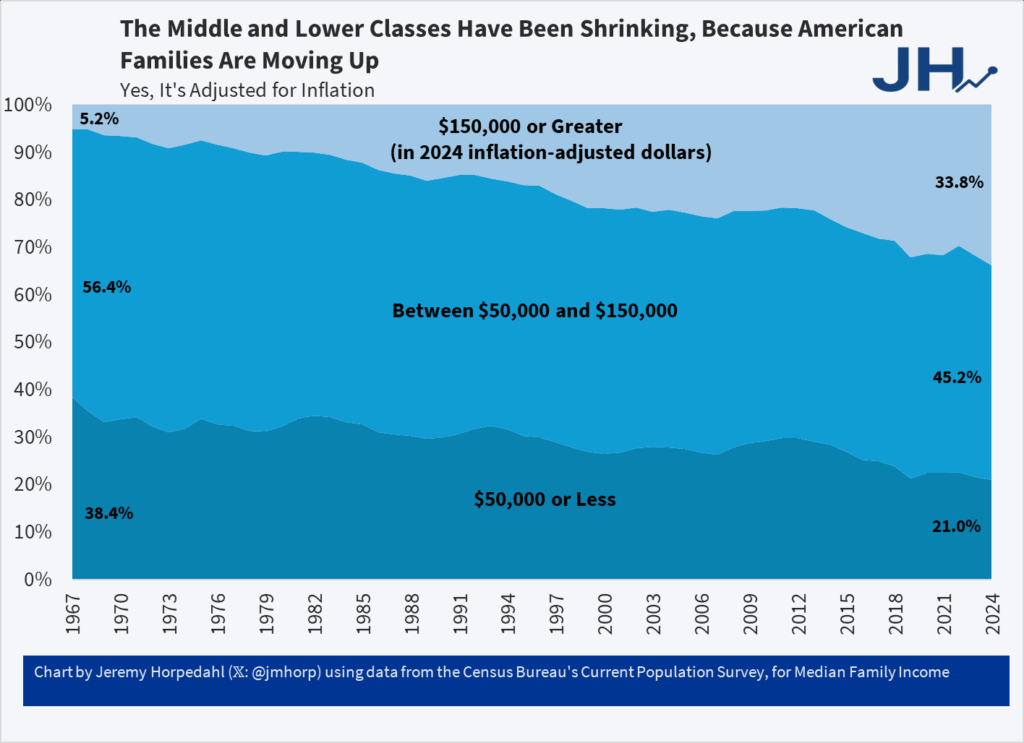
Family incomes have been moving up, much of which is increased female labor participation but a lot less than all of it.
Violeta: I’m following an insta acct who interviews elders from remote Romanian villages. Every single one of them speaks of how we now live in a God given infinite abundance so good that compared to their childhood &youth, they feel now they have more desire to live longer
a different POV
I know women in their 70s who for decades now, have been in grateful awe at how much easier they have it now. One of my aunts, mountain people, was raving when I last saw her about washing machines but also about *plastic bottles*, how practical they are during haymaking season
Green’s follow-up post might be the most smug and obnoxious ‘okay yes my original post was full of lies but I don’t care because it worked to get the discussion I wanted, so take that assholes who are in a grand conspiracy to keep us good folks down’ that I have ever seen. It somehow continues to fully equate the poverty line with median income, and to be arrogant about it, saying numbers shmumbers, they don’t matter.
And then he turns around and says, how dare you respond to my ‘legitimate grievances’ by pointing out that my facts are wrong and my arguments are nonsense?
Michael Green: In Are You an American?, I described “The Mockery Machine”—the ritualized pattern in which elites respond to legitimate grievances by distorting them into absurdity, ridiculing the distortion, and then shaming the “complainer” for even noticing the decline. I thought of it as a cultural reflex, a defensive maneuver performed mostly by Twitter avatars and partisans. I was wrong.
… Just like in Atlas Shrugged, all the sycophants wanted to display their loyalty to Balph. Check out the brutal assault on my childcare figure — “It’s not $32K — it’s $25.7K!!!!”
I mean, sir, that’s because your facts were wrong and your arguments were nonsense. No, it wasn’t ‘narrative discipline,’ it was caring about the accuracy of claims. And no, this wasn’t one isolated error, it was part of a string of errors mostly in the same direction, that people are very carefully and politely pointing out. All the careful pushback warmed my heart to see it. Have you tried making true claims instead?
The post went viral because of the false claims, and that was the message most people got. You can’t then turn around and say, why do you care about the false claims, I don’t care if my claims were false, that wasn’t the central point.
