It was clear within the first ten minutes this would be a rich thread to draw from. In my childhood and education roundups, and of course with my own kids, I have been dealing with the issues Haidt talks about in his new book, The Anxious Generation. Ideally I’d also have read the book, but perfect as enemy of the good and all that.
I will start with my analysis of the podcast, in my now-standard format. Then I will include other related content I was going to put into my next childhood roundup.
-
(0: 00: 30) What makes someone a better parent? Haidt says right wingers and religious folks make better parents, citing that they are increasingly happier and more rooted in communities, liberal kids are more depressed and more vulnerable to phones. But while we should and do care a lot about it, being a good parent is not primarily about whether your kids are happy now. There are realistic margins where it is highly correct to make kids less happy now to give them better futures, and instill in them better skills, values and habits.
-
(0: 01: 20) Tyler says then, why not be a right winger, isn’t this the most important thing? Haidt says no, values do not work that way, you don’t get to simply adapt the ones with better outcomes. He is right. Haidt will note later he is now a centrist, seeing both extremes as too illiberal, which he largely attributes to social media. Also being sufficiently conscious of the need for community and the dangers of phones and dangers of identitarianism (which he discusses later) can plausibly screen off the related mechanisms.
-
(0: 02: 00) Tyler asks who Haidt has met who is most wise, Haidt names two and finds many role models for wisdom. I notice that I find the opposite. I know plenty of very high intelligence (INT) people but find it hard to name very high wisdom (WIS) people I have met. Who is the wise man among us? Perhaps my standards are wrong.
-
(03: 15) Asked about Covid reactions, Haidt attributes the right-wing reaction to concerns about government control rather than purity, notes purity can also be high on the left with spirituality and yoga. I notice he does not mention wokeness or cancel culture as having a strong purity component, despite describing what is happening on campus as psychologically akin to the Chinese Cultural Revolution.
-
(07: 30) Haidt values the Bible because of the need of every culture to have shared stories and reference points, comparing it to Homer and the Greek myths for ancient Greece and Rome. I agree that we need these shared reference points, and I increasingly worry about the fragmentation there, not only away from the Bible but also away from sharing popular culture stories as well, if we also increasingly don’t watch the same TV shows or movies or even play similar video games. If the AI is making up stories and games for you, then they will be different from someone else’s stories and games. Haidt says Babel is the Bible story he gets the most from, whereas he doesn’t get Job. I can guess what he draws from Babel but I think I got those bits from elsewhere.
-
(09: 00) Haidt opposes identitarianism in the sense of putting identity first as an analytical lens, and especially orienting others in this way, often in a mandatory way. He also warns of monomania, a focus on one thing, and notices that it seems rather terrible to teach young people that life is centrally about ranking people according to how good the various races are, no matter which races are put on top.
-
(11: 00) Tyler asks about ‘the disability concept,’ notes that people with say Tourette Syndrome do not obviously have worse outcomes, so do we ‘need some kind of identitarian movement’ to avoid this being called inferior, as ‘both the left and the right go along with this’? Should we be outraged? That… doesn’t seem like what is going on at all, to me? I would ask, don’t we already have such a movement, and isn’t its core strategy to label those who disagree with them or fail to ensure equality of their outcomes as exhibiting ableism? And is not this strategy sufficiently effective that one could reasonably worry about the consequences of saying various things in response? Haidt instead responds that identitarian political movements organizing for politics is fine, it just doesn’t belong in a classroom, citing past rights movements. And he asks, does turning up your identity in the sense of ‘I am a person with ADHD’ lead to better outcomes? He says we don’t know, but that it is ancient wisdom that it is our interpretation of things that upsets us, that such thinking is probably bad for you but he could be wrong. Haidt strikes me as someone who feels unable to speak their mind on this, who is choosing his words carefully and out of fear.
-
(13: 10) Tyler asks, why won’t AI soon solve the screen time problem? The AI agent will process the information and then talk to you. Skipping ahead first to his next question, he asks (in a clearly actually curious tone) “Screen time seems super inefficient. You spend all this time — why not just deal with the digest? Maybe in two, three years, AI cuts your screen time by 2X or 3X. Why is that so implausible?”
-
Haidt absolutely nails the response, pointing out that Tyler is plausibly the fastest and most prolific processor of information on the planet, and he is modeling screen time as someone attempting to efficiently process incoming information to complete a fixed series of tasks. If AI can process information and help you complete those tasks twice as fast, then you could finish your screen tasks in half the time.
-
For Tyler specifically, I buy that this is a lot of what he does with screens, although even then I would ask whether he would want an AI to speed up his watching of movies or NBA games. But let’s exclude those cases from the analysis, since the concern is about phones, and say that mundane AI doubles Tyler’s productivity in using screens to process information and complete tasks. What will happen to Tyler? Well, obviously, he will follow the supply and demand curves, and respond to decreased cost of information by increasing his consumption of information and resulting completion of tasks. It is entirely non-obvious that we should expect this to involve less time on screens, especially if we should effectively include ‘talking to an AI to complete tasks and seek information’ as part of screen time.
-
When thinking about my own consumption, and wow do I have a lot of screen time, I would first strongly say that I think all my interactions with AI should effectively count as screen time. I almost never talk to the AI with voice rather than text, better tech does not seem like it would change that so much, and if I did it would not be functionally different. I also notice that over time, as the efficiency of screens has gone up, my time allocation to screens as responded by rising, not by falling. The ability to use LLMs has definitely net increased my screen time so far. I can imagine ways to reverse this trend, using AI to arrange to be more social and interact more with the world, but at minimum that seems like it requires an active effort, and it does not seem like the way to bet.
