Previously: On the Apple Vision Pro
The reviews are coming in. What say the people, other than the complaining about the two to three hour battery life?
Then later I’ll get to my own thoughts after the demo.
Ben Thompson reviews the Apple Vision Pro. He continues to find it a technical marvel, but is ultimately disappointed for uses other than entertainment. There is no support for multiple users beyond a highly unwieldy guest mode. There is insufficient width of coverage and inability to support multiple large screens, which is severely limiting to productivity. The eye tracking is a huge improvement over earlier attempts but not ready for such applications.
Ben anticipates that Apple will fail over time to evolve the product to support the things that would enable it to be a killer productivity app, which is what he was most excited about. He loves it for movies and watching sports (and presumably television), especially if new offerings support its features, but especially when the device is hard to share the $3,500 price tag is a tough sell.
Ben frames this as an intentional trade-off to maximize the entertainment experience. I do not get this claim. I see no reason the Vision Pro could not in the future support the entertainment experience it offers now, while also offering a distinct productivity experience that allows streaming multiple screens and using more precise controls and letting you use an iPhone or iPad as an additional control panel and navigation guide.
Andrej Karpathy offers his thoughts on the Vision Pro. Amazingly great in some ways, jank in other ways, including overly long setup. Several complaints here gave me hope, since they are concerns that won’t much matter over time, either you get through it or it gets fixed. Device weight is clearly a major issue. The review was essentially saying this is a device that will be great but has not yet handled the last mile.
Vanity Fair on why Tim Cook bet on the Apple Vision Pro, I would not call it ‘all-in’ since Apple will be fine no matter what. A strange article, worried about future versions being essentially too good. Like Thompson’s review, makes clear that the entertainment mode is well ahead of the productivity mode, although its motives lie elsewhere. The anecdote about having trouble finding apps after moving rooms is telling.
Aaron Slodov says ‘it’s amazing and this is the future’ as he moves objects around a room.
Senior Editior Devindra Hardawar of EnGadget calls it ‘beta testing the future.’ Her first warning is of eye strain. Her second is to not even think of buying one unless you are either a developer or an Apple fanatic. Her view is this is the beta, the real version will come a few years later. For now, it’s buggy, heavy, has a very short battery life and lacks native apps. She does find the interface intuitive and easy, and she praises both the ability to watch movies and the Mac integration.
She also notes the iPad Steam Link app works, so yes you can play at least many games on it. Similarly, it seems Sony’s Remote Play app will work for casting a PlayStation. For a Nintendo Switch and full portability, you will need to do more work, with a video capture card with HDMI input and then a USB-C output for the Vision Pro.
ZdNet’s Matthew Miller tried it for a workday. He recommends sticking to MacOS apps (what happened to ‘programs’?) because iPad ones aren’t ready yet, notes that you will need a Bluetooth keyboard to do any real work in practice, finds the ‘personas’ unplayable in practice, and found it hard to do productivity while traveling because of movement constraints and the lenses fogging up. He notes Microsoft’s apps (Word, Excel and so on) work but are currently bare bones.
He thinks it can work for those whose workflows only have 1-3 apps or content creators. He also oddly mentions day traders, from my experience trading no way in hell, you want precision above all, if you are tempted to day trade with the Vision Pro I am going to tell you to quit day trading.
Their editor-in-chief Jason Hiner says try it for yourself, but most people should pass. Cheaper alternatives are coming or already here, and the ecosystem isn’t ready.
Mark Spoonauer of Tom’s Guide emphasizes how good the device is for watching movies, and likes the spatial video and photos features and ability to view photos in a new light, as well. He doesn’t talk about productivity.
Tim Urban, who like many others keeps having holy smoments with VR devices and then getting disappointed that they are not there yet and not finding sustained worthwhile uses, goes through that cycle once again. He is excited for the future, and finds the present super cool already, but thinks that the costs still exceed benefits for now. He expects that we are soon to be on the part of the development curve, like iPhones 3G to 5, where new models are importantly better and you start to get a lot of additional surplus each cycle.
Sam Altman thinks this is big. Point, counterpoint:
Sam Altman: Vision pro is second most impressive tech since the iPhone.