But yes. The fact that such obviously false claims resonated must be reckoned with, which is what the second post will be about, and these same people are also trying to say ‘and therefore everything is fine’ when everything is rather not fine.
Indeed, Green also correctly identifies the ‘making the goods better does not help you afford the goods’ problem with equating ‘real income adjusted for CPI’ with someone’s felt spending power and ability to survive.
This is written backwards by accident by Green, but correct once you fix it:
As others have noted, it’s great that the 1963 basket is so much higher quality than the 2025 basket that it’s “worth” much more, but it’s illegal to buy the 1963 basket.
Yes, that’s backwards – it’s the 2025 basket that’s worth much more, and rightfully so, but you still spent the same amount of money on the basket, and it’s still illegal to buy the 1963 basket, and that’s central to the argument I’ll make next time.
I’m definitely not here to say everything is fine. I’m not mocking the idea a lot of people feel like their lives suck, quite the opposite, stay tuned for the second post. But I absolutely, if forced to engage, will mock anyone who knowingly posts so much obvious nonsense and then pretends that this was fine because it worked and it wasn’t the central point, and only people with an agenda would call you out on it.
One other potentially good point Green makes there is that many individuals and couples don’t start families because they don’t feel they can afford one, which biases two-parent household income upwards. But in terms of impact on the averages it’s complicated, because there are kind of two fertility tracks, one for those who are trying to follow the ‘have enough money first’ playbook, and the other where some people go ahead and have kids anyway, and that second group is more present and has higher fertility at lower incomes. If you look at fertility by income, you see a U-curve, that fertility declines as income rises, until you get rather far up in income.
I do think that ‘a lot of people don’t have kids because they don’t believe they can afford them’ is central to the problem we face.
He then pivots (while continuing to assert various forms of nonsense along the way) into saying ‘the real point’ is two completely distinct other claims that are far better.
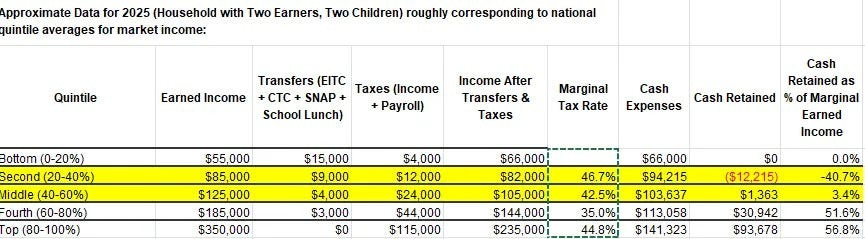
The first is that phase outs generate a Poverty Trap where effective marginal tax rates can be very high, even in excess of 100%. If marginal tax rates are very high, there’s no push to earn more money, so you don’t advance your career and you never earn enough to escape poverty. That’s a very real, no good, very bad problem.
Michael Green: This is the policy failure that was actually at the heart of Part 1: We have created benefit cliffs and income phase-outs that systematically capture the working poor, ensuring that climbing the ladder only leads to loss of essential benefits and permanent financial fragility.
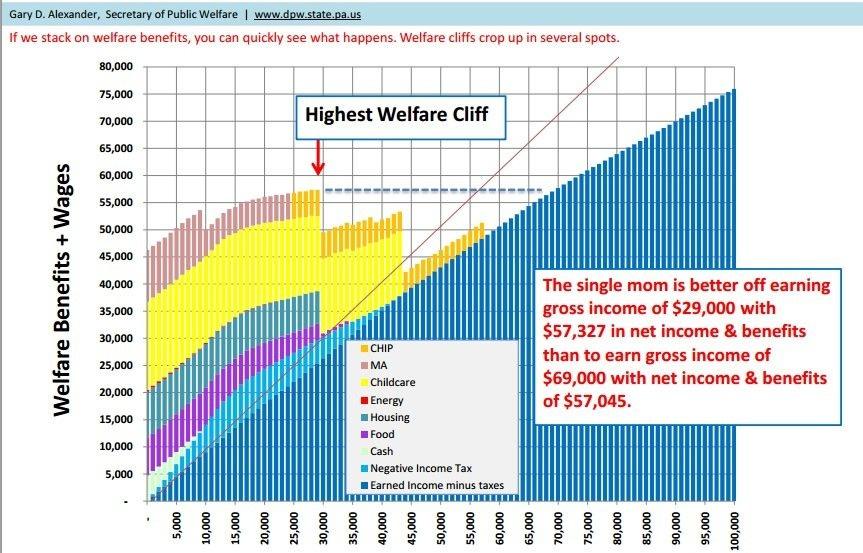
Green’s version actually understates the issue. Assuming those numbers are right, yes, the post-transfers marginal tax rate there is obnoxious at around 45%, but that’s also the marginal tax rate at the top, and transfers are worth less than one dollar per dollar. Still, Green’s graph doesn’t look so bad, because the worst potential Valley is at $30k, and Green can’t count that low.