-
Tyler later emphasizes once again converting to spoken word. That’s worse, you do get how that’s worse? Why would we want to lower the bandwidth, even if you like voice interactions? Even if it wasn’t worse, why the repeated emphasis on earbuds and voice? That is all still ‘screen time’ for all practical purposes, and one could see that as being even more of a steady stream of interruption.
-
For an average person, or an average child, the picture here looks gloomier still, to me. Time spent on television or watching videos or playing games will be made more addictive and to involve better selection via AI, and improve in quality in various senses, but that should tend to increase rather than decrease consumption. A better AI for TikTok that finds better matches to what you want is not going to reduce time on TikTok. Yes, we can get the same level of informed or handle the same number of emails in less time in that future, but our requirements and usage will expand to match. Historical parallels suggest the same, as screens improve we consume more screen time not less. So the question here is whether the new uses are transformative of our ‘screen time’ experience such that they are positive uses of time, especially for children?
-
Returning back to the first question here, Haidt says the primary problem with screens is opportunity cost of time, that they are experience blockers, and half his book is about the importance of play. Kids used to play for hours a day, even though that involved ‘real danger,’ and now they do not do that. Yet we refuse to let kids be kids, do not permit them to go play unsupervised, often this is even illegal. I see this as the best counter-argument against ‘the phones did it,’ if the kids wouldn’t be allowed to play anyway then of course they will be on their phones and computers and televisions. He also points out a bit later that video games used to be scarce and physical enough to encourage playing with friends and being somewhat social, and now you play alone or online (online can still be socially valuable, but is even at its best missing key elements.) AI, Haidt says, is not going to return children to a play-based childhood, it is not going to get you to spend time with friends.
-
Could AI instead be implemented in ways that simulate true play, that involve physical activity, that gives you virtual people to interact with that challenge you and train your social skills and other talents? That is definitely technologically feasible if we want it enough. But will the market give that to us, in practice? Will we choose to consume it? What we have seen so far should make us highly skeptical.
-
Haidt agrees with that prediction: “In theory, I’m sure you’re going to say, “Well, why can’t we just train an AI friend to be like a real friend and get in fights with you sometimes?” Maybe in theory that’s possible, but that’s not what it’s going to be. It’s going to be market-driven. It’s going to be friends and lovers who are incredibly great for you. You never have to adjust to them. You never have to learn how to deal with difficult people, and it’s going to be a complete disaster for human development.”
-
(17: 00) Tyler then responds with a statement that I think generalizes a lot of his perspective on so many things: “Complete disaster strikes me as too strong a term for something that hasn’t happened yet. I think you’re much too confident about that.”
-
I do actually think Haidt is overconfident here, if we confine to the kind of mundane AI (e.g. GPT-5-style) that is under discussion here, with an otherwise untransformed world. But I see the bolded sentence and paraphrases of it often used, by Tyler and by others, to dismiss concerns about future outcomes, in various ways, and especially to dismiss existential risks. If it has not happened yet, this reasoning goes, then how do you know what the consequences would be? How would you even dare to say such a thing is a plausible outcome requiring us to pay real costs to try and prevent it? And my answer is, again and again, that sometimes and in some ways you should be highly uncertain about future outcomes, especially when you lack parallels, but that one still has to use reason and consider how things might work and form probability estimates and not make excuses to look away.
-
There are indeed many things that have not happened yet, that I am confident would be ‘a complete disaster’ if they did happen, or that were clearly highly predictable ‘complete disasters’ before they happened. A large asteroid impact. A widescale global thermonuclear war and many other wars too. A pandemic, consider Covid predictions in January 2020. Various political proposals, especially for redistributions of wealth or widescale political violence. Getting rid of gifted and talented education programs and magnet schools, or not teaching kids advanced skills in the name of ‘equity,’ or many other educational reform proposals. Having the As play three years in a minor league ballpark in Sacramento. The correct response to a large percentage of movie previews. Etc.
-
(17: 30) Haidt then responds a different way: “What do you mean it hasn’t happened yet?” And Tyler clarifies the real question, which is: If screens are making children so miserable, why won’t they use new AI innovations to fix that? Why are they so ‘failing to maximize’? To which the obvious retort is, it is not like there are no alternatives or innovations available now, yet the kids remain miserable. They are not maximizing now. The ‘market’ here has failed us. Children, even more than adults, do not optimize their consumption basket taking into account all dynamics and long term effects, mostly they (as per our experiments, this is not speculation) end up using apps with Skinner boxes and delayed variable rewards and minimal active thinking and applications of various forms of social pressure and so on, in ways that have network effects and punish non-participants, in ways that in practice make people miserable. If you think ‘AI innovations’ will break us out of that, why do you think that? What would that look like?
-
(18: 00) Hadit responds by highlighting the collective action aspect, pointing out the Leonardo Bursztyn paper that many kids would love if everyone else would quit too but otherwise they can’t afford to, even TikTok has strong network effects from shared cultural knowledge.