Peter Wildeford: Disagree, vision pro is the seventh best and the ranking is:
1.) LLMs 2.) CRISPR 3.) mRNA vaccines 4.) semaglutide 5.) Perovskite solar cell 6.) Faster internet 7.) Apple Vision Pro
I have mRNA vaccines at least at #2 here, and I think you can argue #1. Gemini splits LLMs into several discoveries and also suggests EVs, Starlink, self-driving cars, wearable health tech, cloud computing, internet of things, 3D printing, robotics and more. The Apple Vision Pro has potential, but it is hard to put it that high on such a list.
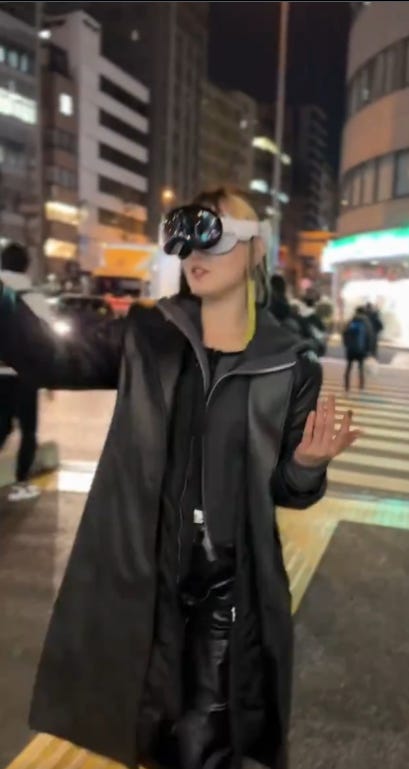
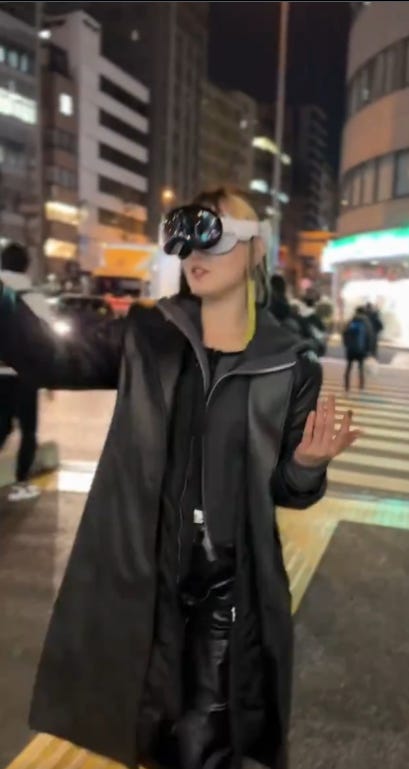
Grimes and derek guy emphasize the importance of aesthetics.
The giant Apple vision Pro is a look. It can be a good look, but if you want that you have to do the work. Which I agree is worth doing if you intend to do this on the regular. Also, she’s in Tokyo, so double cyberpunk points all around.
derek guy: Aesthetically, this is basically how you have to dress to make things like the Vision Pro and Cybertruck look cool. These things mainly look bad in public because there’s no congruity between the business casual gear most ppl wear and these futuristic designs.
Grimes: Good aesthetics are a moral good and directly related to the health of society.
The difference this woman and me? She makes this look good.
So what about my experience? On Thursday, I had the chance to do the demo at the Apple Store at Grand Central. It is about a 20 minute experience, with an employee walking you through various things they want to show off. You can try a few things, but your freedom of movement is highly limited in every sense, and there is no time for you to play around, although they will answer your questions.
There was an attempt to sell me the device, but he didn’t press when I made it clear it was a no on putting down $4k on the spot.
Like most others, I was impressed and disappointed, inspired and frustrated.
The great stuff is really great. The hardware itself is amazing. A true marvel. Visuals are off the charts. All the issues are about the software, and of course the price, except for questions of weight and battery life.
The killer app right now is as a video screen. If you want to watch movies or television, this is a damn good, movie theater level experience. Top notch, and a lot of customization, although I couldn’t make it quite as big as I would have liked during the demo. They didn’t show us the Apple TV+ theater experience, but I assume that is great. If I was richer I would buy purely for this.
The native software support is not there for all the uses of that screen. They will hook up your Mac, but they will not make it easy for your PC, PlayStation or Switch. The good news is there are workarounds.
But why not make this native? If you are selling me a four thousand dollar screen, let me use it with whatever I want, and do not make me work for it, this is 2024.
There are native games, but Apple did not even try to demo those. I assume they are not exciting yet, and Apple historically hates fun anyway.