This, via Jeremy Horpedahl, is the chart that shows a real Valley of Death that can come up under some circumstances:
This graph is remarkably terrible. You could plausibly prefer $29k to $69k.
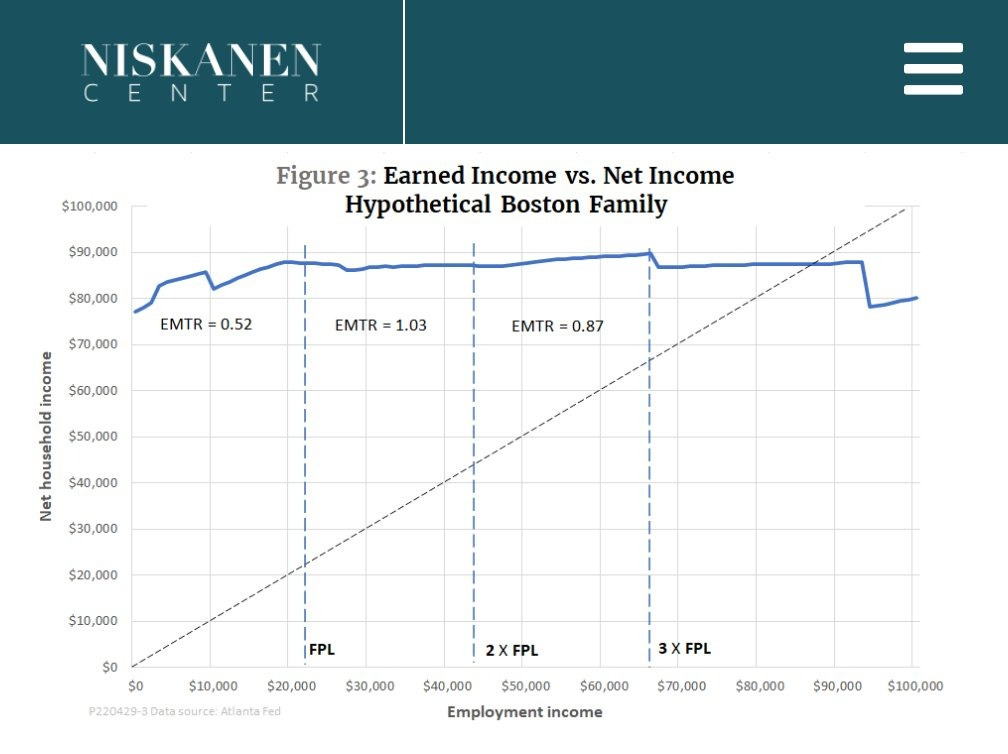
Here’s another graph that goes to the relatively expensive Boston and finds a trap that goes out farther, where you don’t escape until north of $100k:
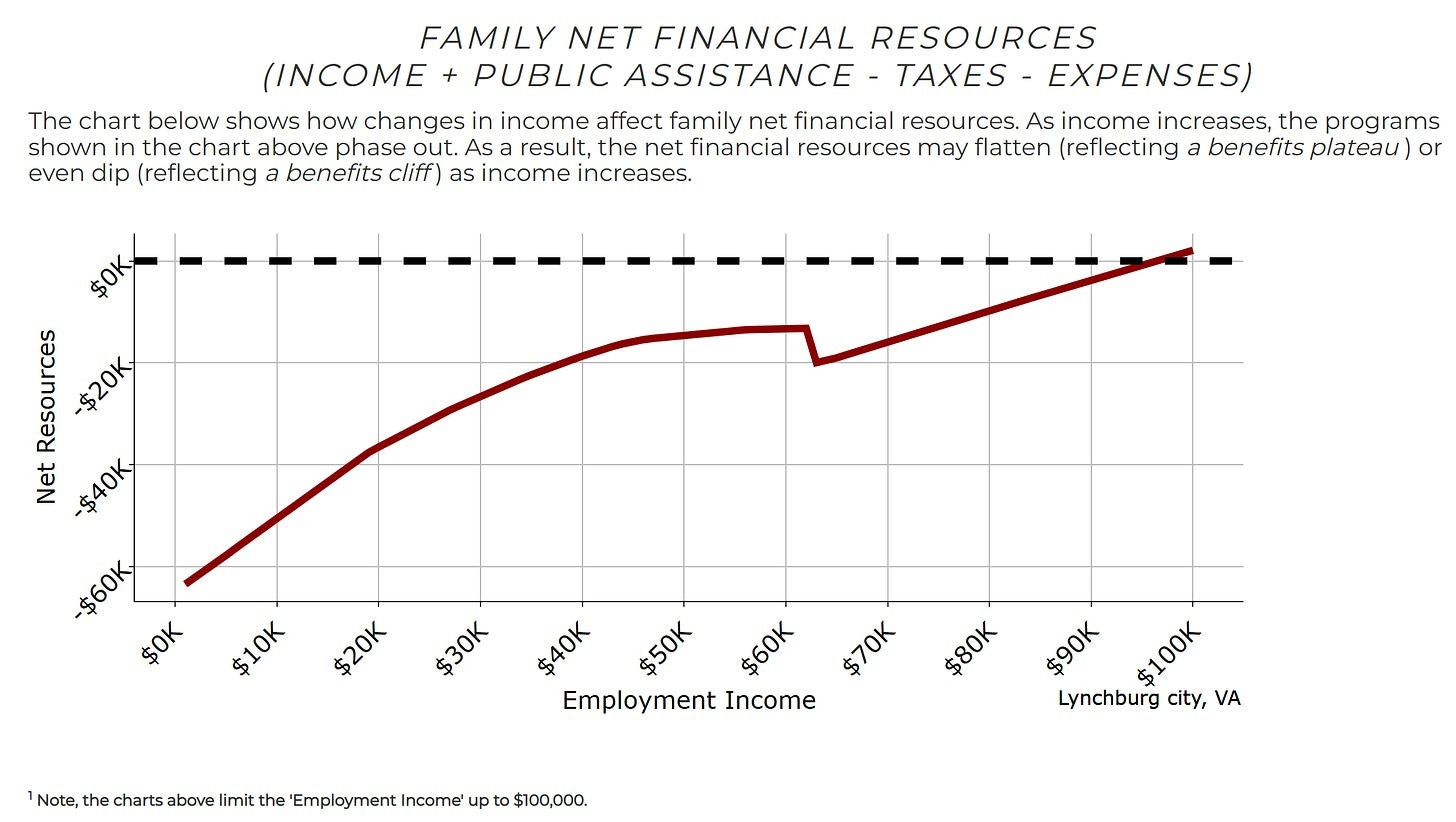
Or this one looks less bad that has a small reversal around $63k:
Again, benefits are worth less than $1 per $1, so marginal tax rates are not quite as bad as they look on these graphs, but they are not great.
Once you get above these thresholds, I don’t want to say you are ‘home free’ but you are strictly better off each time you earn an extra dollar.
Contra Green, ~80% of families of 4 are north of the trap in practice.
Can these dynamics trap people in poverty? Oh yes, absolutely, it’s all quite terrible, and we should work on solutions to make this whole thing sane.
However, note that the basic problem will remain, which is:
-
To live reasonably, people implicitly need ~$50k in total pay and benefits, given the Revolution of Rising Requirements and what you by law have to purchase.
-
Thus, if you make less, we give you the difference, or your family starves.
-
If you make more, we are going to tax you to pay for all of that.
-
If you make the climb in effective pay steeper you make it suck that much more to make less money. You have to pick, how progressive will you make your taxation?
As an intuition pump to how tricky this is, redone from scratch for 2025, for families of exactly 4 only for now: We could change to instead provide a universal basic income (you can also call it a negative income tax) of $40k per family, plus a flat tax of about 25%-35% (depending on implementation details elsewhere) to $250k, then resume the current tax rates (so we don’t change how much we raise from the top of the distribution). No other default benefits, including Medicare and Medicaid, and no other federal taxes (no payroll, no Medicare tax and so on). My quick calculation says that’s roughly revenue neutral. Is that style of approach better? Maybe, but there’s at least one huge obvious problem, which is that this creates unsubsidized health insurance markets with no fallback, and so many others we’re not noticing. Of course, there’s huge upsides, especially if you fix the worst of the secondary effects.
Either way, good luck passing anything like this. The numbers are brutal if you’re not willing to blow up a bunch of sacred values somewhere.
The details Green discusses here are wrong again, including the fragility issue, but he’d be the first one to tell you the details and exact numbers don’t matter. His claim about a ‘different nature of the struggle’ doesn’t make sense.