-
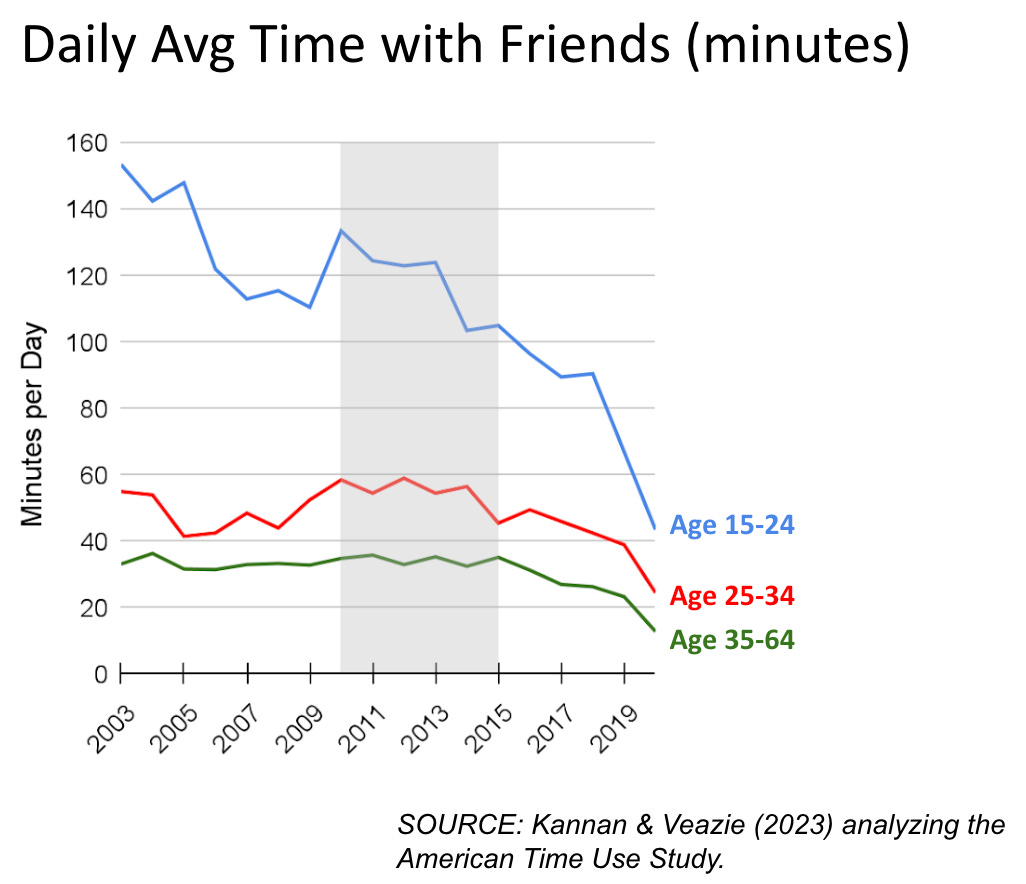
(20: 15) Tyler challenges the importance of face-to-face interaction by noticing that the pandemic didn’t damage well-being for kids too much. Haidt points out that time spent with friends was dramatically down already by 2019, starting in 2012 with smartphones. Tyler counters that time in school is time with people and friends, so the decline in 2020 must have been dramatic, yet well-being problems did not change much.
-
I note that I would be prepared to defy the data (if I need to do that) that mental well-being did not decline a lot for kids, or for everyone else, in 2020 and 2021? I mean, what? Alternatively, we actually have an explanation for this, which is that schools are very bad for children’s mental health, as you would expect given what physically takes place there and how they treat children in most schools. So in 2020, yes we had less social interaction which was bad, but also we had less de facto torture of children via school, which was good, and it roughly cancelled out.
-
(22: 15) Haidt points out time use studies don’t count school as time with friends, that we are talking time out of school. He also points out that time within school is now largely spent with phones, not interacting with friends or those physically next to you, most students check their texts during class. So to the extent that time used to count, now it mostly doesn’t. After 2012, academic achievement goes down, loneliness in school goes up.
-
I would say: You can sort of count time when you are forcibly imprisoned next to arbitrary other people as social time, but that stops working if you instead have the option to ignore them and be on your phone. Also we should totally ban phones in schools, as I’ll discuss later, how is this even a question if teachers are otherwise losing the fight on texting during class, if you don’t think we should ban the phones then at that point we should instead dismantle the schools, what is the point.
-
(24: 15) Tyler reiterates that this was a rather strong natural experiment via shutting down schools. I agree, and I do think Tyler has a good point that school time is more social than time spent isolating in a pandemic even with ubiquitous phone use. My response to that is noted above: That the schools are toxic and depressing. Which Haidt points out. As he says, it’s not a clean experiment.
-
(25: 30) Tyler asks why around 1900 European culture became more neurotic, depressive, negative and hostile, and then 1700s weirdness, and asks aren’t big shifts in mood often happening for small reasons, why attribute it to the phones? Why not simply say that big mood shifts we can’t explain are the norm?
-
But this isn’t history. It is now, and we can observe it in real time, and we indeed have a very good explanation of what happened. It is fine to say we do not today know what caused some previous shifts but why should we then feign ignorance over this one? Yes, in theory it could have been something else that happened at the same time, but so what? And even if it was, shouldn’t we assume that this something that changed was related to the change from phones or social media anyway? What changes in the early 2010s culture weren’t related to that?
-
Tyler keeps pounding on this later, so I want to say clearly: If there was an ‘exogenous mood shift’ in the 2010s, then all plausible candidates for it, including the rise of both wokeness and Trump and the loss of credibility of elites, are causally heavily intertwined with phones and social media. I also want to note that if everyone else is on their phones all the time, your social activities are already crippled by negative network effects, so you might be in a no-win situation, where not using phones would also cripple your social life.
-
(27: 15) Haidt responds also that this happened very quickly, in a single year, what is an example of those that we can’t explain? Tyler says, they kill the British king, the French Revolution. But of course such events are usually a long time coming, and also it is not like we lack an explanation. We know many things that helped cause the French Revolution, this is not a mystery, and it is no mystery why we saw rapid changes once it started. I looked up English kings that got killed to see which ones would count here, which leaves Edward II, Richard II, Henry VI and Charles I. In three cases, it seems like clear reaction to a perception of tyrannical actions by the King, and in the fourth by a dynastic civil war? Is any of that a mystery?
-
(29: 00) Tyler says there are two pieces of evidence that don’t seem to support Haidt’s story out of sample. First, he says, the impact is mostly the Anglosphere and Nordics, so why shouldn’t we say this is a ‘negative mood for reasons we mostly don’t understand’?