The sound is very good natively, but it does leak a bit. They said you can use any headphones with it, and that even the big Bose-style ones can physically work, so that part looks good. I would appreciate the ability to watch things without disturbing those around me. For audio-only, of course, this is massive overkill.
Even better than a video screen were the panoramas, the full 180-degree experiences. The moment of being in the ballpark was fantastic. However, in order to get value, these have to be supported. There is no sign that anyone plans to actually offer MLB or other games in this mode. If and when they do for the Mets, if this is the only way to get that service and the additional costs aren’t too obscene, I think this would put me over the top. Going out to the ballgame is pretty great.
The other immersive environments also looked great, and I would love if we had lots of designed media experiences like that. It would be ten times better if you could meaningfully move around as well. There is a version of this, that is presumably coming within the decade, that will be worth paying a lot to get if necessary.
The special photos and personal video shots are nice, but not vital or killer apps.
The other killer app people mention is Mac integration, but that was not available during the demo.
Reading a book via Kindle seemed highly viable, including highlighting, but is it better than reading on a phone or tablet? My guess is no.
Playing board games with other humans via Tabletop Simulator, or playing Magic: The Gathering against someone who is not there, or other similar activities? Yes, please. That too could be the killer app for me. First they have to get there. For now, you can chat with someone’s avatar, but that is a totally different thing than simulating being in the same location.
What about productivity?
The virtual keyboard is password-entry only. They only track at most two fingers, so you cannot properly type even if you don’t need keys to do so. Effectively this is much slower than on a phone. You can dictate if you want, when that would work. It got regular English sentences reliably, as you would expect. For my name it thought I had a very different (and very Asian) name, whoops. You will 100% need a Bluetooth keyboard to do any real work.
The choice of what to include in the demo reveals what Apple thinks are the strong selling points. They lead with photos and personal videos and panoramas and watching movies. They give almost no attention to productivity of any kind, beyond showing you how to scroll through a web page. No mention of help with physical navigation or helping you with activities like cooking or shopping. No mention of AI of any kind, despite some very obvious things you would want to do there.
The navigation system relies on your eyes and their precision. I definitely worry about eye strain, and I had trouble hitting precise targets reliably. Meanwhile, my brain kept trying to use my hand to navigate like a mouse, which is totally supported once you start a movement, but unsupported otherwise. So they have the technology, but have chosen to deploy it differently than I would like.
Similarly, the Guest mechanism right now is rather poor and broken. You have to configure every time, it does not last, all your work gets lost and so on. It would be a big help if they would outright support multiple profiles.
Where I do see potential for productivity, and also for entertainment to shine as well, is while traveling. If you are on an airplane or a train, and you can suddenly work or watch on a real theater screen, that would be a big game. Travel enough and it is well worth paying for that, or it could even enable more travel.
So overall, yes. I see the potential. This could be an insanely great device with proper software support, both from Apple and support from others. Already it is likely a great device for watching movies. For other purposes, the software and ecosystem are not there yet.
I said in my previous post that I expect the Apple Vision Pro is either worth far more than the price, or it is worth very little, but it was unlikely to be something in between.
Could this still be a dud? Absolutely. What I do not expect is something I’d have been happy to pay $500 or $1,000 for, but not $3,500. Either the game will be changed, or it won’t be changed quite yet. I can’t wait to find out.
What I neglected to think about was the possibility that it would be a great device for narrow use cases, while not being good enough for other uses cases.
In this case, That One Killer App that I am confident in, right now, is as a way to watch movies. Also television or YouTube or other video, potentially, but especially movies where you want to give your full attention and they are designed for the biggest possible screen.
Meanwhile, it is plausible that the other uses are still stuck at zero value until they get a lot better, given the costs of the mode shift involved, the extent to which Apple is protecting its ecosystem, and the potential isolation effects.
It is also plausible they are not zero value at all. I can see a MacBook Air plus a Vision Pro being very good for productivity, and I can see a lot of value in gaming as well. And if they ever get the sports panoramas online, we’re golden.
If you are buying an at-home movie theater level experience, including watching other things if they are high enough resolution to support that, what is that worth on its own?
So here we are, where I know I would pay $1,000 for the device, but am unsure whether I am willing to pay approximately $5,000, on the assumption that this implies being willing to also buy a MacBook Air.
What say you, dear readers? Should I take the plunge?
And what about you? Will you take the plunge?