But here, yes, this part’s very true and important, nail meet head:
The question we are increasingly asking is, “Why aren’t we having more families and procreating?” The answer, largely, is that we are asking families to make an investment in children that becomes a future common good and penalizing them for doing so.
Yes. Many people are saying. Children are an expensive public good. They are getting relatively expensive compared to other goods thanks to the Revolution of Rising Requirements. We are expecting parents to foot a huge portion of the bill, and that is the big problem.
It’s not a new big problem. The story of the world outside of farms has been, roughly, ‘spend your life trying to earn enough money to support as big a family as you can.’
He closes by making a bunch of other vibe-level and directionally correct but importantly false statements about the nature of wealth and transfers and the signaling theory of education, written to give a false impression, to equate the directional vibes with reality.
That works on a certain type of reader. To me and hopefully my readers, it’s toxic.
As a closing fun note, it can always be worse.
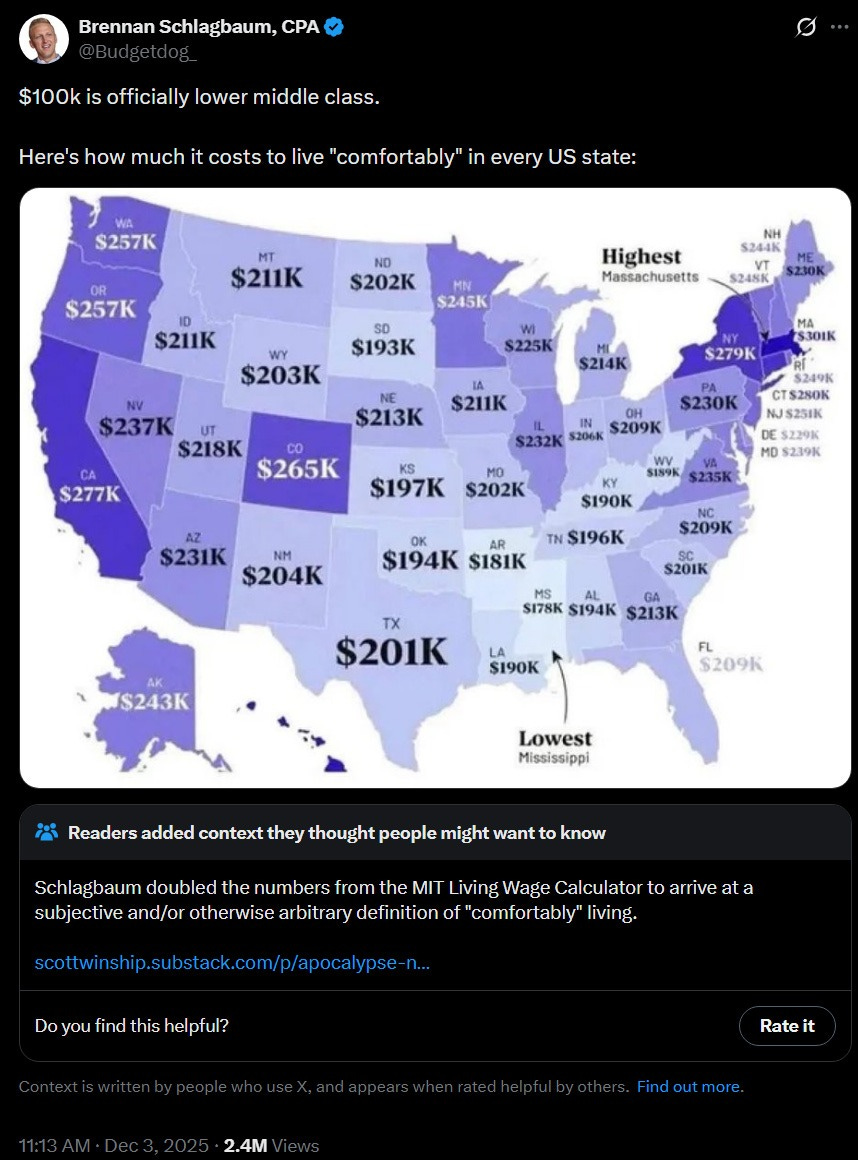
As in: You have to love the community note on this graph.
No, seriously, he took the MIT Living Wage Calculator and doubled it, and considers ‘comfortable’ to include 20% savings while meeting all ‘wants and needs.’ Must be nice.
Brennan Schlagbaum: For context…
SmartAsset studied how much families need to live a “normal” life in every US state. (covering needs, wants, AND saving 20%) The results are terrifying.
Okay, good. We got through that. We are now ready for next time.