-
(30: 00) Both agree girls are more mimetic, and this is one cause of them being impacted more by whatever is happening.
-
(30: 30) Haidt says within the last two months he has learned that conservatives and religious people are protected, and that there is a huge religious impact here: “But that hides the fact that in Eastern Europe, which is getting more religious, the kids are actually healthier now than they were 10 years ago, 15 years ago. Whereas in Catholic Europe, they’re a little worse, and in Protestant Europe, they’re much worse… It’s rather, everyone in the developed world, even in Eastern Europe, everyone — their kids are on phones, but the penetration, the intensity, was faster in the richest countries, the Anglos and the Scandinavians. That’s where people had the most independence and individualism, which was pretty conducive to happiness before the smartphone. But it now meant that these are the kids who get washed away when you get that rapid conversion to the phone-based childhood around 2012. What’s wrong with that explanation?”
-
It seems important to be precise here. What this is saying is that it is the combination of smartphones and individualism that causes the issue. It seems reasonable to have the problems arrive and have biggest impact in the Anglosphere first, where we are richer and most individualistic, and the internet is in our language and we adapt such things faster and have freer societies and more free market attitudes, and already had less emphasis on socialization in various forms including declines in religiosity. (I wrote most of that before hearing Haidt’s explanation, then moved it later.)
-
I do agree that this is still the strongest argument against attributing too much of this to phones alone, but similar concerns are being raised around the world, and I generally don’t see this point as being that strong at this point.
-
(31: 40) Tyler notes that old Americans also seem grumpier. I would say that this is also plausibly downwind of phones and social media. Even if they are not using the devices directly, they see the impact in a rapidly changing culture, in transformed politics and the widespread assertiveness of wokeness, even if you think wokeness is correct and vital you know that putting it in the faces of old people is going to make them grumpier, whether you consider that a cost or a benefit is up to you.
-
(31: 45) Tyler also notes that phone usage explains only a small part of variance in happiness outcomes. Haidt agrees that the overall correlation coefficient is only something like 0.04, but if you focus on social media and girls the correlation coefficient gets up to something like 0.17, that even the skeptics are at between 0.1 and 0.15 without splitting by gender. As noted above, a lot of the impacts here are cultural shifts and network effects, so the coefficient could easily fail to capture a lot of the impact here. We also have to ask what directions causation goes to what extent. It is plausible that being depressed causes you to spend either more time or less time on social media, I can think of mechanisms for both.
-
(34: 10) Tyler asks, why no talk in your book about the extremely large benefits of social media? Which certainly sounds to me like ‘but you will be so much more cool if you smoke and drink with us cool kids,’ but yes, fair, and Haidt says tell me about it, especially for 11-13 year olds.
-
Tyler makes a pretty bold claim here: “At Emergent Ventures, we support many teenagers, young women. Many of them not 13 years old, but very often 16 to 19 years old. They’re doing science. They’re remarkably smart. They get in touch with their collaborations and with each other using social media. They exchange information. They’re doing phenomenally well. They’re an incredible generation, smarter, more dynamic, probably more productive than any other scientific generation ever, and that’s because of social media.”
-
I can totally buy that there are a lot of very smart teenagers out there, that those that are bold and talented and ambitious benefit from using social media to find collaborations. But… the most dynamic and scientifically productive generation? Oh my is citation needed here, I do not believe this, I do not see evidence of this. What seems more likely here is that Tyler gets to see the success stories, the most extraordinary people who make the tech work for them, and does not see others that do not? And of course it is not clear how much of that, even if true, would be due to social media. Yes, it makes it easier to find collaborations, but it also destroys rival means of finding such collaborations, and so on. With earlier tech there were already plenty of places to find like-minded people, and indeed it was in many ways easier to focus on that without distractions, because you were going to dedicated places, both real and virtual.
-
(35: 00) Haidt says he does have a section on benefits, which (matching Tyler’s statement) is almost always for older teenagers, he can see the collaboration story for them, but for 11-13 year olds they have different needs. And Haidt points out that the rival methods social media is crowding out, even on the internet, were superior especially for that group, that the overall non-social-media internet is great.
-
(36: 30) Tyler clarifies that Twitter is how these kids meet, and Haidt confirms Twitter is social media. I am not as sure about that. I see Twitter as a hybrid, that can be used in any mix of both, and as much less of the bad thing than other social media, but of course I am biased, it is vital for my work. I would be happy for a compromise that said kids get Twitter at 13 outside of school hours, say, but other ‘purer’ social media only at 18. Or even better, as per later discussions, you can get only the non-algorithmic ‘following’ version of Twitter at 13.
-
(36: 45) Tyler once again: “It could be the case, maybe only 5 percent of teenagers benefit from this Twitter function, but that could, by far, outweigh the costs, right?” This seems to be a common pattern in Tyler’s thinking that is behind many of his weirdest takes, where he finds things he thinks are massively oversized in their benefits because in a small minority they promote the kinds of talent development or inspiration or capital formation (or what not) that he thinks is most important, and he is willing to throw the rest of life under the bus to get it – see for example discussions over congestion pricing in New York City. It is of course possible that the benefits outweigh the costs even when benefits are concentrated like this, but (aside from not being confident that the
-
In this case, one easy response is to say that this is the kind of child who should have special technical chops and determination and be impossible to stop, and who would rise to the challenge if we tried to stop them, the way hacker kids got around restrictions in the 1980s. If they’re all that do you think you can keep them off Twitter? So the correct solution would be to not let kids have social media, and then be fine when they got onto Twitter anyway. Or of course you could soon have an AI check their usage to confirm they were using it For Science.
-
(37: 10) Tyler agrees that girls 12-14 are likely worse off because of Instagram. He dodges the question of TikTok, but it seems like his objection at that age is entirely about Twitter? Haidt says that we must talk price, the question is whether the age threshold should be 14 or 16, and he thinks that algorithmic feeds should be gated to age 16.
-
(37: 45) Tyler says these kids start doing their online science thing at 13 even if he only sees them at 16, alternatives would be much harder. Haidt points out they could meet in other ways, says it would only be a little harder.
-
(38: 25) Tyler asserts they ‘all make this decision’ to switch Twitter to a non-algorithmic feed. So the common ground seems very obvious here?
-
(38: 45) Haidt claims Gen-Z spends a huge portion of their time and attention managing their network connections, it is the first and last thing they do every day. If true (and I think it is) this seems horrible, they are paying very high maintenance costs and not getting much in social benefits in return, in a way that makes it very costly to opt out. He literally estimates 5-10 hours a day for these activities plus consuming content to keep up. One way to look at this is that we have raised social signaling costs that people can pay and made such payments highly visible, with the opportunities to do this becoming available at random times, and one can see why this would be bad, the worst kind of anxiety-infused life-consuming Skinner box. Haidt refers to Collision noticing no major person in software is under 30, that Gen-Z aren’t starting companies and doing things. What young people are impacting the world?
-
(40: 10) Tyler says young people are doing well where we can measure success, such as at chess. But chess is almost a failure mode for our brightest minds, in many senses, and also illustrates how much current generations are drawn to obsessing over improving legible numbers in various ways that don’t depend on learning through child-style play. Tyler says that these people aren’t founding companies because you need all these synthetic abilities and the nature of production has changed. But one might also say it is the path to developing those styles of abilities that has been effectively blocked by time on phones. Haidt points out that GenZ talent tends to disappear into the prestige economy of social media itself, to likes and followers.
-
(41: 30) Tyler says many at OpenAI and Anthropic are ‘extremely young’ and doing amazing things, that is historically common in software so hard to know how this compares. He again points to Emergent Ventures and says they’re so much smarter and more productive and attentive and disciplined than kids in his day. But how would one know that? I would argue that instead those kids have been better selected. Haidt agrees that this sounds like selection.
-
(42: 45) Tyler once again goes back to, whatever problems there are, why not just think we’ll adjust to them? We adjusted to agriculture and fire and cities, that often the early ride is bumpy but it turns out fine. Sounds a lot like what he says about AI, this super strong prior that people adjust to things and then we’ll be better off. One response would be yes, we adjust, but taking social media away from kids like we took away leaded gasoline is exactly the kind of way in which we adjust.
-
(43: 30) Haidt learns not to trifle with Cowen in adjustment trivia by asking about scurvy. I wonder how the British Navy forgetting why their cure worked and reintroducing scurvy fits into this, but they did rediscover the issue eventually, but it does seem like a poor example, because there are various ways to efficiently fix the issue, the issue is very clear when it is happening, and people have heavy incentive to find an answer. The obvious current lack of adjustment question would likely be fertility, if AI proves somehow not to be transformational. Are we going to adjust? How fast, and how?
-
(45: 00) Tyler says, this 5-10 hour flow of message, the AI will do that for you, and you’ll have a lot more time again. Alas, I think Tyler misunderstands the purpose of that flow of messages. The reason it is a 5-10 hour flow of messages is that this is costly signaling. If everyone hands their message flow to the AI, then the response will be, oh if she cared about me she wouldn’t let the AI handle the messages, or she would but then she would spend time customizing her replies, the replies are either too fast and the AI is doing them without her in the loop or too slow and she is not giving me attention, which means she does not care enough about me.
-
And so on. This is not the kind of trap that efficiency gains can solve, the thing will eat any gains, that is exactly why the situation got worse when the tools got better. Similarly, when Tyler says Gemini will ‘give them a digest’ of what is going on in their friend’s lives, so they can keep up for when you meet in person, well guess what? Now the standard is ‘show me you did not only read the digest.’
-
Could you imagine a world in which AI is so good that no one can tell the difference? You can, but then one must ask why we are even still around and what is our purpose in life and our way of producing things and so on. If we are not even handling our own social communications, are we even ourselves anymore? I don’t know. It is weird.
-
This seems like a very particular goldilocks scenario to me, where the AIs are exactly good enough and given exactly enough leeway and authority to free us where we want to be free, but somehow the world remains fully normal and economic normal, and I don’t have reason to think the zone in question exists at all unless we are engineering it very intentionally. It feels like wishcasting even above and beyond the parts where one doesn’t want to look at existential, catastrophic and systemic risks. I’d love to get the AIs to do the work we dislike and for us to live the parts of our lives we like without AI, but… how? What is the plan, in detail? Can we write stories in that world, maybe, and make them make sense? Seems hard.
-
Later Tyler suggests for example people saying “‘I’m going to form like a little polycule but without sex, and my polycule will be based around not doing so much social media.’ Like my friends and I in high school — we didn’t go to parties. We seceded from that.” This was young Tyler’s solution to the collective action problem, a small group took the collective action, nice solution if everyone is fine with that being the entire collective. And yes, some people will always (in normal worlds) be able to form close-knit groups that ignore everyone else, and a small group of friends can do very well on all fronts, but that has always been highly limited as a strategy, most kids and people are incapable of it or won’t do it under the pressure.
-
Yes, as Tyler says, meeting up with your friends is fun, but when he says ‘kids will find ways of doing this,’ they are not currently finding ways of doing this. Time with friends is way down. Most social activities are way down. Relationships, sex and children are way down. That does not mean we will never adjust, but I see no reason to expect adjustments that fix this. There are lots of things that people used to enjoy a lot or benefit from, that we stopped doing at various points in history, and I do not expect most of them to come back.
-
(46: 15) Haidt frames this as, there’s going to continue to be a ‘dip’ in terms of mental health impact, but that Tyler might be right, we could get superhuman generations in 30-50 years. Well, yes, we could get a lot of very exceptional things in 30-50 years if AI continues to improve.
-
(47: 30) Flagging the huge agreement by all three of us that there is far too much homework, especially in the early grades. My kids school has them do homework with the justification that they need to learn how to do homework, the generalized version of which I would call the worst argument in the world if Scott Alexander hadn’t used that term first for the non-central fallacy. Perhaps instead the worst justification in the world? Which is ‘you need to endure bad thing X now on purpose, so that you get the benefit that it will then be less bad when bad thing X happens to you again later.’ Madness.
-
(48: 00) Haidt frames his book as offering four norms that solve collective action problems and that would help get children time and ability to play as they need to, with number one being no smartphone before high school, let them use flip phones. Second, no social media until sixteen. Third is phone-free schools. Fourth is far more childhood independence, a la Free-Range Kids and Lenore Skenazy.
-
I am strongly in favor of all four planks as norms to strive for, especially taken together, and for the laws to at least facilitate all this. We need to stress the fourth one most of all, you can only take away the phones if kids can otherwise use that time.
-
(51: 05) Tyler asks the right question on the social media rule, who is enforcing these norms? The government or the parents? For the others it is easier to see. For free range kids it is sufficient that the government allowing and encouraging it. For phones in schools that is clearly on the schools and thus mostly the government.
-
(51: 15) Haidt responds that parents cannot enforce this alone without outside help. Quite right, at least once you let them have a phone or computer. So what should we do? Right now, Haidt notes, even the kids below 13, that they are supposed to not allow, do not get kicked out even when it is obvious. Haidt wants to raise the age to 16 and see it enforced as his number one option.
-
(52: 00) Tyler makes clear he is totally opposed to the government telling parents they can’t let their kids use social media. He says ‘so the government will stop me from raising my 15-year-old the way I want to. I’m totally against that.’ I don’t see Tyler generalizing this principle enough, if so? Either way, we agree the social media decision needs to be up to the parents, at least at age 15. That you should require very clear opt-in from the parents, but if you have it, then go ahead.
-
The emphasis on ‘sign a contract to hand over data’ is weird. This cannot be the true objection, can it? Shouldn’t we draw the line where we actually care?
-
(53: 40) Tyler says, Instagram has parental controls but no one uses them. Haidt points out few people are able to use such controls well. I would add, the implementation matters. The defaults matter a ton. Having something in an options menu sounds like a good libertarian solution but in practice adaptation of that will always be very low. Defaults or GTFO. If you made it such that the parents had to give very clear permission for a kid-friendly account, and then again give very clear permission for a fully unlocked account, and you actually made this hard to spoof or to happen without the parents being aware, then you would have something. You need something like the Certificate of Dumb Investment, where you impose some trivial but real inconveniences in the process.
-
(54: 10) Haidt asks the obvious question, what about PornHub? And Tyler says, no, you’re trying to shift it to me, but fundamentally it has to be either up to parents or up to government, and if it is up to parents it will not matter much, and points out Haidt is at least raising the intervention possibility.
-
And I say, no, it is not a binary choice. It is at least a tertiary choice, with a middle third option. If you leave it ‘up to the parents’ as in the parents can in theory tell the child what to do, then that is better than saying the child has a ‘right’ to do it, but in practice we all know that won’t work here. If we say ‘the government bans it’ then that is not good either, although ‘it is banned but parents who want to make it happen anyway by giving them accounts and logins that technically are in the parent’s names can’t actually get stopped or punished in a real way, at most we ever impose a modest fine’ might be a practical response.
-
The third option is that the parents can give the kid an account, but we impose real friction costs of doing so as part of actually enforcing it, in a way that if the kid tries to do it without permission and isn’t unusually savvy, they will definitely get caught. And that the parents have that extra push not to do it, they can’t just go ‘oh fine, it’s easier to let you, sure’ and that’s it. They have to mean it. And have the services actually enforce these rules and procedures often enough that if you don’t go through the hoops, your account might well get deleted.
-
(55: 00) Haidt says a lot about how the government is not doing anything to enable safeguards. Tyler points out that any version of this is effectively a ban, that it would bankrupt such companies if they could be sued every time a kid got on without permission. Haidt says he is not saying that the government should decide, but he thinks parents should be able to sue these companies, that we should sue them over things like constant refresh and endless scroll as well, that section 230 should only apply to what people post.
-
Presumably this is one of those ‘either our legal system has rules for liability that work, or it does not’ situations? As in, if parents sue over their child having access without permission, then that should not automatically entitle them to thousands or millions in damages, they should have to demonstrate that the company was negligent in allowing this. And if they sue over the endless scroll, our legal system should say that is a dumb lawsuit, and toss it. When tech companies say they cannot survive ordinary liability law, that implies strongly that either we should change that underlying law for all cases, or there is something deeply wrong with the business. And we should check to see if what the tech company is doing is regulatory arbitrage.
-
Tyler doubles down, says even if Meta was 99% effective, they’d still be sued into oblivion on the other 1%. Whereas Haidt says correctly, that would be incredible, great success, we happily accept a 1% or even 5%-10% failure rate here. And Haidt says, again I believe correctly, that if Meta did have a 95% or 99% success rate, that success rate would be a strong defense in a lawsuit. Or, alternatively, we could perhaps write a safe harbor rule here to ensure this? As in, you are required to ensure that your system is 95% effective, meaning that for every 5 kids that are on your platform, there are 95 that attempted to get on the platform without permission beyond ‘I tried to sign up, told the truth and was told no,’ and failed to do so, or something similar.
-
I think this is actually a lot easier and less tricky than PornHub. With social media the whole point is a persistent identity. It seems reasonable to provide age verification or parental permission once. Whereas with PornHub, as Snoopy once said, there are some times that you prefer not to be recognized. It would be a major imposition and security risk to require providers of pornography to verify identity.
-
I also don’t feel like the full solution space of this problem is being searched. There feel like there should actually be good technical solutions available.
As a bonus, here are two sections that would have been in my next childhood roundup:
England to give the power to ban mobile phone use on primary and secondary school grounds, students will have to switch them off or risk confiscation. Reactions like this always confuse me:
However, teachers’ unions said that the crackdown was misguided because most schools already imposed a ban. Geoff Barton, general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, branded the reform a “non-policy for a non-problem” and said ministers should focus on limiting children’s access to social media platforms.
I fail to see why this is an issue? I am pretty sure this is not a ‘non-problem.’
Jay Van Bavel: My kids go to a public middle school in NYC where they lock up their phones for the day. This is what the school observed:
“Overall, the program has been a massive success. We are happy to share that we continue to see the benefits of using Yondr, with increased student engagement in the classroom, less time spent in the bathrooms and hallways, more genuine connections within the community and a decrease in reports of cyberbullying.”
We need some RCTs on removing smartphones from entire schools or classrooms to see the impacts (which are often network effects, rather than on individuals).
Some parents worry this will mean they can’t find their kids in case of an emergency.
Not true.
The kids carry the pouches and parents can still easily track their location (if necessary). In an emergency kids can just break open the pouch. It only costs ~$20 to replace.
Sounds good to me as a way to quiet the concerns. It should not be actually necessary to carry the pouches, and I think psychologically it would be better not to do that so kids are not tempted to break the pouch and don’t have to spend willpower to avoid it.
Phil McRae: SMARTPHONE BAN
In the US, a teacher (Mary Garza) instructed her students to set their phones to loud mode. Each time a notification was received they’d stand up & tally it under a suitable category. This occurred during ONE class period. Each mark is a learning disruption
A story confirmed to not mean anything.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: “I grew up in the City Where Nobody Can Sneak Up On Anybody, forced to wear a little hat that went ‘ding ding’ every 2 seconds anytime I went outside my house. I hated that hat. When I was six years old, enough deaf people had moved into the City that the hat acquired flashing LED lights.
Thankfully when we started to get deaf and blind people they stuck to their own city subsection and we didn’t *allhave to wear the vibrating boots that let people feel us coming through their toes… anyways, I hated that City and I told anyone I met that as soon as I was thirteen and had my own bank account I was moving somewhere, anywhere else; and they’d always nod wisely and say, ‘Valid.’
And then I turned thirteen and moved out and it was awesome. Every city is a quiet city for me now. I decided that I’d make my own kids grow up wearing hats that said ‘ding ding’, just so they could appreciate the quiet when they grew up. And for this, they make me move to the City of Clever Parenting Ideas?”
This story doesn’t mean anything, so please don’t try to decode it.
Did you know that Snapchat+, the $4/month subscription service, offers friend rankings? You can check how often a friend interacts with you relative to how often they interact with others. This often goes exactly the way you would think, with both friend and relationship drama ensuing when someone is not ranked high enough.
Even without Snapchat+, the app can show teens where they stand with friends via emojis. This occurs if two people are on each other’s private eight-person best-friend lists.
A yellow heart indicates “Besties” status—these two have sent the most snaps to each other. If they’re besties for at least two consecutive months, they graduate to “Super BFF,” indicated by two red hearts.
Jonathan Haidt: I have said much less about Snapchat than other apps because I know less. But the more I learn, the worse it looks. It’s not just the streaks, designed to hook kids. Their “solar system” maps are even worse.
Katy Potts: I call it the “anxiety app” in online safety training I run – grim – unbelievable they get away with it.
This is the kind of social information where we benefit from lack of clarity. There is a reason groups strive to avoid a known pecking order outside of the top and bottom ranks. Even if you know you are not so relatively close, you don’t need the details in your face, and real ambiguity is even better. For teens I am confident this is far worse, and also it will lead to people strategically gaming the system to get the outcome they want, and every implementation of that I can imagine only makes the whole thing worse.
Jonathan Haidt went on the Free Press podcast, in addition to the one with Tyler Cowen. On TFP, he laid out the case that smartphones are the primary thing ruining childhood this way.
Suppose a salesman in an electronics store told you he had a new product for your 11-year-old daughter that’s very entertaining—even more so than television—with no harmful side effects of any kind, but also no more than minimal benefits beyond the entertainment value. How much would this product be worth to you?
…
What the smartphone user gives up is time. A huge amount of it.
Around 40 hours a week for preteens like your daughter. For teens aged 13 to 18, it’s closer to 50 hours per week. Those numbers—six to eight hours per day—are what teens spend on all screen-based leisure activities.
…
I should note that researchers’ efforts to measure screen time are probably yielding underestimates. When the question is asked differently, Pew Research finds that a third of teens say they are on one of the major social media sites “almost constantly,” and 45 percent of teens report that they use the internet “almost constantly.”
As I said in the main part of the post, if kids are indeed being allowed to spend that kind of time on their phones, that seems obviously deeply unhealthy, and the decision to permit this seems bonkers levels of nuts. No, I do not need a study to see this.
If you are spending that much time on a phone, then unless something is deeply engrossing in a way that for example school almost always isn’t, every minute that you are not on your phone, you are spending part of that minute jonesing for your phone. You are thinking about pulling out your phone. You are using willpower not to.
There aren’t zero useful things to do with phones, but at that point, come on.
There is also this. You can say it isn’t smartphones. It’s obviously largely smartphones.
I do not buy that this can be explained by ‘some unexplained shift in mood.’
Haidt also wrote a book, The Anxious Generation. As I noted earlier I haven’t had opportunity to read it. Candice Odgers reviews it here in Nature. Here is the teaser line of the review.
The evidence is equivocal on whether screen time is to blame for rising levels of teen depression and anxiety — and rising hysteria could distract us from tackling the real causes.
Remember The Law of No Evidence: Any claim there is “no evidence” of something is evidence of bullshit.
One could add a corollary, The Law of Distracting Us From the Real Issue. Which henceforth is: If someone warns that paying attention to X could distract us from the real issue, that is evidence that X is the real issue.
This is because the phrase in question is an attempt at deep magick, to act as if evidence has been presented or an argument made and social cognition has rendered a verdict, when none of that was otherwise the case.
There are of course many cases where X is indeed a distraction from the real issue Y. What these cases mostly have in common is no one using the phrase ‘could distract us from the real issue.’
One could also point out that phones are themselves a massive distraction and time sink, thus even if something else is ‘at fault’ somehow, getting rid of the phones would be a first step to addressing it. Candice doesn’t even have any real objections to Haidt’s actual proposals, calling them mostly reasonable, or objecting to them on the grounds that they would be insufficient because teens would work around them. Which is not exactly making me want to instead do nothing.
Candice does of course pull out the no evidence card as well, saying studies fail to find effects and so on. Yeah, I don’t care. The studies are asking the wrong questions, this is dumb. Then of course she says ‘there are, unfortunately, no simple answers,’ so I am confused what we are even at risk of being distracted from. What does she offer?
Researchers cite access to guns, exposure to violence, structural discrimination and racism, sexism and sexual abuse, the opioid epidemic, economic hardship and social isolation as leading contributors.
The idea that kids today have more contact with guns, violence, structural discrimination and racism, sexism and sexual abuse than they did in the past is obviously backwards. Yes, of course those things continue to make the world worse, but they are much better than they used to be, so it can’t explain a new trend.
Economic hardship is complicated, as I’ve discussed in the past, but certainly there has not been a dramatic rise in economic hardship starting in the mid-2010s.
That leaves the opioid epidemic and social isolation, which are indeed getting worse.
Of course, citing ‘social isolation’ while denying that phones are at fault is a pretty rich thing to say. I am pretty sure a new activity soaking up most non-school hours is going to be bad for social isolation.
The opioid epidemic is bad, but this can’t be primary. The fall in child well-being doesn’t map onto the opioid epidemic. The rate of opioid abuse under 18 is relatively low, only about 1.6%. Even if you include parents, the numbers don’t add up, and the maps don’t match.
Yes, there is narrative among the youth that all these things are worse than ever. And that narrative is bad for mental health. But do you know what is a prime driver of that? Social media and everyone constantly being on their phones. And you know what else? Articles and academics like this one, pushing a narrative that is patently false, except where it is self-fulfilling.
There is an alternative hypothesis that does make sense. One could say that kids are on their phones this much exactly because we do not let kids be kids. If kids are not allowed to go off and do things, then of course they will end up on their phones and computers. We give them no other options.
So yes, we should cover that base as well. Let kids be kids.
The contrast between this and Tyler Cowen’s must better challenges is very clear.
People have gone completely insane. Do not put up with this insanity.
I mean, this would be insane at any age, but thirteen? At thirteen I do not even feel entitled to know which friend’s house my children are going to.
Hannah Posts: It would never occur to me that this would be unexpected or inappropriate. If I’m at Mary Ann’s house playing dolls, ofc her mother’s dearest old friend Miss Margaret would be in the kitchen chatting.
Can you imagine getting that call? Your kid is over at a friend’s house and their mom calls you to ask if her sister can stop by for a coffee
Andrew Rettek: parents like this don’t just stiffle their own kids, they mess with your kids, calling the ~cops if you give your kids “too much” autonomy. And they teach childless people, including their own kids, that this is reasonable behavior and anything less is negligent.
We used to let kids babysit other kids. I remember having at least one sitter, a neighbor from upstairs, who was only twelve or so. As opposed to now, when someone is terrified their 13-year-old is in a house with a friend, their mom and an uncleared third adult. We still use the term ‘babysitter’ but it means paying an adult at least $25 an hour, rather than letting kids learn some responsibility and earn some cash. It is all so insane. I would of course happily let a normal (non-adult) babysitter take the job for my kids, if I could find them and was confident no one would call the cops.
Also, let your kids pay cash or have their own debit card?
Patrick McKenzie: An anecdotally common user behavior I wouldn’t have guessed: many children old enough to go out with friends but not old enough to have independent purchasing power (or payment methods) now order in restaurants via a text message to Mom, who places order through app and pays.
At minimum this requires Mom to be by the phone willing to respond. That is not always an option. What do you do when she is busy?
Also you should not be tracking your kids and their spending like this. If you are old enough to go out with friends, and it is worth spending money to go to a place to eat, then give the kid the money. Don’t scrutinize their food orders. The responses seem confused by this as well.
In reasons you don’t need to devote crazy amounts of attention to your kids news:
Robert Wiblin: If incremental parenting effort for infants had large benefits you’d expect second and third children to do worse than they in fact do, seeing as how they have to share their parents’ attention with siblings while firstborns do not.
They do [a bit worse] but the effect is pretty modest given the reduction in parental effort is presumably large (20%, 30%, maybe more). (Though I guess one could argue it’s offset by learning effects.)
Daniel Eth: Unless there was a similar-sized effect in the opposite direction from better parenting due to learning.
Another hypothesis is that having older siblings is actively helpful, and this makes up for some of the difference. I generally am inclined to believe this.